Photoelectrochemical Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Hematite Thin Films Modified with Ti(IV)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
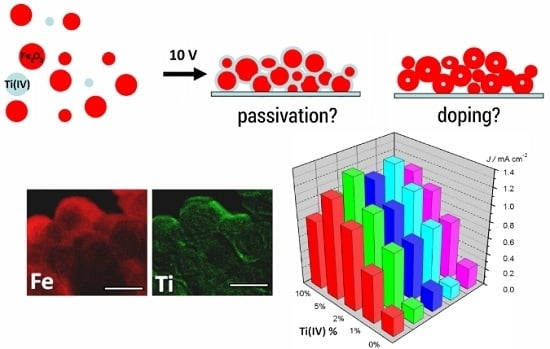
2.1. AFM, XPS, TEM and XANES Characterization
2.2. DC Photoelectrochemical Characterization
2.3. Photoelectrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation and Functionalization with Fe-OEC of Un-Modified and Ti(IV)-Modified Hematite Film
3.2. AFM, XPS, TEM and XANES Characterization
3.3. AC/DC Photoelectrochemical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| B.E. | Binding Energy |
| EIS | Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy |
| ESI | Electron Spectroscopy Imaging |
| Fe-OEC | Iron(III)-based Oxygen Evolving Catalyst |
| FTO | Fluorine Tin-doped Oxide |
| FWHM | Full Width at Half Maximum |
| MS | Mott-Schottky |
| SCLJ | Semiconductor Liquid Junction |
| SILAR | Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
References
- Sivula, K.; le Formal, F.; Grätzel, M. Solar Water Splitting: Progress Using Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Photoelectrodes. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterloh, F.E. Inorganic nanostructures for photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2294–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilley, S.D.; Cornuz, M.; Sivula, K.; Grätzel, M. Light-Induced Water Splitting with Hematite: Improved Nanostructure and Iridium Oxide Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6405–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malara, F.; Minguzzi, A.; Marelli, M.; Morandi, S.; Psaro, R.; dal Santo, V.; Naldoni, A. α-Fe2O3/NiOOH: An Effective Heterostructure for Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5292–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, N.; Cristino, V.; Berardi, S.; Carli, S.; Argazzi, R.; Caramori, S.; Meda, L.; Tacca, A.; Bignozzi, C.A. Hematite Photoanodes Modified with an FeIII Water Oxidation Catalyst. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivula, K. Metal Oxide Photoelectrodes for Solar Fuel Production, Surface Traps, and Catalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahr, B.; Gimenez, S.; Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Bisquert, J.; Hamann, T.W. Photoelectrochemical and Impedance Spectroscopic Investigation of Water Oxidation with “Co-Pi”-Coated Hematite Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16693–16700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle Carbonare, N.; Carli, S.; Argazzi, R.; Orlandi, M.; Bazzanella, N.; Miotello, A.; Caramori, S.; Bignozzi, C.A. Improvement of the electron collection efficiency in porous hematite using a thin iron oxide underlayer: towards efficient all-iron based photoelectrodes. Phy. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 29661–29670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Enache, C.S.; van de Krol, R. Photoelectrochemical Characterization of Sprayed α-Fe2O3 Thin Films: Influence of Si Doping and SnO2 Interfacial Layer. Int. J. Photoenergy 2008, 2008, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, O.; Beardslee, J.A.; Hamann, T. Substrate Dependent Water Splitting with Ultrathin α-Fe2O3 Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 16494–16503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasscock, J.A.; Barnes, P.R.F.; Plumb, I.C.; Savvides, N. Enhancement of Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Production from Hematite Thin Films by the Introduction of Ti and Si. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16477–16488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-S.; Kleiman-Shwarsctein, A.; Forman, A.J.; Hazen, D.; Park, J.-N.; McFarland, E.W. Pt-Doped α-Fe2O3 Thin Films Active for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3803–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, S.Y.; Kumar, M.H.; Bassi, P.S.; Seng, H.L.; Barber, J.; Wong, L.H. Improving the Efficiency of Hematite Nanorods for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting by Doping with Manganese. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5852–5859. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman-Shwarsctein, A.; Hu, Y.-S.; Forman, A.J.; Stucky, G.D.; McFarland, E.W. Electrodeposition of α-Fe2O3 Doped with Mo or Cr as Photoanodes for Photocatalytic Water Splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15900–15907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.; Shrivastav, R.; Dass, S.; Satsangi, R.V. Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Generation using Al Doped Nanostructured Hematite Thin Films. In Chemistry of Phytopotentials: Health, Energy and Environmental Perspectives; Khemani, D.L., Srivastava, M.M., Srivastava, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liang, C.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z.; Shao, G.; Zhang, L. Ge-doped hematite nanosheets with tunable doping level, structure and improved photoelectrochemical performance. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, I.-C.; Yoon, K.B. Effect of metal doping, doped structure, and annealing under argon on the properties of 30 nm thick ultrathin hematite photoanodes. Phy. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 21936–21940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munetoshi, S.; Hiroyasu, Y.; Hitoshi, T. Enhanced Photocurrent in Rh-Substituted α-Fe2O3 Thin Films Grown by Pulsed Laser Deposition. Appl. Phy. Express 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhou, J.; Dong, C.-L.; Hu, Y.; Tseng, E.N.; Guo, P.; Guo, L.; Mao, S.S. Surface Engineered Doping of Hematite Nanorod Arrays for Improved Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ling, Y.; Wheeler, D.A.; George, K.E.N.; Horsley, K.; Heske, C.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, Y. Facile Synthesis of Highly Photoactive α-Fe2O3-Based Films for Water Oxidation. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3503–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabaev, T.S.; Ajmal, M.; Hong, N.H.; Kim, H.-K.; Hwang, Y.-H. Ti-doped hematite thin films for efficient water splitting. Appli. Phys. A 2014, 118, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Xie, T. Highly photoactive Ti-doped α-Fe2O3 nanorod arrays photoanode prepared by a hydrothermal method for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 129, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, N.T.; Mullins, C.B. Photoelectrochemical Performance of Nanostructured Ti- and Sn-Doped α-Fe2O3 Photoanodes. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6474–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioult, M.; Magnan, H.; Stanescu, D.; Barbier, A. Single Crystalline Hematite Films for Solar Water Splitting: Ti-Doping and Thickness Effects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Shi, T.; Xu, G.; Ji, S.; Ye, C. Photocurrent Enhancement for Ti-Doped Fe2O3 Thin Film Photoanodes by an In Situ Solid-State Reaction Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhong, J.; Pu, A.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.-T. Ti-doped hematite nanostructures for solar water splitting with high efficiency. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, O.; Klahr, B.M.; Hamann, T.W. Highly photoactive Ti-doped α-Fe2O3 thin film electrodes: Resurrection of the dead layer. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franking, R.; Li, L.; Lukowski, M.A.; Meng, F.; Tan, Y.; Hamers, R.J.; Jin, S. Facile post-growth doping of nanostructured hematite photoanodes for enhanced photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.G.; Kretschmer, I.E.; Kandiel, T.A.; Ahmed, A.Y.; Rashwan, F.A.; Bahnemann, D.W. A Facile Surface Passivation of Hematite Photoanodes with TiO2 Overlayers for Efficient Solar Water Splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24053–24062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monllor-Satoca, D.; Bartsch, M.; Fabrega, C.; Genc, A.; Reinhard, S.; Andreu, T.; Arbiol, J.; Niederberger, M.; Morante, J.R. What do you do, titanium? Insight into the role of titanium oxide as a water oxidation promoter in hematite-based photoanodes. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3242–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shaner, M.R.; Beardslee, J.A.; Lichterman, M.; Brunschwig, B.S.; Lewis, N.S. Amorphous TiO2 coatings stabilize Si, GaAs, and GaP photoanodes for efficient water oxidation. Science 2014, 344, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, X.; Thaweesak, S.; Xu, H.; Xing, Z.; Zou, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, L. A Scalable Colloidal Approach to Prepare Hematite Films for Efficient Solar Water Splitting. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 12314–12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; de Groot, F.M.F.; Sawatzky, G.A.; Voogt, F.C.; Hibma, T.; Okada, K. In situ XPS analysis of various iron oxide films grown by NO2-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustynski, J.; Alexander, B.D.; Solarska, R. Metal Oxide Photoanodes for Water Splitting. In Photocatalysis; Bignozzi, C.A., Ed.; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 303, pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Asakura, K.; Xie, P.; Wang, J.; He, H. An XAFS study on the specific microstructure of active species in iron titanate catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Today 2013, 201, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, P.S.; Gurudayal; Wong, L.H.; Barber, J. Iron based photoanodes for solar fuel production. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 11834–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J; Gao, B.; Han, S.Y.; Jung, M.H.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Ko, T.; Lee, C.; Lee, W.I. Heterojunction of FeTiO3 Nanodisc and TiO2 Nanoparticle for a Novel Visible Light Photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19179–19184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, V.; Berardi, S.; Caramori, S.; Argazzi, R.; Carli, S.; Meda, L.; Tacca, A.; Bignozzi, C.A. Efficient solar water oxidation using photovoltaic devices functionalized with earth-abundant oxygen evolving catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13083–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Seol, M.; Lee, J.; Yong, K. Highly Efficient Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Generation Using Hierarchical ZnO/WOx Nanowires Cosensitized with CdSe/CdS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 25429–25436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Electrode samples are available from the authors.











© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalle Carbonare, N.; Boaretto, R.; Caramori, S.; Argazzi, R.; Dal Colle, M.; Pasquini, L.; Bertoncello, R.; Marelli, M.; Evangelisti, C.; Bignozzi, C.A. Photoelectrochemical Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Hematite Thin Films Modified with Ti(IV). Molecules 2016, 21, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070942
Dalle Carbonare N, Boaretto R, Caramori S, Argazzi R, Dal Colle M, Pasquini L, Bertoncello R, Marelli M, Evangelisti C, Bignozzi CA. Photoelectrochemical Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Hematite Thin Films Modified with Ti(IV). Molecules. 2016; 21(7):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070942
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalle Carbonare, Nicola, Rita Boaretto, Stefano Caramori, Roberto Argazzi, Maurizio Dal Colle, Luca Pasquini, Renzo Bertoncello, Marcello Marelli, Claudio Evangelisti, and Carlo Alberto Bignozzi. 2016. "Photoelectrochemical Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Hematite Thin Films Modified with Ti(IV)" Molecules 21, no. 7: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070942
APA StyleDalle Carbonare, N., Boaretto, R., Caramori, S., Argazzi, R., Dal Colle, M., Pasquini, L., Bertoncello, R., Marelli, M., Evangelisti, C., & Bignozzi, C. A. (2016). Photoelectrochemical Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Hematite Thin Films Modified with Ti(IV). Molecules, 21(7), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070942