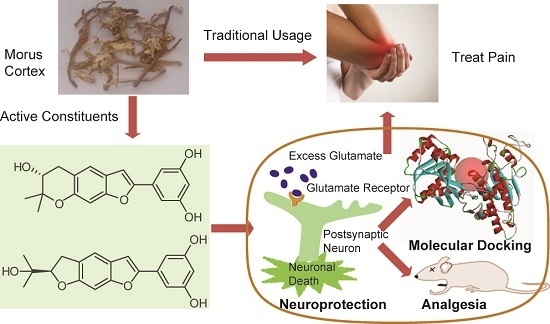
Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Analysis
2.2. Neuroprotective Activities
2.3. Postulating the Neuroprotective Pathway by Molecular Docking
2.4. Analgesic Activities
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instruments
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Animals
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
3.5. Acid Hydrolysis of Compounds 1–4
3.6. Neuroprotective Assay
3.7. Acetic Acid-Induced Abdominal Constrictions
3.8. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, G.M.; Abdel Bar, F.M.; Baraka, H.N.; Gohar, A.A.; Lahloub, M.F. A new antioxidant stilbene and other constituents from the stem bark of Morus nigra L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Gupta, G.; Afzal, M.; Kazmi, I.; Anwar, F. Antiulcer and antioxidant activities of a new steroid from Morus alba. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapche, G.D.W.F.; Amadou, D.; Waffo Teguo, P.; Donfack, J.H.; Fozing, C.D.; Harakat, D.; Tchana, A.N.; Merillon, J.M.; Moundipa, P.F.; Ngadjui, B.T.; et al. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant arylbenzofurans and flavonoids from the twigs of Morus mesozygia. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Jin, H.G.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.P. The root barks of Morus alba and the flavonoid constituents inhibit airway inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, C.; Krisa, S.; Pechamat, L.; Nassra, M.; Delaunay, J.C.; Marchal, A.; Badoc, A.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Merillon, J.M. Polyphenols from the stems of Morus alba and their inhibitory activity against nitric oxide production by lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia. Fitoterapia 2014, 97, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, H.Y.; Son, K.H.; Kwon, C.S.; Kwon, G.S.; Kang, S.S. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of 18 prenylated flavonoids isolated from medicinal plants: Morus alba L., Morus mongolica Schneider, Broussnetia papyrifera (L.) Vent, Sophora flavescens Ait and Echinosophora koreensis Nakai. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grienke, U.; Richter, M.; Walther, E.; Hoffmann, A.; Kirchmair, J.; Makarov, V.; Nietzsche, S.; Schmidtke, M.; Rollinger, J.M. Discovery of prenylated flavonoids with dual activity against influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethakamsetty, L.; Ganapaty, S.; Bharathi, K.M. Phytochemical and antimicrobial examination of the root extracts of Morus Indica. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2013, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fukai, T.; Oku, Y.; Hano, Y.; Terada, S. Antimicrobial activities of hydrophobic 2-arylbenzofurans and an isoflavone against vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.L.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, S.; Park, D.; Kim, S.H.; Um, J.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, C.H.; Jang, J.H.; et al. Morusin induces cell death through inactivating STAT3 signaling in prostate cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Yan, G.R.; Xu, Z.J.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.L.; Hou, A.J.; Wang, H.Y. Inhibitory effects of (2′R)-2′,3′-dihydro-2′-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-2,6′-bibenzofuran-6,4′-diol on mushroom tyrosinase and melanogenesis in B16-F10 melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.Y. New 2-arylbenzofurans with selective cytotoxicity from Morus wittiorum. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.R.G.D.S.; Souza, G.R.; Araujo, E.C.D.C.; Silva, F.S.; Tolentino De Lima, J.; Ribeiro, L.A.D.A.; Nunes, X.P.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; Quintans, L.J., Jr.; Viana Dos Santos, M.R. Medicinal plants and natural compounds from the genus Morus (Moraceae) with hypoglycemic activity: a review. In Glucose Tolerance; Chackrewarthy, S., Ed.; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Tan, Y.X.; Chen, R.Y.; Kang, J. The latest review on the polyphenols and their bioactivities of Chinese Morus plants. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.; Harmalkar, D.S.; Xu, X.; Jang, K.; Lee, K. Bioactive benzofuran derivatives: Moracins A-Z in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Zhang, H. Study on anti-inflammatory action and analgesic effect of single antirheumatic Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 2012, 5, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- De, M.P.M.; Vilela, F.C.; Da, S.M.J.D.; Dos, S.M.H.; Alves da Silva, G.; Giusti Paiva, A. Antinociceptive effect of the extract of Morus nigra leaves in mice. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.T.; Xie, T.B.; Lin, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of total flavonoids in Cortex Mori. Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao 2013, 24, 2580–2582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, L. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of cis-mulberroside A from Ramulus mori. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, M.M.; Bittar, M.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Yunes, R.A.; Messana, I.; Delle Monache, F.; Ferrari, F. Antinociceptive properties of morusin, a prenylflavonoid isolated from Morus nigra root bark. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2000, 55, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoni, R. Role of presynaptic glutamate receptors in pain transmission at the spinal cord level. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleakman, D.; Alt, A.; Nisenbaum, E.S. Glutamate receptors and pain. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 17, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C. Neuroprotective phenolics in medicinal plants. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1611–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossio Mora, F.P.; Arias Echeverria, L.L.; Vara Salazar, Y.I.; Aldaba Arevalo, E.; San Sebastian Larzabal, E.; Zubia Olascoaga, A. Polysubstituted Benzofurans and Medicinal Applications Thereof. European Patent 2388255A1, 23 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Yum, J.H.; Rho, Y.K.; Oh, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Chang, H.B.; Choi, D.H.; Leem, M.-J.; Choi, E.J.; Ryu, J.M.; et al. Inhibition of HCV replicon cell growth by 2-arylbenzofuran derivatives isolated from Mori Cortex Radicis. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.G.; Yu, D.Q.; Lu, Z.M.; Chen, R.Y. Isolation and identification of phenolic compounds from Morus macroura Miq. Zhongguo Yaowu Huaxue Zazhi 2006, 16, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kapche, G.D.W.F.; Fozing, C.D.; Donfack, J.H.; Fotso, G.W.; Amadou, D.; Tchana, A.N.; Bezabih, M.; Moundipa, P.F.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Abegaz, B.M. Prenylated arylbenzofuran derivatives from Morus mesozygia with antioxidant activity. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.Y. 2-arylbenzofuran derivatives from Morus wittiorum. Yaoxue Xuebao 2008, 43, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, C.A.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Yao, S.Y.; Xue, D.Q.; Zhang, R.P.; Chen, J.J. Mulberrofuran G and Isomulberrofuran G from Morus alba L.: Anti-hepatitis B Virus Activity and Mass Spectrometric Fragmentation. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2012, 60, 8197–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukai, T.; Hano, Y.; Hirakura, K.; Nomura, T.; Uzawa, J.; Fukushima, K. Constituents of the cultivated mulberry tree. XXV. Constituents of root bark of Morus lhou Koidz. V. Structures of two natural hypotensive Diels-Alder type adducts, mulberrofurans F and G, from the cultivated mulberry tree (Morus lhou Koidz.). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Ryu, Y.B.; Curtis Long, M.J.; Ryu, H.W.; Baek, Y.S.; Kang, J.E.; Lee, W.S.; Park, K.H. Tyrosinase inhibitory polyphenols from roots of Morus lhou. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2009, 57, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Maham, M.; Salaryan, P.; Enayati, A.; Sajjadi, S.A.; Naderi, K. Optimal extraction method of phenolics from the root of Euphorbia condylocarpa. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2011, 47, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.D.; Nemec, J.; Ning, B.M. Anti-HIV flavonoids from Morus alba. Yunnan Zhiwu Yanjiu 1995, 17, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, T.; Fukai, T.; Hano, Y.; Uzawa, J. Structure of sanggenon C, a natural hypotensive Diels-Alder adduct from Chinese crude drug “Sang-Bai-Pi” (Morus root barks). Heterocycles 1981, 16, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Fukai, T.; Hano, Y.; Uzawa, J. Structure of sanggenon D, a natural hypotensive Diels-Alder adduct from Chinese crude drug “Sang-Bai-Pi” (Morus root barks). Heterocycles 1982, 17, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.; Zhang, Q.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, R.Y.; Zheng, Z.F.; Yu, D.Q. Chemical constituents of the stem bark of Morus cathayana. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.K. NMR Spectroscopy in the structural elucidation of oligosaccharides and glycosides. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3307–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat, N.T.; Jin, X.; Lee, K.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibitory benzofurans and chalcone-derived Diels-Alder adducts from Morus species. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Xia, Y.; Jin, Y.; Dat, N.T.; Gajulapati, K.; Choi, Y.; Hong, Y.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, K. The first total synthesis of moracin O and moracin P, and establishment of the absolute configuration of moracin O. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1879–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lyu, D.H.; Koo, U.; Lee, S.J.; Hong, S.S.; Kim, K.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.; Mar, W. Inhibitory effect of 2-arylbenzofurans from the Mori Cortex Radicis (Moraceae) on oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell death of SH-SY5Y cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiechio, S.; Nicoletti, F. Metabotropic glutamate receptors and the control of chronic pain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Robertson, D.H.; Brooks, C.L., III; Vieth, M. Detailed analysis of grid-based molecular docking: A case study of CDOCKER-A CHARMm-based MD docking algorithm. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koska, J.; Spassov, V.Z.; Maynard, A.J.; Yan, L.; Austin, N.; Flook, P.K.; Venkatachalam, C.M. Fully automated molecular mechanics based induced fit protein−ligand docking method. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.W.; Ko, W.M.; Park, J.H.; Seo, K.H.; Oh, E.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Lim, D.W.; Han, D.; et al. Isoprenylated flavonoids from the root bark of Morus alba and their hepatoprotective and neuroprotective activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.



| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7.17 s | 7.07 s | 7.15 s | 7.07 s |
| 4 | 7.29 s | 7.30 s | 7.27 s | 7.34 s |
| 7 | 6.93 s | 6.94 s | 6.92 s | 6.98 s |
| 8 | 3.02 dd (16.4, 6.0), 2.72 dd (16.4, 7.0) | 3.14 m b, 2.83 dd (16.6, 6.7) | 3.01 dd (16.5, 5.2), 2.70 dd (16.5, 8.1) | 3.16 m c, 3.35 m * |
| 9 | 3.67 dd (7.0, 6.0) | 3.95 dd (6.7, 5.9) | 3.66 dd (8.1, 5.2) | 4.75 t (8.8) |
| 11 | 1.31 s | 1.34 s | 1.31 s | 1.28 s |
| 12 | 1.18 s | 1.24 s | 1.18 s | 1.21 s |
| 2′ | 6.91 d (2.1) | 6.68 d (1.5) | 6.96 br s | 6.67 d (2.0) |
| 4′ | 6.43 t (2.1) | 6.21 t (1.5) | 6.44 br s | 6.21 t (2.0) |
| 6′ | 6.89 d (2.1) | 6.68 d (1.5) | 6.88 br s | 6.67 d (2.0) |
| 1″ | 4.85 d (6.7) | 4.33 d (7.7) | 4.83 d (7.6) | 4.42 d (7.8) |
| 2″ | 3.60 m a | 2.94 dd (8.0, 7.7) | 3.22 t (7.6) | 2.88 t (8.2) |
| 3″ | 3.49 dd (8.5, 3.2) | 3.14 m b | 3.27 t (8.5) | 3.16 m c |
| 4″ | 3.70 brs | 3.03 t (9.1) | 3.16 t (9.0) | 3.04 t (8.0) d |
| 5″ | 3.60 dd (11.2, 1.5) a, 3.75 dd (11.2, 3.2) | 3.14 m b | 3.35 m * | 3.04 d (8.0) d |
| 6″ | ---- | 3.68 br d (11.3), 3.43 dd (11.3, 6.2) | 3.71 br.d (11.4), 3.48 m | 3.35 m *, 3.45 br.d (11.3) |
| Position | 1 a | 2 b | 3 | 4 | Position | 1 a | 2 b | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 154.0 | 153.8 | 154.1 | 154.2 | 1′ | 131.5 | 131.5 | 131.6 | 131.6 |
| 3 | 101.8 | 101.1 | 101.7 | 101.7 | 2′ | 103.4 | 102.4 | 103.5 | 102.2 |
| 3a | 121.9 | 122.2 | 122.0 | 122.0 | 3′ | 158.8 | 158.8 | 159.1 | 158.8 |
| 4 | 120.9 | 121.0 | 120.9 | 116.1 | 4′ | 103.9 | 102.8 | 103.8 | 102.6 |
| 5 | 117.2 | 116.5 | 117.2 | 124.3 | 5′ | 158.8 | 158.8 | 158.8 | 158.8 |
| 6 | 151.2 | 150.8 | 151.2 | 158.1 | 6′ | 104.8 | 102.4 | 104.8 | 102.2 |
| 7 | 98.4 | 98.5 | 98.4 | 92.3 | 1″ | 100.8 | 100.2 | 100.8 | 97.4 |
| 7a | 153.8 | 154.6 | 153.9 | 154.2 | 2″ | 72.4 | 73.8 | 73.3 | 73.5 |
| 8 | 31.2 | 27.6 | 31.3 | 29.8 | 3″ | 70.3 | 77.0 | 76.6 | 77.0 |
| 9 | 67.4 | 73.4 | 68.1 | 88.9 | 4″ | 68.0 | 70.3 | 69.7 | 70.1 |
| 10 | 77.3 | 76.3 | 77.3 | 77.1 | 5″ | 65.5 | 77.0 | 77.1 | 76.6 |
| 11 | 25.8 | 25.8 | 25.8 | 23.4 | 6″ | 61.4 | 60.7 | 60.9 | |
| 12 | 20.3 | 21.3 | 20.4 | 21.8 |
| Compounds | Cell Viability (%) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Injured reagent | l-Glu b | Na2S2O4 c | 3-NP c |
| Control | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Injured control | 0.0 ###,d | 0.0 ###,e | 0.0 ###,f |
| Moracin P 3’-O-α-l-arabinopyranoside (1) | −5.0 ± 2.6 | −0.4 ± 1.3 | ---- |
| Moracin P 9-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (2) | −2.0 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 1.34 | ---- |
| Moracin P 3’-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (3) | 1.9 ± 3.3 | 7.1 ± 2.52 | ---- |
| Moracin O 10-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (4) | −4.4 ± 0.4 | −1.4 ± 0.5 | ---- |
| Moracin O (5) | 56.0 ± 5.1 ** | 12.4 ± 1.5 | ---- |
| Oxyresveratrol (6) | 12.7 ± 5.4 | ---- | ---- |
| Moracin R (7) | 50.0 ± 4.5 ** | 0.9 ± 1.4 | −3.3 ± 2.6 |
| Moracin P (8) | 40.1 ± 4.4 * | 9.0 ± 2.1 | 0.3 ± 3.8 |
| Mulberroside C (9) | −6.0 ± 2.0 | 0.0 ± 2.1 | ---- |
| Norartocarpetin (13) | 21.7 ± 3.9 | ---- | ---- |
| Morusin (15) | 20.2 ± 4.8 | ---- | ---- |
| Sanggenon C (16) | 13.5 ± 4.4 | ---- | ---- |
| Resveratrol g | 12.0 ± 2.4 | ---- | ---- |
| Samples | Dosage (mg/kg, i.p.) | Mean Numbers of Writhes ± SD | Inhibition Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 | 17 ± 6 | ---- |
| Moracin O (5) | 80 | 0 ± 1 * | 98% |
| Moracin R (7) | 80 | 5 ± 3 * | 76% |
| Moracin P (8) | 80 | 1 ± 1 * | 95% |
| Morusin (15) | 80 | 1 ± 1 * | 95% |
| Paracetamol | 200 | 1 ± 1 * | 95% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, M.-F.; Hou, W.-Z.; Xu, R.-M.; Gao, J.; Lu, A.-Q.; Xie, M.-P.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.-J.; Peng, Y.; et al. Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR1. Molecules 2017, 22, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020236
Wang Y-N, Liu M-F, Hou W-Z, Xu R-M, Gao J, Lu A-Q, Xie M-P, Li L, Zhang J-J, Peng Y, et al. Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR1. Molecules. 2017; 22(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ya-Nan, Mao-Feng Liu, Wei-Zhen Hou, Rui-Ming Xu, Jie Gao, An-Qi Lu, Mei-Ping Xie, Lan Li, Jian-Jun Zhang, Ying Peng, and et al. 2017. "Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR1" Molecules 22, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020236
APA StyleWang, Y. -N., Liu, M. -F., Hou, W. -Z., Xu, R. -M., Gao, J., Lu, A. -Q., Xie, M. -P., Li, L., Zhang, J. -J., Peng, Y., Ma, L. -L., Wang, X. -L., Shi, J. -G., & Wang, S. -J. (2017). Bioactive Benzofuran Derivatives from Cortex Mori Radicis, and Their Neuroprotective and Analgesic Activities Mediated by mGluR1. Molecules, 22(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020236