Finding and Producing Probiotic Glycosylases for the Biocatalysis of Ginsenosides: A Mini Review
Abstract
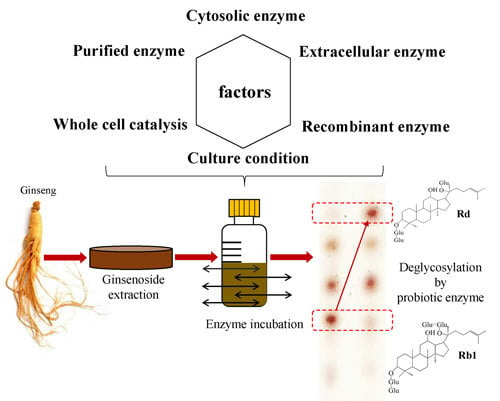
:1. Ginsenosides
2. Biocatalytic Process of Ginsenosides Using Probiotic Enzymes
3. Commercial Application
4. Recombinant Glycosylase Expression in Escherichia coli
5. Recombinant Glycosylase Expression in Probiotic Bacteria
6. Classical Probiotic Enzyme Preparation
7. The Use of Modified MRS for Enzyme Production
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, L.; Zhao, Y. Current Evaluation of the Millennium Phytomedicine-Ginseng (I): Etymology, Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Market and Regulations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Sasa, H.; Kita, T.; Hirata, J.; Tode, T.; Nagata, I. Inhibition of Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation in Vitro by Ginsenoside Rh2 and Adjuvant Effects to Cisplatin in Vivo. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1991, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Amemura, A.; Harada, T. Purification And Properties of a β-1,6-Glucosidase from Flavobacterium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 377, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hahm, D.H.; Yang, D.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Shim, I. Effect of Crude Saponin of Korean Red Ginseng on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in the Rat. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 97, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avakian, E.; Sugimoto, R.; Taguchi, S.; Horvath, S. Effect of Panax ginseng Extract on Energy Metabolism during Exercise in Rats. Planta Med. 1984, 50, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.U.; Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Hepatoprotective Effect of Ginsenoside Rb1 and Compound K on Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Liver Injury. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Mcdaniel, W.F. Ginseng Improves Strategic Learning by Normal and Brain-Damaged Rats. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Yamabe, N.; Yokozawa, T. Stereospecificity in Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activities of Four Ginsenosides Produced by Heat Processing. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5028–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.D.; Rhee, D.K.; Lee, Y.H. Biological Activities and Chemistry of Saponins from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Phytochem. Rev. 2005, 4, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Chen, F.; Li, C. Absorption, Disposition, and Pharmacokinetics of Saponins from Chinese Medicinal Herbs: What Do We Know and What Do We Need to Know More? Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Hu, Q.; Chen, X.; Jia, X. A Novel Drug-Phospholipid Complex Enriched with Micelles: Preparation and Evaluation in Vitro and in Vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Garle, M.; Lund, E.; Bjorkhem, I.; Eneroth, P. Analysis of Ginsenosides by Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry: Release of 20 S-Protopanaxadiol and 20 S-Protopanaxatriol for Quantitation. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 210, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.A.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.H. Constitutive β-Glucosidases Hydrolyzing Ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 from Human Intestinal Bacteria. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H. Proof of the Mysterious Efficacy of Ginseng: Basic and Clinical Trials: Metabolic Activation of Ginsenoside: Deglycosylation by Intestinal Bacteria and Esterification with Fatty Acid. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Du, F.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Niu, W.; Wang, F.; Mao, Y.; et al. Absorption and Disposition of Ginsenosides after Oral Administration of Panax Notoginseng Extract to Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Yoo, H.H.; Gu, W.; Yu, D.H.; Jin, M.J.; Choi, H.L.; Yuan, K.; Guerin-Deremaux, L.; Kim, D.H. Effect Of a Soluble Prebiotic Fiber, NUTRIOSE, on the Absorption of Ginsenoside Rd in Rats Orally Administered Ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of Ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by Food Microorganisms. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Lee, B.H.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Differential transformation of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng by lactic acid bacteria. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 16, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, S.; Ogawa, J.; Kataoka, M.; Kobayashi, M. Screening of Novel Microbial Enzymes for the Production of Biologically and Chemically Useful Compounds. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 1997, 58, 45–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, Y.; Jung, E.Y.; Suh, H.J. Enzymatic Transformation of Ginsenosides in Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) Extract Prepared by Spezyme and Optidex. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musende, A.G.; Eberding, A.; Wood, C.A.; Adomat, H.; Fazli, L.; Hurtado-Coll, A.; Jia, W.; Bally, M.B.; Guns, E.S.T. A Novel Oral Dosage Formulation of the Ginsenoside Aglycone Protopanaxadiol Exhibits Therapeutic Activity against a Hormone-Insensitive Model of Prostate Cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2012, 23, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Effects of Ascorbic Acid on α-l-Arabinofuranosidase and α-l-Arabinopyranosidase Activities from Bifidobacterium Longum RD47 and Its Application to Whole Cell Bioconversion of Ginsenoside. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Nose, M.; Ogihara, Y. Alkaline Cleavage of Ginsenosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinovskaya, G.V.; Vorob’ev, O.Y.; Makhan’kov, V.V.; Denisenko, V.A.; Uvarova, N.I.; Elyakov, G.B. Glycosides of the Epigeal Part of Panax ginseng. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1992, 28, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.H.; Park, M.H.; Han, Y.N.; Woo, L.K.; Sankawa, U.; Yahara, S.; Tanaka, O. Degradation of Ginseng Saponins under Mild Acidic Conditions. Planta Med. 1982, 44, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, K.; Liu, Q.; Wan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, R.-Z.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, P.; Qi, L. Rapid Preparation of Rare Ginsenosides by Acid Transformation and Their Structure-Activity Relationships against Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, J.M.; Wang, Z.G.; Peng, W.; Hu, H.L.; Fu, C.M. Biotransformation, a Promising Technology for Anti-Cancer Drug Development. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5599–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanapat, M.; Kang, S.; Polyorach, S. Development of Feeding Systems and Strategies of Supplementation to Enhance Rumen Fermentation and Ruminant Production in the Tropics. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Jung, I.; Park, S.; Ahn, Y; Huh, C.; Kim, D. Comparative Analysis of the Gut Microbiota in People with Different Levels of Ginsenoside Rb1 Degradation to Compound K. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, T.; Teng, Y.; Wu, B.; You, M.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, M. Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability of 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 through Improved Understanding of Its Absorption and Efflux Mechanisms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Microorganisms & Microbial-Derived Ingredients Used in Food (Partial List). Available online: http://www.fda.gov/food/ingredientspackaginglabeling/gras/microorganismsmicrobialderivedingredients/default.htm (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/dockets/95s0316/95s-0316-rpt0282-tab-03-ref-19-joint-faowho-vol219.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Heyman, M.; Ménard, S. Probiotic Microorganisms: How They Affect Intestinal Pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Increasing Health Awareness Expected to Result in Probiotics Market Size Worth USD 52.34 Billion by 2020: Grand View Research, Inc. Available online: http://finance.yahoo.com/news/increasing-health-awareness-expected-result-103000587.html (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Leonardi, A.; Raimondi, S.; Simone, M.; Quartieri, A. Potential Impact of Probiotic Consumption on the Bioactivity of Dietary Phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9551–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeg, I.H.; So, S.H. The World Ginseng Market and the Ginseng (Korea). J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant Protein Expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotoarivonina, H.; Hermant, B.; Monthe, N.; Rémond, C. The Hemicellulolytic Enzyme Arsenal of Thermobacillus Xylanilyticus Depends on the Composition of Biomass Used for Growth. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Na, J.; Kim, M.K.; Bang, M.; Yang, D. Microbial Conversion of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside F2 and Gypenoside XVII by Intrasporangium sp. GS603 Isolated from Soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Skretas, G.; Georgiou, G. Strain Engineering for Improved Expression of Recombinant Proteins in Bacteria. Microb. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeshen, N.A.; Baeshen, M.N.; Sheikh, A.; Bora, R.S.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Ramadan, H.A.I.; Saini, K.S.; Redwan, E.M. Cell Factories for Insulin Production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.H.; Min, J.W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Enzymatic Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Compound K by Recombinant β-Glucosidase from Microbacterium Esteraromaticum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3776–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Cui, C.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jin, F.X.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Enzymatic Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 and Gypenoside XVII into Ginsenosides Rd and F2 by Recombinant β-Glucosidase from Flavobacterium Johnsoniae. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.H.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Characterization of the Ginsenoside-Transforming Recombinant β-Glucosidase from Actinosynnema Mirum and Bioconversion of Major Ginsenosides into Minor Ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 97, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Characterization of a Ginsenoside-Transforming β-Glucosidase from Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus and Its Application for Enhanced Production of Minor Ginsenoside F2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Hyun, Y.J.; Kim, D.H. Cloning And Characterization of α-l-Arabinofuranosidase and Bifunctional α-l-Arabinopyranosidase/β-d-Galactopyranosidase from Bifidobacterium Longum H-1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.J. Cloning And Characterization of Ginsenoside Ra1-Hydrolyzing β-d-Xylosidase from Bifidobacterium Breve K-110. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaevska, M.; Hruska, K. Mycobacteria in Water, Feedstocks and Food: Analysis of Publications. Vet. Med. 2010, 12, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Mosayebi, Z.; Movahedian, A.; Soori, T. Flavobacterium Sepsis Outbreak Due to Contaminated Distilled Water in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Verma, R.K.; Saraf, S.A. Nutraceuticals: New era of medicine and health. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2010, 3, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kaswurm, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Maischberger, T.; Kulbe, K.D.; Michimayr, H. Evaluation of the food grade expression systems NICE and pSIP for the production of 2,5-diketo-d-gluconic acid reductase from Corynebacterium glutamicum. AMB Express 2013, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterbauer, C.; Maischberger, T.; Haltrich, D. Food-grade gene expression in lactic acid bacteria. Biotechnol. J. 2011, 6, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.Y. Identification of the β-Glucosidase Gene from Bifidobacterium Animalis Subsp. Lactis and Its Expression in B. Bifidum BGN4. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Moon, J.S.; Im, W.T.; Han, N.S. Production of Ginsenoside F2 by Using Lactococcus Lactis with Enhanced Expression of β-Glucosidase Gene from Paenibacillus Mucilaginosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, L.J.; Harvey, S.M.; Tiersky, L.A. Attitudes about Condoms and Condom Use among College Students. J. Am. Coll. Health 1996, 44, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.B. Consumer Attitude of Risk and Benefits toward Genetically Modified (GM) Foods in South Korea: Implications for Food Policy. Eng. Econ. 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Safety and Sustainability Center. Available online: http://www.greenerchoices.org/pdf/cr_fsasc_gmo_final_report_10062014.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Restrictions on Genetically Modified Organisms: European Union. Available online: http://www.loc.gov/law/help/restrictions-on-gmos/eu.php#Opinion (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Chi, H.; Kim, D.H.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of Ginsenosides Rb2 and Rc from Panax ginseng by Food Microorganisms. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.H.; Cheng, L.Q.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Son, N.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Jin, H.O.; Yang, D.C. Bioconversion of Ginsenoside Rd into Compound K by Lactobacillus pentosus DC101 Isolated from Kimchi. J. Ginseng Res. 2010, 34, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.H.; Piao, J.Y.; Min, J.W.; Yang, D.U.; Lee, H.N.; Yang, D.C. Bioconversion of Ginsenoside Rb1 into Compound K by Leuconostoc Citreum LH1 Isolated from Kimchi. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Li, G.H.; Choi, K.T.; Yang, D.C. Microbial Transformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Compound K by Lactobacillus Paralimentarius. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüürmann, J.; Quehl, P.; Festel, G.; Jose, J. Bacterial Whole-Cell Biocatalysts by Surface Display of Enzymes: Toward Industrial Application. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8031–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, C.C. Enzymatic and Whole Cell Catalysis: Finding New Strategies for Old Processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Youn, S.Y.; Ji, G.E.; Park, M.S. Whole Cell Biotransformation of Major Ginsenosides Using Leuconostocs and Lactobacilli. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.; Zheng, H.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Optimization of β-Glucuronidase Activity from Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Rh2 and Its Use for Biotransformation of Baicalin and Wogonoside. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Whole-Cell Biocatalysis for Producing Ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, B.M.; Stanton, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P. Survival of Probiotic Lactobacilli in Acidic Environments Is Enhanced in the Presence of Metabolizable Sugars. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3060–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Ji, G.E. Enhancement of Anti-Tumorigenic Polysaccharide Production, Adhesion, and Branch Formation of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 by Phytic acid. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 749–754. [Google Scholar]
- National Yogurt Association, Live and Active Culture Yogurt Seal Program. Available online: http://aboutyogurt.com/AboutYogurt08/files/ccLibraryFiles/Filename/000000000046/12%2013%2013_LAC%20Seal%20Guidelines%20with%20Appendices.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Veen, P.V.D.; Arst, H.N.; Flipphi, M.J.A.; Visser, J. Extracellular Arabinases in Aspergillus Nidulans: The Effect of Different Cre Mutations on Enzyme Levels. Arch. Microbiol. 1994, 162, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueimonde, M.; Noriega, L.; Margolles, A.; Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.D.L. Induction of α-l-Arabinofuranosidase Activity by Monomeric Carbohydrates in Bifidobacterium Longum and Ubiquity of Encoding Genes. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 187, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, S.; Modi, H.A. Optimization of Fermentation Medium for the Production of Glucose Isomerase Using Streptomyces sp. SB-P1. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, S.; Demain, A.L. Metabolic Regulation and Overproduction of Primary Metabolites. Microbial. Biotechnol. 2008, 1, 283–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.R.; Youn, S.Y.; Ji, G.E.; Park, M.S. Production of α- and β-galactosidases from Bifidobacterium Longum Subsp. Longum RD47 J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ginsenosides | Chemical Names |
|---|---|
| Rb1 | 3-O-[b-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20-O-[b-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Rb2 | 3-O-[b-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20-O-[a-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Rc | 3-O-[b-d-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20-O-[a-l-arabinofuranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Rd | 3-O-[b-d-Glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Re | 6-O-[a-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxatriol |
| Rg1 | 6-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxatriol |
| Rg2 | 6-O-[a-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-2)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxatriol |
| Rh1 | 6-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxatriol |
| Rh2 | 3-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| F1 | 20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxatriol |
| F2 | 3-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Compound K | 20-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Compound O | 3-O-b-d-glucopyranosyl-20-O-[a-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Compound Y | 20-O-[a-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
| Mc | 20-O-[a-l-arabinofuranosyl-(1-6)-b-d-glucopyranosyl]-20(S)-protopanaxadiol |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ku, S. Finding and Producing Probiotic Glycosylases for the Biocatalysis of Ginsenosides: A Mini Review. Molecules 2016, 21, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050645
Ku S. Finding and Producing Probiotic Glycosylases for the Biocatalysis of Ginsenosides: A Mini Review. Molecules. 2016; 21(5):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKu, Seockmo. 2016. "Finding and Producing Probiotic Glycosylases for the Biocatalysis of Ginsenosides: A Mini Review" Molecules 21, no. 5: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050645
APA StyleKu, S. (2016). Finding and Producing Probiotic Glycosylases for the Biocatalysis of Ginsenosides: A Mini Review. Molecules, 21(5), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050645