Comparative Analysis of Click Chemistry Mediated Activity-Based Protein Profiling in Cell Lysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Activity-Based Probes and Fluorescent Tags

2.2. Tandem Labeling Experiments
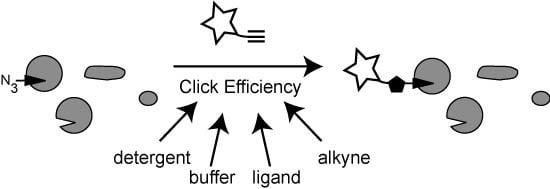
2.2.1. The Influence of Click Chemistry Reagents

2.2.2. The Influence of Lysis Conditions

3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Culture and Generation of Lysates
3.3. Bioorthogonal Labeling Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, I.; Ting, A.Y. Site-specific labeling of proteins with small molecules in live cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Chemistry in living systems. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, W.P.; Dang, T.H.T.; Tate, E.W. Activity-based probes: Discovering new biology and new drug targets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravatt, B.F.; Wright, A.T.; Kozarich, J.W. Activity-based protein profiling: from enzyme chemistry to proteomic chemistry. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 383–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurink, P.P.; Prely, L.M.; van der Marel, G.A.; Bischoff, R.; Overkleeft, H.S. Photoaffinity Labeling in Activity-Based Protein Profiling. Top. Curr. Chem. 2012, 324, 85–113. [Google Scholar]
- Haedke, U.; Kuttler, E.V.; Vosyka, O.; Yang, Y.; Verhelst, S.H.L. Tuning probe selectivity for chemical proteomics applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sadaghiani, A.M.; Verhelst, S.H.L.; Bogyo, M. Tagging and detection strategies for activity-based proteomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.D. Click chemistry and bioorthogonal reactions: Unprecedented selectivity in the labeling of biological molecules. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6571–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornoe, C.W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-Triazoles by regiospecific copper(i)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speers, A.E.; Adam, G.C.; Cravatt, B.F. Activity-based protein profiling in vivo using a copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne [3+2] cycloaddition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4686–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speers, A.E.; Cravatt, B.F. Profiling enzyme activities in vivo using click chemistry methods. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, L.I.; van der Linden, W.A.; Li, N.; Li, K.Y.; Liu, N.; Hoogendoorn, S.; van der Marel, G.A.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S. Bioorthogonal chemistry: applications in activity-based protein profiling. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, V.; Presolski, S.I.; Ma, C.; Finn, M.G. Analysis and Optimization of Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9879–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besanceney-Webler, C.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, T.; Feng, L.; Soriano del Amo, D.; Wang, W.; Klivansky, L.M.; Marlow, F.L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P. Increasing the efficacy of bioorthogonal click reactions for bioconjugation: A comparative study. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8051–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, V.; Steinmetz, N.F.; Manchester, M.; Finn, M.G. Labeling live cells by copper-catalyzed alkyne--azide click chemistry. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1912–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hong, S.; Tran, A.; Jiang, H.; Triano, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, P. Sulfated ligands for the copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 2796–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, W.A.; Li, N.; Hoogendoorn, S.; Ruben, M.; Verdoes, M.; Guo, J.; Boons, G.J.; van der Marel, G.A.; Florea, B.I.; Overkleeft, H.S. Two-step bioorthogonal activity-based proteasome profiling using copper-free click reagents: A comparative study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, H.C.; Loureiro, J.; Spooner, E.; van der Velden, A.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Pollington, A.M.; Maehr, R.; Starnbach, M.N.; Ploegh, H.L. Mechanism-based probe for the analysis of cathepsin cysteine proteases in living cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.J.; Kembhavi, A.A.; Brown, M.A.; Kirschke, H.; Knight, C.G.; Tamai, M.; Hanada, K. L-trans-Epoxysuccinyl-leucylamido(4-guanidino)butane (E-64) and its analogues as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases including cathepsins B, H and L. Biochem. J. 1982, 201, 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Dommerholt, J.; Schmidt, S.; Temming, R.; Hendriks, L.J.; Rutjes, F.P.; van Hest, J.C.; Lefeber, D.J.; Friedl, P.; van Delft, F.L. Readily accessible bicyclononynes for bioorthogonal labeling and three-dimensional imaging of living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9422–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.R.; Hilgraf, R.; Sharpless, K.B.; Fokin, V.V. Polytriazoles as copper(I)-stabilizing ligands in catalysis. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 2853–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hahne, H.; Kuster, B.; Verhelst, S.H.L. A simple and effective cleavable linker for chemical proteomics applications. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, N.J.; Baskin, J.M.; Prescher, J.A.; Lo, A.; Bertozzi, C.R. A comparative study of bioorthogonal reactions with azides. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geel, R.; Pruijn, G.J.; van Delft, F.L.; Boelens, W.C. Preventing thiol-yne addition improves the specificity of strain-promoted azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Debets, M.F.; van Berkel, S.S.; Dommerholt, J.; Dirks, A.T.; Rutjes, F.P.; van Delft, F.L. Bioconjugation with strained alkenes and alkynes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Verhelst, S.H.L. Comparative Analysis of Click Chemistry Mediated Activity-Based Protein Profiling in Cell Lysates. Molecules 2013, 18, 12599-12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012599
Yang Y, Yang X, Verhelst SHL. Comparative Analysis of Click Chemistry Mediated Activity-Based Protein Profiling in Cell Lysates. Molecules. 2013; 18(10):12599-12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012599
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yinliang, Xiaomeng Yang, and Steven H. L. Verhelst. 2013. "Comparative Analysis of Click Chemistry Mediated Activity-Based Protein Profiling in Cell Lysates" Molecules 18, no. 10: 12599-12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012599
APA StyleYang, Y., Yang, X., & Verhelst, S. H. L. (2013). Comparative Analysis of Click Chemistry Mediated Activity-Based Protein Profiling in Cell Lysates. Molecules, 18(10), 12599-12608. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012599