Directed Formation of DNA Nanoarrays through Orthogonal Self-Assembly
Abstract
:1. Introduction

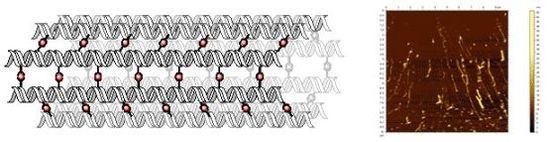
2. Results and Discussion



3. Experimental
4. Conclusions

Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Chen, J.H.; Seeman, N.C. Synthesis from DNA of a molecule with the connectivity of a cube. Nature 1991, 350, 631–633. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, M.; Seeman, N.C.; Majima, T. DNA Tube Structures Controlled by a Four-Way-Branched DNA Connector. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6074–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, N.C. Structural DNA Nanotechnology: Growing Along with Nano Letters. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.P.; Berry, R.M.; Turberfield, A.J. The single-step synthesis of a DNA tetrahedron. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1372–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Erben, C.M.; Goodman, R.P.; Turberfield, A.J. Single-molecule protein encapsulation in a rigid DNA cage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7414–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Lubrich, D.; Turberfield, A.J. DNA hairpins: Fuel for autonomous DNA devices. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, J.; Turberfield, A.J. DNA nanomachines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBean, T. Hydrogels: DNA bulks up. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Pistol, C.; Ahn, S.J.; Reif, J.H.; Lebeck, A.R.; Dwyer, C.; LaBean, T.H. Finite-size, fully addressable DNA tile lattices formed by hierarchical assembly procedures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, P.W.K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kershner, R.J.; Bozano, L.D.; Micheel, C.M.; Hung, A.M.; Fornof, A.R.; Cha, J.N.; Rettner, C.T.; Bersani, M.; Frommer, J.; Rothemund, P.W.K.; Wallraff, G.M. Placement and orientation of individual DNA shapes on lithographically patterned surfaces. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.G.; Sharma, J.; Liu, M.H.; Jahn, K.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. Scaffolded DNA Origami of a DNA Tetrahedron Molecular Container. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2445–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.G.; Lindsay, S.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. Self-assembled water-soluble nucleic acid probe tiles for label-free RNA hybridization assays. Science 2008, 319, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Lazarides, A.A.; Storhoff, J.J.; Pesce, L.; Mirkin, C.A. The Structural Characterization of Oligonucleotide-Modified Gold Nanoparticle Networks Formed by DNA Hybridization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 12375–12380. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Mirkin, C.A. Dip-pen nanolithography-based methodology for preparing arrays of nanostructures functionalized with oligonucleotides. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1472–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; McLaughlin, C.K.; Aldaye, F.A.; Hamblin, G.D.; Rys, A.Z.; Rouiller, I.; Sleiman, H.F. Metal-nucleic acid cages. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, P.K.; Karam, P.; Aldaye, F.A.; McLaughlin, C.K.; Hamblin, G.D.; Cosa, G.; Sleiman, H.F. Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Katsuda, Y.; Hidaka, K.; Sugiyama, H. Regulation of DNA Methylation Using Different Tensions of Double Strands Constructed in a Defined DNA Nanostructure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Zhong, H.; Neff, D.; Norton, M.L. NTA Directed Protein Nanopatterning on DNA Origami Nanoconstructs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6660–6661. [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky, A.K.; Belcher, A.M. Label-free and high-resolution protein/DNA nanoarray analysis using Kelvin probe force microscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilemann, M.; Kasper, R.; Tinnefeld, P.; Sauer, M. Dissecting and reducing the heterogeneity of excited-state energy transport in DNA-Based photonic wires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16864–16875. [Google Scholar]
- Tumpane, J.; Sandin, P.; Kumar, R.; Powers, V.E.C.; Lundberg, E.P.; Gale, N.; Baglioni, P.; Lehn, J.M.; Albinsson, B.; Lincoln, P.; Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Brown, T.; Norden, B. Addressable high-information-density DNA nanostructures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 440, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandy, T.J.; Brewer, A.; Burns, J.R.; Marth, G.; Nguyen, T.; Stulz, E. DNA as supramolecular scaffold for functional molecules: progress in DNA nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Malinovskii, V.L.; Wenger, D.; Häner, R. Nucleic acid-guided assembly of aromatic chromophores. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 410–422. [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod, S.H.; Marx, A. Novel strategies for the site-specific covalent labelling of nucleic acids. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5675–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.; Le Gac, S.; Cornelissen, J.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Rowan, A.E. Macromolecular multi-chromophoric scaffolding. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1576–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Wengel, J. Nucleic acid nanotechnology - towards Angstrom-scale engineering. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, D.J.; Tor, Y. Donor/acceptor interactions in systematically modified Ru-II-Os-II oligonucleotides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13231–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammmana, A.; Pescitelli, G.; Asakawa, T.; Jockusch, S.; Petrovic, A.G.; Monaco, R.R.; Purrello, R.; Turro, N.J.; Nakanishi, K.; Ellestad, G.A.; Balaz, M.; Berova, N. Role of Environmental Factors on the Structure and Spectroscopic Response of 5 '-DNA-Porphyrin Conjugates Caused by Changes in the Porphyrin-Porphyrin Interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11853–11866. [Google Scholar]
- Fendt, L.A.; Bouamaied, I.; Thöni, S.; Amiot, N.; Stulz, E. DNA as supramolecular scaffold for porphyrin arrays on the nanometer scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15319–15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamaied, I.; Nguyen, T.; Rühl, T.; Stulz, E. Supramolecular helical porphyrin arrays using DNA as a scaffold. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Brewer, A.; Stulz, E. Duplex Stabilization and Energy Transfer in Zipper Porphyrin-DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1974–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, A.; Siligardi, G.; Neylon, C.; Stulz, E. Introducing Structural Flexibility Into Porphyrin-DNA Zipper Arrays. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Enthart, E.; Wagenknecht, H.-A. Structure-Sensitive and Self-Assembled Helical Pyrene Array Based on DNA Architecture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3372–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegaard, D.; Madsen, A.S.; Astakhova, I.V.; Malakhov, A.D.; Babu, B.R.; Korshun, V.A.; Wengel, J. Pyrene-perylene as a FRET pair coupled to the N2'-functionality of 2'-amino-LNA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Shimomura, Y.; Ohtoshi, Y.; Sasa, K.; Hayashi, H.; Nakano, H.; Yamana, K. Pyrene aromatic arrays on RNA duplexes as helical templates. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, B.; Schuster, G.B. DNA-Directed Synthesis of Aniline and 4-Aminobiphenyl Oligomers: Programmed Transfer of Sequence Information to a Conjoined Polymer Nanowire. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2965–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czlapinski, J.L.; Sheppard, T.L. Nucleic acid template-directed assembly of metallosalen-DNA conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8618–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskii, V.L.; Samain, F.; Häner, R. Helical Arrangement of Interstrand Stacked Pyrenes in a DNA Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4464–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirges, C.T.; Timper, J.; Fischler, M.; Sologubenko, A.S.; Mayer, J.; Simon, U.; Carell, T. Controlled Nucleation of DNA Metallization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumstark, D.; Wagenknecht, H.A. Fluorescent hydrophobic zippers inside duplex DNA: Interstrand stacking of perylene-3,4 : 9,10-tetracarboxylic acid bisimides as artificial DNA base dyes. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalek, M.; Madsen, A.S.; Wengel, J. Effective Modulation of DNA Duplex Stability by Reversible Transition Metal Complex Formation in the Minor Groove. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9392–9400. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen, K.K.; Jensen, T.B.; Wengel, J. Synthesis of an Unlocked Nucleic Acid Terpyridine Monomer and Binding of Divalent Metal Ion in Nucleic Acid Duplexes. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 8838–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rys, A.Z.; McLaughlin, C.K.; Sleiman, H.F. Templated Ligand Environments for the Selective Incorporation of Different Metals into DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9919–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Pignot-Paintrand, I.; Dumy, P.; Defrancq, E. Design and synthesis of novel hybrid metal complex-DNA conjugates: Key building blocks for multimetallic linear DNA nanoarrays. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sleiman, H.F. Templated synthesis of highly stable, electroactive, and dynamic metal-DNA branched junctions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, N.; Ebner, A.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Tampe, R.; Howorka, S. Chemical Tags Mediate the Orthogonal Self-Assembly of DNA Duplexes into Supramolecular Structures. Small 2010, 6, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühl, T.; Stulz, E. Synthesis of new building blocks for use in supramolecular DNA architectures. Supramol. Chem. 2010, 22, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beller, C.; Bannwarth, W. Noncovalent attachment of nucleotides by fluorous fluorous interactions: Application to a simple purification principle for synthetic DNA fragments. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, W.H.; Berry, D.A.; Stoy, P.; Jung, K.Y.; Sercel, A.D. Fluorous affinity purification of oligonucleotides. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 7114–7122. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of Lead Citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienberger, F.; Costa, L.T.; Zhu, R.; Kada, G.; Reithmayer, M.; Chtcheglova, L.; Rankl, C.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Thalhammer, S.; Pastushenko, V.; Heckl, W.M.; Blaas, D.; Hinterdorfer, P. Dynamic force microscopy imaging of plasmid DNA and viral RNA. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Burns, J.R.; Zekonyte, J.; Siligardi, G.; Hussain, R.; Stulz, E. Directed Formation of DNA Nanoarrays through Orthogonal Self-Assembly. Molecules 2011, 16, 4912-4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16064912
Burns JR, Zekonyte J, Siligardi G, Hussain R, Stulz E. Directed Formation of DNA Nanoarrays through Orthogonal Self-Assembly. Molecules. 2011; 16(6):4912-4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16064912
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurns, Jonathan R., Jurgita Zekonyte, Giuliano Siligardi, Rohanah Hussain, and Eugen Stulz. 2011. "Directed Formation of DNA Nanoarrays through Orthogonal Self-Assembly" Molecules 16, no. 6: 4912-4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16064912
APA StyleBurns, J. R., Zekonyte, J., Siligardi, G., Hussain, R., & Stulz, E. (2011). Directed Formation of DNA Nanoarrays through Orthogonal Self-Assembly. Molecules, 16(6), 4912-4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16064912