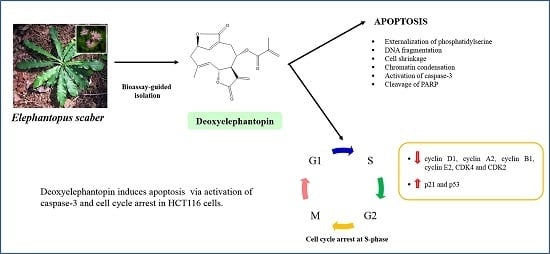
Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification of the Bioactive Compounds, Deoxyelephantopin and Isodeoxyelephantopin via a Bioassay-Guided Approach
2.2. DET and isoDET Inhibited the Proliferation of HCT116 Cells
2.3. Apoptotic Morphological Changes by DET
2.4. Externalization of Phosphatidylserine by DET
2.5. Modulatory Effects of DET on Apoptosis-Related Protein Expression
2.6. Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest by DET
2.7. Modulatory Effects of DET on Cell Cycle-Related Protein Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Isolation of Active Phytochemicals from the Ethyl Acetate Fraction of E. scaber via a Bioassay-Guided Approach
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cytotoxic Effect Determined by MTT Assay
4.5. Induction of Nuclear Morphological Changes by Hoechst 33342 and PI
4.6. Externalization of Phosphatidylserine Detected by Annexin V and PI Staining
4.7. Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DET | deoxyelephantopin |
| IsoDET | isodeoxyelephantopin |
References
- Kabeer, F.A.; Sreedevi, G.B.; Nair, M.S.; Rajalekshmi, D.S.; Gopalakrishnan, L.P.; Kunjuraman, S.; Prathapan, R. Antineoplastic effects of deoxyelephantopin, a sesquiterpene lactone from elephantopus scaber, on lung adenocarcinoma (A549) cells. J. Integr. Med. 2013, 11, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.Y.; Zhou, S.F.; Gao, S.H.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhang, S.F.; Tang, M.K.; Sun, J.N.; Ma, D.L.; Han, Y.F.; Fong, W.F.; et al. New perspectives on how to discover drugs from herbal medicines: Cam’s outstanding contribution to modern therapeutics. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 627375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, A.; Ghadiri, A.; Dessauge, F.; Duhamel, M.; Rebollo, M.P.; Alvarez-Franco, F.; Rebollo, A. Modulating apoptosis as a target for effective therapy. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Kadioglu, O.; Wiench, B.; Wei, Z.; Gao, C.; Luo, M.; Gu, C.; Zu, Y.; Efferth, T. Cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis by cajanin stilbene acid from cajanus cajan in breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, A.K.; Liu, H.; Suzui, M.; Vural, M.E.; Xiao, D.; Weinstein, I.B. Resveratrol induces growth inhibition, S-phase arrest, apoptosis, and changes in biomarker expression in several human cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camargo, M.S.; Oliveira, M.T.; Santoni, M.M.; Resende, F.A.; Oliveira-Hohne, A.P.; Espanha, L.G.; Nogueira, C.H.; Cuesta-Rubio, O.; Vilegas, W.; Varanda, E.A. Effects of nemorosone, isolated from the plant clusia rosea, on the cell cycle and gene expression in mcf-7 bus breast cancer cell lines. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas-Silva, M.D.; Weinberg, R.A. The restriction point and control of cell proliferation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougarede, R.; Della Seta, F.; Zarzov, P.; Schwob, E. Hierarchy of S-phase-promoting factors: Yeast Dbf4-Cdc7 kinase requires prior s-phase cyclin-dependent kinase activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3795–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, E.A. Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Dutta, A. p21 in cancer: Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartel, A.L.; Tyner, A.L. The role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammer, M.L.; Johns, E.A. Tapping an amazonian plethora: Four medicinal plants of marajo island, para (Brazil). J. Ethnopharmacol. 1993, 40, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; Yen, M.H. The evaluation of hepatoprotective effects of Taiwan folk medicine “Teng-Khia-U”. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 45, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, P.; Govindarajan, R. Cancer—An ayurvedic perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Wu, X.; Chung, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, W. Antiproliferative activities of five chinese medicinal herbs and active compounds in elephantopus scaber. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farha, A.K.; Dhanya, S.R.; Mangalam, S.N.; Remani, P. Anti-metastatic effect of deoxyelephantopin from elephantopus scaber in A549 lung cancer cells in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Lo, C.P.; Chiu, C.Y.; Shyur, L.F. Deoxyelephantopin, a novel multifunctional agent, suppresses mammary tumour growth and lung metastasis and doubles survival time in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farha, A.K.; Dhanya, S.R.; Mangalam, S.N.; Geetha, B.S.; Latha, P.G.; Remani, P. Deoxyelephantopin impairs growth of cervical carcinoma siha cells and induces apoptosis by targeting multiple molecular signaling pathways. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2014, 30, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, B.S.; Nair, M.S.; Latha, P.G.; Remani, P. Sesquiterpene lactones isolated from elephantopus scaber l. Inhibits human lymphocyte proliferation and the growth of tumour cell lines and induces apoptosis in vitro. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 721285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabeer, F.A.; Sreedevi, G.B.; Nair, M.S.; Rajalekshmi, D.S.; Gopalakrishnan, L.P.; Prathapan, R. Isodeoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber (Didancao) induces cell cycle arrest and caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in breast carcinoma T47D cells and lung carcinoma A549 cells. Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, H.; Nair, M.S.; Takada, Y.; Sheeja, D.B.; Kumar, M.A.; Oommen, O.V.; Aggarwal, B.B. Isodeoxyelephantopin, a novel sesquiterpene lactone, potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis through suppression of nuclear factor-κb (NF-κb) activation and NF-κb-regulated gene expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5910–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Supriady, H.; Goh, B.H.; Kadir, H.A. Elephantopus scaber induces apoptosis through ROS-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway in HCT116 human colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- But, P.P.; Hon, P.; Cao, H.; Chan, T.W.D.; Wu, B.; Mak, T.C.W.; Che, C. Sesquiterpene lactones from elephantopus scaber. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Thana, N.N.; Fotso, S.; Sevvana, M.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Fiebig, H.H.; Kelter, G.; Laatsch, H. Sesquiterpene lactones from elephantopus scaber. Z. Naturforsch. 2005, 60b, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, M.H.; Gil da Costa, R.M.; Lopes, C.; Bastos, M.M. Sesquiterpene lactones: Adverse health effects and toxicity mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, K.T. Costunolide-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells: Involvement of c-jun N-terminal kinase activation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Markaki, M.; Palikaras, K.; Tavernarakis, N. Crosstalk between apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3448–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermes, I.; Haanen, C.; Steffens-Nakken, H.; Reutelingsperger, C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled annexin v. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 184, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Cleavage of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase measured in situ in individual cells: Relationship to DNA fragmentation and cell cycle position during apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 255, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrik, I.N.; Golks, A.; Krammer, P.H. Caspases: Pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrego, D.; Tomczak, A.P.; Zahed, F.; Stuhmer, W.; Pardo, L.A. Potassium channels in cell cycle and cell proliferation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Xue, Z.; Lu, Y.; Narsinh, K.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Bu, Q.; Wang, F.; Liang, J.; et al. Molecular imaging of p53 signal pathway in lung cancer cell cycle arrest induced by cisplatin. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Chung, H.Y.; Li, Y. Deoxyelephantopin from elephantopus scaber l. Induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in the human nasopharyngeal cancer cne cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieging, K.T.; Mello, S.S.; Attardi, L.D. Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roninson, I.B. Tumor cell senescence in cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dotto, G.P. p21(WAF1/Cip1): More than a break to the cell cycle? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1471, M43–M56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Yu, J.H.; Wu, J.N.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; Minami, M.; Ikejima, T. p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through a caspase-3-independent, but caspase-9-dependent pathway in oridonin-treated MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottifredi, V.; McKinney, K.; Poyurovsky, M.V.; Prives, C. Decreased p21 levels are required for efficient restart of DNA synthesis after s phase block. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5802–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Choi, K.M.; Kim, W.; Jeon, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Hong, J.T.; Yun, Y.P.; Yoo, H.S. Hinokitiol inhibits cell growth through induction of S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and suppresses tumor growth in a mouse xenograft experiment. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of deoxyelephanotpin and isodeoxyelephantopiin are available from the authors.







| Position | δH, J (Hz) isoDET (But et al., [24]) | δH, J (Hz) Compound 1 | δC isoDET (But et al., [24]) | δC Compound 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.16, s | 7.14, s | 150.0 | 149.4 |
| 2 | 5.38, d (4.5) | 5.37, d (4.5) | 79.4 | 79.6 |
| 3a | 2.39, dd (4.5, 14.0) | 2.39, dd (4.5, 14.6) | 40.0 | 40.2 |
| 3b | 2.94, d (14.0) | 2.93, d (14.6) | ||
| 4 | 135.4 | 135.5 | ||
| 5 | 5.13, d (10.0) | 5.13, d (10.1) | 125.2 | 125.5 |
| 6 | 5.17, d (10.0) | 5.17, d (10.1) | 78.7 | 78.8 |
| 7 | 3.15, m | 3.15, m | 49.8 | 50.0 |
| 8 | 4.53, ddd (4.0, 4.0, 12.0) | 4.52, ddd (4.0, 4.0, 12.4) | 74.0 | 74.1 |
| 9a | 2.74, dd (4.0, 12.0) | 2.74, dd (4.0, 12.4) | 30.0 | 30.2 |
| 9b | 3.06, dd (12.0, 12.0) | 3.04, dd (12.0, 12.4) | ||
| 10 | 131.4 | 131.6 | ||
| 11 | 134.0 | 134.1 | ||
| 12 | 169.4 | 169.6 | ||
| 13a | 5.65, d (3.2) | 5.64, d (3.6) | 123.0 | 123.3 |
| 13b | 6.20, d (4.0) | 6.20, d (4.1) | ||
| 14 | 1.78, s | 1.78, s | 21.5 | 21.7 |
| 15 | 174.3 | 174.4 | ||
| 16 | 166.5 | 166.7 | ||
| 17 | 135.4 | 135.5 | ||
| 18 | 1.93, s | 1.93, s | 18.1 | 18.3 |
| 19a | 5.67, s | 5.67, s | 126.8 | 127.0 |
| 19b | 6.15, s | 6.14, s |
| Position | δH, J (Hz) DET (Than et al., [25]) | δH, J (Hz) Compound 2 | δC DET (Than et al., [25]) | δC Compound 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.08, br s | 7.06, br s | 153.5 | 153.3 |
| 2 | 5.46, td (1.8, 3.9) | 5.46, td (1.8, 4.1) | 81.4 | 81.4 |
| 3a | 2.69, ddd (1.2, 2.1, 13.4) | 2.70, ddd (1.2, 2.1, 13.4) | 41.2 | 41.5 |
| 3b | 2.85, dd (4.5, 13.8) | 2.86, dd (4.6, 13.8) | ||
| 4 | 135.5 | 135.7 | ||
| 5 | 4.77, br d (10.5) | 4.78, br d (10.5) | 133.6 | 133.9 |
| 6 | 5.13, dd (8.1, 10.5) | 5.14, dd (8.2, 10.5) | 78.0 | 78.0 |
| 7 | 2.94, dt (3.6, 7.5) | 2.94, dt (3.6, 7.7) | 52.2 | 52.5 |
| 8 | 4.65, ddd (2.1, 3.6, 11.4) | 4.65, ddd (1.8, 3.6, 11.6) | 71.5 | 71.6 |
| 9a | 2.78, d (12.3) | 2.79, d (12.4) | 33.4 | 33.7 |
| 9b | 3.02, ddd (1.7, 3.0, 12.6) | 3.01, ddd (1.7, 3.0, 12.5) | ||
| 10 | 128.3 | 128.7 | ||
| 11 | 134.0 | 134.1 | ||
| 12 | 169.3 | 169.4 | ||
| 13a | 5.65, br d (3.3) | 5.65, br d (3.2) | 123.6 | 123.8 |
| 13b | 6.23, br d (3.9) | 6.23, br d (3.6) | ||
| 14 | 1.85, d (1.5) | 1.84, d (1.4) | 20.0 | 20.2 |
| 15 | 172.5 | 172.5 | ||
| 16 | 166.4 | 166.5 | ||
| 17 | 135.9 | 136.1 | ||
| 18 | 1.93, dd (1.2, 1.4) | 1.93, s | 18.2 | 18.3 |
| 19a | 5.66, d (1.5) | 5.66, d (1.8) | 126.6 | 126.8 |
| 19b | 6.14, t (1.2) | 6.14, t (1.2) |
| Cell Lines | IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Deoxyelephantopin | Isodeoxyelephantopin | 5-Fluorouracil a | |
| HCT116 | 0.73 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 0.73 ± 0.02 |
| CCD841-CoN | 21.69 ± 0.92 | NA | >25 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, C.K.; Chan, G.; Awang, K.; Abdul Kadir, H. Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Molecules 2016, 21, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030385
Chan CK, Chan G, Awang K, Abdul Kadir H. Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030385
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Chim Kei, Gomathi Chan, Khalijah Awang, and Habsah Abdul Kadir. 2016. "Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest" Molecules 21, no. 3: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030385
APA StyleChan, C. K., Chan, G., Awang, K., & Abdul Kadir, H. (2016). Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Molecules, 21(3), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030385