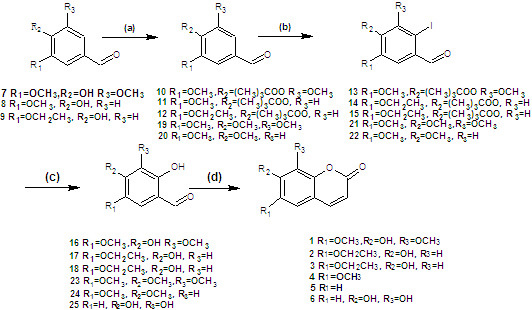
2. Results and Discussion
Coumarins
1,
2, and
3 were synthesized from simple starting materials (
Scheme 1). The hydroxyl group was protected using pivaloyl chloride [
27] to give the corresponding products in 100% yield. These compounds were then iodinated in 80%, 77%, 80% yields, respectively, using
N-iodo-succinimide [
28,
29], followed by hydrolysis using cuprous oxide, pyridine-2-aldoxime, tetrabutylammonium bromide, and cesium hydroxide [
30]. The resulting
o-hydroxybenzaldehydes were finally reacted with ethyl (triphenylphosphoranylidene) acetate in
N,
N-diethylaniline, forming coumarins
1,
2, and
3 as described above [
26].
Scheme 1.
Syntheses of coumarins 1, 2, and 3.
Scheme 1.
Syntheses of coumarins 1, 2, and 3.
Reagents and conditions: (a) (CH3)3COCl, DMAP, Et3N, CH2Cl2; (b) 10 NIS, CF3COOH, CH3CN, reflux; 11,12 N-iodosuccinimide (NIS), CF3SO3H, MeOH; (c) CsOH, syn-2-pyridinealdoxime, Cu2O, Bu4NBr, N2, H2O; (d) (C6H5)3P=CHCOOCH2CH3, Et2NPh, N2, reflux.
It was envisaged that this method could be applied to the synthesis of 6,7-dimethoxy-8-hydroxycoumarin (
34) and 5,6,7,8-tetrahydroxycoumarin (
35) (
Scheme 2).
Scheme 2.
Attempted syntheses of coumarins 34, 35.
Scheme 2.
Attempted syntheses of coumarins 34, 35.
Reagents and conditions: (a) 26 (CH3)3COCl, DMAP, Et3N, CH2Cl2; 27 MeSO4, K2CO3, CH3CN; (b) 28 NIS, CF3COOH, CH3CN, reflux; 29 NIS, CF3SO3H, MeOH; (c) CsOH, syn-2-pyridinealdoxime, Cu2O, Bu4NBr, N2, H2O.
Protection of the hydroxyl groups using pivaloyl chloride and iodination of the resulting compounds proceeded as expected, but hydrolysis of the iodo-compounds 30 and 31 failed to afford the desired products 32 and 33. It was presumed that both electronic effects and steric hindrance of the three methoxy groups and the hydroxyl group at the ortho position of 30 and 31 affected the success of these reactions.
Synthesis of coumarins
4 and
5 (
Scheme 3) began with the iodination of 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (
19) and veratraldehyde (
20), respectively, both in 99% yield. Hydrolysis of 2-iodo-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (
21) and 2-iodo-4,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (
22) afforded 2-hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (
23) and 2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (
24) in 83% and 85% yield, respectively. Finally, the
o-hydroxybenzaldehydes
23 and
24 were converted to the corresponding coumarins
4 and
5. The overall yield of
4 and
5 was higher compared to that of compounds
1–
3.
Scheme 3.
Syntheses of coumarins 4 and 5.
Scheme 3.
Syntheses of coumarins 4 and 5.
Reagents and conditions: (a) 19 NIS, CF3COOH, CH3CN, reflux; 20 NIS, CF3SO3H, MeOH; (b) CsOH, syn-2-pyridinealdoxime, Cu2O, Bu4NBr, N2, H2O; (c) (C6H5)3P=CHCOOCH2CH3, Et2NPh, N2, reflux.
Finally, daphnetin (
6) was synthesized using the one-pot Wittig/cyclization reaction from commercially available 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzaldhyde in 65% yield (
Scheme 4).
Scheme 4.
Synthetic procedures of coumarin 6.
Scheme 4.
Synthetic procedures of coumarin 6.
Reagents and conditions: (a) (C6H5)3P=CHCOOCH2CH3, Et2NPh, N2, reflux.
This result for daphnetin (
6) was identical compared to the previously reported synthesis [
26]. Similarly for scopoletin (
2), the overall yield of 50.4% (for four steps) is comparable to that of the previously reported synthesis (52.8%) [
24]. However, for isofraxidin (
1) and scoparone (
5), the yields of 57.6% and 77.4% are significantly higher compared to those obtained previously [
23,
25]. The key step in this novel method is the hydrolysis of the iodinated compound, as substituents on the phenyl group have a great influence on this reaction. Activating groups can reduce the probability of hydrolysis and steric hindrance at the
ortho position also influences the reaction.
3. Experimental
All solvents and commercially available reagents were purchased from the suppliers and used without further purification. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded using Bruker DPX 500 (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) and 300 spectrometers, respectively. Spectra were recorded in CDCl3 and DMSO solutions and chemical shifts are reported in parts per million (ppm) relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the standard. IR spectra were recorded on an Infinity Spectrum One spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Mass spectra (Applied Biosystems, Toronto, Canada) were recorded on an Agilent 1100 Series VS (ES, 4000 V) mass spectrometer. Melting points were measured using a Büchi B-450 apparatus (Shanghaishenguang, Shanghai, China). Flash chromatography was performed with ACROS silica gel (particle size 0.030–0.040 mm, pore diameter ca. 6 nm) using a glass column.
3.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Coumarins 1–6
The appropriate o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1 mmol) and ethyl(triphenylphosphoranylidene) acetate (1.2 mmol) were dissolved in N,N-diethylaniline (1.5 mL) and the resulting mixture was stirred under a N2 atmosphere and reflux for 15 min. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure (1 mmHg, 52 °C) and the resulting brown oil was purified by column chromatography (petroleum ether-ethyl acetate, 3:1).
7-Hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (
Isofraxidin,
1)
. Yellow solid. Yield: 80%. mp (°C): 147–148.5 (lit. 148–149) [
13].
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3): 3.95 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 4.10 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 6.16 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.29 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 3-CH), 6.66 (s, 1H, OH), 7.60 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 4-CH);
13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3) 56.6 (OCH
3), 61.2 (OCH
3), 105.0 (C-5), 110.7 (C-4a), 112.5 (C-3), 135.2 (C-8), 143.5 (C-7), 144.5 (C-8a), 145.3 (C-4), 146.1 (C-6), 160.6 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm
−1) 1699 (C=O), 1570 (C=C), 3327 (br, OH); HRMS (EI):
m/z 223 [M+H
+].
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (
Scopoletin,
2)
. Yellow solid. Yield: 85%. mp (°C): 202.7–204.4 (lit. 204) [
15].
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3): 3.82 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 6.23 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 3-CH), 6.79 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.23 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.92 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 4-CH), 10.33 (s, 1H, OH);
13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3) 56.4 (OCH
3), 103.2 (C-8), 110.0 (C-5), 111.0 (C-3), 112.1 (C-4a), 144.9 (C-4), 145.7 (C-6), 150.0 (C-7), 151.6 (C-8a), 161.1 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm
−1) 1558 (C=C), 1683 (C=O), 3334 (br, OH). HRMS (EI):
m/z 193 [M+H
+].
7-Hydroxy-6-ethoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (3). Yellow solid. Yield: 80%. mp (°C): 138.5–142.0. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.37 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3), 4.06 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H, OCH2-), 6.23 (d, J 9.5 Hz, 1H, 3-CH), 6.81 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.90 (d, J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 4-CH), 10.27 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 15.1 (CH3), 64.8 (-CH2O-), 103.2 (C-8), 111.0 (C-5), 111.2 (C-3), 112.1 (C-4a), 144.8 (C-4), 144.9 (C-6), 149.9 (C-7), 151.9 (C-8a), 161.1 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1558 (C=C), 1699 (C=O), 1716, 3383 (br, OH);.HRMS (EI): m/z 207 [M+H+].
6,7,8-Trimethoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (
Dimethylfraxetin,
4)
. Yellow solid. Yield: 81%. mp (°C): 103.8–104.5 (lit. 104–105) [
31].
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3): 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 4.00 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 4.04 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 6.35 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz,1H, 3-CH), 6.69 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.63 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 4-CH);
13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3) 56.3 (OCH
3), 61.5 (OCH
3), 61.8 (OCH
3), 103.7 (C-5), 114.3 (C-4a), 115.2 (C-8), 141.2 (C-6), 143.1 (C-7), 143.5 (C-4), 145.9 (C-8), 150.1 (C-8a), 160.5 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm
−1) 1566 (C=C), 1716 (C=O). HRMS (EI):
m/z 237 [M+H
+].
6,7-Dimethoxy-2H-chromen-2-one (
Scoparone,
5)
. Yellow solid. Yield: 91%. mp (°C): 142.6–148.4 (lit. 145–146) [
18].
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3): 3.81 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 3.87 (s, 3H, OCH
3), 6.30 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 3-CH), 7.07 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.25 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.955 (d,
J = 9.5 Hz, 1H, 4-CH);
13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3) 56.3 (OCH
3), 56.6 (OCH
3), 100.5 (C-8) 109.3 (C-5), 111.6 (C-4a), 113.1 (C-3), 144.8 (C-6), 146.3 (C-4), 149.9 (C-8a), 153.0 (C-7), 161.0 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm
−1) 1516 (C=C), 1558, 1708 (C=O), 1616, 3566 (br, OH). HRMS (EI):
m/z 207 [M+H
+].
7,8-Dihydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one (
Daphnetin,
6)
. Yellow solid. Yield: 65%. mp (°C): 265.7–267.2 (lit. 265−268) [
21].
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3): 6.20 (d,
J = 6.5 Hz, 1H, 3-CH), 6.81 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.03 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.91 (d,
J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, 4-CH), 9.79 (d,
J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, OH), 9.80 (d,
J =7.0Hz, 1H, OH);
13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl
3) 111.7 (C-3), 112.5 (C-4a), 112.9 (C-6), 119.3 (C-5), 132.6 (C-8), 144.2 (C-8a), 145.6 (C-4), 150.1 (C-7), 160.9 (C-2); IR (KBr, cm
−1) 1674 (C=O), 1508 (C=C), 1589. HRMS (EI):
m/z 179 [M+H
+].
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 10–12
The corresponding phenol (3 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (5 mL) and 4-dimethylamiopyridine (0.1 mmol) was added. The reaction was stirred for 0.5 h before addition of pivaloyl chloride (6 mmol) followed by dropwise addition of triethylamine (6 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The reaction solution was poured into dichloromethane (100 mL) and washed with saturated sodium chloride solution (2 × 100 mL) and saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (2 × 100 mL). The organic phase was collected, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and filtered, and then the solvent was removed in vacuo to obtain compounds 10–12.
4-Formyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (10, C14H18O5). Yellow solid. Yield 100%. mp (°C): 108–110.9. 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz): 1.39 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 3.88 (s, 6H, OCH3), 7.14 (s, 2H, Ar), 9.91 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 27.2 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 39.2 (CC=O), 56.37 (2 × OCH3), 106.2 (C-3,5) 134.1 (C-1), 134.4 (C-4), 153.0 (C-2,6), 175.8 (C=O), 191.2 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1751 (C=O), 1691, 1608; MS (EI): m/z 267 [M+H+].
4-Formyl-2-methoxyphenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (11, C13H16O4). White solid. Yield: 100%. mp (°C): 83.8–95.0. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.38 (s, 9H, C(CH3)), 3.88 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.19 (d, J = 7.5Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.46 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.48 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 9.95 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 27.2 (3 × CH3), 39.2(CC=O), 56.1 (OCH3), 110.8 (C-2), 123.4 (C-6), 124.8 (C-5), 135.1 (C-1), 145.6 (C-4), 152.1 (C-3), 176.1 (-COO-), 191.2 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1689 (C=O), 1749. MS (EI): m/z 237 [M+H+].
2-Ethoxy-4-formylphenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (12, C14H18O4). White solid. Yield: 100%. mp (°C): 83.8–85.3. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.38 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 1.41 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3), 4.10 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H, OCH2-), 7.19 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.46 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.46 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, Ar), 9.93 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 14.6 (CH3), 27.2 (CH3), 39.2 (CC=O), 64.5 (-OCH2-), 111.4 (C-2), 123.3 (C-6), 124.6 (C-5), 135.0 (C-1), 145.6 (C-4), 151.4 (C-3), 176.0 (C=O), 191.2 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1699 (C=O), 1602; MS (EI): m/z 251 [M+H+].
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 13, 21, 22.
The appropriate benzaldehyde (3 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (5 mL) and N-iodosuccinimide (6 mmol) was added. Trifluoroacetic acid (0.3 μmol) was then added dropwise and the reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 6 h. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction solution was quenched by the addition of sodium sulfite (3 mmol) and stirred for five minutes. Subsequently, CH2Cl2 (100 mL) was added and the solution was extracted with saturated sodium chloride solution (3 × 100 mL). The organic phase was collected, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. Column chromatography (petroleum ether-ethyl acetate, 40:1) afforded the corresponding iodinated compound.
4-Formyl-3-iodo-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (13, C14H17O5). Yellow solid. Yield: 80%. mp (°C): 100.7–102.5. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.40 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 3.86 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.85 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.37 (s, 1H, Ar), 10.08 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 27.1 (CH3), 39.3 (CC=O), 56.5 (OCH3), 61.5 (OCH3), 90.3 (C-2), 108.6 (C-6), 133.0 (C-4), 139.0 (C-1), 153.0 (C-5), 152.3 (C-3), 175.3 (C=O), 191.0 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1691 (C=O), 1759; MS (EI): m/z 393 [M+H+].
2-Iodo-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (21, C10H11O3). Yellow solid. Yield: 99%. mp (°C): 67.6–68.1. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.97 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.92 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.35 (s, 1H, OCH3), 10.05 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 61.2 (OCH3), 61.0 (OCH3), 56.3 (OCH3), 91.6 (C-2), 108.6 (C-6), 130.6 (C-1), 147.8 (C-4), 153.0 (C-5), 154.1 (C-3), 195.3 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1687 (C=O); MS (EI): m/z 323 [M+H+].
2-Iodo-4,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (22, C9H9O2). Yellow solid. Yield: 99%. mp (°C):: 145.1–145.5. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.92 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.96 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.31 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.42 (s, 1H, Ar), 9.87 (s, 1H, Ar); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 56.1 (OCH3), 56.5 (OCH3), 92.8 (C-4), 111.1 (C-5), 121.8 (C-1), 128.4 (C-6), 149.8 (C-3), 154.5 (C-2), 194.9 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1672 (C=O); MS (EI): m/z 293 [M+H+].
3.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 14 and 15
The appropriate benzaldehyde (3 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (20 mL) and N-iodosuccinimide (6 mmol) was added. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (6 mmol) was then added dropwise and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The reaction was quenched by the addition of sodium sulfite and the reaction mixture was stirred for five minutes. Subsequently, dichloromethane (100 mL) was added and the solution was extracted with saturated sodium chloride solution (3 × 100 mL). The organic phase was collected, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and filtered; then, the solvent was removed in vacuo. Column chromatography (petroleum ether-ethyl acetate, 40:1) afforded the corresponding iodinated compound.
4-Formyl-5-iodo-2-methoxyphenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (14, C13H15O4). Yellow solid. Yield: 77%. mp (°C): 98.4. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.36 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 3.86 (s, 3H, OCH3), 7.50 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.58 (s, 1H, Ar), 9.96 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 27.1 (3 × CH3), 39.2 (CC=O), 56.2 (OCH3), 89.6 (C-2), 112.7 (C-6), 133.2 (C-3), 134.1 (C-1), 145.7 (C-4), 152.3 (C-5), 175.7 (-COO-), 194.9 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1693 (C=O), 1751; MS (EI): m/z 363 [M+H+].
2-Ethoxy-4-formyl-5-iodophenyl-2,2-dimethylpropanoate (15, C14H17O4). Yellow solid. Yield: 80%. mp (°C): 81.7–83.8. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.37 (s, 9H, C(CH3)3), 1.39 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H, -CH3), 4.08 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H, OCH2-), 7.47 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.58 (s, 1H, Ar), 9.95 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 14.5 (CH3), 27.1 (CH3), 39.2 (CC=O), 64.7 (-OCH2-), 89.4 (C-2), 113.3 (C-6), 133.1 (C-3), 134.0 (C-1), 145.8 (C-4), 151.6 (C-5), 175.7 (C=O), 195.0 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1685 (C=O), 1759; MS (EI): m/z 377 [M+H+].
3.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 16–18, 23 and 24
To the appropriate iodinated compound (2 mmol) was added Cu2O (0.1 mmol), pyridine-2-aldoxime (0.2 mmol), tetrabutylammonium bromide (0.4 mmol), cesium hydroxide monohydrate (10 mmol), and water (2 mL) and the mixture was stirred under N2 atmosphere for 10 h. The reaction mixture was acidified to pH 5–7 with 1 M hydrochloric acid. The aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 100 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and filtered; the solvent was then removed in vacuo. Column chromatography (petroleum ether-ethyl acetate: 20:1) afforded the corresponding phenol.
2,4-Dihydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (16, C9H10O5). Yellow solid. Yield: 90%. mp (°C): 87.5–89.8. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.01 (s, 3H, OCH3), 6.41 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.75 (s, 1H, OH), 9.70 (s, 1H, OH), 11.30 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 56.6 (OCH3), 60.9 (OCH3), 108.9 (C-6), 112.9 (C-1), 134.6 (C-3), 141.2 (C-4), 146.9 (C-2), 151.6 (C-5), 194.6 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 3350 (br, OH), 1650 (C=O); MS (EI): m/z 199 [M+H+].
2,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde (17, C8H8O4). Yellow solid. Yield: 77%. mp (°C): 152.1−153.2. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.92 (s, 3H, OCH3), 6.41 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.53 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.89 (s, 1H, OH), 9.68 (s, 1H, OH), 11.34 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 56.5 (OCH3), 103.2 (C-3), 112.9 (C-1), 113.3 (C-6), 140.7 (C-5), 154.4 (C-4), 159.6 (C-2), 193.8 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 3292 (br, OH), 1635 (C=O); MS (EI): m/z 169 [M+H+].
5-Ethoxy-2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (18, C9H10O4). Yellow solid. Yield: 77%. mp (°C): 131.8−134.4. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 1.47 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3), 4.12 (q, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H, OCH2-), 6.49 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.53 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.88 (s, 1H, OH), 9.65 (s, 1H, OH), 11.33 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 14.8 (CH3), 65.3 (-CH2O), 103.1 (C-3), 113.3 (C-1), 113.9 (C-6), 139.9 (C-5), 154.6 (C-4), 159.5 (C-2), 193.8 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1627 (C=O), 1699, 3367 (br, OH); MS (EI): m/z 183 [M+H+].
2-Hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (23, C10H12O4). Yellow solid. Yield: 83%. mp (°C): 46.0–46.6. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.87 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.94 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.05 (s, 3H, OCH3), 6.78 (s, 1H), 9.78 (s, 1H, OH), 11.01 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 61.4 (OCH3), 61.1 (OCH3), 56.5 (OCH3), 109.2 (C-6), 115.2 (C-1), 141.0 (C-3), 146.3 (C-4), 150.3 (C-2), 151.8 (C-5), 194.9 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1641 (C=O), 3240 (br, OH); MS (EI): m/z 213 [M+H+].
2-Hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (24, C9H10O3). Yellow solid. Yield: 85%. mp (°C): 105.5–112.8. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): 3.88 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.94 (s, 3H, OCH3), 6.48 (s, 1H, Ar), 6.91 (s, 1H, Ar), 9.71 (s, 1H, OH), 11.40 (s, 1H, CHO); 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) 56.4 (OCH3), 56.4 (OCH3), 100.1 (C-3), 112.9 (C-1), 113.2 (C-6), 143.0 (C-5), 157.2 (C-2), 159.4 (C-4), 194.0 (CHO); IR (KBr, cm−1) 1624 (C=O), 3446 (br, OH); MS (EI): m/z 183 [M+H+].