Size Control of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Excess Ligands as a Function of Reaction Temperature and Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
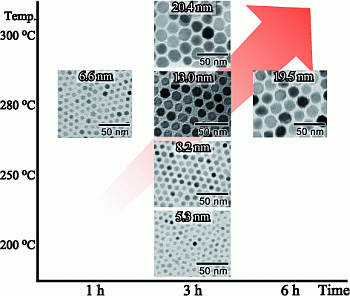
| Reaction temperature (°C) | Reaction time (h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 6 | |
| 200 | 5.3 ± 0.6 nm | ||
| 250 | 8.2 ± 0.6 nm | ||
| 280 | 6.6 ± 1.0 nm | 13.0 ± 0.9 nm | 19.5 ± 1.7 nm |
| 300 | 20.4 ± 2.2 nm | ||






3. Experimental Section
3.1. Apparatus and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockenberger, J.; Scher, E.C.; Alivisatos, A.P. A new nonhydrolytic single-precursor approach to surfactant-capped nanocrystals of transition metal oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11595–11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, T. Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2003, 8, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8204–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Casula, M.F.; Jun, Y.-W.; Zaziski, D.J.; Chan, E.M.; Corrias, A.; Alivisatos, A.P. The concept of delayed nucleation in nanocrystal growth demonstrated for the case of iron oxide nanodisks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, N.; Park, M.; Kim, B.H.; An, K.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis of uniform ferrimagnetic magnetite nanocubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 454–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.-G.; Noh, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, N.-M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, M.; Moon, W.K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T. Water-dispersible ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes with extremely high r2 relaxivity for highly sensitive in vivo MRI of tumors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.-H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 2005, 1, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, J.W.; Kraitchman, D.L. Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Cheon, J. Chemical design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5122–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, G.; Eden, H.S.; Ai, H.; Chen, X. Surface-engineered magnetic nanoparticle platforms for cancer imaging and therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinvivas, M.; Armtzen, E.H.J.G.; Bulte, J.W.M.; Heerschap, A.; de Vries, I.J.M.; Figdor, C.G. Imaging of cellular therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2575–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Peng, S.; Xu, C.; Sun, S. Porous hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticles for targeted delivery and controlled release of cisplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10637–10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Y.; Kim, J.; Na, H.B.; Kim, D.; Baek, J.S.; Ko, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Hyeon, T. Wrap–bake–peel process for nanostructural transformation from β-FeOOH nanorods to biocompatible iron oxide nanocapsules. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, C.; Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, S. pH controlled release of chromone from chromone-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14436–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jang, J.-T.; Choi, J.-S.; Moon, S.H.; Noh, S.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, K.I.; Cheon, J. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat. Nanotech. 2011, 6, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.-P.; Wilhelm, J.-P.C.; Servais, J.; Ménager, C.; Bacri, J.-C.; Gazeau, F. Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Xing, R.; Xu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Gao, S.; Sun, S. Synthesis, Functionalization, and biomedical applications of multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2729–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gu, H.; Xu, B. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: Design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandhar, A.P.; Ferguson, R.M.; Krishnan, K.M. Monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles optimized for magnetic fluid hyperthermia: Implications in biological systems. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07B310. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G.; Xu, W.; Liang, S.; Yin, D. Zinc blende and wurtzite cadmium sulfide nanocrystals with strong photoluminescence and ultrastability. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 299, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.A.; Ryu, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Choi, W.; Hoffmann, M.R. Photocatalytic hydrogen production with visible light over Pt-interlinked hybrid composites of cubic-phase and hexagonal-phase CdS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12069–12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehara, M.; Arakawa, H.; Honda, T.; Saruyama, M.; Teranishi, T. Large-scale synthesis of high-quality metal sulfide semiconductor quantum dots with tunable surface-plasmon resonance frequencies. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 9230–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, M.; Tanaka, I.; Muramatsu, A. Preparation of manganese doped cadmium sulfide nanoparticles in zincblende phase and their magnetic properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 9003–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, M.; Kanehara, M.; Teranishi, T. One-pot synthesis of large FePt nanoparticles from metal salts and their thermal stability. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3485–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, M.; Nishida, R.; Muramatsu, A. Preparation of wüstite nanoparticles by a solventless synthetic procedure. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.B.; Kagan, C.R.; Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse nanocrystals and close-packed nanocrystals assemblies. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 2000, 30, 545–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, E.V.; Talapin, D.V.; Schnablegger, H.; Konorwski, A.; Festin, Ö.; Svedlindh, P.; Haase, M.; Weller, H. Study of nucleation and growth in the organometallic synthesis of magnetic alloy nanocrystals: The role of nucleation rate in size control of CoPt3 nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9090–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontijn, W.F.J.; van der Zaag, P.J.; Devillers, M.A.C.; Brabers, V.A.M.; Metselaar, R. Optical and magneto-optical polar Kerr spectra of Fe3O4 and Mg2+- or Al3+-substituted Fe3O4. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, 5432–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Myers, M.; Bosnick, K.A.; Brus, L.E. Magnetite Fe3O4 nanocrystals: Spectroscopic observation of aqueous oxidation kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7501–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the magnetite nanoparticles are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakaya, M.; Nishida, R.; Muramatsu, A. Size Control of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Excess Ligands as a Function of Reaction Temperature and Time. Molecules 2014, 19, 11395-11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811395
Nakaya M, Nishida R, Muramatsu A. Size Control of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Excess Ligands as a Function of Reaction Temperature and Time. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11395-11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811395
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakaya, Masafumi, Ryo Nishida, and Atsushi Muramatsu. 2014. "Size Control of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Excess Ligands as a Function of Reaction Temperature and Time" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11395-11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811395
APA StyleNakaya, M., Nishida, R., & Muramatsu, A. (2014). Size Control of Magnetite Nanoparticles in Excess Ligands as a Function of Reaction Temperature and Time. Molecules, 19(8), 11395-11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811395