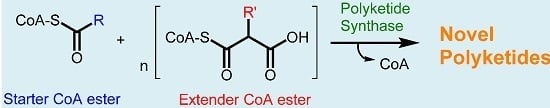
Exploiting the Biosynthetic Potential of Type III Polyketide Synthases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Insights into Type III PKSs
2.1. Chalcone Synthases and the Basis of Polyketide Synthesis
2.2. Stilbene Synthases and the Functional Divergence of Type III PKSs
2.3. Truncation Products and Chain Length Specificity
2.4. Other Members of Type III PKS from Plants
2.4.1. p-Coumaroyl Triacetic Acid Synthase and Stilbenecarboxylate Synthase
2.4.2. Bibenzyl Synthase
2.4.3. Benzalacetone Synthase
2.4.4. Type III Polyketide Synthases from Curcuma longa
2.4.5. Benzophenone Synthase and Biphenyl Synthase
2.4.6. Acridone Synthase and Quinolone Synthase
2.4.7. Phloroglucinol Synthase, Alkylresorcinol Synthase, and Alkylpyrone Synthase
2.5. Bacterial Type III PKSs
2.5.1. 1,3,6,8-Tetrahydroxynaphthalene Synthase (THNS)
2.5.2. Phloroglucinol Synthase from Pseudomonas fluorescens
2.5.3. 3,5-Dihydroxyphenylacetic Acid Synthase
2.5.4. Biosynthesis of Alkylpyrones by PKS11 and PKS18
2.5.5. Pyrone Synthases from S. coelicolor
2.5.6. Other Bacterial Type III PKSs
2.6. Fungal Type III PKSs
3. Precursor-Directed Biosynthesis of Polyketides
4. Insights into Mutagenesis Studies
4.1. Dissection of Catalytic and Structural Roles of Residues via Mutagenesis
4.2. Structure-Based Engineering and the Versatility of Type III PKSs
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACP | Acyl carrier protein |
| ACS | Acridone synthase |
| ALS | Aloesone synthase |
| AnPKS | Aspergillus niger polyketide synthase |
| ARAS2 | Alkyl-resorcylic acid synthase 2 |
| BAS | Benzalacetone synthase |
| BBS | Bibenzyl synthase |
| BIS | Biphenyl synthase |
| BPS | Benzophenone synthase |
| CHS | Chalcone synthase |
| CoA | Coenzyme A |
| CsyA | Chalcone synthase-like A |
| CTAL | Coumaroyl triacetic acid lactone |
| CTAS | p-coumaroyl triacetic acid synthase |
| CURS | Curcumin synthase |
| CUS | Curcuminoid synthase |
| DCS | Diketide-CoA synthase |
| DpgA | 3,5-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid synthase |
| GCS | Germicidin synthase |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteamine |
| OKS | Octaketide synthase |
| ORAS | 2′-oxoalkylresorcylic acid synthase |
| PCS | Pentaketide chromone synthase |
| PhlD | Phloroglucinol synthase |
| PKS | Polyketide synthase |
| PpASCL | Physcomitrella patens anther-specific chalcone synthase-like enzyme |
| 2-PS | 2-pyrone synthase |
| QNS | Quinolone synthase |
| STCS | Stilbenecarboxylate synthase |
| STS | Stilbene synthase |
| THNS | 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene synthase |
References
- Collie, J.N. Derivatives of the multiple keten group. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunton, J.; Weissman, K.J. Polyketide biosynthesis: A millennium review. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 380–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calne, R.Y.; Collier, D.S.; Lim, S.; Pollard, S.G.; Samaan, A.; White, D.J.; Thiru, S. Rapamycin for immunosuppression in organ allografting. Lancet 1989, 2, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, A.W.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, J.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E.; et al. Mevinolin—A highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.F.; Hopwood, D.A. Actinorhodin is a chromosomally-determined antibiotic in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Gen. Microbiol. 1976, 96, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtkooper, R.H.; Mouchiroud, L.; Ryu, D.; Moullan, N.; Katsyuba, E.; Knott, G.; Williams, R.W.; Auwerx, J. Mitonuclear protein imbalance as a conserved longevity mechanism. Nature 2013, 497, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsuta, K.; Hosokawa, S. Total syntheses of polyketide-derived bioactive natural products. Chem. Rec. 2006, 6, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, A.J.; Donovan, F.W. Studies in relation to biosynthesis. I. Some possible routes to derivatives of orcinol and phloroglucinol. Aust. J. Chem. 1953, 6, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.J.; Khosla, C. Engineering the acyltransferase substrate specificity of assembly line polyketide synthases. J. R. Soc. Interface R. Soc. 2013, 10, 20130297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I. Novel applications of plant polyketide synthases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, M.; Race, P.R. Progress challenges and opportunities for the re-engineering of trans-at polyketide synthases. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B. Polyketide biosynthesis beyond the type I, II and III polyketide synthase paradigms. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.J. Polyketides, proteins and genes in fungi: Programmed nano-machines begin to reveal their secrets. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 2010–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C., Jr.; Vickery, C.R.; Burkart, M.D.; Noel, J.P. Confluence of structural and chemical biology: Plant polyketide synthases as biocatalysts for a bio-based future. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, N.; Ohnishi, Y.; Fujii, I.; Shibuya, M.; Ebizuka, Y.; Horinouchi, S. A new pathway for polyketide synthesis in microorganisms. Nature 1999, 400, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bangera, M.G.; Thomashow, L.S. Identification and characterization of a gene cluster for synthesis of the polyketide antibiotic 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol from Pseudomonas fluorescens Q2-87. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3155–3163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, V.; Nicholson, G.J.; Ries, J.; Recktenwald, J.; Schefer, A.B.; Shawky, R.M.; Schroder, J.; Wohlleben, W.; Pelzer, S. A polyketide synthase in glycopeptide biosynthesis: The biosynthesis of the non-proteinogenic amino acid (S)-3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38370–38377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshime, Y.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Fujii, I.; Kitamoto, K. Discovery of a novel superfamily of type III polyketide synthases in Aspergillus oryzae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, N.; Awakawa, T.; Horinouchi, S. Pentaketide resorcylic acid synthesis by type III polyketide synthase from Neurospora crassa. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14476–14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Zhao, H. Cloning and characterization of a type III polyketide synthase from Aspergillus niger. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6085–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuz, R.; Heller, W.; Hahlbrock, K. Substrate specificity of chalcone synthase from petroselinum hortense. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 6730–6734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, J.L.; Jez, J.M.; Bowman, M.E.; Dixon, R.A.; Noel, J.P. Structure of chalcone synthase and the molecular basis of plant polyketide biosynthesis. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Austin, M.B.; Noel, J.P. The chalcone synthase superfamily of type III polyketide synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2003, 20, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jez, J.M.; Ferrer, J.L.; Bowman, M.E.; Dixon, R.A.; Noel, J.P. Dissection of malonyl-coenzyme a decarboxylation from polyketide formation in the reaction mechanism of a plant polyketide synthase. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, M.B.; Bowman, M.E.; Ferrer, J.L.; Schroder, J.; Noel, J.P. An aldol switch discovered in stilbene synthases mediates cyclization specificity of type III polyketide synthases. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Morita, H. Structure and function of the chalcone synthase superfamily of plant type III polyketide synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 809–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, M.K.; Wongsantichon, J.; Cheung, V.W.N.; Chow, J.Y.; Robinson, R.C.; Yew, W.S. Synthetic polyketide enzymology: Platform for biosynthesis of antimicrobial polyketides. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4033–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropf, S.; Lanz, T.; Rensing, S.A.; Schroder, J.; Schroder, G. Evidence that stilbene synthases have developed from chalcone synthases several times in the course of evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1994, 38, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, F.; Suh, D.Y.; Sankawa, U.; Nishioka, M.; Akiyama, T.; Shibuya, M.; Ebizuka, Y. Cross-reaction of chalcone synthase and stilbene synthase overexpressed in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1999, 460, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomura, Y.; Torayama, I.; Suh, D.Y.; Xiang, T.; Kita, A.; Sankawa, U.; Miki, K. Crystal structure of stilbene synthase from Arachis hypogaea. Proteins 2005, 60, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.M.; Carney, R.L. Biogenetically modeled synthesis of β-resorcylic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 2053–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helariutta, Y.; Elomaa, P.; Kotilainen, M.; Griesbach, R.J.; Schroder, J.; Teeri, T.H. Chalcone synthase-like genes active during corolla development are differentially expressed and encode enzymes with different catalytic properties in Gerbera hybrida (asteraceae). Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 28, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckermann, S.; Schroder, G.; Schmidt, J.; Strack, D.; Edrada, R.A.; Helariutta, Y.; Elomaa, P.; Kotilainen, M.; Kilpelainen, I.; Proksch, P.; et al. New pathway to polyketides in plants. Nature 1998, 396, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jez, J.M.; Austin, M.B.; Ferrer, J.L.; Bowman, M.E.; Schroder, J.; Noel, J.P. Structural control of polyketide formation in plant-specific polyketide synthases. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Utsumi, Y.; Oguro, S.; Noguchi, H. The first plant type III polyketide synthase that catalyzes formation of aromatic heptaketide. FEBS Lett. 2004, 562, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Watanabe, T.; Lou, W.; Noguchi, H. Active site residues governing substrate selectivity and polyketide chain length in aloesone synthase. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Kondo, S.; Oguro, S.; Noguchi, H.; Sugio, S.; Abe, I.; Kohno, T. Structural insight into chain-length control and product specificity of pentaketide chromone synthase from Aloe arborescens. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuuchi, Y.; Shi, S.-P.; Wanibuchi, K.; Kojima, A.; Morita, H.; Noguchi, H.; Abe, I. Novel type III polyketide synthases from Aloe arborescens. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Oguro, S.; Utsumi, Y.; Sano, Y.; Noguchi, H. Engineered biosynthesis of plant polyketides: Chain length control in an octaketide-producing plant type III polyketide synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12709–12716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, T.; Shibuya, M.; Liu, H.M.; Ebizuka, Y. P-coumaroyltriacetic acid synthase, a new homologue of chalcone synthase, from Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 263, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckermann, C.; Schroder, G.; Eckermann, S.; Strack, D.; Schmidt, J.; Schneider, B.; Schroder, J. Stilbenecarboxylate biosynthesis: A new function in the family of chalcone synthase-related proteins. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisig-Muller, R.; Gnau, P.; Kindl, H. The inducible 9,10-dihydrophenanthrene pathway: Characterization and expression of bibenzyl synthase and s-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 317, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Takahashi, H.; Morita, H.; Noguchi, H. Benzalacetone synthase. A novel polyketide synthase that plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of phenylbutanones in Rheum palmatum. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 3354–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Shimokawa, Y.; Tanio, M.; Kato, R.; Noguchi, H.; Sugio, S.; Kohno, T.; Abe, I. A structure-based mechanism for benzalacetone synthase from Rheum palmatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimokawa, Y.; Morita, H.; Abe, I. Structure-based engineering of benzalacetone synthase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5099–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Lu, P.; Cang, H.; Ma, L. Protein preparation, crystallization and preliminary x-ray analysis of Polygonum cuspidatum bifunctional chalcone synthase/benzalacetone synthase. Acta Crystallogr. Sec. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuyama, Y.; Kita, T.; Funa, N.; Horinouchi, S. Curcuminoid biosynthesis by two type III polyketide synthases in the herb curcuma longa. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11160–11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Wanibuchi, K.; Nii, H.; Kato, R.; Sugio, S.; Abe, I. Structural basis for the one-pot formation of the diarylheptanoid scaffold by curcuminoid synthase from oryza sativa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19778–19783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerhues, L.; Liu, B. Biosynthesis of biphenyls and benzophenones—evolution of benzoic acid-specific type III polyketide synthases in plants. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Falkenstein-Paul, H.; Schmidt, W.; Beerhues, L. Benzophenone synthase and chalcone synthase from Hypericum androsaemum cell cultures: Cdna cloning, functional expression, and site-directed mutagenesis of two polyketide synthases. Plant J. 2003, 34, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nualkaew, N.; Morita, H.; Shimokawa, Y.; Kinjo, K.; Kushiro, T.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Ebizuka, Y.; Abe, I. Benzophenone synthase from garcinia mangostana l. Pericarps. Phytochemistry 2012, 77, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerhues, L. Benzophenone synthase from cultured cells of Centaurium erythraea. FEBS Lett. 1996, 383, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Raeth, T.; Beuerle, T.; Beerhues, L. Biphenyl synthase, a novel type III polyketide synthase. Planta 2007, 225, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, A.; Maier, W.; Groger, D.; Deutzmann, R. Purification and properties of acridone synthase from cell suspension cultures of Ruta graveolens L. Z. Naturforsch. C 1994, 49, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Springob, K.; Lukacin, R.; Ernwein, C.; Groning, I.; Matern, U. Specifities of functionally expressed chalcone and acridone synthases from Ruta graveolens. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 6552–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resmi, M.S.; Verma, P.; Gokhale, R.S.; Soniya, E.V. Identification and characterization of a type III polyketide synthase involved in quinolone alkaloid biosynthesis from Aegle marmelos correa. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7271–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukacin, R.; Schreiner, S.; Matern, U. Transformation of acridone synthase to chalcone synthase. FEBS Lett. 2001, 508, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Shimokawa, Y.; Matsui, T.; Kinjo, K.; Kato, R.; Noguchi, H.; Sugio, S.; Morita, H.; Abe, I. Cloning and structure-function analyses of quinolone- and acridone-producing novel type III polyketide synthases from Citrus microcarpa. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28845–28858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslet-Cladiere, L.; Delage, L.; Leroux, C.J.; Goulitquer, S.; Leblanc, C.; Creis, E.; Gall, E.A.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Czjzek, M.; Potin, P. Structure/function analysis of a type III polyketide synthase in the brown alga ectocarpus siliculosus reveals a biochemical pathway in phlorotannin monomer biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3089–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanaga, A.; Horinouchi, S. Enzymatic synthesis of bis-5-alkylresorcinols by resorcinol-producing type III polyketide synthases. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Grienenberger, E.; Lallemand, B.; Colpitts, C.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Souza Cde, A.; Geoffroy, P.; Heintz, D.; Krahn, D.; Kaiser, M.; et al. LAP6/POLYKETIDE SYNTHASE A and LAP5/POLYKETIDE SYNTHASE B encode hydroxyalkyl α-pyrone synthases required for pollen development and sporopollenin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 4045–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Kim, S.S.; Posehn, S.E.; Jepson, C.; Kim, S.Y.; Wiedemann, G.; Reski, R.; Wee, A.G.; Douglas, C.J.; Suh, D.Y. Ppascl, a moss ortholog of anther-specific chalcone synthase-like enzymes, is a hydroxyalkylpyrone synthase involved in an evolutionarily conserved sporopollenin biosynthesis pathway. New Phytol. 2011, 192, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, N.; Ohnishi, Y.; Ebizuka, Y.; Horinouchi, S. Properties and substrate specificity of rppa, a chalcone synthase-related polyketide synthase in Streptomyces griseus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4628–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumikawa, M.; Shipley, P.R.; Hopke, J.N.; O’Hare, T.; Xiang, L.; Noel, J.P.; Moore, B.S. Expression and characterization of the type III polyketide synthase 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene synthase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, M.B.; Izumikawa, M.; Bowman, M.E.; Udwary, D.W.; Ferrer, J.L.; Moore, B.S.; Noel, J.P. Crystal structure of a bacterial type III polyketide synthase and enzymatic control of reactive polyketide intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45162–45174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, J.; Xian, M.; Zhao, H.; Frost, J.W. Biosynthesis of phloroglucinol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5332–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, W.; Rubin-Pitel, S.B.; Zhao, H. Characterization of the substrate specificity of phld, a type III polyketide synthase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 32036–32047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.C.; McLoughlin, S.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Walsh, C.T. Role of the active site cysteine of dpga, a bacterial type III polyketide synthase. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-C.; Li, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lyu, S.-Y.; Wu, C.-J.; Li, T.-L. Chain elongation and cyclization in type III pks dpga. ChemBioChem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2012, 13, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; Yadav, G.; Mohanty, D.; Gokhale, R.S. A new family of type III polyketide synthases in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44780–44790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Saxena, P.; Marathe, U.B.; Gokhale, R.S.; Shanmugam, V.M.; Rukmini, R. A novel tunnel in mycobacterial type III polyketide synthase reveals the structural basis for generating diverse metabolites. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokulan, K.; O’Leary, S.E.; Russell, W.K.; Russell, D.H.; Lalgondar, M.; Begley, T.P.; Ioerger, T.R.; Sacchettini, J.C. Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis polyketide synthase 11 (pks11) reveals intermediates in the synthesis of methyl-branched alkylpyrones. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 16484–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Barona-Gomez, F.; Corre, C.; Xiang, L.; Udwary, D.W.; Austin, M.B.; Noel, J.P.; Moore, B.S.; Challis, G.L. Type III polyketide synthase beta-ketoacyl-acp starter unit and ethylmalonyl-coa extender unit selectivity discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14754–14755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruschow, S.; Buchholz, T.J.; Seufert, W.; Dordick, J.S.; Sherman, D.H. Substrate profile analysis and acp-mediated acyl transfer in Streptomyces coelicolor type III polyketide synthases. ChemBioChem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2007, 8, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemler, J.A.; Buchholz, T.J.; Geders, T.W.; Akey, D.L.; Rath, C.M.; Chlipala, G.E.; Smith, J.L.; Sherman, D.H. Biochemical and structural characterization of germicidin synthase: Analysis of a type III polyketide synthase that employs acyl-acp as a starter unit donor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7359–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeya, M.; Kim, T.S.; Tiwari, M.K.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Lee, J.K. A type III polyketide synthase from Rhizobium etli condenses malonyl coas to a heptaketide pyrone with unusually high catalytic efficiency. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 3103–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, N.; Ozawa, H.; Hirata, A.; Horinouchi, S. Phenolic lipid synthesis by type III polyketide synthases is essential for cyst formation in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6356–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanaga, A.; Funa, N.; Awakawa, T.; Horinouchi, S. Direct transfer of starter substrates from type I fatty acid synthase to type III polyketide synthases in phenolic lipid synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satou, R.; Miyanaga, A.; Ozawa, H.; Funa, N.; Katsuyama, Y.; Miyazono, K.; Tanokura, M.; Ohnishi, Y.; Horinouchi, S. Structural basis for cyclization specificity of two azotobacter type III polyketide synthases: A single amino acid substitution reverses their cyclization specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34146–34157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awakawa, T.; Sugai, Y.; Otsutomo, K.; Ren, S.; Masuda, S.; Katsuyama, Y.; Horinouchi, S.; Ohnishi, Y. 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-6-(1-methyl-2-oxoalkyl)pyran-2-one synthesis by a type III polyketide synthase from Rhodospirillum centenum. ChemBioChem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2013, 14, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muggia, L.; Grube, M. Type III polyketide synthases in lichen mycobionts. Fungal Biol. 2010, 114, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Saxena, P.; Rahman, A.; Singh, P.K.; Kasbekar, D.P.; Gokhale, R.S.; Sankaranarayanan, R. Structural insights into biosynthesis of resorcinolic lipids by a type III polyketide synthase in Neurospora crassa. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 162, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin-Pitel, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Vu, T.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Zhao, H.; Nair, S.K. Distinct structural elements dictate the specificity of the type III pentaketide synthase from Neurospora crassa. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Nonaka, T.; Fujii, I. Fungal type III polyketide synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Koen, T.; Takahashi, H.; Suda, C.; Kitamoto, K.; Fujii, I. Aspergillus oryzae csyb catalyzes the condensation of two beta-ketoacyl-coas to form 3-acetyl-4-hydroxy-6-alkyl-alpha-pyrone. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19976–19984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeya, M.; Kim, T.S.; Tiwari, M.K.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Lee, J.K. The Botrytis cinerea type III polyketide synthase shows unprecedented high catalytic efficiency toward long chain acyl-coas. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 2864–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoigawa, J.; Morimoto, K.; Shiono, Y.; Uesugi, S.; Kimura, K.I.; Kataoka, T. Allantopyrone a, an α-pyrone metabolite from an endophytic fungus, inhibits the tumor necrosis factor α-induced nuclear factor kappab signaling pathway. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.M.; Zheng, C.J.; Song, X.P.; Han, C.R.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, G.Y. Antibacterial α-pyrone derivatives from a mangrove-derived fungus Stemphylium sp. 33231 from the south China sea. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Takahashi, Y.; Lou, W.; Noguchi, H. Enzymatic formation of unnatural novel polyketides from alternate starter and nonphysiological extension substrate by chalcone synthase. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samappito, S.; Page, J.; Schmidt, J.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Kutchan, T.M. Molecular characterization of root-specific chalcone synthases from Cassia alata. Planta 2002, 216, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Noguchi, H.; Schroder, J.; Abe, I. Novel polyketides synthesized with a higher plant stilbene synthase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.L.; Spiteller, D.; Spencer, J.B. Identification of a pentaketide stilbene produced by a type III polyketide synthase from pinus sylvestris and characterisation of free coenzyme a intermediates. ChemBioChem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 10, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.-P.; Wanibuchi, K.; Morita, H.; Endo, K.; Noguchi, H.; Abe, I. Enzymatic formation of unnatural novel chalcone, stilbene, and benzophenone scaffolds by plant type III polyketide synthase. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karppinen, K.; Hokkanen, J.; Mattila, S.; Neubauer, P.; Hohtola, A. Octaketide-producing type III polyketide synthase from hypericum perforatum is expressed in dark glands accumulating hypericins. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 4329–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Abe, T.; Wanibuchi, K.; Noguchi, H. Enzymatic formation of quinolone alkaloids by a plant type III polyketide synthase. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 6063–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakimoto, T.; Mori, T.; Morita, H.; Abe, I. Cytotoxic tetramic acid derivative produced by a plant type-III polyketide synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4746–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, M.K.; Chow, J.Y.; Cheung, V.W.; Lim, Y.P.; Yew, W.S. Establishing a toolkit for precursor-directed polyketide biosynthesis: Exploring substrate promiscuities of acid-coa ligases. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klundt, T.; Bocola, M.; Lutge, M.; Beuerle, T.; Liu, B.; Beerhues, L. A single amino acid substitution converts benzophenone synthase into phenylpyrone synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30957–30964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jez, J.M.; Bowman, M.E.; Noel, J.P. Expanding the biosynthetic repertoire of plant type III polyketide synthases by altering starter molecule specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5319–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Watanabe, T.; Morita, H.; Kohno, T.; Noguchi, H. Engineered biosynthesis of plant polyketides—Manipulation of chalcone synthase. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I.; Morita, H.; Oguro, S.; Noma, H.; Wanibuchi, K.; Kawahara, N.; Goda, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Kohno, T. Structure-based engineering of a plant type III polyketide synthase: Formation of an unnatural nonaketide naphthopyrone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5976–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, I. Engineered biosynthesis of plant polyketides: Structure-based and precursor-directed approach. Top. Curr. Chem. 2010, 297, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wanibuchi, K.; Morita, H.; Noguchi, H.; Abe, I. Enzymatic formation of an aromatic dodecaketide by engineered plant polyketide synthase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2083–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, H.; Yamashita, M.; Shi, S.P.; Wakimoto, T.; Kondo, S.; Kato, R.; Sugio, S.; Kohno, T.; Abe, I. Synthesis of unnatural alkaloid scaffolds by exploiting plant polyketide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13504–13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, N.; Ohnishi, Y.; Ebizuka, Y.; Horinouchi, S. Alteration of reaction and substrate specificity of a bacterial type III polyketide synthase by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gruschow, S.; Dordick, J.S.; Sherman, D.H. Molecular analysis of the role of tyrosine 224 in the active site of Streptomyces coelicolor rppa, a bacterial type III polyketide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12765–12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











































© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, Y.P.; Go, M.K.; Yew, W.S. Exploiting the Biosynthetic Potential of Type III Polyketide Synthases. Molecules 2016, 21, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060806
Lim YP, Go MK, Yew WS. Exploiting the Biosynthetic Potential of Type III Polyketide Synthases. Molecules. 2016; 21(6):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060806
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Yan Ping, Maybelle K. Go, and Wen Shan Yew. 2016. "Exploiting the Biosynthetic Potential of Type III Polyketide Synthases" Molecules 21, no. 6: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060806
APA StyleLim, Y. P., Go, M. K., & Yew, W. S. (2016). Exploiting the Biosynthetic Potential of Type III Polyketide Synthases. Molecules, 21(6), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060806