Upconversion Luminescence Sensitized pH-Nanoprobes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of pH-Sensor
3. Structure of UCNPs and Upconversion Processes
4. Development in Photon Upconversion Based pH-Probes
4.1. Upconversion Based pH-Sensing Membranes
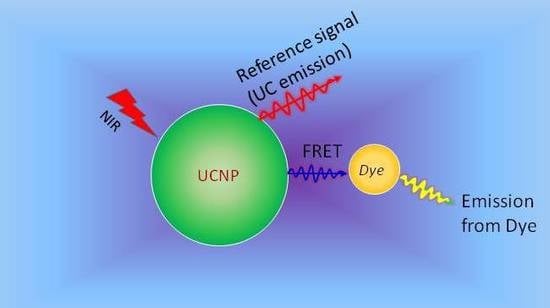
4.2. Upconversion Nanoparticles as pH-Sensors
5. Biosafety of Upconversion Based Probes
5.1. Toxicity Analysis of Upconversion Nanoparticles
5.2. Bio-Distribution and Excretion of Upconversion Nanoparticles
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drees, C.; Raj, A.N.; Kurre, R.; Busch, K.B.; Haase, M.; Piehler, J. Engineered upconversion nanoparticles for resolving protein interactions inside living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11668–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, L.C.; Ang, L.Y.; Alonso, S.; Zhang, Y. Bacterial imaging with photostable upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2987–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäferling, M. Nanoparticle-based luminescent probes for intracellular sensing and imaging of pH. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 378–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.J.J.L.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, H.S.; Wolfeis, O.S. Optical Ammonia Sensor Based on Upconverting Luminescent Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5002–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Park, S.; Yoon, J.; Shin, I. Recent progress in the development of near-infrared fluorescent probes for bioimaging applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Hu, Y.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent probes and bioimaging: Alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and pH. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4619–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4185–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Heo, C.H.; Kim, H.M. Benzimidazole-based ratiometric two-photon fluorescent probes for acidic pH in live cells and tissues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17969–17977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornig, S.; Biskup, C.; Graefe, A.; Wotschadlo, J.; Liebert, T.; Mohr, G.J.; Heinze, T. Biocompatible fluorescent nanoparticles for pH-sensoring. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Sengupta, B.; Zedayko, T.; Baird, B.; Wiesner, U. Core/Shell fluorescent silica nanoparticles for chemical sensing: Towards single-particle laboratories. Small 2006, 2, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-S.; Sun, Y.; Vernier, P.T.; Liang, C.-H.; Chong, S.Y.C.; Gundersen, M.A. pH-sensitive Photoluminescence of CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS Quantum Dots in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, S.; Schäferling, M. Chemical sensing and imaging based on photon upconverting nano-and microcrystals: A review. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2015, 3, 034004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Abbineni, G.; Clevenger, A.; Mao, C.; Xu, S. Upconversion nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface modification and biological applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 710–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Banerjee, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Upconversion nanoparticles in biological labeling, imaging, and therapy. Analyst 2010, 135, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäferling, M.; Resch-Genger, U. Luminescent Nanoparticles for Chemical Sensing and Imaging. In Reviews in Fluorescence 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 71–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mahata, M.K.; Tiwari, S.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, K.; Rai, V.K. YVO4: Er3+/Yb3+ phosphor for multifunctional applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2014, 31, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Chen, G.; Yang, C. Sensing using rare-earth-doped upconversion nanoparticles. Theranostics 2013, 3, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahata, M.K.; Koppe, T.; Kumar, K.; Hofsäss, H.; Vetter, U. Demonstration of Temperature Dependent Energy Migration in Dual-Mode YVO4: Ho3+/Yb3+ Nanocrystals for Low Temperature Thermometry. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Shi, B.; Jin, D.; Liu, X. Controlling upconversion nanocrystals for emerging applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahata, M.K.; Kumari, A.; Rai, V.K.; Kumar, K. Er3+, Yb3+ doped yttrium oxide phosphor as a temperature sensor. Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Trends in Applied Physics and Material Science: RAM 2013, Bikaner, India, 1–2 February 2013; pp. 1270–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Jung, M.; Han, Y.; Lee, G.; Shin, K.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.T. Stochastic Photon Emission from Non-Blinking Upconversion Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 21073–21079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Antaris, A.L.; Dai, H. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaque, D.; Richard, C.; Viana, B.; Soga, K.; Liu, X.; Solé, J.G. Inorganic nanoparticles for optical bioimaging. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2016, 8, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.I.; Lee, K.T.; Suh, Y.D.; Hyeon, T. Upconverting nanoparticles: A versatile platform for wide-field two-photon microscopy and multi-modal in vivo imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, C.H.; Capobianco, J.A. Photon upconversion nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Qiu, H.; Prasad, P.N.; Chen, X. Upconversion nanoparticles: Design, nanochemistry, and applications in theranostics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5161–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Upconversion luminescent materials: Advances and applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 115, 395–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, H.S.; Kele, P.; Saleh, S.M.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Upconverting luminescent nanoparticles for use in bioconjugation and bioimaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, L.; Liu, X.; Xue, B.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; et al. Accurate Quantitative Sensing of Intracellular pH based on Self-ratiometric Upconversion Luminescent Nanoprobe. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näreoja, T.; Deguchi, T.; Christ, S.; Peltomaa, R.; Prabhakar, N.; Fazeli, E.; Perälä, N.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Arppe, R.; Soukka, T.; et al. Ratiometric Sensing and Imaging of Intracellular pH Using Polyethylenimine-Coated Photon Upconversion Nanoprobes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Chang, Y.N.; Yin, W.; Liu, X.; Xiao, D.; Xing, G.; Zhao, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Biocompatible and flexible graphene oxide/upconversion nanoparticle hybrid film for optical pH sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Long, Y.; Lei, P.; Dong, L.; Du, K.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H. A pH-responsive assembly based on upconversion nanocrystals and ultrasmall nickel nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 9666–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Raval, Y.; Chen, H.; Tzeng, T.R.J.; DesJardins, J.D.; Anker, J.N. Development of luminescent pH sensor films for monitoring bacterial growth through tissue. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Kumar, A.; Tan, A.; Jin, S.; Mozhi, A.; Liang, X.J. pH-sensitive nano-systems for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlmeier, A.; Gorris, H.H. Surface modification and characterization of photon-upconverting nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1526–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qiao, S. Effects of surface modification of upconversion nanoparticles on cellular uptake and cytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2016, 32, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. Fluorescent probes and nanoparticles for intracellular sensing of pH values. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2014, 2, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wencel, D.; Abel, T.; McDonagh, C. Optical chemical pH sensors. Anal. Chem. 2013, 86, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, T. Zwischenmolekulare energiewanderung und fluoreszenz. Ann. Phys. 1948, 437, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, R.M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1995, 6, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Huang, W.; Liu, X. Enabling Förster Resonance Energy Transfer from Large Nanocrystals through Energy Migration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15972–15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmer, E.; Acosta-Mora, P.; Méndez-Ramos, J.; Fischer, S. Optical nanoprobes for biomedical applications: Shining a light on upconverting and near-infrared emitting nanoparticles for imaging, thermal sensing, and photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4365–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, W.B. The symbol for pH. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörenson, S.P.L. Enzyme Studies II. The Measurement and Meaning of Hydrogen Ion Concentration in Enzymatic Processes. Biochem. Z. 1909, 21, 131–200. [Google Scholar]
- Janata, J. Do optical sensors really measure pH? Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksa, M.; Komura, H.; Wu, R.; Shah, K.G.; Wang, P. A novel method to determine the engulfment of apoptotic cells by macrophages using pHrodo succinimidyl ester. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 342, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloembergen, N. Solid state infrared quantum counters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1959, 2, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzel, F. Upconversion and anti-stokes processes with f and d ions in solids. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 139–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, H.; Ptacek, P.; Eickmeier, H.; Haase, M. Synthesis of Hexagonal Yb3+, Er3+-Doped NaYF4 Nanocrystals at Low Temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, H.; Ptacek, P.; Kömpe, K.; Haase, M. Lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals in aqueous solution displaying strong up-conversion emission. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, M.K.; Hofsäss, H.C.; Vetter, U. Photon-Upconverting Materials: Advances and Prospects for Various Emerging Applications. In Luminescence—An Outlook on the Phenomena and Their Applications; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, M.; Schäfer, H. Upconverting nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5808–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, B. Optical absorption intensities of rare-earth ions. Phys. Rev. 1962, 127, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofelt, G. Intensities of crystal spectra of rare-earth ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, A.; Xu, J.; Yang, P.; He, F.; Xu, L. Upconversion processes: Versatile biological applications and biosafety. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12248–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennerberg, D.; Lin, Z. Upconversion nanocrystals: Synthesis, properties, assembly and applications. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Ivanov, I.A.; Qu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Plasmonic modulation of the upconversion fluorescence in NaYF4: Yb/Tm hexaplate nanocrystals using gold nanoparticles or nanoshells. Angew. Chem. Ger. Edit. 2010, 122, 2927–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, P. Intense ultraviolet upconversion luminescence from Tm3+∕Yb3+: β-YF3 nanocrystals embedded glass ceramic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 051920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. Upconversion luminescence of monodisperse CaF2: Yb3+/Er3+ nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14200–14201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Jung, T.; Lee, E.; Lee, G.; Goh, Y.; Heo, J.; Jung, M.; Jo, E.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.G.; et al. Distinct mechanisms for the upconversion of NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ nanoparticles revealed by stimulated emission depletion. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 9739–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heer, S.; Kömpe, K.; Güdel, H.U.; Haase, M. Highly efficient multicolour upconversion emission in transparent colloids of lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Si, R.; Yan, Z.G.; Sun, L.D.; You, L.P.; Yan, C.H. High-quality sodium rare-earth fluoride nanocrystals: Controlled synthesis and optical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6426–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, R.; Vetrone, F.; Mahalingam, V.; Cuccia, L.A.; Capobianco, J.A. Controlled synthesis and water dispersibility of hexagonal phase NaGdF4: Ho3+/Yb3+ nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chi, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, R.; Guo, H. Novel upconversion behavior in Ho3+-doped transparent oxyfluoride glass-ceramics containing NaYbF4 nanocrystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 2073–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellé, F.; Dhaouadi, M.; Michely, L.; Aschehoug, P.; Toncelli, A.; Veronesi, S.; Tonelli, M. Spectroscopic properties and upconversion in Pr3+: YF3 nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 17453–17460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, D. Controlled synthesis of hexagon shaped lanthanide-doped LaF3 nanoplates with multicolor upconversion fluorescence. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 3875–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Boyer, J.C.; Bovero, E.; van Veggel, F.C. Up-conversion of 980 nm light into white light from sol-gel derived thin film made with new combinations of LaF3: Ln3+ nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2392–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhen, Z. Oleic acid (OA)-modified LaF3: Er, Yb nanocrystals and their polymer hybrid materials for potential optical-amplification applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Advances in the theoretical understanding of photon upconversion in rare-earth activated nanophosphors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1635–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Peng, D.; Ju, Q.; Wang, F. Photon upconversion in core–shell nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Pandey, A.; Dey, R.; Rai, V.K. Simultaneous influence of Zn2+/Mg2+ on the luminescent behaviour of La2O3: Tm3+–Yb3+ phosphors. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 21844–21851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, M.K.; Koppe, T.; Mondal, T.; Brüsewitz, C.; Kumar, K.; Rai, V.K.; Hofsäss, H.; Vetter, U. Incorporation of Zn2+ ions into BaTiO3: Er3+/Yb3+ nanophosphor: An effective way to enhance upconversion, defect luminescence and temperature sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 20741–20753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Mahata, M.K.; Swart, H.C.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, K. Enhancement of upconversion, temperature sensing and cathodoluminescence in the K+/Na+ compensated CaMoO4: Er3+/Yb3+ nanophosphor. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 5362–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, P.Z.; Yan, C.H. Upconversion of rare earth nanomaterials. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2015, 66, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadort, A.; Zhao, J.; Goldys, E.M. Lanthanide upconversion luminescence at the nanoscale: Fundamentals and optical properties. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 13099–13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, P.; Tu, D.; Ma, E.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X. Lanthanide-doped upconversion nano-bioprobes: Electronic structures, optical properties, and biodetection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1379–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.N.; Peng, H.; Stich, M.I.J.; Achatz, D.; Wolfbeis, O.S. pH sensor based on upconverting luminescent lanthanide nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2009, 33, 5000–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Ma, Y.; Llu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Yang, H.R.; Lv, W.; Yu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Dye-conjugated upconversion nanoparticles for ratiometric imaging of intracellular pH values. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 6616–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, M.; Escudero, A.; Núñez, N.O.; Becerro, A.I.; Ocaña, M. Europium-doped NaGd(WO4)2 nanophosphors: Synthesis, luminescence and their coating with fluorescein for pH sensing. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 11575–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Song, S.; Zhang, H. A long-wave optical pH sensor based on red upconversion luminescence of NaGdF4 nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55897–55899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, E. One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5572–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, R.J.; Simbürger, J.M.; Soukka, T.; Schäferling, M. Background-free referenced luminescence sensing and imaging of pH using upconverting phosphors and color camera read-out. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5535–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.Y. Polymeric optodes based on upconverting nanorods for fluorescent measurements of pH and metal ions in blood samples. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arppe, R.; Nareoja, T.; Nylund, S.; Mattsson, L.; Koho, S.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Soukka, T.; Schaferling, M. Photon upconversion sensitized nanoprobes for sensing and imaging of pH. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6837–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H.Y. Direct fluorescent measurement of blood potassium with polymeric optical sensors based on upconverting nanomaterials. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2617–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Hernandez-Gil, J.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X.; Lyu, G.M.; Bañobre-López, M.; Gallo, J.; Sun, L.D.; Yan, C.; Long, N.J. Design and validation of a new ratiometric intracellular pH imaging probe using lanthanide-containing upconverting nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 13957–13965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dong, H.; Yu, M.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Wei, L.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, H. NIR ratiometric luminescence detection of pH fluctuation in living cells with hemicyanine derivative-assembled upconversion nanophosphors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 29, 8863–8869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, T.S.; Anderson, R.E.; Fischer, H.C.; Newbigging, S.; Chan, W.C. In vivo quantum-dot toxicity assessment. Small 2010, 6, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Clearance pathways and tumor targeting of imaging nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6655–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Feng, W.; Yang, P.; Huang, C.; Li, F. The biosafety of lanthanide upconversion nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, A.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Yang, T.; Wu, D.; Wu, L.; Li, F. Core–shell NaYF4: Yb3+, Tm3+@FexOy nanocrystals for dual-modality T 2-enhanced magnetic resonance and NIR-to-NIR upconversion luminescent imaging of small-animal lymphatic node. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, F. Long-term in vivo biodistribution imaging and toxicity of polyacrylic acid-coated upconversion nanophosphors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7078–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Shao, M.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z. In vivo pharmacokinetics, long-term biodistribution and toxicology study of functionalized upconversion nanoparticles in mice. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Water-stable NaLuF4-based upconversion nanophosphors with long-term validity for multimodal lymphatic imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, G.H.; Hwang, M.P.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, K.H. A systematic in-vivo toxicity evaluation of nanophosphor particles via zebrafish models. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, J.X. Upconversion nanomaterials: Synthesis, mechanism, and applications in sensing. Sensors 2012, 12, 2414–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, R.A.; Zhang, Y. Biocompatibility of silica coated NaYF4 upconversion fluorescent nanocrystals. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4122–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Rao, L.; Yi, Z.; Zeng, S.; Hao, J. Simultaneous synthesis and amine-functionalization of single-phase BaYF5: Yb/Er nanoprobe for dual-modal in vivo upconversion fluorescence and long-lasting X-ray computed tomography imaging. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6023–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Ipe, B.I.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Xing, B. NIR light controlled photorelease of siRNA and its targeted intracellular delivery based on upconversion nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tu, D.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X. Lanthanide-doped luminescent nanoprobes: Controlled synthesis, optical spectroscopy, and bioapplications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6924–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccache, R.; Chevallier, P.; Lagueux, J.; Gossuin, Y.; Laurent, S.; Vander Elst, L.; Chilian, C.; Capobianco, J.A.; Fortin, M.A. High relaxivities and strong vascular signal enhancement for NaGdF4 nanoparticles designed for dual MR/optical imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Zeng, J.; Hou, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y.; Qiao, R.; Shen, L.; Lei, H.; Yang, W.; et al. Magnetic/upconversion fluorescent NaGdF4: Yb, Er nanoparticle-based dual-modal molecular probes for imaging tiny tumors in vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7227–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.K.; Rufaihah, A.J.; Zhang, Y. Upconversion fluorescence imaging of cells and small animals using lanthanide doped nanocrystals. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Shi, Z.Y.; Smith, S.; Birnbaum, D.; Kopelman, R. Submicrometer intracellular chemical optical fiber sensors. Science 1992, 258, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, H.A.; Hoyer, M.; Philbert, M.A.; Kopelman, R. Optical nanosensors for chemical analysis inside single living cells. 1. Fabrication, characterization, and methods for intracellular delivery of PEBBLE sensors. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4831–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindell, J.A. Lysosomal acidification mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012, 74, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, J.C. Accuracy and precision in quantitative fluorescence microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











| Host Material | Dopant Ions | Major Emission Bands | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | Green | Red | |||
| β-NaYF4 | Yb3+/Er3+ | 525, 545 | 655 | [61] | |
| β-NaYF4 | Yb3+/Tm3+ | 461, 478 | 527 | 650 | [62] |
| β-NaYF4 | Tm3+/Eu3+ | 450, 475 | [63] | ||
| NaGdF4 | Ho3+/Yb3+ | 486 | 541 | 647, 751 | [64] |
| NaYbF4 | Yb3+/Ho3+ | 480 | 541 | 645 | [65] |
| YF3 | Pr3+ | 483, 485 | [66] | ||
| LaF3 | Yb3+/Tm3+ | 475.2 | 698 | 800.2 | [67] |
| LaF3 | Yb3+/Ho3+ | 542.4 | 644.7, 657.8 | [68] | |
| LaF3 | Yb3+/Er3+ | 520.8, 545 | 658.8 | [69] | |
| pH-Probe | Response Time | pH Range | Method | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCNPs | Indicator | ||||
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ | bromothymol blue | N/A | 2–11 | Absolute intensity of 548 nm and 658 nm bands | [78] |
| Y2O2S:Er3+/Yb3+ (film) | Bromocresol green | ~10 min | 5–10 | Ratio of 671 nm to 661 nm | [34] |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ with graphene oxide (film) | (No dye) | 1 min | 5–8 | Changes in emission intensity of 540 nm | [32] |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ aminosilane coated | pHrodoTM Red | N/A | 2.5–7.2 | Ratio of UC emission at 540 nm to the dye emission at 590 nm | [85] |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+-PEI | pHrodoTM Red | N/A | 5–7 | Ratio of UC emission at 540 nm to the dye emission at 590 nm | [31] |
| NaYF4:Tm3+/Yb3+ | Fluoroscein isothiocynate | N/A | 3–7 | Ratio of UC emission at 475 nm to 645 nm | [30] |
| Y2O3Tm3+@SiO2 | Xylenol orange | N/A | 4–8 | Ratio of UC emission at 450 nm and 646 nm | [79] |
| NaGd(WO4)2:Eu3+ | Fluoroscein isothiocyanate allylamine hydrocloride | N/A | 4–10 | Ratio of fluoroscein emission at 512 nm to RE emission at 611 nm | [80] |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+ | Bromothymol blue | N/A | 6–8 | Absolute UC emission at 650 nm | [81] |
| Commercial phosphor:Er3+ (film) | Neutral red | 23 s | 5–8.5 | Ratio of green to red UC emission | [83] |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+@NaYF4@Ni | (No dye) | N/A | 5–7.4 | Quenching and recovery of green and red UC bands | [33] |
| NaGdF4@NaYF4:Yb3+/Tm3+@NaYF4-PAA | hemicyanine | 6.8–9 | Ratio of 650 nm to 513 nm | [88] | |
| NaYF4:Er3+/Yb3+(film) | ETH 5418 | N/A | 6–11 | Ratio of UC emission bands at 656 nm to 542 nm | [84] |
| NaGdF4:Tm3+/Yb3+@NaGdF4:Nd3+/Yb3+ @NaYF4-PEI | Fluorescein | N/A | 4.7–7.4 | Ratio of dye emission at 515 nm to UC emission at 645 nm | [87] |
| pH | Intensity Ratio | Untreated Cells | Nigericin Treated Cells | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Events | % of Total Population | No. of Events | % of Total Population | ||
| 7.2–7.5 | <0.1 | 41 | 5 | 12 | 9 |
| 6.0–7.2 | 0.1–0.4 | 637 | 77 | 119 | 91 |
| <6.0 | >0.4 | 144 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahata, M.K.; Bae, H.; Lee, K.T. Upconversion Luminescence Sensitized pH-Nanoprobes. Molecules 2017, 22, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122064
Mahata MK, Bae H, Lee KT. Upconversion Luminescence Sensitized pH-Nanoprobes. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahata, Manoj Kumar, Hyeongyu Bae, and Kang Taek Lee. 2017. "Upconversion Luminescence Sensitized pH-Nanoprobes" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122064
APA StyleMahata, M. K., Bae, H., & Lee, K. T. (2017). Upconversion Luminescence Sensitized pH-Nanoprobes. Molecules, 22(12), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122064