Assessment of Time and Frequency Domain Entropies to Detect Sleep Apnoea in Heart Rate Variability Recordings from Men and Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Subjects and Signals under Study
2.2. Analysis in Frequency Domain: Spectral Entropy
2.3. Nonlinear Analysis in Time Domain: Multiscale Entropy
2.4. Logistic Regression: Automatic Feature Selection and Classification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
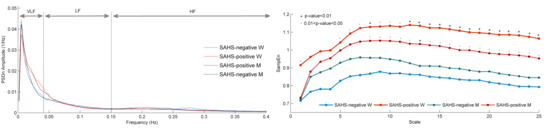
3.1. Spectral Entropy
3.2. Multiscale Entropy
3.3. Feature Selection and Classification Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez-Jiménez, F.; Kuniyoshi, F.H.S.; Gami, A.; Somers, V.K. Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Chest 2008, 133, 793–804. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.P.; Schneider, H.; Schwartz, A.R.; Smith, P.L. Adult obstructive sleep apnea: Pathophysiology and diagnosis. Chest 2007, 132, 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Ramar, K.; Rogers, R.; Schwab, R.J.; Weaver, E.M.; et al. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.A.; Kinnear, W.J.M. Sleep on the cheap: The role of overnight oximetry in the diagnosis of sleep apnoea hypopnoea syndrome. Thorax 1999, 54, 958–959. [Google Scholar]
- Iber, C.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Chesson, A.L.; Quan, S.F. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Flemons, W.W.; Littner, M.R.; Rowley, J.A.; Gay, P.; Anderson, W.M.; Hudgel, D.W.; McEvoy, R.D.; Loube, D.I. Home diagnosis of sleep apnea: A systematic review of the literature. Chest 2003, 124, 1543–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Flemons, W.W.; Douglas, N.J.; Kuna, S.T.; Rodenstein, D.O.; Wheatley, J. Access to diagnosis and treatment of patients with suspected sleep apnea. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 668–672. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Joseph, K.P.; Kannathal, N.; Lim, C.M.; Suri, J.S. Heart rate variability: A review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault, C.; Winkle, R.; Connolly, S.; Melvin, K.; Tilkian, A. Cyclical variation of the heart rate in sleep apnoea syndrome: Mechanisms and usefulness of 24 h electrocardiography as a screening technique. Lancet 1984, 323, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bonsignore, M.R.; Romano, S.; Marrone, O.; Chiodi, M.; Bonsignore, G. Different heart rate patterns in obstructive apneas during NREM sleep. Sleep 1997, 20, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Grote, L.; Peter, J.H.; Bunde, A. Comparison of detrended fluctuation analysis and spectral analysis for heart rate variability in sleep and sleep apnea. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Gula, L.J.; Krahn, A.D.; Skanes, A.; Ferguson, K.A.; George, C.; Yee, R.; Klein, G.J. Heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea: A prospective study and frequency domain analysis. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2003, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; Wessel, N.; Riedl, M.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Rostig, S.; Glos, M.; Suhrbier, A.; Malberg, H.; Fietze, I. Cardiovascular and respiratory dynamics during normal and pathological sleep. Chaos 2007, 17, 015116. [Google Scholar]
- Gapelyuk, A.; Riedl, M.; Suhrbier, A.; Kraemer, J.F.; Bretthauer, G.; Malberg, H.; Kurths, J.; Penzel, T.; Wessel, N. Cardiovascular regulation in different sleep stages in the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Biomed. Technik. (Biomed. Eng.) 2011, 56, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L. Is the normal heartbeat chaotic or homeostatic? News Physiol. Sci. 1991, 6, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, N.; Riedl, M.; Kurths, J. Is the normal heart rate “chaotic” due to respiration? Chaos 2009, 19, 028508. [Google Scholar]
- Poza, J.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A.; García, M. Extraction of spectral based measures from MEG background oscillations in Alzheimerʼs disease. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.C.; Wu, H.T.; Chen, H.R.; Liu, A.B.; Yeh, J.J.; Lo, M.T.; Tsao, J.H.; Tang, C.-J.; Tsai, I.-T.; Sun, C.-K. Application of a Modified Entropy Computational Method in Assessing the Complexity of Pulse Wave Velocity Signals in Healthy and Diabetic Subjects. Entropy 2014, 16, 4032–4043. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, R.; Rieta, J.J. Sample entropy of the main atrial wave predicts spontaneous termination of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 917–922. [Google Scholar]
- Hornero, R.; Álvarez, D.; Abásolo, D.; del Campo, F.; Zamarrón, C. Utility of approximate entropy from overnight pulse oximetry data in the diagnosis of the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Angari, H.M.; Sahakian, A.V. Use of sample entropy approach to study heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.D.; Peng, C.K.; Goldberger, A.L. Multiscale analysis of heart rate dynamics: Entropy and time irreversibility measures. Cardiovasc. Eng. 2008, 8, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.D.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of biological signals. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 021906. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.D.; Peng, C.K.; Goldberger, A.L.; Hausdorff, J.M. Multiscale entropy analysis of human gait dynamics. Physica A 2003, 330, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, J.; Abásolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; López, M. Analysis of electroencephalograms in Alzheimer’s disease patients with multiscale entropy. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Cho, R.Y.; Mizuno, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Murata, T.; Takahashi, K.; Wada, Y. Antipsychotics reverse abnormal EEG complexity in drug-naive schizophrenia: A multiscale entropy analysis. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hans, P.; Dewandre, P.Y.; Brichant, J.F.; Bonhomme, V. Comparative effects of ketamine on Bispectral Index and spectral entropy of the electroencephalogram under sevoflurane anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 94, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.L.; Hung, J.W.; Lee, L.S. Robust entropy-based endpoint detection for speech recognition in noisy environments. ICSLP 1998, 98, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Abásolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Álvarez, D.; Poza, J. Entropy analysis of the EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, D.; Hornero, R.; Marcos, J.V.; Wessel, N.; Penzel, T.; Glos, M.; del Campo, F. Assessment of Feature Selection and Classification Approaches to Enhance Information from Overnight Oximetry in the Context of Apnea Diagnosis. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2013, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnemeier, H.; Wiegand, U.K.; Brandes, A.; Kluge, N.; Katus, H.A.; Richardt, G.; Potratz, J. Circadian profile of cardiac autonomic nervous modulation in healthy subjects. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 791–799. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Marcus, C.L.; Mehra, R.; Parthasarathy, S.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar]
- Baselli, G.; Cerutti, S.; Civardi, S.; Lombardi, F.; Malliani, A.; Merri, M.; Pagani, M.; Rizzo, G. Heart rate variability signal processing: A quantitative approach as an aid to diagnosis in cardiovascular pathologies. Int. J. Biol. Med. Comput. 1987, 20, 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, D.; Gaydecki, P.A.; Zaidi, A.; Fitzpatrick, A.P. The use of the Hilbert transform in ECG signal analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, P.D. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes del Paso, G.A.; Langewitz, W.; Mulder, L.J.; Roon, A.; Duschek, S. The utility of low frequency heart rate variability as an index of sympathetic cardiac tone: A review with emphasis on a reanalysis of previous studies. Psychophysiology 2013, 50, 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Sztajzel, J. Heart rate variability: A noninvasive electrocardiographic method to measure the autonomic nervous system. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2004, 134, 514–522. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, T.; Shinosaki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Toi, S.; Ukai, S.; Iyama, A.; Katsuda, Y.; Hirano, M. Quantification of EEG irregularity by use of the entropy of the power spectrum. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1991, 79, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh, J.W.; Steyn-Ross, D.A.; Steyn-Ross;, M.L.; Grant, C.; Ludbrook, G. Cortical entropy changes with general anaesthesia: Theory and experiment. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, 921–934. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1999, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, R.; Rieta, J.J. A review on sample entropy applications for the non-invasive analysis of atrial fibrillation electrocardiograms. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control. 2010, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, D.J.; Malhotra, A. Pathophysiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc. Am. Thoracic Soc. 2008, 5, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Hornero, R.; Álvarez, D.; Marcos, J.V.; del Campo, F. Linear and nonlinear analysis of airflow recordings to help in sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome diagnosis. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Álvarez, D.; Marcos, J.V.; del Campo, F.; Hornero, R. Pattern recognition in airflow recordings to assist in the sleep apnoea–hypopnoea syndrome diagnosis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, M.; Müller, A.; Kraemer, J.F.; Penzel, T.; Kurths, J.; Wessel, N. Cardio-Respiratory Coordination Increases during Sleep Apnea. PLoS One 2014, 9, e93866. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, J.V.; Hornero, R.; Álvarez, D.; del Campo, F.; Zamarrón, C.; López, M. Utility of multilayer perceptron neural network classifiers in the diagnosis of the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome from nocturnal oximetry. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2008, 92, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, J.V.; Hornero, R.; Álvarez, D.; del Campo, F.; Zamarrón, C. Assessment of four statistical pattern recognition techniques to assist in obstructive sleep apnoea diagnosis from nocturnal oximetry. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 971–978. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, D.; Hornero, R.; Marcos, J.V.; del Campo, F. Multivariate analysis of blood oxygen saturation recordings in obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Angari, H.M.; Sahakian, A.V. Automated recognition of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome using support vector machine classifier. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Caseiro, P.; Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Andrade, A. Screening of obstructive sleep apnea using Hilbert-Huang decomposition of oronasal airway pressure recordings. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Fiz, J.A.; Jane, R.; Solà-Soler, J.; Abad, J.; García, M.; Morera, J. Continuous analysis and monitoring of snores and their relationship to the apnea-hypopnea index. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 854–862. [Google Scholar]
- Karunajeewa, A.S.; Abeyratne, U.R.; Hukins, C. Multi-feature snore sound analysis in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, F.; Pichot, V.; Sforza, E.; Duverney, D.; Costes, F.; Garet, M.; Barthélémy, J.C. Predicting sleep apnoea syndrome from heart period: A time-frequency wavelet analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 937–942. [Google Scholar]
- Ravelo-García, A.G.; Saavedra-Santana, P.; Juliá-Serdá, G.; Navarro-Mesa, J.L.; Navarro-Esteva, J.; Álvarez-López, X.; Gapelyuk, A.; Penzel, T.; Wessel, N. Symbolic dynamics marker of heart rate variability combined with clinical variables enhance obstructive sleep apnea screening. Chaos 2006, 24, 024404. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; McNames, J.; de Chazal, P.; Raymond, B.; Murray, A.; Moody, G. Systematic comparison of different algorithms for apnoea detection based on electrocardiogram recordings. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peter, J.H. The apnea-ECG database. In Computers in Cardiology 2000, Proceedings of Conference in Computers in Cardiology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2000; pp. 255–258.
- Peduzzi, P.; Concato, J.; Kemper, E.; Holford, T.R.; Feinstein, A.R. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Kapsimalis, F.; Kryger, M.H. Gender and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, part 1: Clinical features. Sleep 2002, 25, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Constant, I.; Laude, D.; Murat, I.; Elghozi, J.L. Pulse rate variability is not a surrogate for heart rate variability. Clin. Sci. 1999, 97, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, E.; Orini, M.; Bailón, R.; Vergara, J.M.; Mainardi, L.; Laguna, P. Photoplethysmography pulse rate variability as a surrogate measurement of heart rate variability during non-stationary conditions. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 1271. [Google Scholar]




| Women
| Men
| |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | |
| #Subjects | 28 | 26 | 41 | 93 |
| Age (years) | 49.2 ± 8.6 | 58.3 ± 14.3 | 46.0 ± 13.1 | 51.1 ± 11.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 ± 6.9 | 28.8 ± 5.8 | 28.8 ± 5.6 | 29.2 ± 2.9 |
| AHI (e/h) | 3.3 ± 2.3 | 32.8 ± 24.7 | 4.1 ± 2.5 | 33.0 ± 22.5 |
| Women
| Men
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | p-value | SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | p-value | |
| SEVLF | 0.959 ± 0.020 | 0.971 ± 0.011 | <0.01 | 0.958 ± 0.020 | 0.966 ± 0.018 | <0.01 |
| SELF | 0.984 ± 0.011 | 0.959 ± 0.028 | <10−4 | 0.983 ± 0.012 | 0.960 ± 0.035 | <10−4 |
| SEHF | 0.979 ± 0.021 | 0.970 ± 0.022 | 0.158 | 0.983 ± 0.015 | 0.976 ± 0.023 | 0.219 |
| SEVLF-HF | 0.899 ± 0.060 | 0.863 ± 0.051 | <0.05 | 0.900 ± 0.053 | 0.873 ± 0.061 | <0.05 |
| Number of Features | Features Selected | |
|---|---|---|
| Women | 5 | SEVLF, SELF, SampEn1, SampEn2, and SampEn7 |
| Men | 12 | SEVLF, SELF, SEVLF-HF, SampEn2, SampEn10, SampEn13, SampEn16, SampEn17, and SampEn20- SampEn23 |
| All | 15 | SEVLF, SELF, SEVLF-HF, SampEn2, SampEn7, SampEn9, SampEn11, SampEn13, SampEn14, SampEn17, and SampEn19- SampEn23 |
| Se(%) | Sp(%) | Acc(%) | PPV(%) | NPV(%) | LR+ | LR− | AROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRFSBE-W | 80.8 | 89.3 | 85.2 | 87.5 | 83.3 | 7.6 | 0.215 | 0.951 |
| LRFSBE-M | 87.1 | 56.1 | 77.6 | 81.8 | 65.7 | 1.98 | 0.230 | 0.895 |
| LRFSBE-All | 79.8 | 59.4 | 72.3 | 77.2 | 63.1 | 1.97 | 0.340 | 0.885 |
| Women
| Men
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | p-Value | SAHS-Negative | SAHS-Positive | p-Value | |
| PVLF | 0.425 ± 0.153 | 0.489 ± 0.170 | 0.076 | 0.437 ± 0.167 | 0.503 ± 0.168 | <0.05 |
| PLF | 0.236 ± 0.052 | 0.241 ± 0.068 | 0.897 | 0.250 ± 0.051 | 0.250 ± 0.068 | 0.640 |
| PHF | 0.234 ± 0.087 | 0.199 ± 0.118 | 0.058 | 0.228 ± 0.102 | 0.183 ± 0.108 | <0.01 |
| PLF/HF | 1.164 ± 0.514 | 1.639 ± 1.065 | 0.130 | 1.407 ± 0.874 | 1.898 ± 1.247 | <0.05 |
| Study | Signal | #Subjects | Classifier | #Features | Validation | AHI Threshold | Se (%) | Sp (%) | Acc (%) | AROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roche et al. 2003 [56] | HRV | 147 | Tree | 8 | k-fold | 10 | 64.2+ | 75.6+ | 69.3+ | – |
| Marcos et al. 2008 [49] | SpO2 | 187 | MLP | 3 | Hold-out | 10 | 89.8 | 79.4 | 85.5 | 0.900 |
| Marcos et al. 2009 [50] | SpO2 | 187 | LDA QDA KNN LR | 6 6 6 6 | Hold-out Hold-out Hold-out Hold-out | 10 10 10 10 | 86.6 91.1 88.1 85.1 | 80.4 78.3 84.8 87.0 | 84.1 85.8 86.7 85.8 | 0.925 0.913 0.822 0.930 |
| Caseiro et al. 2010 [53] | Airflow | 41 | Threshold | 1 | – | 5 | 81.0 | 95.0 | 87.8+ | 0.877 |
| Álvarez et al. 2010 [51] | SpO2 | 148 | LR | 4 | Loo | 10 | 92.0 | 85.4 | 89.7 | 0.967 |
| Fiz et al. 2010 [54] | Snoring | 37 | LR | 9 | – – | 5 15 | 87.0 80.0 | 71.4 90.9 | 81.1+ 86.5+ | 0.850 0.920 |
| Karunajeewa et al. 2011 [55] | Snoring | 41 | LR | 11 | Loo | 10 | 89.3 | 92.3 | 90.2+ | 0.967 |
| Al-Angari et al. 2012 [52] | SpO2 Respiratory effort HRV | 100 | SVM | 2 5 5 | – – – | 5 5 5 | 91.8 85.7 79.6 | 98.0 92.2 78.4 | 95.0 89.0 79.0 | – – – |
| Gutiérrez-Tobal et al. 2012 [46] | Airflow | 148 | LR | 3 | Loo | 10 | 88.0 | 70.8 | 82.4 | 0.903 |
| Ravelo-Garcia et al. 2014 [57] | HRV | 97 | LR | 5 | k-fold | 10 | 88.7 | 82.9 | 86.6+ | 0.941 |
| This study (LRFSBE-W) | HRV | 54 | LR | 5 | Loo | 10 | 80.8 | 89.3 | 85.2 | 0.951 |
| This study (LRFSBE-M) | HRV | 134 | LR | 13 | Loo | 10 | 87.1 | 56.1 | 77.6 | 0.895 |
| This study (LRFSBE-All) | HRV | 188 | LR | 15 | Loo | 10 | 79.8 | 59.4 | 72.3 | 0.885 |
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Álvarez, D.; Gomez-Pilar, J.; Del Campo, F.; Hornero, R. Assessment of Time and Frequency Domain Entropies to Detect Sleep Apnoea in Heart Rate Variability Recordings from Men and Women. Entropy 2015, 17, 123-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17010123
Gutiérrez-Tobal GC, Álvarez D, Gomez-Pilar J, Del Campo F, Hornero R. Assessment of Time and Frequency Domain Entropies to Detect Sleep Apnoea in Heart Rate Variability Recordings from Men and Women. Entropy. 2015; 17(1):123-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17010123
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Tobal, Gonzalo C., Daniel Álvarez, Javier Gomez-Pilar, Félix Del Campo, and Roberto Hornero. 2015. "Assessment of Time and Frequency Domain Entropies to Detect Sleep Apnoea in Heart Rate Variability Recordings from Men and Women" Entropy 17, no. 1: 123-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17010123
APA StyleGutiérrez-Tobal, G. C., Álvarez, D., Gomez-Pilar, J., Del Campo, F., & Hornero, R. (2015). Assessment of Time and Frequency Domain Entropies to Detect Sleep Apnoea in Heart Rate Variability Recordings from Men and Women. Entropy, 17(1), 123-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17010123