A LC-MS-Based Method for Quantification of Biomarkers from Serum of Allergic Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of the LC-MS Method

| Compounds | Linear ranges | Linear equations | Correlation coefficients ( r) | LOD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTB4 | 1–50 a | y = 0.5632x + 0.8554 | 0.9986 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| PGD2 | 1–50 a | y = 4.8623x + 2.5414 | 0.9986 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| AA | 1–50 b | y = 0.8905x + 0.2334 | 0.9984 | 2.5 | 7.0 |
| HI | 10–500 a | y = 0.6579x + 0.4889 | 0.9979 | 1.5 | 4.5 |
| LA | 1–50 b | y = 1.1658x + 0.6996 | 0.9981 | 5.0 | 12.0 |
| VAL | 5–100 b | y = 0.9825x + 0.7466 | 0.9973 | 2.0 | 8.0 |
| Intra-day | Inter-day | Recovery | Stability | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| spiked | Meansured | RSD | Accuracy | Meansured | RSD | Accuracy | Mean | RSD | Accuracy | RSD | ||||
| Cpds | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | ||||||
| LBT4 a | 5 | 5.05 | 1.42 | 101.00 | 4.95 | 1.33 | 98.96 | 81.08 | 3.60 | 97.50 | 5.41 | |||
| 10 | 9.74 | 4.32 | 97.40 | 9.18 | 4.46 | 91.82 | 84.22 | 4.14 | 96.89 | 3.97 | ||||
| 40 | 36.87 | 6.55 | 92.18 | 39.40 | 7.17 | 98.49 | 85.72 | 4.08 | 94.31 | 4.16 | ||||
| PGD2 a | 5 | 4.67 | 6.29 | 93.40 | 4.78 | 3.27 | 95.57 | 76.16 | 5.40 | 93.85 | 5.37 | |||
| 10 | 9.81 | 1.92 | 98.10 | 8.93 | 5.36 | 89.29 | 79.33 | 3.92 | 97.14 | 1.35 | ||||
| 40 | 39.02 | 8.51 | 97.55 | 38.39 | 6.86 | 95.97 | 82.61 | 2.71 | 93.56 | 3.97 | ||||
| AA b | 5 | 4.78 | 1.40 | 95.60 | 4.69 | 6.86 | 93.85 | 81.46 | 2.47 | 101.7 | 4.09 | |||
| 10 | 9.74 | 2.46 | 97.40 | 9.09 | 3.83 | 90.87 | 86.00 | 5.03 | 90.71 | 2.04 | ||||
| 40 | 36.55 | 5.98 | 91.38 | 38.81 | 6.51 | 97.02 | 85.05 | 3.08 | 91.19 | 3.76 | ||||
| HI a | 50 | 47.10 | 1.43 | 94.20 | 46.05 | 1.34 | 92.09 | 87.30 | 2.72 | 90.57 | 5.45 | |||
| 100 | 98.02 | 6.73 | 98.02 | 90.72 | 2.93 | 90.72 | 83.92 | 4.77 | 95.57 | 4.49 | ||||
| 400 | 380.2 | 2.74 | 95.05 | 364.1 | 6.17 | 91.02 | 85.31 | 4.49 | 112.5 | 4.65 | ||||
| LA b | 5 | 5.23 | 5.87 | 104.6 | 4.66 | 8.45 | 93.14 | 92.57 | 5.68 | 93.09 | 1.96 | |||
| 10 | 9.67 | 1.33 | 96.70 | 9.46 | 4.01 | 94.63 | 86.66 | 3.40 | 99.50 | 4.46 | ||||
| 40 | 36.49 | 2.24 | 91.23 | 36.64 | 1.19 | 91.59 | 83.24 | 0.73 | 95.87 | 2.87 | ||||
| VAL b | 10 | 9.83 | 1.27 | 98.30 | 9.82 | 0.35 | 98.19 | 84.33 | 3.59 | 89.26 | 0.48 | |||
| 40 | 37.44 | 0.68 | 93.60 | 36.86 | 3.95 | 92.14 | 82.10 | 3.60 | 91.33 | 0.97 | ||||
| 80 | 78.46 | 4.21 | 98.08 | 77.54 | 1.91 | 96.92 | 83.70 | 1.70 | 96.58 | 2.90 | ||||
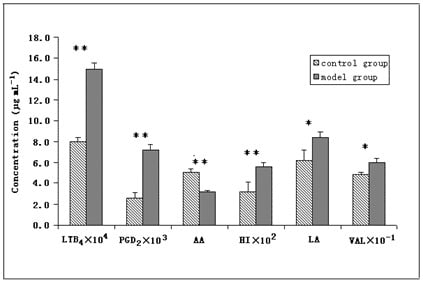
2.2. Application to Contents Analysis of Endogenous Substances in Serum

3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Animals
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Chromatographic Conditions
3.4. Sample Preparation
| Level | Result |
|---|---|
| - | Negative: normal |
| + | weakly positive: restlessness, piloerection, jitter, scratching nose |
| ++ | Positive: sneeze, cough, breathlessness, emiction, bowel, dacryorrhea |
| +++ | strongly positive: dyspnea, wheezing rale, Peliosis, Instability of gait, jump, gasp, cramp, tropic, Cheyne-Stokes breathing |
| ++++ | very strongly positive: die |
3.5. Calibration and Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Aberg, N.; Hesselmar, B.; Aberg, B.; Eriksson, B. Increase of asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema in Swedish schoolchildren between 1979 and 1991. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1995, 25, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.B. Allergy and allergic diseases-first of two parts. New Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karol, M.H. Respiratory allergy: what are the uncertainties? Toxicol. 2002, 181/182, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanti, J.A.; Malka-Rais, J.; Castro, H.J.; de Inocencio, J.M.; Sabra, A. Developmental immunology: clinical application to allergy-immunology. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003, 90, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cookson, W.O.C. Asthma genetics. Chest 2002, 121, 7S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larche, M.; Robinson, D.S.; Kay, A.B. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eling, T.; Tainer, B.; Ally, A.; Warnock, R. Separation of arachidonic acid metabolites by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Meth. Enzymol. 1982, 86, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommery, J.; Pommery, N.; Hénichart, J.P. Modification of eicosanoid profile in human blood treated by dual COX/LOX inhibitors. Prostagland. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2005, 73, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, L.; Bieniek, E.; Weissmann, N.; Schutte, H.; Siblius, U.; Gunther, A.; Bier, J.; Mayer, K.; Henneking, K.; Padberg, W.; Grimm, H.; Seeger, W.; Grimminger, F. Simultaneous analysis of 4- and 5-series lipoxygenase and cytochrome P450 products from different biological sources by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic technique. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 261, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Henden, T.; Strand, H.; Borde, E.; Semb, A.G.; Larsen, T.S. Measurements of leukotrienes in human plasma by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Prostagland. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 1993, 49, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.G.; Henderson, L.; Narayanan, J.; Alonso-Galicia, M.; Falck, J.R.; Roman, R.J. Fluorescent HPLC assay for 20-HETE and other P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H863–H871. [Google Scholar]
- Nithipatikom, K.; Pratt, P.F.; Campbell, W.B. Determination of EETs using microbore liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H857–H862. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, L.A.; Giner, R.M.; Paul-Clark, M.J.; Peretti, M.; Perrett, D. An isocratic HPLC method for the quantitation of eicosanoids in human platelets. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.F.; Kenneth, I.S.; Michael, R.B.; Mary, F.B.; Luella, J.R.; Susan, A.J. Determination of bioactive eicosanoids in brain tissue by a sensitive reversed-phase liquid chromatographic method with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 803, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderNoot, V.A.; VanRollins, M. Capillary electrophoresis of cytochrome P-450 epoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid. 1. Resolution of regioisomers. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5859–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithipatikom, K.; DiCamelli, R.F.; Kohler, S.; Gumina, R.J.; Falck, J.R.; Campbell, W.B.; Gross, G.J. Determination of cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in coronary venous plasma during ischemia and reperfusion in dogs. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 292, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrios, T. Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to assess in vivo synthesis of prostaglandins, thromboxane, leukotrienes, isoprostanes and related compounds in humans. J. Chromatogr. B 1998, 717, 201–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroki, T.; Takanori, H.; Tsuyoshi, M.; Hironori, N.; Tohru, Y.; Yoshihisa, T.; Michinao, M. Simultaneous quantification of prostaglandins, isoprostane and thromboxane in cell-cultured medium using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 774, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kwack, K.; Kim, D.Y.; Ji, G.E. Oral probiotic bacterial administration suppressed allergic responses in an ovalbumin-induced allergy mouse model. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 45, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang Q., Jia X.D.; Wang, W.; Li, N. Study on allergenicity model of BN Rat. Chin J Food Hyg 2008, 20, 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.G.; Qin, H.D.; Wang, H.S.; Shi, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.P. Sensitivity in type I hypersensitivity compared between BN rats and Wistar rats. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 24, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.Z.; Lu, S.; Yin, P.Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, F.X.; Xu, G.W. Metabonomics study of liver cancer based on ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with HILIC and RPLC separations. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 650, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, L.J.; Chen, W.G.; Lin, L.; Song, X.Y.; Yan, X.M.; Hang, W.; Huang, B.L. Metabonomics research of diabetic nephropathy and type 2 diabetes mellitus based on UPLC–oaTOF-MS system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 650, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.R. Drug therapy Advances in H1-Antihistamines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors;
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.J.; Gao, X.Y.; Lu, J.Q.; Zhang, H.G. A LC-MS-Based Method for Quantification of Biomarkers from Serum of Allergic Rats. Molecules 2010, 15, 3356-3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053356
Bai YJ, Gao XY, Lu JQ, Zhang HG. A LC-MS-Based Method for Quantification of Biomarkers from Serum of Allergic Rats. Molecules. 2010; 15(5):3356-3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053356
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yu Jing, Xiao Yan Gao, Jian Qiu Lu, and Hong Gui Zhang. 2010. "A LC-MS-Based Method for Quantification of Biomarkers from Serum of Allergic Rats" Molecules 15, no. 5: 3356-3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053356
APA StyleBai, Y. J., Gao, X. Y., Lu, J. Q., & Zhang, H. G. (2010). A LC-MS-Based Method for Quantification of Biomarkers from Serum of Allergic Rats. Molecules, 15(5), 3356-3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15053356