Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
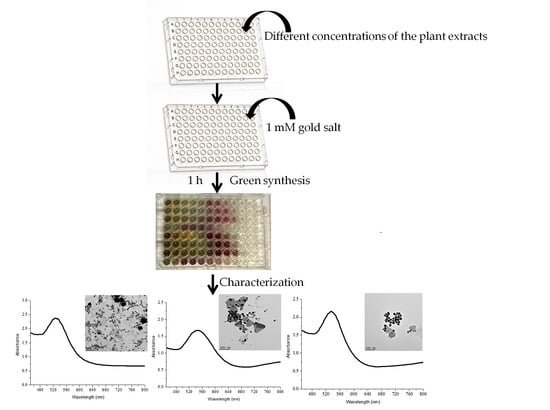
2.1. Synthesis of AuNPs and Their UV-Vis Analysis
2.2. Particle Size Diameter, Distribution and Shape Analysis
2.2.1. DLS Analysis
2.2.2. HRTEM and EDX Analysis
2.3. Stability of the AuNPs
2.4. Effect of Temperature on AuNPs Characteristics
2.5. Effect of Concentration and Determination of OC for Each Plant Extract
2.6. Plant Phytochemicals Role in Bio-Reduction of Gold Salt
3. Materials and Methodology
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instruments
3.3. Plant Collection
3.4. Preparation of the Plant Extracts
3.5. Screening of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesis
3.6. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Analysis
3.7. Stability Testing of the Synthesized AuNPs
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geethalakshmi, R.; Sarada, D.V.L. Gold and silver nanoparticles from Trianthema decandra: synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Banerjee, P. Green nanotechnology—A new hope for medical biology. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M. Some interesting properties of metals confined in time and nanometer space of different shapes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2256–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Yang, M.; Qu, X.; Huai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, C. Tuning photothermal properties of gold nanodendrites for in vivo cancer therapy within a wide near infrared range by simply controlling their degree of branching. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadeer, N.; Murphy, C. Recent Progress in Cancer Thermal Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4691–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D. Formation of colloidal silver nanoparticles stabilized by Na+-poly(γ-glutamic acid)-silver nitrate complex via chemical reduction process. Colloids Surf. B 2007, 59, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, K.; Witcomb, M.; Scurrell, M. Self-assembly of silver nanoparticles in a polymer solvent: Formation of a nanochain through nanoscale soldering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 90, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, L. New pathway for the synthesis of ultrafine silver nanoparticles from bulk silver substrates in aqueous solutions by sonoelectrochemical methods. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Kakita, T.; Tsuji, M. Preparation of nano-size particles of silver with femto second laser ablation in water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 206, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.; Malinsky, M.; Haynes, C.; Van Duyne, R. Nanosphere lithography: Tunable localized surface plasmon resonance spectra of silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 10549–10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukman, A.; Gong, B.; Marjo, C.; Roessner, U.; Harris, A. Facile synthesis, stabilization, and anti-bacterial performance of discrete Ag nanoparticles using Medicago sativa seed exudates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core—Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Deepak, V.; Ram Kumar Pandian, S.; Gurunathan, S. Biological synthesis of gold nanocubes from Bacillus licheniformis. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5356–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Ahmad, A.; Pasricha, R.; Sastry, M. Bioreduction of chloroaurate ions by geranium leaves and its endophytic fungus yields gold nanoparticles of different shapes. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, S. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankamwar, B. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (green-gold) using leaf extract of Terminalia catappa. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 7, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Arockiya Aarthi Rajathi, F.; Arumugam, R.; Saravanan, S.; Anantharaman, P. Phyto fabrication of gold nanoparticles assisted by leaves of Suaeda monoica and its free radical scavenging property. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 135, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, K.; Annamalai, S.; Shanmugasundaram, H. One-step green synthesis and characterization of leaf extract-mediated biocompatible silver and gold nanoparticles from Memecylon umbellatum. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, J.; Goldblatt, P. Plants of the Greater Cape Floristic Region 1: The Core Cape flora, Strelitzia29; South African National Biodiversity Institute: Pretoria, South Africa, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, L.; Arunachalam, J. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of small gold nanoparticles using aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract: Their application as antibiotic carriers. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 2012, 4, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nune, S.; Chanda, N.; Shukla, R.; Katti, K.; Kulkarni, R.; Thilakavathi, S.; Mekapothula, S.; Kannan, R.; Katti, K.V. Green nanotechnology from tea: Phytochemicals in tea as building blocks for production of biocompatible gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Jackman, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, P.; Cho, N.; Kim, D. Strategies for enhancing the sensitivity of plasmonic nanosensors. Nano Today 2015, 10, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, M.; Mady, M.; Ghannam, M. Physical properties of different gold nanoparticles: Ultraviolet-visible and fluorescence measurements. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifuddin, N.; Wong, C.; Yasumira, A. Rapid biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatant of bacteria with microwave irradiation. Eur. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Sakthivel, N. Coriander leaf mediated biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4588–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipway, A.; Lahav, M.; Gabai, R.; Willner, I. Investigations into the electrostatically induced aggregation of Au nanoparticles. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8789–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Kónya, Z.; Puntes, V.; Kiricsi, I.; Miao, C.X.; Ager, J.; Alivisatos, A.; Somorjai, G. Encapsulation of metal (Au, Ag, Pt) nanoparticles into the mesoporous SBA-15 structure. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4396–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Oza, G.; Mewada, A.; Sharon, M. Green synthesis of highly stable gold nanoparticles using Momordica charantia as nano fabricator. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 4, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Kamitsos, E. Effect of temperature on the direct synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by poly (dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) Homopolymer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 22754–22759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, G.; Lu, Z.; Che, C. Fabrication of gold nanoparticles with different morphologies in HEPES buffer. Rare Metals 2010, 29, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, C.; Hornyak, G.; Stockert, J.; Martin, C. Template-synthesized nanoscopic gold particles: Optical spectra and the effects of particle size and shape. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 2963–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiri, Y.; Elia, P.; Zach, R.; Hazan, S.; Kolusheva, S.; Porat, Z. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as reducing agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4007–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, A. Green chemistry synthesis of gold nanoparticles using lactic acid as a reducing agent. Micro Nano Lett. 2010, 5, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-León, E.; Iñiguez-Palomares, R.; Navarro, R.; Herrera-Urbina, R.; Tánori, J.; Iñiguez-Palomares, C.; Maldonado, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using reducing agents obtained from natural sources (Rumex hymenosepalus extracts). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, N.; Shukla, R.; Zambre, A.; Mekapothula, S.; Kulkarni, R.; Katti, K.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Fent, G.; Casteel, S.; Boote, E.; et al. An effective strategy for the synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles using cinnamon phytochemicals for phantom CT imaging and photoacoustic detection of cancerous cells. Pharm. Res. 2010, 28, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, B. Biological synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus and Diopyros kaki leaf extracts. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X. Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: The third role of citrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13939–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Li, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. Controllable biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles from a Eucommia ulmoides bark aqueous extract. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 142, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.; Mondal, S.; Basu, S.; Laskar, R.; Mandal, D. Biogenic synthesis of Au and Ag nanoparticles using aqueous solutions of Black Tea leaf extracts. Colloids Surf. B. 2009, 71, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, L.; Arunachalam, J. Green synthetic route for the size controlled synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of garlic (Allium Sativum). Adv. Mater. Lett. 2013, 4, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; He, N.; Hong, J.; Chen, C. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jamróz, P.; di Cenzo, G.; Sergiel, I.; Kozlecki, T.; Pohl, P. Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles prepared with aqueous extracts of Lamiaceae plants and the effect of follow-up treatment with atmospheric pressure glow micro discharge. Arabian J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasthuri, J.; Veerapandian, S.; Rajendiran, N. Biological synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using apiin as reducing agent. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 68, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleel Basha, S.; Govindaraju, K.; Manikandan, R.; Ahn, J.; Bae, E.; Singaravelu, G. Phytochemical mediated gold nanoparticles and their PTP 1B inhibitory activity. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 75, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.; Silva, A.; Saraiva, S.; Sobral, A.; Cardoso, S. Characterization of phenolic constituents and evaluation of antioxidant properties of leaves and stems of Eriocephalus africanus. Arabian J. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdero, C.; Bohlmann, F.; Müller, M. Sesquiterpene lactones and other constituents from Eriocephalus species. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Meyer, J.; Jimeno, M.; Rodríguez, B. Bioactive Diterpenes from Orthosiphon labiatus and Salvia africana-lutea. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdillahi, H.; Finnie, J.; Van Staden, J. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase and phenolic contents of four Podocarpus species used in traditional medicine in South Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addo, E.; Chai, H.; Hymete, A.; Yeshak, M.; Slebodnick, C.; Kingston, D.; Rakotondraibe, L. Antiproliferative constituents of the roots of Ethiopian Podocarpus falcatus and structure revision of 2α-hydroxynagilactone F and nagilactone I. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijman, P.; Joubert, E.; Ferreira, D.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Green, I.; Gelderblom, W. Antioxidant activity of the dihydrochalcones aspalathin and nothofagin and their corresponding flavones in relation to other rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) flavonoids, epigallocatechin gallate, and trolox. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6678–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyn, P.; van Heerden, F.; Vleggaart, R. Toxic constituents of the Asclepiadaceae. Structure elucidation of the cynafosides, toxic pregnane glycosides of Cynanchum africanum R. Br. S. Afr. J. Chem. 1989, 42, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zdero, C.; Bohlmann, F. Glycerol derivatives and other constituents from Metalasia species. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 2179–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Poobrasert, O.; Kennelly, E.; Chin, C.; Ho, C.; Huang, M.; Garrison, S.A.; Cordell, G.A. Cytotoxic activity of steroidal saponins from Asparagus officinalis. Acta Hortic. 1999, 479, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, H.; Seong, J.; Oh, S.; Lee, C.; Bang, J.; Seong, N.; Song, K. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from the rhizomes of Asparagus oligoclonos. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, T.; Bastow, K.; Shibano, M.; Lee, K.; Chen, D. Filiasparosides A−D, cytotoxic steroidal saponins from the roots of Asparagus filicinus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Some samples of the AuNPs are available from the authors.










| Plant name | 25 °C | 70 °C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC (mg/mL) | λmax (nm) | PD (nm) | Pdi | ZP (mV) | OC (mg/mL) | λmax (nm) | PD (nm) | Pdi | ZP (mV) | |
| 1 Aspalathus hispida | * | * | * | * | * | 0.5 | 534 | 34 | 0.564 | −13 |
| 2 Aspalathus linearis | 0.5 | 536 | 99 | 0.343 | −23 | 0.5 | 536 | 61 | 0.315 | −20 |
| 3 Asparagus rubicundus | * | * | * | * | * | 1 | 538 | 28 | 0.66 | −22 |
| 4 Cynanchum africanum | 2 | 558 | 110 | 0.396 | −14 | 0.5 | 546 | 99 | 0.407 | −21 |
| 5 Dicerothamnus rhinocertis | * | * | * | * | * | 0.5 | 534 | 63 | 0.551 | −41 |
| 6 Eriocephalus africanus | 1 | 554 | 67 | 0.565 | −23 | 0.5 | 542 | 102 | 0.326 | −23 |
| 7 Hermannia alnifolia | 1 | 536 | 78 | 0.398 | −21 | 0.5 | 536 | 66 | 0.42 | −27 |
| 8 Indigofera brachystachya | 1 | 548 | 87 | 0.371 | −16 | 1 | 534 | 100 | 0.477 | −41 |
| 9 Lobostemon glaber | 0.5 | 552 | 218 | 0.76 | −23 | 0.5 | 540 | 136 | 0.217 | −26 |
| 10 Metalasia muricata | 1 | 546 | 65 | 0.469 | −16 | 0.25 | 544 | 61 | 0.352 | −14 |
| 11 Nidorella foetida | 0.5 | 564 | 124 | 0.231 | −24 | 0.5 | 548 | 97 | 0.243 | −28 |
| 12 Otholobium bracteolatum | 4 | 546 | 47 | 0.525 | −20 | 1 | 542 | 53 | 0.423 | −25 |
| 13 Podocarpus falcatus | 1 | 538 | 141 | 0.6 | −15 | 0.5 | 540 | 102 | 0.577 | −15 |
| 14 Podocarpus latifolius | 2 | 540 | 76 | 0.46 | −16 | 1 | 540 | 54 | 0.513 | −18 |
| 15 Salvia africana-lutea | 1 | 534 | 148 | 0.466 | −25 | 0.5 | 534 | 69 | 0.202 | −23 |
| 16 Searsia dissecta | 0.5 | 538 | 62 | 0.405 | −12 | 0.5 | 538 | 68 | 0.299 | −14 |
| 17 Senecio pubigerus | 1 | 538 | 75 | 0.519 | −18 | 0.5 | 536 | 49 | 0.469 | −15 |
| 18 Camellia sinensis (Black tea) | 2 | 538 | 63 | 0.535 | −0.2 | 1 | 540 | 23 | 0.67 | −19 |
| 19 Camellia sinensis (Green tea) | 1 | 535 | 104 | 0.61 | −12 | 1 | 534 | 47 | 0.376 | −12 |
| 20 EGCG | 0.125 | 532 | 45 | 0.324 | −26 | 0.125 | 534 | 52 | 0.311 | −22 |
| Nanoparticles Characteristics | 25 °C | 70 °C |
|---|---|---|
| λmax (nm) | 543 ± 9 | 539 ± 4 |
| particle diameter (nm) | 97 ± 44 | 68 ± 29 |
| Pdi | 0.465 ± 0.127 | 0.419 ± 0.14 |
| Plant Name | Family Name | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| Aspalathus hispida | Fabaceae | 1463158/NBG |
| Asparagus rubicundus | Asparagaceae | 1463146/NBG |
| Cynanchum africanum | Apocynaceae | 1463157/NBG |
| Dicerothamnus rhinocertis | Asteraceae | 1463148/NBG |
| Eriocephalus africanus | Asteraceae | 1463147/NBG |
| Hermannia alnifolia | Malvaceae | 1463145/NBG |
| Indigofera brachystachya | Fabaceae | 1463156/NBG |
| Lobostemon glaber | Boraginaceae | 1463149/NBG |
| Metalasia muricata | Asteraceae | 1463150/NBG |
| Nidorella foetida | Asteraceae | 1463153/NBG |
| Otholobium bracteolatum | Fabaceae | 1463155/NBG |
| Podocarpus falcatus | Podocarpaceae | * |
| Podocarpus latifolius | Podocarpaceae | * |
| Salvia africana-lutea | Lamiaceae | 1463154/NBG |
| Searsia dissecta | Anacardiaceae | 1463151/NBG |
| Senecio pubigerus | Asteraceae | 1463152/NBG |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbagory, A.M.; Cupido, C.N.; Meyer, M.; Hussein, A.A. Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method. Molecules 2016, 21, 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111498
Elbagory AM, Cupido CN, Meyer M, Hussein AA. Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method. Molecules. 2016; 21(11):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111498
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbagory, Abdulrahman M., Christopher N. Cupido, Mervin Meyer, and Ahmed A. Hussein. 2016. "Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method" Molecules 21, no. 11: 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111498
APA StyleElbagory, A. M., Cupido, C. N., Meyer, M., & Hussein, A. A. (2016). Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method. Molecules, 21(11), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111498