Cyber Situational Awareness in Computer Networks
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Sensor Networks".
Viewed by 184636
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Alexios Mylonas
Dr. Alexios Mylonas
 Dr. Alexios Mylonas
Dr. Alexios Mylonas
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
School of Physics, Engineering and Computer Science (SPECS), University of Hertfordshire, Hatfield AL10 9AB, UK
Interests: cybersecurity; privacy; incident response; threat intelligence and web security
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
We live in an interconnected world in which, on a daily basis, we rely on new technologies (sensors for wearable systems, unmanned vehicles, robots, etc.) to provide services that improve our everyday life. However, in the current threat landscape, the increasing pervasiveness of these new technologies provide new vectors which once exploited allow threat actors to materialize their objectives. In recent years, cybercrime has become more sophisticated and organized, and organizations and/or nations have been targeted. The sophisticated tactics, techniques and procedures used by threat actors, coupled with the volume of data that is being produced by these technologies, make the continuous development of defensive mechanisms and the increase of our situational awareness against newly introduced cyber threats absolutely necessary.
This Topical Collection invites contributions that investigate and address these challenges by describing original ideas, methods and/or real-world experiences on cyber situational awareness in our technological paradigm.
Dr. Alexios Mylonas
Dr. Nikolaos Pitropakis
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Cybercrime and digital forensics
- Incident response
- Security information, event management and analytics
- Host-based intrusion detection
- Cyber situational awareness
- Network security
- Network forensics
- IoT security and privacy
- Privacy-preserving machine learning
- Adversarial machine learning
- Privacy-preserving blockchain implementations
- Cloud computing security
- AI-accelerated intrusion detection
- Usable security and risk management
- Surveys and state-of-the-art reports in the above areas
Published Papers (24 papers)
Open AccessArticle
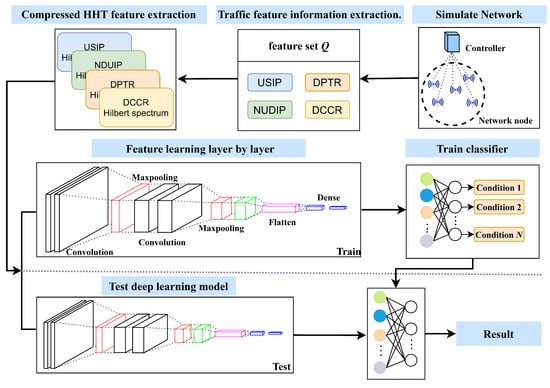
A Method for Detecting LDoS Attacks in SDWSN Based on Compressed Hilbert–Huang Transform and Convolutional Neural Networks
by
Yazhi Liu, Ding Sun, Rundong Zhang and Wei Li
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1840
Abstract
Currently, Low-Rate Denial of Service (LDoS) attacks are one of the main threats faced by Software-Defined Wireless Sensor Networks (SDWSNs). This type of attack uses a lot of low-rate requests to occupy network resources and hard to detect. An efficient detection method has
[...] Read more.
Currently, Low-Rate Denial of Service (LDoS) attacks are one of the main threats faced by Software-Defined Wireless Sensor Networks (SDWSNs). This type of attack uses a lot of low-rate requests to occupy network resources and hard to detect. An efficient detection method has been proposed for LDoS attacks with the features of small signals. The non-smooth small signals generated by LDoS attacks are analyzed employing the time–frequency analysis method based on Hilbert–Huang Transform (HHT). In this paper, redundant and similar Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) are removed from standard HHT to save computational resources and to eliminate modal mixing. The compressed HHT transformed one-dimensional dataflow features into two-dimensional temporal–spectral features, which are further input into a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to detect LDoS attacks. To evaluate the detection performance of the method, various LDoS attacks are simulated in the Network Simulator-3 (NS-3) experimental environment. The experimental results show that the method has 99.8% detection accuracy for complex and diverse LDoS attacks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Zero-Day Malware Detection and Effective Malware Analysis Using Shapley Ensemble Boosting and Bagging Approach
by
Rajesh Kumar and Geetha Subbiah
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 6289
Abstract
Software products from all vendors have vulnerabilities that can cause a security concern. Malware is used as a prime exploitation tool to exploit these vulnerabilities. Machine learning (ML) methods are efficient in detecting malware and are state-of-art. The effectiveness of ML models can
[...] Read more.
Software products from all vendors have vulnerabilities that can cause a security concern. Malware is used as a prime exploitation tool to exploit these vulnerabilities. Machine learning (ML) methods are efficient in detecting malware and are state-of-art. The effectiveness of ML models can be augmented by reducing false negatives and false positives. In this paper, the performance of bagging and boosting machine learning models is enhanced by reducing misclassification. Shapley values of features are a true representation of the amount of contribution of features and help detect top features for any prediction by the ML model. Shapley values are transformed to probability scale to correlate with a prediction value of ML model and to detect top features for any prediction by a trained ML model. The trend of top features derived from false negative and false positive predictions by a trained ML model can be used for making inductive rules. In this work, the best performing ML model in bagging and boosting is determined by the accuracy and confusion matrix on three malware datasets from three different periods. The best performing ML model is used to make effective inductive rules using waterfall plots based on the probability scale of features. This work helps improve cyber security scenarios by effective detection of false-negative zero-day malware.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
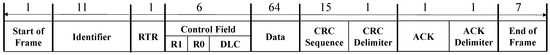
CANon: Lightweight and Practical Cyber-Attack Detection for Automotive Controller Area Networks
by
Youngmi Baek and Seongjoo Shin
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3319
Abstract
Automotive cyber-physical systems are in transition from the closed-systems to open-networking systems. As a result, in-vehicle networks such as the controller area network (CAN) have become essential to connect to inter-vehicle networks through the various rich interfaces. Newly exposed security concerns derived from
[...] Read more.
Automotive cyber-physical systems are in transition from the closed-systems to open-networking systems. As a result, in-vehicle networks such as the controller area network (CAN) have become essential to connect to inter-vehicle networks through the various rich interfaces. Newly exposed security concerns derived from this requirement may cause in-vehicle networks to pose threats to automotive security and driver’s safety. In this paper, to ensure a high level of security of the in-vehicle network for automotive CPS, we propose a novel lightweight and practical cyber defense platform, referred to as CANon (CAN with origin authentication and non-repudiation), to be enabled to detect cyber-attacks in real-time. CANon is designed based on the hierarchical approach of centralized-session management and distributed-origin authentication. In the former, a gateway node manages each initialization vector and session of origin-centric groups consisting of two more sending and receiving nodes. In the latter, the receiving nodes belonging to the given origin-centric group individually perform the symmetric key-based detection against cyber-attacks by verifying each message received from the sending node, namely origin authentication, in real-time. To improve the control security, CANon employs a one-time local key selected from a sequential hash chain (SHC) for authentication of an origin node in a distributed mode and exploits the iterative hash operations with randomness. Since the SHC can constantly generate and consume hash values regardless of their memory capacities, it is very effective for resource-limited nodes for in-vehicle networks. In addition, through implicit key synchronization within a given group, CANon addresses the challenges of a key exposure problem and a complex key distribution mechanism when performing symmetric key-based authentication. To achieve lightweight cyber-attack detection without imposing an additive load on CAN, CANon uses a keyed-message authentication code (KMAC) activated within a given group. The detection performance of CANon is evaluated under an actual node of Freescale S12XF and virtual nodes operating on the well-known CANoe tool. It is seen that the detection rate of CANon against brute-force and replay attacks reaches 100% when the length of KMAC is over 16 bits. It demonstrates that CANon ensures high security and is sufficient to operate in real-time even on low-performance ECUs. Moreover, CANon based on several software modules operates without an additive hardware security module at an upper layer of the CAN protocol and can be directly ported to CAN-FD (CAN with Flexible Data rate) so that it achieves the practical cyber defense platform.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
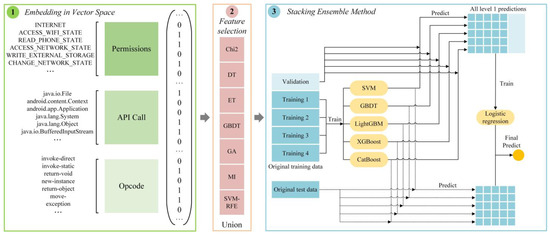
MFDroid: A Stacking Ensemble Learning Framework for Android Malware Detection
by
Xusheng Wang, Linlin Zhang, Kai Zhao, Xuhui Ding and Mingming Yu
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 3767
Abstract
As Android is a popular a mobile operating system, Android malware is on the rise, which poses a great threat to user privacy and security. Considering the poor detection effects of the single feature selection algorithm and the low detection efficiency of traditional
[...] Read more.
As Android is a popular a mobile operating system, Android malware is on the rise, which poses a great threat to user privacy and security. Considering the poor detection effects of the single feature selection algorithm and the low detection efficiency of traditional machine learning methods, we propose an Android malware detection framework based on stacking ensemble learning—MFDroid—to identify Android malware. In this paper, we used seven feature selection algorithms to select permissions, API calls, and opcodes, and then merged the results of each feature selection algorithm to obtain a new feature set. Subsequently, we used this to train the base learner, and set the logical regression as a meta-classifier, to learn the implicit information from the output of base learners and obtain the classification results. After the evaluation, the F1-score of MFDroid reached 96.0%. Finally, we analyzed each type of feature to identify the differences between malicious and benign applications. At the end of this paper, we present some general conclusions. In recent years, malicious applications and benign applications have been similar in terms of permission requests. In other words, the model of training, only with permission, can no longer effectively or efficiently distinguish malicious applications from benign applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
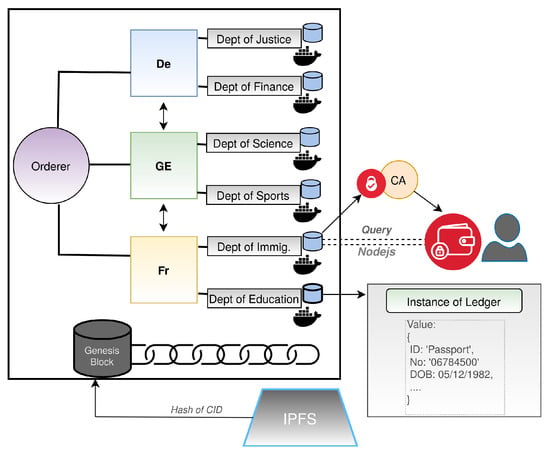
GLASS: A Citizen-Centric Distributed Data-Sharing Model within an e-Governance Architecture
by
Owen Lo, William J. Buchanan, Sarwar Sayeed, Pavlos Papadopoulos, Nikolaos Pitropakis and Christos Chrysoulas
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4607
Abstract
E-governance is a process that aims to enhance a government’s ability to simplify all the processes that may involve government, citizens, businesses, and so on. The rapid evolution of digital technologies has often created the necessity for the establishment of an e-Governance model.
[...] Read more.
E-governance is a process that aims to enhance a government’s ability to simplify all the processes that may involve government, citizens, businesses, and so on. The rapid evolution of digital technologies has often created the necessity for the establishment of an e-Governance model. There is often a need for an inclusive e-governance model with integrated multiactor governance services and where a single market approach can be adopted. e-Governance often aims to minimise bureaucratic processes, while at the same time including a
digital-by-default approach to public services. This aims at administrative efficiency and the reduction of bureaucratic processes. It can also improve government capabilities, and enhances trust and security, which brings confidence in governmental transactions. However, solid implementations of a distributed data sharing model within an e-governance architecture is far from a reality; hence, citizens of European countries often go through the tedious process of having their confidential information verified. This paper focuses on the sinGLe sign-on e-GovernAnce Paradigm based on a distributed file-exchange network for security, transparency, cost-effectiveness and trust (GLASS) model, which aims to ensure that a citizen can control their relationship with governmental agencies. The paper thus proposes an approach that integrates a permissioned blockchain with the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). This method demonstrates how we may encrypt and store verifiable credentials of the GLASS ecosystem, such as academic awards, ID documents and so on, within IPFS in a secure manner and thus only allow trusted users to read a blockchain record, and obtain the encryption key. This allows for the decryption of a given verifiable credential that stored on IPFS. This paper outlines the creation of a demonstrator that proves the principles of the GLASS approach.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
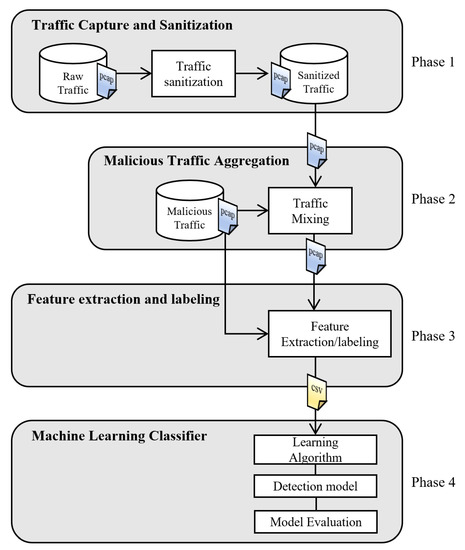
A Novel Framework for Generating Personalized Network Datasets for NIDS Based on Traffic Aggregation
by
Pablo Velarde-Alvarado, Hugo Gonzalez, Rafael Martínez-Peláez, Luis J. Mena, Alberto Ochoa-Brust, Efraín Moreno-García, Vanessa G. Félix and Rodolfo Ostos
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2908
Abstract
In this paper, we addressed the problem of dataset scarcity for the task of network intrusion detection. Our main contribution was to develop a framework that provides a complete process for generating network traffic datasets based on the aggregation of real network traces.
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we addressed the problem of dataset scarcity for the task of network intrusion detection. Our main contribution was to develop a framework that provides a complete process for generating network traffic datasets based on the aggregation of real network traces. In addition, we proposed a set of tools for attribute extraction and labeling of traffic sessions. A new dataset with botnet network traffic was generated by the framework to assess our proposed method with machine learning algorithms suitable for unbalanced data. The performance of the classifiers was evaluated in terms of macro-averages of
F1-score (0.97) and the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (0.94), showing a good overall performance average.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
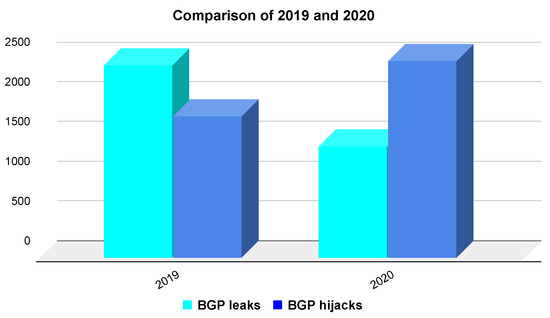
Secure Inter-Domain Routing Based on Blockchain: A Comprehensive Survey
by
Lukas Mastilak, Pavol Helebrandt, Marek Galinski and Ivan Kotuliak
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3987
Abstract
The whole Internet consists of thousands of autonomous systems that transfer data with one another. The BGP plays a significant role in routing, but its behaviour is essentially naive, trusting neighbours without authenticating advertised IP prefixes. This is the main reason why BGP
[...] Read more.
The whole Internet consists of thousands of autonomous systems that transfer data with one another. The BGP plays a significant role in routing, but its behaviour is essentially naive, trusting neighbours without authenticating advertised IP prefixes. This is the main reason why BGP endures various path manipulation attacks. Recently, conventional methods for securing BGP have been implemented, i.e., BGPSec with RPKI. However, these approaches are centralised with a single point of failure that may be compromised, invalidating the whole security mechanism. There have been multiple decentralised projects dealing with various mechanisms, mostly built on Ethereum and blockchain networks. Some with ambition to strengthen existing centralised mechanisms, others to replace them. In this article, we present the first comprehensive survey on blockchain solutions to enforce BGP security, with complex explanations of their contributions and a comparison with different aspects. We explain how blockchain technology can provide an alternative to prevent the false origin of IP prefixes or hijacking AS paths. Moreover, we describe new blockchain-based attacks that BGP would face after the inclusion of blockchain into the inter-domain routing. Finally, we answer the defined research questions and discuss the potential open issues for further study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
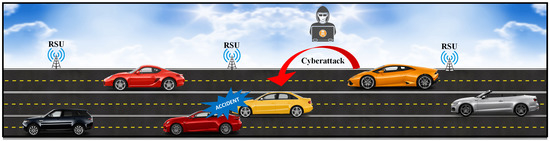
HDL-IDS: A Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for Intrusion Detection in the Internet of Vehicles
by
Safi Ullah, Muazzam A. Khan, Jawad Ahmad, Sajjad Shaukat Jamal, Zil e Huma, Muhammad Tahir Hassan, Nikolaos Pitropakis, Arshad and William J. Buchanan
Cited by 66 | Viewed by 7668
Abstract
Internet of Vehicles (IoV) is an application of the Internet of Things (IoT) network that connects smart vehicles to the internet, and vehicles with each other. With the emergence of IoV technology, customers have placed great attention on smart vehicles. However, the rapid
[...] Read more.
Internet of Vehicles (IoV) is an application of the Internet of Things (IoT) network that connects smart vehicles to the internet, and vehicles with each other. With the emergence of IoV technology, customers have placed great attention on smart vehicles. However, the rapid growth of IoV has also caused many security and privacy challenges that can lead to fatal accidents. To reduce smart vehicle accidents and detect malicious attacks in vehicular networks, several researchers have presented machine learning (ML)-based models for intrusion detection in IoT networks. However, a proficient and real-time faster algorithm is needed to detect malicious attacks in IoV. This article proposes a hybrid deep learning (DL) model for cyber attack detection in IoV. The proposed model is based on long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit (GRU). The performance of the proposed model is analyzed by using two datasets—a combined DDoS dataset that contains CIC DoS, CI-CIDS 2017, and CSE-CIC-IDS 2018, and a car-hacking dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves higher attack detection accuracy of 99.5% and 99.9% for DDoS and car hacks, respectively. The other performance scores, precision, recall, and F1-score, also verify the superior performance of the proposed framework.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
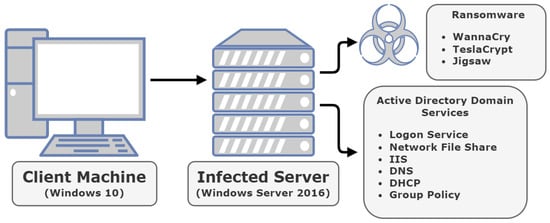
Ransomware: Analysing the Impact on Windows Active Directory Domain Services
by
Grant McDonald, Pavlos Papadopoulos, Nikolaos Pitropakis, Jawad Ahmad and William J. Buchanan
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 9049
Abstract
Ransomware has become an increasingly popular type of malware across the past decade and continues to rise in popularity due to its high profitability. Organisations and enterprises have become prime targets for ransomware as they are more likely to succumb to ransom demands
[...] Read more.
Ransomware has become an increasingly popular type of malware across the past decade and continues to rise in popularity due to its high profitability. Organisations and enterprises have become prime targets for ransomware as they are more likely to succumb to ransom demands as part of operating expenses to counter the cost incurred from downtime. Despite the prevalence of ransomware as a threat towards organisations, there is very little information outlining how ransomware affects Windows Server environments, and particularly its proprietary domain services such as Active Directory. Hence, we aim to increase the cyber situational awareness of organisations and corporations that utilise these environments. Dynamic analysis was performed using three ransomware variants to uncover how crypto-ransomware affects Windows Server-specific services and processes. Our work outlines the practical investigation undertaken as WannaCry, TeslaCrypt, and Jigsaw were acquired and tested against several domain services. The findings showed that none of the three variants stopped the processes and decidedly left all domain services untouched. However, although the services remained operational, they became uniquely dysfunctional as ransomware encrypted the files pertaining to those services.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
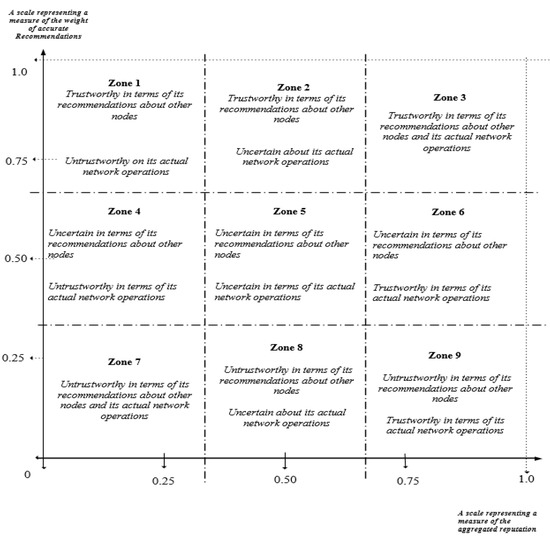
A Robust Dirichlet Reputation and Trust Evaluation of Nodes in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
by
Eric Chiejina, Hannan Xiao, Bruce Christianson, Alexios Mylonas and Chidinma Chiejina
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 2440
Abstract
The distributed nature of mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) presents security challenges and vulnerabilities which sometimes lead to several forms of attacks. To improve the security in MANETs, reputation and trust management systems (RTMS) have been developed to mitigate some attacks and threats
[...] Read more.
The distributed nature of mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) presents security challenges and vulnerabilities which sometimes lead to several forms of attacks. To improve the security in MANETs, reputation and trust management systems (RTMS) have been developed to mitigate some attacks and threats arising from abnormal behaviours of nodes in networks. Generally, most reputation and trust systems in MANETs focus mainly on penalising uncooperative network nodes. It is a known fact that nodes in MANETs have limited energy resources and as such, the continuous collaboration of cooperative nodes will lead to energy exhaustion. This paper develops and evaluates a robust Dirichlet reputation and trust management system which measures and models the reputation and trust of nodes in the network, and it incorporates candour into the mode of operations of the RTMS without undermining network security. The proposed RTMS employs Dirichlet probability distribution in modelling the individual reputation of nodes and the trust of each node is computed based on the node’s actual network performance and the accuracy of the second-hand reputations it gives about other nodes. The paper also presents a novel candour two-dimensional trustworthiness evaluation technique that categorises the behaviours of nodes based on their evaluated total reputation and trust values. The evaluation and analyses of some of the simulated behaviours of nodes in the deployed MANETs show that the candour two-dimensional trustworthiness evaluation technique is an effective technique that encourages and caters to nodes that continuously contribute to the network despite the reduction in their energy levels.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Adaptive, Situation-Based Risk Assessment and Security Enforcement Framework for the Maritime Sector
by
Christos Grigoriadis, Romain Laborde, Antonin Verdier and Panayiotis Kotzanikolaou
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3044
Abstract
Maritime processes involve actors and systems that continuously change their underlying environment, location and threat exposure. Thus, risk mitigation requires a dynamic risk assessment process, coupled with an adaptive, event driven security enforcement mechanism, to efficiently deal with dynamically evolving risks in a
[...] Read more.
Maritime processes involve actors and systems that continuously change their underlying environment, location and threat exposure. Thus, risk mitigation requires a dynamic risk assessment process, coupled with an adaptive, event driven security enforcement mechanism, to efficiently deal with dynamically evolving risks in a cost efficient manner. In this paper, we propose an adaptive security framework that covers both situational risk assessment and situational driven security policy deployment. We extend MITIGATE, a maritime-specific risk assessment methodology, to capture situations in the risk assessment process and thus produce fine-grained and situation-specific, dynamic risk estimations. Then, we integrate DynSMAUG, a situation-driven security management system, to enforce adaptive security policies that dynamically implement security controls specific to each situation. To validate the proposed framework, we test it based on maritime cargo transfer service. We utilize various maritime specific and generic systems employed during cargo transfer, to produce dynamic risks for various situations. Our results show that the proposed framework can effectively assess dynamic risks per situation and automate the enforcement of adaptive security controls per situation. This is an important improvement in contrast to static and situation-agnostic risk assessment frameworks, where security controls always default to worst-case risks, with a consequent impact on the cost and the applicability of proper security controls.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions
by
Malak Aljabri, Sumayh S. Aljameel, Rami Mustafa A. Mohammad, Sultan H. Almotiri, Samiha Mirza, Fatima M. Anis, Menna Aboulnour, Dorieh M. Alomari, Dina H. Alhamed and Hanan S. Altamimi
Cited by 41 | Viewed by 10491
Abstract
The significant growth in the use of the Internet and the rapid development of network technologies are associated with an increased risk of network attacks. Network attacks refer to all types of unauthorized access to a network including any attempts to damage and
[...] Read more.
The significant growth in the use of the Internet and the rapid development of network technologies are associated with an increased risk of network attacks. Network attacks refer to all types of unauthorized access to a network including any attempts to damage and disrupt the network, often leading to serious consequences. Network attack detection is an active area of research in the community of cybersecurity. In the literature, there are various descriptions of network attack detection systems involving various intelligent-based techniques including machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models. However, although such techniques have proved useful within specific domains, no technique has proved useful in mitigating all kinds of network attacks. This is because some intelligent-based approaches lack essential capabilities that render them reliable systems that are able to confront different types of network attacks. This was the main motivation behind this research, which evaluates contemporary intelligent-based research directions to address the gap that still exists in the field. The main components of any intelligent-based system are the training datasets, the algorithms, and the evaluation metrics; these were the main benchmark criteria used to assess the intelligent-based systems included in this research article. This research provides a rich source of references for scholars seeking to determine their scope of research in this field. Furthermore, although the paper does present a set of suggestions about future inductive directions, it leaves the reader free to derive additional insights about how to develop intelligent-based systems to counter current and future network attacks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Denial-of-Service Attack on IEC 61850-Based Substation Automation System: A Crucial Cyber Threat towards Smart Substation Pathways
by
Suleman Ashraf, Mohammad H. Shawon, Haris M. Khalid and S. M. Muyeen
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 5117
Abstract
The generation of the mix-based expansion of modern power grids has urged the utilization of digital infrastructures. The introduction of Substation Automation Systems (SAS), advanced networks and communication technologies have drastically increased the complexity of the power system, which could prone the entire
[...] Read more.
The generation of the mix-based expansion of modern power grids has urged the utilization of digital infrastructures. The introduction of Substation Automation Systems (SAS), advanced networks and communication technologies have drastically increased the complexity of the power system, which could prone the entire power network to hackers. The exploitation of the cyber security vulnerabilities by an attacker may result in devastating consequences and can leave millions of people in severe power outage. To resolve this issue, this paper presents a network model developed in OPNET that has been subjected to various Denial of Service (DoS) attacks to demonstrate cyber security aspect of an international electrotechnical commission (IEC) 61850 based digital substations. The attack scenarios have exhibited significant increases in the system delay and the prevention of messages, i.e., Generic Object-Oriented Substation Events (GOOSE) and Sampled Measured Values (SMV), from being transmitted within an acceptable time frame. In addition to that, it may cause malfunction of the devices such as unresponsiveness of Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), which could eventually lead to catastrophic scenarios, especially under different fault conditions. The simulation results of this work focus on the DoS attack made on SAS. A detailed set of rigorous case studies have been conducted to demonstrate the effects of these attacks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
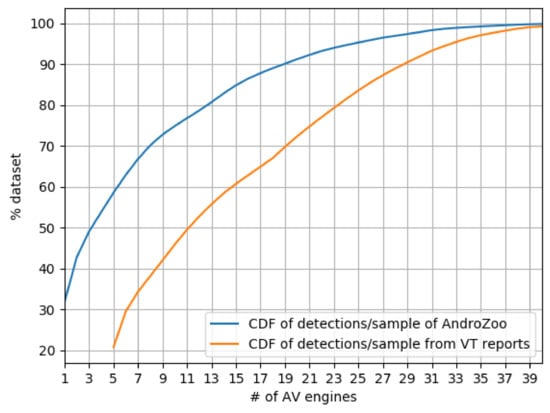
An Analysis of Android Malware Classification Services
by
Mohammed Rashed and Guillermo Suarez-Tangil
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 5566
Abstract
The increasing number of Android malware forced antivirus (AV) companies to rely on automated classification techniques to determine the family and class of suspicious samples. The research community relies heavily on such labels to carry out prevalence studies of the threat ecosystem and
[...] Read more.
The increasing number of Android malware forced antivirus (AV) companies to rely on automated classification techniques to determine the family and class of suspicious samples. The research community relies heavily on such labels to carry out prevalence studies of the threat ecosystem and to build datasets that are used to validate and benchmark novel detection and classification methods. In this work, we carry out an extensive study of the Android malware ecosystem by surveying white papers and reports from 6 key players in the industry, as well as 81 papers from 8 top security conferences, to understand how malware datasets are used by both. We, then, explore the limitations associated with the use of available malware classification services, namely VirusTotal (VT) engines, for determining the family of an Android sample. Using a dataset of 2.47 M Android malware samples, we find that the detection coverage of VT’s AVs is generally very low, that the percentage of samples flagged by any 2 AV engines does not go beyond 52%, and that common families between any pair of AV engines is at best 29%. We rely on clustering to determine the extent to which different AV engine pairs agree upon which samples belong to the same family (regardless of the actual family name) and find that there are discrepancies that can introduce noise in automatic label unification schemes. We also observe the usage of generic labels and inconsistencies within the labels of top AV engines, suggesting that their efforts are directed towards accurate detection rather than classification. Our results contribute to a better understanding of the limitations of using Android malware family labels as supplied by common AV engines.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Misinformation vs. Situational Awareness: The Art of Deception and the Need for Cross-Domain Detection
by
Constantinos-Giovanni Xarhoulacos, Argiro Anagnostopoulou, George Stergiopoulos and Dimitris Gritzalis
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4140
Abstract
The world has been afflicted by the rise of misinformation. The sheer volume of news produced daily necessitates the development of automated methods for separating fact from fiction. To tackle this issue, the computer science community has produced a plethora of approaches, documented
[...] Read more.
The world has been afflicted by the rise of misinformation. The sheer volume of news produced daily necessitates the development of automated methods for separating fact from fiction. To tackle this issue, the computer science community has produced a plethora of approaches, documented in a number of surveys. However, these surveys primarily rely on one-dimensional solutions, i.e., deception detection approaches that focus on a specific aspect of misinformation, such as a particular topic, language, or source. Misinformation is considered a major obstacle for situational awareness, including cyber, both from a company and a societal point of view. This paper explores the evolving field of misinformation detection and analytics on information published in news articles, with an emphasis on methodologies that handle multiple dimensions of the fake news detection conundrum. We analyze and compare existing research on cross-dimensional methodologies. Our evaluation process is based on a set of criteria, including a predefined set of performance metrics, data pre-processing features, and domains of implementation. Furthermore, we assess the adaptability of each methodology in detecting misinformation in real-world news and thoroughly analyze our findings. Specifically, survey insights demonstrate that when a detection approach focuses on several dimensions (e.g., languages and topics, languages and sources, etc.), its performance improves, and it becomes more flexible in detecting false information across different contexts. Finally, we propose a set of research directions that could aid in furthering the development of more advanced and accurate models in this field.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
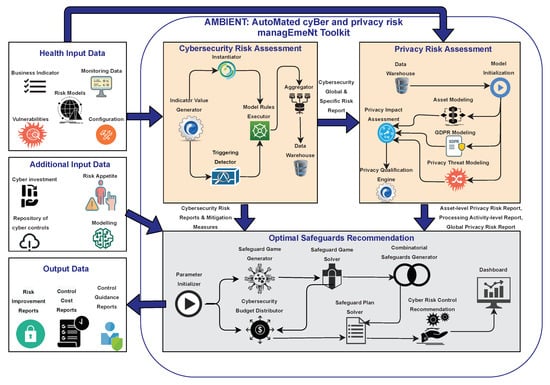
Automated Cyber and Privacy Risk Management Toolkit
by
Gustavo Gonzalez-Granadillo, Sofia Anna Menesidou, Dimitrios Papamartzivanos, Ramon Romeu, Diana Navarro-Llobet, Caxton Okoh, Sokratis Nifakos, Christos Xenakis and Emmanouil Panaousis
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 9745
Abstract
Addressing cyber and privacy risks has never been more critical for organisations. While a number of risk assessment methodologies and software tools are available, it is most often the case that one must, at least, integrate them into a holistic approach that combines
[...] Read more.
Addressing cyber and privacy risks has never been more critical for organisations. While a number of risk assessment methodologies and software tools are available, it is most often the case that one must, at least, integrate them into a holistic approach that combines several appropriate risk sources as input to risk mitigation tools. In addition, cyber risk assessment primarily investigates cyber risks as the consequence of vulnerabilities and threats that threaten assets of the investigated infrastructure. In fact, cyber risk assessment is decoupled from privacy impact assessment, which aims to detect privacy-specific threats and assess the degree of compliance with data protection legislation. Furthermore, a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) is conducted in a proactive manner during the design phase of a system, combining processing activities and their inter-dependencies with assets, vulnerabilities, real-time threats and Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that may occur during the dynamic life-cycle of systems. In this paper, we propose a cyber and privacy risk management toolkit, called AMBIENT (Automated Cyber and Privacy Risk Management Toolkit) that addresses the above challenges by implementing and integrating three distinct software tools. AMBIENT not only assesses cyber and privacy risks in a thorough and automated manner but it also offers decision-support capabilities, to recommend optimal safeguards using the well-known repository of the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls. To the best of our knowledge, AMBIENT is the first toolkit in the academic literature that brings together the aforementioned capabilities. To demonstrate its use, we have created a case scenario based on information about cyber attacks we have received from a healthcare organisation, as a reference sector that faces critical cyber and privacy threats.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
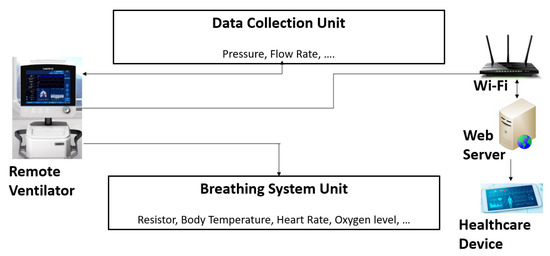
Cyber Risks Prediction and Analysis in Medical Emergency Equipment for Situational Awareness
by
George Burke and Neetesh Saxena
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3209
Abstract
In light of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency administered the standards for producing a Rapidly Manufactured Ventilator System (RMVS) free of charge due to the United Kingdom’s shortfall of ventilator systems throughout health centers. The standards delineate the
[...] Read more.
In light of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency administered the standards for producing a Rapidly Manufactured Ventilator System (RMVS) free of charge due to the United Kingdom’s shortfall of ventilator systems throughout health centers. The standards delineate the minimum requirements in which a Rapidly Manufactured Ventilator System must encompass to be admissible for usage within hospitals. This work commences by evaluating the standards provided by the government to identify any potential security vulnerabilities that may arise due to the succinct development standards provided by the MHRA. This research investigates what cyber considerations are taken to safeguard a patient’s health and medical data to improve situational awareness. A tool for a remotely accessible, low-cost ventilator system is developed to reveal what a malicious actor may be able to inflict on a modern ventilator and its adverse impact.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
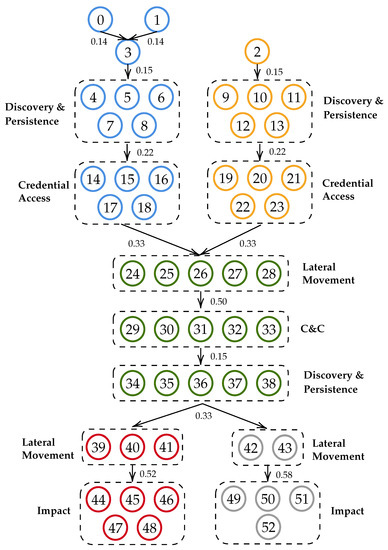
Game-Theoretic Decision Support for Cyber Forensic Investigations
by
Antonia Nisioti, George Loukas, Stefan Rass and Emmanouil Panaousis
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3032
Abstract
The use of anti-forensic techniques is a very common practice that stealthy adversaries may deploy to minimise their traces and make the investigation of an incident harder by evading detection and attribution. In this paper, we study the interaction between a cyber forensic
[...] Read more.
The use of anti-forensic techniques is a very common practice that stealthy adversaries may deploy to minimise their traces and make the investigation of an incident harder by evading detection and attribution. In this paper, we study the interaction between a cyber forensic Investigator and a strategic Attacker using a game-theoretic framework. This is based on a Bayesian game of incomplete information played on a multi-host cyber forensics investigation graph of actions traversed by both players. The edges of the graph represent players’ actions across different hosts in a network. In alignment with the concept of Bayesian games, we define two Attacker types to represent their ability of deploying anti-forensic techniques to conceal their activities. In this way, our model allows the Investigator to identify the optimal investigating policy taking into consideration the cost and impact of the available actions, while coping with the uncertainty of the Attacker’s type and strategic decisions. To evaluate our model, we construct a realistic case study based on threat reports and data extracted from the MITRE ATT&CK STIX repository, Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), and interviews with cyber-security practitioners. We use the case study to compare the performance of the proposed method against two other investigative methods and three different types of Attackers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
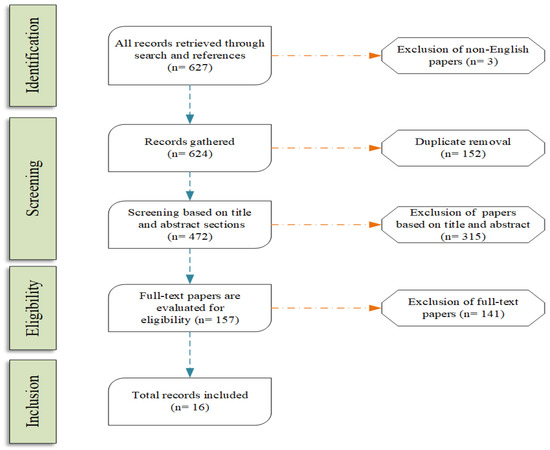
Influence of Human Factors on Cyber Security within Healthcare Organisations: A Systematic Review
by
Sokratis Nifakos, Krishna Chandramouli, Charoula Konstantina Nikolaou, Panagiotis Papachristou, Sabine Koch, Emmanouil Panaousis and Stefano Bonacina
Cited by 111 | Viewed by 28699
Abstract
Background: Cybersecurity is increasingly becoming a prominent concern among healthcare providers in adopting digital technologies for improving the quality of care delivered to patients. The recent reports on cyber attacks, such as ransomware and WannaCry, have brought to life the destructive nature of
[...] Read more.
Background: Cybersecurity is increasingly becoming a prominent concern among healthcare providers in adopting digital technologies for improving the quality of care delivered to patients. The recent reports on cyber attacks, such as ransomware and WannaCry, have brought to life the destructive nature of such attacks upon healthcare. In complement to cyberattacks, which have been targeted against the vulnerabilities of information technology (IT) infrastructures, a new form of cyber attack aims to exploit human vulnerabilities; such attacks are categorised as social engineering attacks. Following an increase in the frequency and ingenuity of attacks launched against hospitals and clinical environments with the intention of causing service disruption, there is a strong need to study the level of awareness programmes and training activities offered to the staff by healthcare organisations.
Objective: The objective of this systematic review is to identify commonly encountered factors that cybersecurity postures of a healthcare organisation, resulting from the ignorance of cyber threat to healthcare. The systematic review aims to consolidate the current literature being reported upon human behaviour resulting in security gaps that mitigate the cyber defence strategy adopted by healthcare organisations. Additionally, the paper also reviews the organisational risk assessment methodology implemented and the policies being adopted to strengthen cybersecurity.
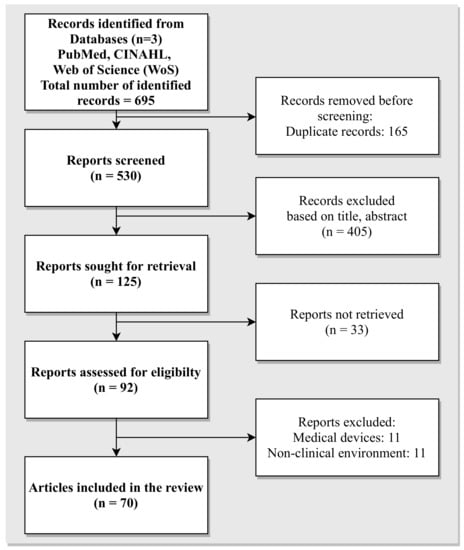
Methods: The topic of cybersecurity within healthcare and the clinical environment has attracted the interest of several researchers, resulting in a broad range of literature. The inclusion criteria for the articles in the review stem from the scope of the five research questions identified. To this end, we conducted seven search queries across three repositories, namely (i) PubMed
®/MED-LINE; (ii) Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL); and (iii) Web of Science (WoS), using key words related to cybersecurity awareness, training, organisation risk assessment methodologies, policies and recommendations adopted as counter measures within health care. These were restricted to around the last 12 years.
Results: A total of 70 articles were selected to be included in the review, which addresses the complexity of cybersecurity measures adopted within the healthcare and clinical environments. The articles included in the review highlight the evolving nature of cybersecurity threats stemming from exploiting IT infrastructures to more advanced attacks launched with the intent of exploiting human vulnerability. A steady increase in the literature on the threat of phishing attacks evidences the growing threat of social engineering attacks. As a countermeasure, through the review, we identified articles that provide methodologies resulting from case studies to promote cybersecurity awareness among stakeholders. The articles included highlight the need to adopt cyber hygiene practices among healthcare professionals while accessing social media platforms, which forms an ideal test bed for the attackers to gain insight into the life of healthcare professionals. Additionally, the review also includes articles that present strategies adopted by healthcare organisations in countering the impact of social engineering attacks. The evaluation of the cybersecurity risk assessment of an organisation is another key area of study reported in the literature that recommends the organisation of European and international standards in countering social engineering attacks. Lastly, the review includes articles reporting on national case studies with an overview of the economic and societal impact of service disruptions encountered due to cyberattacks.
Discussion: One of the limitations of the review is the subjective ranking of the authors associated to the relevance of literature to each of the research questions identified. We also acknowledge the limited amount of literature that focuses on human factors of cybersecurity in health care in general; therefore, the search queries were formulated using well-established cybersecurity related topics categorised according to the threats, risk assessment and organisational strategies reported in the literature.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Retrospective IP Address Geolocation for Geography-Aware Internet Services
by
Dan Komosny
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 8788
Abstract
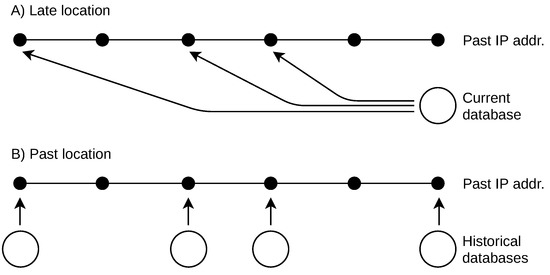
The paper deals with the locations of IP addresses that were used in the past. This retrospective geolocation suffers from continuous changes in the Internet space and a limited availability of past IP location databases. I analyse the retrospective geolocation of IPv4 and
[...] Read more.
The paper deals with the locations of IP addresses that were used in the past. This retrospective geolocation suffers from continuous changes in the Internet space and a limited availability of past IP location databases. I analyse the retrospective geolocation of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses over five years. An approach is also introduced to handle missing past IP geolocation databases. The results show that it is safe to retrospectively locate IP addresses by a couple of years, but there are differences between IPv4 and IPv6. The described parametric model of location lifetime allows us to estimate the time when the address location changed in the past. The retrospective geolocation of IP addresses has a broad range of applications, including social studies, system analyses, and security investigations. Two longitudinal use cases with the applied results are discussed. The first deals with geotargeted online content. The second deals with identity theft prevention in e-commerce.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Towards a Machine Learning Based Situational Awareness Framework for Cybersecurity: An SDN Implementation
by
Yannis Nikoloudakis, Ioannis Kefaloukos, Stylianos Klados, Spyros Panagiotakis, Evangelos Pallis, Charalabos Skianis and Evangelos K. Markakis
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 5496
Abstract
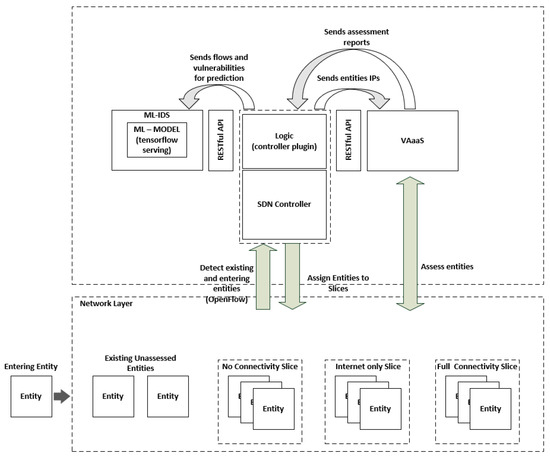
The ever-increasing number of internet-connected devices, along with the continuous evolution of cyber-attacks, in terms of volume and ingenuity, has led to a widened cyber-threat landscape, rendering infrastructures prone to malicious attacks. Towards addressing systems’ vulnerabilities and alleviating the impact of these threats,
[...] Read more.
The ever-increasing number of internet-connected devices, along with the continuous evolution of cyber-attacks, in terms of volume and ingenuity, has led to a widened cyber-threat landscape, rendering infrastructures prone to malicious attacks. Towards addressing systems’ vulnerabilities and alleviating the impact of these threats, this paper presents a machine learning based situational awareness framework that detects existing and newly introduced network-enabled entities, utilizing the real-time awareness feature provided by the SDN paradigm, assesses them against known vulnerabilities, and assigns them to a connectivity-appropriate network slice. The assessed entities are continuously monitored by an ML-based IDS, which is trained with an enhanced dataset. Our endeavor aims to demonstrate that a neural network, trained with heterogeneous data stemming from the operational environment (common vulnerability enumeration IDs that correlate attacks with existing vulnerabilities), can achieve more accurate prediction rates than a conventional one, thus addressing some aspects of the situational awareness paradigm. The proposed framework was evaluated within a real-life environment and the results revealed an increase of more than 4% in the overall prediction accuracy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Contextualized Filtering for Shared Cyber Threat Information
by
Athanasios Dimitriadis, Christos Prassas, Jose Luis Flores, Boonserm Kulvatunyou, Nenad Ivezic, Dimitris A. Gritzalis and Ioannis K. Mavridis
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3406
Abstract
Cyber threat information sharing is an imperative process towards achieving collaborative security, but it poses several challenges. One crucial challenge is the plethora of shared threat information. Therefore, there is a need to advance filtering of such information. While the state-of-the-art in filtering
[...] Read more.
Cyber threat information sharing is an imperative process towards achieving collaborative security, but it poses several challenges. One crucial challenge is the plethora of shared threat information. Therefore, there is a need to advance filtering of such information. While the state-of-the-art in filtering relies primarily on keyword- and domain-based searching, these approaches require sizable human involvement and rarely available domain expertise. Recent research revealed the need for harvesting of business information to fill the gap in filtering, albeit it resulted in providing coarse-grained filtering based on the utilization of such information. This paper presents a novel contextualized filtering approach that exploits standardized and multi-level contextual information of business processes. The contextual information describes the conditions under which a given threat information is actionable from an organization perspective. Therefore, it can automate filtering by measuring the equivalence between the context of the shared threat information and the context of the consuming organization. The paper directly contributes to filtering challenge and indirectly to automated customized threat information sharing. Moreover, the paper proposes the architecture of a cyber threat information sharing ecosystem that operates according to the proposed filtering approach and defines the characteristics that are advantageous to filtering approaches. Implementation of the proposed approach can support compliance with the Special Publication 800-150 of the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Analysis, Trends, and Usage in Critical Infrastructures
by
Gustavo González-Granadillo, Susana González-Zarzosa and Rodrigo Diaz
Cited by 98 | Viewed by 33655
Abstract
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems have been widely deployed as a powerful tool to prevent, detect, and react against cyber-attacks. SIEM solutions have evolved to become comprehensive systems that provide a wide visibility to identify areas of high risks and proactively
[...] Read more.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems have been widely deployed as a powerful tool to prevent, detect, and react against cyber-attacks. SIEM solutions have evolved to become comprehensive systems that provide a wide visibility to identify areas of high risks and proactively focus on mitigation strategies aiming at reducing costs and time for incident response. Currently, SIEM systems and related solutions are slowly converging with big data analytics tools. We survey the most widely used SIEMs regarding their critical functionality and provide an analysis of external factors affecting the SIEM landscape in mid and long-term. A list of potential enhancements for the next generation of SIEMs is provided as part of the review of existing solutions as well as an analysis on their benefits and usage in critical infrastructures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Comparative Analysis of Honeypots on Different Cloud Platforms
by
Christopher Kelly, Nikolaos Pitropakis, Alexios Mylonas, Sean McKeown and William J. Buchanan
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 8940
Abstract
In 2019, the majority of companies used at least one cloud computing service and it is expected that by the end of 2021, cloud data centres will process 94% of workloads. The financial and operational advantages of moving IT infrastructure to specialised cloud
[...] Read more.
In 2019, the majority of companies used at least one cloud computing service and it is expected that by the end of 2021, cloud data centres will process 94% of workloads. The financial and operational advantages of moving IT infrastructure to specialised cloud providers are clearly compelling. However, with such volumes of private and personal data being stored in cloud computing infrastructures, security concerns have risen. Motivated to monitor and analyze adversarial activities, we deploy multiple honeypots on the popular cloud providers, namely Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Microsoft Azure, and operate them in multiple regions. Logs were collected over a period of three weeks in May 2020 and then comparatively analysed, evaluated and visualised. Our work revealed heterogeneous attackers’ activity on each cloud provider, both when one considers the volume and origin of attacks, as well as the targeted services and vulnerabilities. Our results highlight the attempt of threat actors to abuse popular services, which were widely used during the COVID-19 pandemic for remote working, such as remote desktop sharing. Furthermore, the attacks seem to exit not only from countries that are commonly found to be the source of attacks, such as China, Russia and the United States, but also from uncommon ones such as Vietnam, India and Venezuela. Our results provide insights on the adversarial activity during our experiments, which can be used to inform the Situational Awareness operations of an organisation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Human Factors affecting cyber security within Healthcare organisations: A Systematic Review
Authors: Sokratis Nifakos; Krishna Chandramouli; Panos Parachristou; Sabine Kocha; Emmanuil Panaousis; Stefano Bonacina
Affiliation: a. Karolinska Institutet, Sweden,
b. Queen Mary University of London, UK,
c. University of Greenwich, UK
Abstract: Background: The success of adopting digital transformation strategies within healthcare sector is dependent upon the cooperation and acceptance of such solutions among healthcare stakeholders including administrators, front line staff, IT personnel, patients and others. With increasing reports of cybersecurity attacks against hospitals and clinical environments, there is a strong need to study the level of awareness programs and training activities offered to the staff by healthcare organisations
Objective: The objective of this systematic review is to identify commonly encountered factors that cybersecurity posture of a healthcare organisation resulting from the ignorance of cyber threat to healthcare. The systematic review aims to consolidate the current literature being reported upon human behaviour resulting in security gaps that mitigates the cyber defense strategy adopted by healthcare organisations. Additionally, the paper also reviews organizational risk assessment methodology implemented and the policies being adopted to strengthen cybersecurity.
Methods: We conducted five separate searchers through PubMed (MED-LINE) using key words related to cybersecurity awareness, training , organisation risk assessment methodologies, policies and recommendations adopted as counter measures within healthcare. These were restricted to past 10 years (2010-2021), and have identified more 76 papers that met the objective criteria.
Title: A Method for Detecting LDoS Attacks based on improved Hilbert-Huang Transform and Convolutional Neural Network
Authors: Yazhi Liu,Ding Sun,Wei Li, Rundong Zhang
Affiliation: College of Artificial intelligence, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China