Novel Brain Complexity Measures Based on Information Theory
Abstract
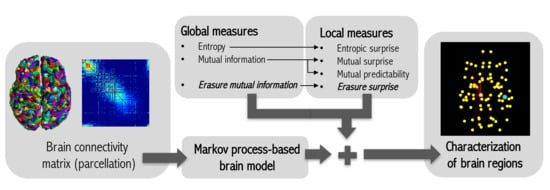
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Information Theory Basis
2.2. Markov Process-Based Brain Model
2.3. Global Informativeness Measures
2.3.1. Entropy
2.3.2. Mutual Information
2.3.3. Erasure Mutual Information
2.4. Local Informativeness Measures
2.4.1. Entropic Surprise
2.4.2. Mutual Surprise
2.4.3. Mutual Predictability
2.4.4. Erasure Surprise
3. Material
3.1. Synthetic Network Models
3.2. Human Datasets
3.2.1. Anatomic Dataset
3.2.2. Functional Dataset
3.3. Standard Network Measures
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Global Measures
4.2. Local Measures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sporns, O.; Tononi, G.; Kötter, R. The human connectome: A structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felleman, D.J.; Essen, D.C.V. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 1991, 1, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, P. From Diffusion MRI to Brain Connectomics. Ph.D. Thesis, École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann, P.; Kurant, M.; Gigandet, X.; Thiran, P.; Wedeen, V.J.; Meuli, R.; Thiran, J.P. Mapping human whole-brain structural networks with diffusion MRI. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, P.; Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Gerhard, S.; Grant, P.E.; Wedeen, V.; Meuli, R.; Thiran, J.P.; Honey, C.J.; Sporns, O. MR connectomics: Principles and challenges. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 194, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sporns, O. The human connectome: Origins and challenges. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.T.; Bassett, D.S. Brain graphs: Graphical models of the human brain connectome. Ann. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 7, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, O. The human connectome: A complex network. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2011, 1224, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.R.; Liao, W.; Stramaglia, S.; Ding, J.R.; Chen, H.; Marinazzo, D. A blind deconvolution approach to recover effective connectivity brain networks from resting state fMRI data. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passingham, R.E.; Stephan, K.E.; Kotter, R. The anatomical basis of functional localization in the cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M. A tutorial in connectome analysis: Topological and spatial features of brain networks. NeuroImage 2011, 57, 892–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, C.; Reijneveld, J. Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2007, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ’small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 69, 066133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, H.; Knoblauch, K.; Toroczkai, Z. Why data coherence and quality is critical for understanding interareal cortical networks. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colizza, V.; Flammini, A.; Serrano, M.A.; Vespignani, A. Detecting rich-club ordering in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harriger, L.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Sporns, O. Rich club organization of macaque cerebral cortex and its role in network communication. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Heuvel, M.; Kahn, R.; Goñi, J.; Sporns, O. High-cost, high-capacity backbone for global brain communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11372–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sporns, O.; Chialvo, D.R.; Kaiser, M.; Hilgetag, C.C. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cognit. Sci. 2004, 8, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tononi, G.; Sporns, O.; Edelman, G.M. A measure for brain complexity: Relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5033–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrelec, G.; Bellec, P.; Krainik, A.; Duffau, H.; Pélégrini-Issac, M.; Lehéricy, S.; Benali, H.; Doyon, J. Regions, systems, and the brain: Hierarchical measures of functional integration in fMRI. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazono, J.; Kanai, R.; Oizumi, M. Efficient algorithms for searching the minimum information partition in integrated information theory. Entropy 2018, 20, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tononi, G.; Edelman, G.M.; Sporns, O. Complexity and coherency: Integrating information in the brain. Trends Cognit. Sci. 1998, 2, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Tononi, G.; Edelman, G.M. Connectivity and complexity: The relationship between neuroanatomy and brain dynamics. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tononi, G.; Sporns, O.; Edelman, G.M. A complexity measure for selective matching of signals by the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tononi, G.; McIntosh, A.R.; Russell, D.P.; Edelman, G.M. Functional clustering: Identifying strongly interactive brain regions in neuroimaging data. NeuroImage 1998, 7, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, G.M.; Gally, J.A. Degeneracy and complexity in biological systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13763–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tononi, G.; Sporns, O.; Edelman, G.M. Measures of degeneracy and redundancy in biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3257–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crossley, N.; Mechelli, A.; Scott, J.; Carletti, F.; Fox, P.; McGuire, P.; Bullmore, E. The hubs of the human connectome are generally implicated in the anatomy of brain disorders. Brain 2014, 137, 2382–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meskaldji, D.E.; Fischi-Gomez, E.; Griffa, A.; Hagmann, P.; Morgenthaler, S.; Thiran, J.P. Comparing connectomes across subjects and populations at different scales. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Heuvel, M.P.; Pol, H.E.H. Exploring the brain network: A review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, J.R.; Takahashi, D.Y.; Hoexter, M.Q.; Massirer, K.B.; Fujita, A. Measuring network’s entropy in ADHD: A new approach to investigate neuropsychiatric disorders. NeuroImage 2013, 77, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papo, D.; Buldú, J.M.; Boccaletti, S.; Bullmore, E.T. Complex network theory and the brain. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2014, 369, 20130520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmati, E.; Bardera, A.; Boada, I. Brain parcellation based on information theory. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 151, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, R.W. A First Course in Information Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.P.; Crutchfield, J.P. Discovering Noncritical Organization: Statistical Mechanical, Information Theoreticand Computational Views of Patterns in One-Dimensional Spin Systems; Working Paper 98-04-026; Santa Fe Institute: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchfield, J.P.; Packard, N. Symbolic dynamics of noisy chaos. Physica D 1983, 7, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P. Toward a quantitative theory of self-generated complexity. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1986, 25, 907–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R. The Dripping Faucet as a Model Chaotic System; Aerial Press: Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Szépfalusy, P.; Györgyi, G. Entropy decay as a measure of stochasticity in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. A 1986, 33, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D.P. A Brief Introduction to: Information Theory, Excess Entropy and Computational Mechanics; Lecture notes; Department of Physics, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Verdú, S.; Weissman, T. The information lost in erasures. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2008, 54, 5030–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D.; Crutchfield, J. Structural information in two-dimensional patterns: Entropy convergence and excess entropy. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 051104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWeese, M.R.; Meister, M. How to measure the information gained from one symbol. Network Comput. Neural Syst. 1999, 10, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornito, A.; Zalesky, A.; Breakspear, M. Graph analysis of the human connectome: Promise, progress, and pitfalls. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, E.L.; Jahanshad, N.; Toga, A.W.; McMahon, K.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Martin, N.G.; Wright, M.J.; Thompson, P.M. Test-retest reliability of graph theory measures of structural brain connectivity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Nice, France, 1–5 October 2012; Ayache, N., Delingette, H., Golland, P., Mori, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 7512, pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Messé, A.; Rudrauf, D.; Giron, A.; Marrelec, G. Predicting functional connectivity from structural connectivity via computational models using MRI: An extensive comparison study. NeuroImage 2015, 111, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Ribeiro, A.; Miguel Lacerda, L.; Ferreira, H.A. Multimodal imaging brain connectivity analysis toolbox (MIBCA). PeerJ PrePrints 2014, 2, e699v1. [Google Scholar]
- Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Sporns, O.; Thiran, J.; Do, K.; Maeder, P.; Meuli, R.; Hagmann, P.; Bovet, P.; Do, K. Mapping the human connectome at multiple scales with diffusion spectrum MRI. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 203, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Essen, D.V.; Ugurbil, K.; Auerbach, E.; Barch, D.; Behrens, T.; Bucholz, R.; Chang, A.; Chen, L.; Corbetta, M.; Curtiss, S.; et al. The Human Connectome Project: A data acquisition perspective. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hodge, M.R.; Horton, W.; Brown, T.; Herrick, R.; Olsen, T.; Hileman, M.E.; McKay, M.; Archie, K.A.; Cler, E.; Harms, M.P.; et al. ConnectomeDB—Sharing human brain connectivity data. NeuroImage 2016, 124, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christidi, F.; Karavasilis, E.; Samiotis, K.; Bisdas, S.; Papanikolaou, N. Fiber tracking: A qualitative and quantitative comparison between four different software tools on the reconstruction of major white matter tracts. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2016, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; He, H. VisualConnectome: Toolbox for brain network visualization and analysis. In Proceedings of the Organization on human Brain Mapping, 2011, Québec City, QC, Canada, 26–30 June 2011. [Google Scholar]














| Global | Local | |
|---|---|---|
| Stationary | Entropy | Entropic surprise |
| Causal | Mutual Information | Mutual surprise |
| Mutual predictability | ||
| Contextual | Erasure Mutual Information | Erasure surprise |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonmati, E.; Bardera, A.; Feixas, M.; Boada, I. Novel Brain Complexity Measures Based on Information Theory. Entropy 2018, 20, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070491
Bonmati E, Bardera A, Feixas M, Boada I. Novel Brain Complexity Measures Based on Information Theory. Entropy. 2018; 20(7):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070491
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonmati, Ester, Anton Bardera, Miquel Feixas, and Imma Boada. 2018. "Novel Brain Complexity Measures Based on Information Theory" Entropy 20, no. 7: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070491
APA StyleBonmati, E., Bardera, A., Feixas, M., & Boada, I. (2018). Novel Brain Complexity Measures Based on Information Theory. Entropy, 20(7), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20070491