Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of MHE on Cell Viability
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of MHE on NO Production
2.3. Effects of MHE on Inflammatory Cytokines and mRNA Expression
2.4. Effects of MHE on iNOS, COX-2, and HO-1 Expression
2.5. Effects of MHE on LPS-Induced NF-κB Nuclear Translocation and IκBα Phosphorylation in Macrophages
2.6. Effects of MHE on MAPK Phosphorylation in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages
2.7. Effects of MHE on Inflammatory Cytokine Production in LPS-Induced Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages
2.8. Representative Chromatograms of the Constituents in MHE
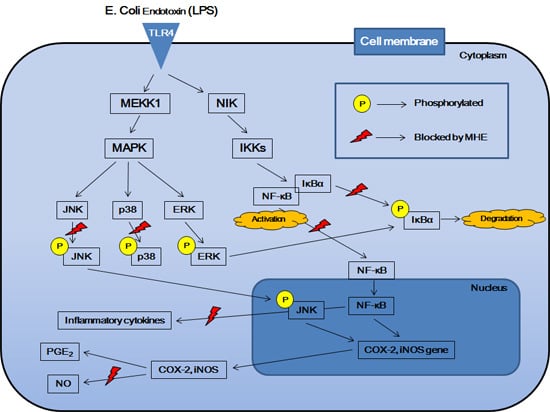
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Reagents and Cell Culture
4.3. Preparation of Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages
4.4. Cell Viability Using the CCK Assay
4.5. Nitrite Concentration Using the Griess Test
4.6. Cytokine Production Using ELISA Assays
4.7. Preparation of Whole Cell, Cytosolic, and Nuclear Fractions
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time RT-PCR
4.10. Chromatographic Conditions
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MH | Melandrii Herba |
| MHE | Melandrii Herba ethanol extract |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| NF | nuclear factor |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| HO | heme oxygenase |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| IL | interleukin |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| IκBα | inhibitor of NF-κB alpha |
| ERK | extracellular regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| PG | prostaglandin |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CCK | cell counting kit |
| NC | Nitrocellulose |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| RIPA | radio immunoprecipitation assay |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| SD | standard deviation |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Perry, L.M.; Metzger, J. Medicinal Plants of East and Southeast Asia: Attributed Properties and Uses; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, I.S.; Han, Y.B.; Woo, W.S.; Kang, S.S.; Lotter, H.; Wagner, H. Sapogenins from Melandrium firmum. Planta Med. 1989, 55, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, E.H.; Woo, W.S.; Chmurny, G.N.; Hilton, B.D. Melandrioside A, a saponin from Melandrium firmum. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.S.; Hwang, N.K.; Kim, D.H.; Moon, T.C.; Son, J.K.; Chang, H.W. Chemical constituents of Melandrium firmum Rohrbach and their anti-inflammatory activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Liang, G. A novel compound C12 inhibits inflammatory cytokine production and protects from inflammatory injury in vivo. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, M.C.; Vinolo, M.A.; Crisma, A.R.; Fock, R.A.; Borelli, P.; Tirapegui, J.; Curi, R.; Rogero, M.M. High-fat diet blunts activation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peritoneal macrophages of Wistar rats. Nutrition 2013, 29, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammatory mechanisms: The molecular basis of inflammation and disease. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S140–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzi, S.; Wasko, M.C. Inflammation-mediated rheumatic diseases and atherosclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-κB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Hong, J.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, W.M. Dried Ginger (Zingiber officinalis) Inhibits Inflammation in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Cancer and inflammation: An old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 677–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J.; Karin, M. Nuclear factor-κB. A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappas, M.; Permezel, M.; Georgiou, H.M.; Rice, G.E. Nuclear factor κB regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in human gestational tissues in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Suh, S.J.; Yang, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, S.; Jo, T.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, Y.I.; Ahn, G.W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of bark of Dioscorea batatas DECNE through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expressions in RAW264.7 cells via NF-κB and ERK1/2 inactivation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saklatvala, J. Inflammatory signaling in cartilage: MAPK and NF-κB pathways in chondrocytes and the use of inhibitors for research into pathogenesis and therapy of osteoarthritis. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanden Berghe, W.; Plaisance, S.; Boone, E.; De Bosscher, K.; Schmitz, M.L.; Fiers, W.; Haegeman, G. p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways are required for nuclear factor-κB p65 transactivation mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 3285–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: A 10-year update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.C.; Duan, Z.J. Signal transduction of innate immunity to virus infection. Bing Du Xue Bao 2012, 28, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.B.; Knudtson, K.L.; Monick, M.M.; Hunninghake, G.W. The p38 mitogen activated protein kinase is required for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. The role of TATA-binding protein (TBP). J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30858–30863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ku, K.T.; Huang, Y.L.; Huang, Y.J.; Chiou, W.F. Miyabenol A inhibits LPS-induced NO production via IKK/IκB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the p38 and PI3K pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8911–8918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Nie, S.P.; Wang, J.Q.; Yin, P.F.; Li, W.J.; Xie, M.Y. Polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum induces tumor necrosis factor-α secretion via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt, mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.E.; Waters, W.R.; Rudolph, K.M.; Drew, M.L. Comparative nitric oxide production by LPS-stimulated monocyte-derived macrophages from Ovis canadensis and Ovis aries. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.C.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, W.K.; Ha, J.H.; Gu, M.J.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of pyeongwisan on LPS-stimulated murine macrophages and mouse models of acetic acid-induced writhing response and xylene-induced ear edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashino, T.; Yamanaka, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Shimokawa, H.; Sekikawa, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Shioda, S.; Numazawa, S.; Yoshida, T. Negative feedback regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression by heme oxygenase-1 induction in macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Hommes, D.W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; van Deventer, S.J. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signal transduction pathways and novel anti-inflammatory targets. Gut 2003, 52, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadas, I.; Terencio, M.C.; Guillén, I.; Ferrándiz, M.L.; Coloma, J.; Payá, M.; Alcaraz, M.J. Coregulation between cyclo-oxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the time-course of murine inflammation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshak, A.K.; Jackson, J.R.; McGough, K.; Chabot-Fletcher, M.; Mochan, E.; Marshall, L.A. Manipulation of distinct NFκB proteins alters interleukin-1beta-induced human rheumatoid synovial fibroblast prostaglandin E2 formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31496–31501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmedtje, J.F., Jr.; Ji, Y.S.; Liu, W.L.; DuBois, R.N.; Runge, M.S. Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-κB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jian, C.X.; Li, M.Z.; Zheng, W.Y.; He, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Fan, Q.S.; Hu, Y.H.; Li, C.J. Tormentic acid inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response in human gingival fibroblasts via inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, T.M.; Bennett, P.R. The role of nuclear factor κB in human labour. Reproduction 2005, 130, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.R.; McFadden, G. NFkB inhibitors: Strategies from poxviruses. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3125–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolcet, X.; Llobet, D.; Pallares, J.; Matias-Guiu, X. NF-κB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch. 2005, 446, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Giampieri, F.; Gasparrini, M.; Mazzoni, L.; Quiles, J.L.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 154–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.D.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of an IκBα/NFκB complex. Cell 1998, 95, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Delhase, M. The IκB kinase (IKK) and NF-κB: Key elements of proinflammatory signalling. Semin. Immunol. 2000, 12, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. IκB kinases: Key regulators of the NF-κB pathway. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefaloyianni, E.; Gaitanaki, C.; Beis, I. ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK signaling pathways, through MSK1, are involved in NF-κB transactivation during oxidative stress in skeletal myoblasts. Cell Signal. 2006, 18, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, T.; Penninger, J.M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2838–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Dong, C. MAP kinases in immune responses. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.Y.; Liu, J.T.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.D.; Liu, C.H. PPARα activator fenofibrate modulates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory responses in vascular smooth muscle cells via the TLR4-dependent signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Kim, M.M.; Mendis, E.; Kim, S.K. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells by carboxybutyrylated glucosamine takes place via down-regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated nuclear factor-κB signaling. Immunology 2008, 123, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.J.; Yoon, W.J.; Sohn, E.H.; Ham, Y.M.; Jang, S.A.; Kwon, J.E.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Sohn, E.; Park, S.Y.; et al. The analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Litsea japonica fruit are mediated via suppression of NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Shin, I.S.; Seo, C.S.; Lee, N.H.; Ha, H.K.; Son, J.K.; Shin, H.K. Effects of Melandrium firmum methanolic extract on testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in Wistar rats. Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.Y.; Li, S.; Zhen, Y.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Shao, X.; Luo, Z.G. Cardioprotection of vitexin on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat via regulating inflammatory cytokines and MAPK pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, S.M.; Carvalho, T.T.; Staurengo-Ferrari, L.; Hohmann, M.S.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr. Vitexin inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative stress, and cytokines. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, F.R.; Silva, M.D.; Córdova, M.M.; Schambach, T.R.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Santos, A.R. Anti-inflammatory action of hydroalcoholic extract, dichloromethane fraction and steroid α-spinasterol from Polygala sabulosa in LPS-induced peritonitis in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.S.; Xiang, Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Lin, K.M.; Zhang, X.F. Dietary blue pigments derived from genipin, attenuate inflammation by inhibiting LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via the NF-κB inactivation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34122. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples and extracts are available from the authors.







| Target Gene | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | F: 5′-TTCTGTCTACTGAACTTCGGGGTGATCGGTCC-3′ |
| R: 5′-GTATGAGATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGTGTGGG-3′ | |
| IL-6 | F: 5′-TCCAGTTGCCTTCTTGGGAC-3′ |
| R: 5′-GTGTAATTAAGCCTCCGACTTG-3′ | |
| IL-1β | F: 5′-ATGGCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT-3′ |
| R: 5′-CAGGACAGGTATAGATTCTTTCCTTT-3′ | |
| iNOS | F: 5′-GGCAGCCTGTGAGACCTTTG-3′ |
| R: 5′-GCATTGGAAGTGAAGCGTTTC-3′ | |
| COX-2 | F: 5′-TGAGTACCGCAAACGCTTCTC-3′ |
| R: 5′-TGGACGAGGTTTTTCCACCAG-3′ | |
| HO-1 | F: 5′-TGAAGGAGGCCACCAAGGAGG-3′ |
| R: 5′-AGAGGTCACCCAGGTAGCGGG-3′ | |
| β-actin | F: 5′-AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC-3′ |
| R: 5′-CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT-3′ |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.H.; Oh, Y.-C.; Cho, W.-K.; Lee, B.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages. Molecules 2016, 21, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060818
Jeong YH, Oh Y-C, Cho W-K, Lee B, Ma JY. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages. Molecules. 2016; 21(6):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060818
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Yun Hee, You-Chang Oh, Won-Kyung Cho, Bohyoung Lee, and Jin Yeul Ma. 2016. "Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages" Molecules 21, no. 6: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060818
APA StyleJeong, Y. H., Oh, Y. -C., Cho, W. -K., Lee, B., & Ma, J. Y. (2016). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages. Molecules, 21(6), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21060818