MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
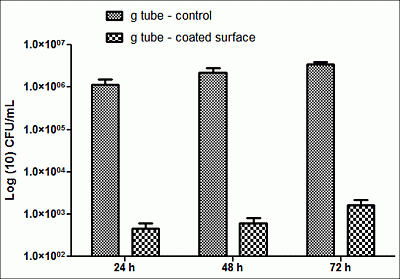
2. Results and Discussion











3. Experimental
3.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4@CV
3.2. MAPLE Target Preparation and Deposition of Fe3O4@CV-Based Thin Coating
3.3. Characterization of Fe3O4@CV and Prepared Thin Coating
3.3.1. XRD
3.3.2. IRM
3.3.3. SEM
3.3.4. Interaction with Eukaryotic Cells
3.3.5. Interaction with Prokaryotic Cells
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locher, J.L.; Bonner, J.A.; Carroll, W.R.; Caudell, J.J.; Keith, J.N.; Kilgore, M.L.; Ritchie, C.S.; Roth, D.L.; Tajeu, G.S.; Allison, J.J. Prophylactic percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in treatment of head and neck cancer: A comprehensive review and call for evidence-based medicine. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keung, E.Z.; Liu, X.; Nuzhad, A.; Rabinowits, G.; Patel, V. In-hospital and long-term outcomes after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with malignancy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomberg, J.; Lagergren, J.; Martin, L.; Mattsson, F.; Lagergren, P. Complications after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in a prospective study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, I.B.; Sunner, J.A.; Arciola, C.R.; Cristiani, P. Microbially-influenced corrosion: Damage to prostheses, delight for bacteria. Int. J. Artif. Org. 2006, 29, 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, V. Quorum sensing in biofilms: How to destroy the bacterial citadels or their cohesion power? Anaerobe 2011, 17, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, K.; Hu, H.; Jacombs, A.S.; Bradshaw, D.A.; Deva, A.K. A review of bacterial biofilms and their role in device-associated infection. Healthc. Infect. 2013, 18, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holban, A.M.; Cartelle Gestal, M.; Grumezescu, A.M. New molecular strategies for reducing implantable medical devices associated infections. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Holban, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Anghel, A.G.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Biohybrid nanostructured iron oxide nanoparticles and Satureja hortensis to prevent fungal biofilm development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18110–18123. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.; Tran, P.A. Nanomaterial-Based treatments for medical device-associated infections. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2481–2494. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M. Improved wound dressings: Novel approaches. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Holban, A.M.; Gheorghe, I.; Vlad, M.; Anghel, G.A.; Balaure, P.C.; Chifiriuc, C.M.; Ciuca, I.M. Improved activity of aminoglycosides entrapped in silica networks against microbial strains isolated from otolaryngological infections. Farmacia 2014, 62, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Voicu, G.; Huang, K.-S.; Yang, C.-H.; Ficai, A.; Vasile, B.S.; Grumezescu, V.; Bleotu, C.; Chifiriuc, M.C. New silica nanostructure for the improved delivery of topical antibiotics used in the treatment of staphylococcal cutaneous infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 476, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, I.; Grumezescu, A.M. Hybrid nano-structured coating for increased resistance of prosthetic devices to staphylococcal colonization. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, I.; Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Ficai, A.; Anghel, A.G.; Maganu, M.; Lazar, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Modified wound dressing with phyto-nanostructured coating to prevent staphylococcal and pseudomonal biofilms development. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, C.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Caliceti, P.; Genta, I. Sub-unit vaccine against S. aureus-mediated infections: Set-up of nano-sized polymeric adjuvant. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Nafee, N.; Youssef, A.; El-Gowelli, H.; Asem, H.; Kandil, S. Antibiotic-free nanotherapeutics: Hypericin nanoparticles thereof for improved in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial photodynamic therapy and wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; McLoughlin, P.; O’Sullivan, L.; Prieto, M.L.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hughes, H. Development of a novel antimicrobial seaweed extract-based hydrogel wound dressing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Belcarz, A.; Zima, A.; Ginalska, G. Biphasic mode of antibacterial action of aminoglycoside antibiotics-loaded elastic hydroxyapatite–glucan composite. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echezarreta-López, M.M.; Landin, M. Using machine learning for improving knowledge on antibacterial effect of bioactive glass. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M. Novel strategies to eradicate bacterial communities based on nano and biomaterials. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Andronescu, E.; Anghel, G.A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Protective effect of magnetite nanoparticle/Salvia officinalis essential oil hybrid nanobiosystem against fungal colonization on the Provox® voice section prosthesis. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2012, 7, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Saviuc, C.; Chifiriuc, C.M.; Hristu, R.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Balaure, P.; Stanciu, G.; Lazar, V. Inhibitory activity of Fe3O4/Oleic acid/usnic acid—Core/shell/extra-shell nanofluid on S. aureus biofilm development. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2011, 10, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Albu, M.G.; Ficai, A.; Dragu, D. Wound dressing based collagen biomaterials containing usnic acid as quorum sensing inhibitor agent: Synthesis, characterization and bioevaluation. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Cotar, A.I.; Andronescu, E.; Ficai, A.; Ghitulica, C.D.; Grumezescu, V.; VasileB, S.; Chifiriuc, M.C. In vitro activity of the new water dispersible Fe3O4@usnic acid nanostructure against planktonic and sessile bacterial cells. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1766. [Google Scholar]
- Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Grumezescu, V.; Chifiriuc, C.M.; Radulescu, R. Magnetite-usnic acid nanostructured bioactive material with antimicrobial activity. Rom. J. Mater. 2013, 43, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaiescu, D.E.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Buteica, A.S.; Mogosanu, D.E.; Balaure, P.C.; Mihaiescu, O.M.; Trăistaru, V.; Vasile, B.S. Bioassay and electrochemical evaluation of controlled release behavior of cephalosporins from magnetic nanoparticles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2012, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, V.; Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Socol, G.; Ficai, A.; Vasile, B.S.; Trusca, R.; Bleotu, C.; Lazar, V.; Chifiriuc, C.M.; et al. Usnic acid loaded biocompatible magnetic PLGA-PVA microspheres thin films fabricated by MAPLE with increased resistance to staphylococcal colonization. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviuc, C.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bleotu, C.; Holban, A.M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Balaure, P.; Lazar, V. Culture methods versus flow cytometry for the comparative assessment of antifungal activity of Eugenia caryophyllata thunb. (Myrtaceae) essential oil. Farmacia 2013, 61, 912–919. [Google Scholar]
- Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Ficai, A.; Voicu, G.; Cocos, O.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Eugenia cayophyllata essential oil-SiO2 biohybrid structure for the potentiation of antibiotics activity. Rom. J. Mater. 2013, 43, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Saviuc, C.; Cotar, A.I.; Holban, A.M.; Banu, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Phenotypic and molecular evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureusvirulence patterns in the presence of some essential oils and their major compounds. Lett. Appl. NanoBiosci 2013, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Saviuc, C.; Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Bleotu, C.; Banu, O.; Lazar, V.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Testing antifungal activity of some essential oils using flow cytometry. Lett. Appl. NanoBiosci. 2012, 1, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Charernsriwilaiwat, N.; Rojanarata, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Sukma, M.; Opanasopit, P. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofiber mats loaded with Garcinia mangostana extracts. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Bi, H.; Xie, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, D. Natural borneol enhances geniposide ophthalmic absorption in rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 445, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviuc, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Banu, O.; Chifiriuc, C.; Mihaiescu, D.; Balaure, P.; Lazar, V. Biocompatible magnetic MWCNTs based on phytocomponents from Eugenia carryophyllata. Rev. Chim. Bucharest 2012, 63, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Saviuc, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Hristu, R.; Stanciu, G.; Oprea, E.; Radulescu, V.; Lazar, V. Hybrid Nanosystem for Stabilizing Essential Oils in Biomedical Applications. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2011, 6, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, I.; Holban, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Efficient surface functionalization of wound dressings by a phytoactive nanocoating refractory to Candida albicans biofilm development. Biointerphases 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.K.; Ringeisen, B.R.; Krizman, D.B.; Frondoza, C.G.; Brooks, M.; Bubb, D.M.; Auyeung, R.C.Y.; Piqué, A.; Spargo, B.; McGill, R.A.; et al. Laser transfer of biomaterials: Matrix-assisted pulsed laser evaporation MAPLEand MAPLE Direct Write. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricato, A.P.; Luches, A. Applications of the matrix-assisted pulsed laser evaporation method for the deposition of organic, biological and nanoparticle thin films: A review. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 105, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, R.; Popescu, C.; Dorcioman, G.; Miroiu, F.M.; Socol, G.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Gittard, S.D.; Miller, P.R.; Narayan, R.J.; Enculescu, M.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of biopolymer–antibiotic thin films fabricated by advanced pulsed laser methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 278, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, S.; Cristescu, R.; Popescu, A.C.; Popescu, C.E.; Dorcioman, G.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Ciucu, A.A.; Balan, A.; Stamatin, I.; Fagadar-Cosma, E.; et al. Functionalized porphyrin conjugate thin films deposited by matrix assisted pulsed laser evaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 278, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristescu, R.; Popescu, C.; Socol, G.; Iordache, I.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronie, A.; Stamatin, I.; Chifiriuc, C.; et al. Magnetic core/shell nanoparticle thin films deposited by maple: Investigation by chemical, morphological and in vitro biological assays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 9250–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshayesh, S.; Dehghani, H. Synthesis of magnetite-porphyrin nanocomposite and its applicationas a novel magnetic adsorbent for removing heavy cations. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 2614–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieppo, L.; Saarakkala, S.; Närhi, T.; Helminen, H.J.; Jurvelin, J.S.; Rieppo, J. Application of second derivative spectroscopy for increasing molecular specificity of fourier transform infrared spectroscopic imaging of articular cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumezescu, V.; Socol, G.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Holban, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Trușcǎ, R.; Bleotu, C.; Balaure, P.C.; Cristescu, R.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Functionalized antibiofilm thin coatings based on PLA-PVA microspheres loaded with usnic acid natural compounds fabricated by MAPLE. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 302, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaiescu, D.E.; Cristescu, R.; Dorcioman, G.; Popescu, C.; Nita, C.; Socol, G.; Mihailescu, I.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Tamas, D.; Enculescu, M.; et al. Functionalized magnetite silica thin films fabricated by MAPLE with antibiofilm properties. Biofabrication 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the Fe3O4@CV and thin coatings are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anghel, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Chirea, M.; Grumezescu, V.; Socol, G.; Iordache, F.; Oprea, A.E.; Anghel, I.; Holban, A.M. MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes. Molecules 2014, 19, 8981-8994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19078981
Anghel AG, Grumezescu AM, Chirea M, Grumezescu V, Socol G, Iordache F, Oprea AE, Anghel I, Holban AM. MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes. Molecules. 2014; 19(7):8981-8994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19078981
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnghel, Alina Georgiana, Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, Mariana Chirea, Valentina Grumezescu, Gabriel Socol, Florin Iordache, Alexandra Elena Oprea, Ion Anghel, and Alina Maria Holban. 2014. "MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes" Molecules 19, no. 7: 8981-8994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19078981
APA StyleAnghel, A. G., Grumezescu, A. M., Chirea, M., Grumezescu, V., Socol, G., Iordache, F., Oprea, A. E., Anghel, I., & Holban, A. M. (2014). MAPLE Fabricated Fe3O4@Cinnamomum verum Antimicrobial Surfaces for Improved Gastrostomy Tubes. Molecules, 19(7), 8981-8994. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19078981