Lambda-Display: A Powerful Tool for Antigen Discovery
Abstract
:1. Overview of Display Technologies
2. The Lambda Bacteriophage

3. Lambda Vectors for Display Applications

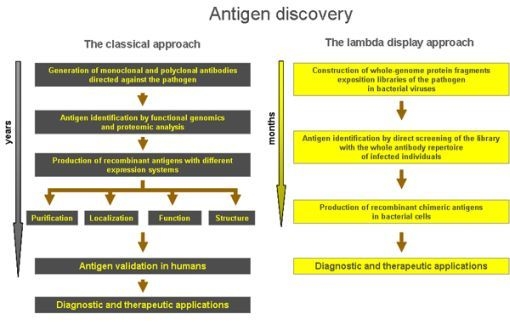
4. Lambda Display for Antigen Discovery
5. Clinical Applications and Perspective
| Organism | Applications | Libraries | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxoplasma gondii | Antigen discovery | Whole parasite cDNA and stage-specific gene collections | Identification of a large panel of antigens containing B- and T-cell epitopes | [38,46,47] |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Development of diagnostic immunoassays | Whole parasite cDNA and stage-specific gene collections | Assay prototypes for diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis in pregnant women and infants | [63,64,65] |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Development of DNA-based vaccines | Stage-specific gene collections | DNA vaccines conferring protective immunity against chronic toxoplasmosis | [48,66,68] |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Antigen discovery for vaccine development | Genomic DNA | Identification of a large panel of immunodominant antigens | [52] |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Epitope mapping | Genomic DNA | Isolation and characterization of streptococci conserved epitopes | [53] |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | Antigen discovery for diagnostic applications | Genomic DNA | Isolation and characterization of B-cell regions for diagnostic immunoassays | [56,69] |
| Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) | Antigen discovery | Genomic DNA | Identification of a large panel of B-cell epitopes | [57] |
| Human Hepatis C Virus (HCV) | Antigen discovery | Whole viral cDNA | Molecular dissection of the B-cell response | [29] |

6. Conclusions

References
- Rowley, M.J.; O’Connor, K.; Wijeywickrema, L. Phage display for epitope determination: A paradigm for identifying receptor-ligand interactions. Biotechnol. Ann. Rev. 2004, 10, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P.; Petrenko, V.A. Phage display. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 391–410. [Google Scholar]
- Cull, M.G.; Miller, J.F.; Schatz, P.J. Screening for receptor ligands using large libraries of peptides linked to the C terminus of the lac repressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Lipovsek, D.; Pluckthun, A. In-vitro protein evolution by ribosome display and mRNA display. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 290, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheakis, L.C.; Bhatt, R.R.; Dower, W.J. An in vitro polysome display system for identifying ligands from very large peptide libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9022–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.W.; Szostak, J.W. RNA-peptide fusions for the in vitro selection of peptides and proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12297–12302. [Google Scholar]
- Boder, E.T.; Wittrup, K.D. Yeast surface display for screening combinatorial polypeptide libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponigro, G.; Abedi, M.R.; Hurlburt, A.P.; Maxfield, A.; Judd, W.; Kamb, A. Transdominant genetic analysis of a growth control pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7508–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, P.; Cohen, B.; Jessen, T.; Grishina, I.; Mc Coy, J.; Brent, R. Genetic selection of peptide aptamers that recognize and inhibit cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature 1996, 380, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etz, H.; Minh, D.B.; Schellack, C.; Nagy, E.; Meinke, A. Bacterial phage receptors, versatile tools for display of polypeptides on the cell surface. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6924–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Murray, K.S.; Van Cleave, V.; La Vallie, E.R.; Stahl, M.L.; Mc Coy, J.M. Expression of thioredoxin random peptide libraries on the Escherichia coli cell surface as functional fusions to flagellin: A system designed for exploring protein–protein interactions. Biotechnology 1995, 13, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, T.C.; Smith, D.L.; Sorger, P.K.; Drees, B.L.; O’Rourke, S.M.; Hughes, T.R.; Roberts, C.J.; Friend, S.H.; Fields, S.; Murray, A.W. Genetic selection of peptide inhibitors of biological pathways. Science 1999, 285, 591–595. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, B.; Aruffo, A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: Novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Buffolano, W.; Del Pezzo, M.; Minenkova, O.; Pavoni, E.; Pucci, A.; Cortese, R.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. Molecular dissection of the human B-cell response against Toxoplasma gondii infection by lambda display of cDNA libraries. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Gargano, N.; Ricci, S.; Oggioni, M.; Garufi, G.; Peppoloni, S.; Pozzi, G.; Felici, F. Discovery of a novel Streptococcus pneumoniae antigen by screening a whole genome lambda-display library. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 262, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; De Paolis, F.; Montagnani, F.; Cellesi, C.; Gargano, N. Discovery of new Mycoplasma pneumoniae antigens by use of a whole-genome lambda-display library. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; De Paolis, F.; Spadoni, A.; Del Porto, P.; Buffolano, W.; Gargano, N. Molecular dissection of the human B-cell response against cytomegalovirus infection by lambda-display. J. Virol. Meth. 2008, 151, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Pucci, A.; Minenkova, O.; Spadoni, A.; Bruno, L.; Buffolano, W.; Soldati, D.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. Identification of a human immunodominant B-cell epitope within the GRA1 antigen of Toxoplasma gondii by phage display of cDNA libraries. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar]
- De Paolis, F.; Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Oggioni, M.; Montagnani, F.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. Identification of a human immunodominant B-cell epitope within IgA1 protease of Streptococcus pneumoniae. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, R.; Monaci, P.; Luzzago, A.; Santini, C.; Bartoli, F.; Cortese, I.; Fortugno, P.; Galfre, G.; Nicosia, A.; Felici, F. Selection of biologically active peptides by phage display of random peptide libraries. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1996, 7, 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Deroo, S.; Muller, C.P. Antigenic and immunogenic phage displayed mimotopes as substitute antigens: Applications and limitations. Comb. Chem. High Through. Screen. 2001, 4, 75–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Griffiths, A.D.; Hawkins, R.E.; Hoogenboom, H.R. Making antibodies by phage display technology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareni, G. Peptide display on filamentous phage capsid. A new powerful tool to study protein-ligand interaction. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.H.; Drees, B.; Nardelli, G.; Bader, G.D.; Brannetti, B.; Castagnoli, L.; Evangelista, M.; Ferracuti, S.; Nelson, B.; Paoluzi, S.; Quondam, M.; Zucconi, A.; Hogue, C.W.; Fields, S.; Boone, C.; Cesareni, G. A combined experimental and computational strategy to define protein interaction networks for peptide recognition modules. Science 2002, 295, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, D.R. Phage display. Immunotechnology 1995, 1, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hoess, R.H.; Bennett, J.S.; DeGrado, W.F. Use of phage display to probe the evolution of binding specificity and affinity in integrins. Protein Eng. 2003, 16, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, E.A.; Schatz, P.J.; Johnson, S.S.; Dower, W.J. Membrane insertion defects caused by positive charges in the early mature region of protein pIII of filamentous phage fd can be corrected by prlA suppressors. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 4296–4305. [Google Scholar]
- Gallusser, A.; Kuhn, A. Initial steps in protein membrane insertion. Bacteriophage M13 procoat protein binds to the membrane surface by electrostatic interaction. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Crameri, R.; Kodzius, R. The powerful combination of phage surface display of cDNA libraries and high throughput screening. Comb. Chem. High. Through. Screen. 2001, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jesper, L.S.; De Keyser, A.; Stanssens, P.E. Lambda ZLG6: A phage lambda vector for high-efficiency allowing and surface expression of cDNA libraries on filamentous phage. Gene 1996, 173, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, I.S. Assembly of functional bacteriophage lambda virions incorporating C terminal peptide or protein fusions with the major tail protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 248, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, I.N.; Maruyama, H.I.; Brenner, S. Lambda foo: A lambda phage vector for the expression of foreign proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8273–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikawa, Y.G.; Maruyama, I.N.; Brenner, S. Surface display of proteins on bacteriophage lambda heads. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, C.; Brennan, D.; Mennuni, C.; Hoess, R.H.; Nicosia, A.; Cortese, R.; Luzzago, A. Efficient display of an HCV cDNA expression library as C-terminal fusion to the capsid protein D of bacteriophage lambda. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 282, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, N.; Hoess, R.H. Display of peptides and proteins on the surface of bacteriophage lambda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1609–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Griffin, K.; Studier, W.S.; Mc Cormick, M.; Berg, J.; Novy, R.; Mierendorf, R. T7 Select Phage Display System: A powerful new protein display system based on bacteriophage T7. Innovations 1996, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Efimov, V.P.; Nepluev, I.V.; Mesyanzhinov, V.V. Bacteriophage T4 as a surface display vector. Virus Genes 1995, 10, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.J.; Lewis, G.K.; Wingfield, P.T.; Locke, E.G.; Steven, A.C.; Black, L.W. Phage display of intact domains at high copy number: a system based on SOC, the small outer capsid protein of bacteriophage T4. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Forrer, P.; Dauter, Z.; Conway, J.F.; Cheng, N.; Cerritelli, M.E.; Steven, A.C.; Pluckthun, A.; Wlodawer, A. Novel fold and capsid-binding properties of the lambda-phage display platform protein gpD. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Dokland, T.; Murialdo, H. Structural transitions during maturation of bacteriophage lambda capsids. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 233, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucconi, A.; Dente, L.; Santonico, E.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G. Selection of ligands by panning of domain libraries displayed on phage lambda reveals new potential partners of Synaptojanin 1. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, L.; Zucconi, A.; Quondam, M.; Rossi, M.; Vaccaro, P.; Panni, S.; Paoluzi, S.; Santonico, E.; Dente, L.; Cesareni, G. Alternative bacteriophage display systems. Comb. Chem. High Throug. Screen. 2001, 4, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, M.; Maruyama, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Dohi, K.; Maruyama, I.N. Affinity selection of cDNA libraries by lambda phage surface display. Gene 2000, 256, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minenkova, O.; Pucci, A.; Pavoni, E.; De Tomassi, A.; Fortugno, P.; Gargano, N.; Cianfriglia, M.; Barca, S.; De Placido, S.; Martignetti, A.; Felici, F.; Cortese, R.; Monaci, P. Identification of tumor-associated antigens by screening phage-displayed human cDNA libraries with sera from tumor patients. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Capone, S.; Mennuni, C.; Lahm, A.; Tramontano, A.; Luzzago, A.; Nicosia, A. Bacteriophage lambda display of complex cDNA libraries: A new approach to functional genomics. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro, P.; Pavoni, E.; Monteriù, G.; Pucci, A.; Felici, F.; Minenkova, O. Efficient display of scFv antibodies on bacteriophage lambda. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 310, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmley, S.F.; Smith, G.P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: Affinity purification of target genes. Gene 1988, 73, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A.; Davis, R.W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, R.; Remington, J.S. Toxoplasmosi: The time has come. New Engl. J. Med. 1998, 318, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristina, M.; Del Porto, P.; Buffolano, W.; Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Guglietta, S.; Piccolella, E.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. The Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite antigens BAG1 and MAG1 induce early humoral and cell-mediated immune responses upon human infection. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Nielsen, V.H.; Del Porto, P.; Buffolano, W.; Guglietta, S.; Felici, F.; Petersen, E.; Gargano, N. A combination of antigenic regions of Toxoplasma gondii microneme proteins induce immunity against oral infection with parasite cysts. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglietta, S.; Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Buffolano, W.; Del Porto, P.; Gargano, N. Age-dependent impairment of functional helper T cell responses to immunodominant epitopes of Toxoplasma gondii antigens in congenitally infected individuals. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedson, D.S.; Anthony, J.; Scott, G. The burden of pneumococcal disease among adults in developed and developing countries: What is known and what is not known. Vaccine 1999, 17, S11–S18. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen, E.I. Pathogenesis of pneumococcal inflammation: Otitis media. Vaccine 2000, 19, S38–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, D.; Schlaeffer, F.; Horowitz, S.; Horovitz, O.; Porath, A. Mycoplasma pneumoniae community-acquired pneumonia: A review of 101 hospitalized adult patients. Respiration 1996, 63, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamine, J.M.; Ho, K.C.; Loechel, S.; Hu, P.C. Evidence that UGA is read as a tryptophan codon rather than as a stop codon by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 504–506. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, D.; Wallon, M.; Peyron, F.; Petersen, E.; Peckham, C.S.; Gilbert, R. Mother to child transmission of toxoplasmosis: risk estimates for clinical counseling. Lancet 1999, 353, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, R.; Grass, L. the European Multicentre Study on Congenital Toxoplasmosis. Effect of timing and type of treatment on the risk of mother to child transmission of Toxoplasma gondii. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2003, 110, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wallon, M.; Kodjikian, L.; Binquet, C.; Garweg, J.; Fleury, J.; Quantin, C.; Peyron, F. Long-term ocular prognosis in 327 children with congenital toxoplasmosis. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, J.M.; Joynson, D.H. Duration of specific immunoglobulin A antibody following acute toxoplasmosis as determined by enzyme immunoassay and immunosorbent agglutination assay. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1993, 12, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.W.L. Diagnosis. In Human Toxoplasmosis; Ho-Yen, D.O., Joss, A.W.L., Eds.; Oxford Medical Publications: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 79–118. [Google Scholar]
- Beghetto, E.; Buffolano, W.; Spadoni, A.; Del Pezzo, M.; Di Cristina, M.; Minenkova, O.; Petersen, E.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. Use of an immunoglobulin G avidity assay based on recombinant antigens for diagnosis of primary Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5414–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffolano, W.; Beghetto, E.; Del Pezzo, M.; Spadoni, A.; Di Cristina, M.; Petersen, E.; Gargano, N. The use of recombinant antigens for the early postnatal management of newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5916–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Bruno, L.; Buffolano, W.; Gargano, N. Chimeric antigens of Toxoplasma gondii: towards standardization of toxoplasmosis serodiagnosis by using recombinant products. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.V.; Di Cristina, M.; Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Petersen, E.; Gargano, N. Toxoplasma gondii: DNA vaccination with bradyzoite antigens induces protective immunity in mice against oral infection with parasite cysts. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 112, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongert, E.; Verhelst, D.; Abady, M.; Petersen, E.; Gargano, N. Protective Th1 immune responses against chronic toxoplasmosis induced by a protein-protein vaccine combination but not by its DNA-protein counterpart. Vaccine 2008, 41, 5289–5295. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, C.; De Craeye, S.; Jongert, E.; Gargano, N.; Beghetto, E.; Del Porto, P.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Petersen, E. Induction of partial protection against infection with Toxoplasma gondii genotype II by DNA vaccination with recombinant chimeric tachyzoite antigens. Vaccine 2009, 27, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar]
- Montagnani, F.; De Paolis, F.; Beghetto, E.; Gargano, N. Use of recombinant chimeric antigens for the serodiagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Beghetto, E.; Gargano, N. Lambda-Display: A Powerful Tool for Antigen Discovery. Molecules 2011, 16, 3089-3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16043089
Beghetto E, Gargano N. Lambda-Display: A Powerful Tool for Antigen Discovery. Molecules. 2011; 16(4):3089-3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16043089
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeghetto, Elisa, and Nicola Gargano. 2011. "Lambda-Display: A Powerful Tool for Antigen Discovery" Molecules 16, no. 4: 3089-3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16043089
APA StyleBeghetto, E., & Gargano, N. (2011). Lambda-Display: A Powerful Tool for Antigen Discovery. Molecules, 16(4), 3089-3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16043089