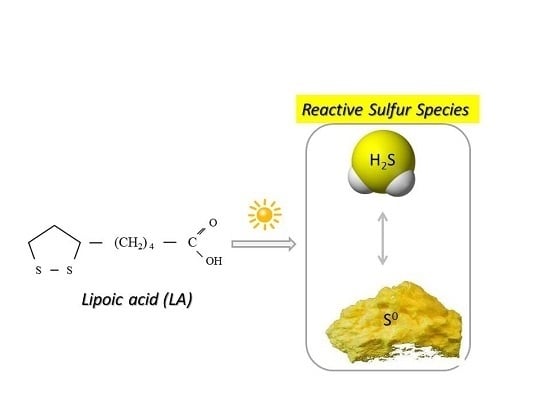
Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Homogenate Preparation
2.3. Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfane Sulfur Formation from Lipoic Acid
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Determination of H2S Level
2.4.2. Determination of Sulfane Sulfur
2.4.3. Determination of H2S by Diffusion Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogen Sulfide Formation from Lipoic Acid
3.2. Sulfane Sulfur Formation from Lipoic Acid
3.3. pH- and Time-Dependent H2S Formation from Lipoic Acid Detected by Diffusion Assay
3.4. Time-Dependent Sulfane Sulfur Formation from Lipoic Acid in the Presence or Absence of EDTA
3.5. H2S and Sulfane Sulfur Formation from Lipoic Acid or Dihydrolipoic Acid in the Presence of Rat Liver or Kidney Homogenate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, L.J.; DeBusk, B.G.; Gunsalus, I.C.; Hornberger, C.S. Crystalline α-lipoic acid: A catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science 1951, 114, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen Shay, K.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitner, H. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double blind study on the clinical efficacy of a cream containing 5% α-lipoic acid related to photoageing of facial skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakici, N.; Fakkel, T.M.; van Neck, J.W.; Verhagen, A.P.; Coert, J.H. Systematic review of treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilska, A.; Dubiel, M.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Włodek, L. Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcykiewicz, B.; Wiśniowski, Z.; Iciek, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Górny, M.; Włodek, L.; Książek, P. The effects of lipoic acid supplementation on the estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nefrol. Dial. Pol. 2016, 20, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, M.; Bednarski, M.; Bilska, A.; Iciek, M.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. The role of lipoic acid in prevention of nitroglycerin tolerance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Dudek, M.; Knutelska, J.; Włodek, L. The effect of lipoic acid administration on the urinary excretion of thiocyanate in rats exposed to potassium cyanide. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2015, 72, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sokołowska, M.; Niedzielska, E.; Iciek, M.; Bilska, A.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Włodek, L. The effect of the uremic toxin cyanate (CNO−) on anaerobic cysteine metabolism and oxidative processes in the rat liver: A protective effect of lipoate. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 21, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biewenga, G.P.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1997, 29, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Witt, E.H.; Tritschler, H.J. Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Włodek, L. Lipoic acid - the drug of the future? Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petersen Shay, K.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Hagen, T.M. Is α-lipoic acid a scavenger of reactive oxygen species in vivo? Evidence for its initiation of stress signaling pathways that promote endogenous antioxidant capacity. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilska, A.; Dudek, M.; Iciek, M.; Kwiecień, I.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. Biological actions of lipoic acid associated with sulfane sulfur metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iciek, M.; Marcykiewicz, B.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Kłapcińska, J. The effect of lipoate on anaerobic cysteine metabolism in erythrocytes of patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmunt, M.; Dudek, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Bednarski, M.; Mogilski, S.; Knutelska, J.; Sapa, J. Anti-inflammatory activity of lipoic acid in mice peritonitis model. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Knutelska, J.; Mogilski, S.; Bednarski, M.; Zygmunt, M.; Iciek, M.; Sapa, J.; Bugajski, D.; Filipek, B.; Włodek, L. Are anti-inflammatory properties of lipoic acid associated with the formation of hydrogen sulfide? Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Knutelska, J.; Bednarski, M.; Nowiński, L.; Zygmunt, M.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Otto, M.; Żytka, I.; Sapa, J.; et al. Alpha lipoic acid protects the heart against myocardial post ischemia-reperfusion arrhythmias via KATP channel activation in isolated rat hearts. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Raźny, K.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Sapa, J.; Włodek, L.; Filipek, B. Hypotensive effect of alpha-lipoic acid after a single administration in rats. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2016, 16, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.Z.; Hayon, E. One-electron reduction of the disulfide linkage in aqueous solution. Formation, protonation, and decay kinetics of the RSSR-radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 7950–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezyk, S.P. Rate constant determination for the reaction of sulfhydryl species with the hydrated electron in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 1995, 99, 13970–13975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.R.; Edwards, J.O. Effect of solvent on the photolysis of α-lipoic acid. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34, 3131–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsugo, S.; Han, D.; Tritschler, H.J.; Packer, L. Decomposition of alpha-lipoic acid derivatives by photoirradiation-formation of dihydrolipoic acid from alpha-lipoic acid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1996, 38, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wada, N.; Wakami, H.; Konishi, T.; Matsugo, S. The effect of biothiol on UV irradiated α-lipoic acid. Biofactors 2008, 34, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, N.; Wakami, H.; Konishi, T.; Matsugo, S. The degradation and regeneration of α-lipoic acid under the irradiation of UV light in the existence of homocysteine. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 44, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R. Lipoic acid: A multifunctional antioxidant. Biofactors 2003, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Pattillo, C.B.; Pardue, S.; Bir, S.C.; Wang, R.; Kevil, C.G. Measurement of plasma hydrogen sulfide in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.L. Sulfane sulfur. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 143, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toohey, J.I. Ketomethylthiobutyric acid formation from methylthioadenosine: A diffusion assay. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 223, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morine, G.H.; Kuntz, R.R. Observations of C-S and S-S bond cleavage in the photolysis of disulfides in solution. Photochem. Photobiol. 1981, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, C.V.; Garnett, M. Electrochemical behavior of the super antioxidant, α-lipoic acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 3607–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, G.; Lu, C.; Sander, W. The photochemistry of lipoic acid: Photoionization and observation of a triplet excited state of a disulfide. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2005, 6, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toohey, J.I. Sulfur signaling: Is the agent sulfide or sulfane? Anal. Biochem. 2011, 413, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Kwiecień, I.; Górny, M.; Włodek, L. S-sulfhydration as a cellular redox regulation. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, S.; Ogasawara, Y. Sulfur Atom in its Bound State Is a Unique Element Involved in Physiological Functions in Mammals. Molecules 2016, 21, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, H.; Orion, E.; Wolf, R. Balneotherapy in dermatology. Dermatol. Ther. 2003, 16, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Komy, M.; Shalaby, S.; Hegazy, R.; Abdel Hay, R.; Sherif, S.; Bendas, E. Assessment of cubosomal alpha lipoic acid gel efficacy for the aging face: A single-blinded, placebo-controlled, right-left comparative clinical study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, P.S.; Balogh, B.; Pinney, A.J.; Zakhem, G.; Lozier, A.; Amin, M.A.; Stinson, W.A.; Schiopu, E.; Khanna, D.; Fox, D.A.; et al. Lipoic acid plays a role in scleroderma: Insights obtained from scleroderma dermal fibroblasts. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Gao, L.; Feng, S.; Song, K.; Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Shen, H. The protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on systemic sclerosis associated skin and lung fibrosis in mice model. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, N.; Okazaki, T.; Nishino, T. Cytosolic metcaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase is evolutionary related to mitochondrial rhodanese. Striking similarity in active site amino acid sequence and the increase in the mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase activity of rhodanese by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16230–16235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villarejo, M.; Westley, J. Mechanism of rhodanese catalysis of thiosulfate-lipoate oxidation-reduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 4016–4020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volini, M.; Westley, J. The mechanism of the rhodanese-catalyzed thiosulfate-lipoate reaction. Kinetic analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 5168–5176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mikami, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Kimura, Y.; Nagahara, N.; Ogasawara, Y.; Kimura, H. Thioredoxin and dihydrolipoic acid are required for 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase to produce hydrogen sulfide. Biochem. J. 2011, 439, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not available.






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Górny, M.; Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M.; Włodek, L. Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur. Molecules 2017, 22, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030388
Bilska-Wilkosz A, Iciek M, Kowalczyk-Pachel D, Górny M, Sokołowska-Jeżewicz M, Włodek L. Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030388
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilska-Wilkosz, Anna, Małgorzata Iciek, Danuta Kowalczyk-Pachel, Magdalena Górny, Maria Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, and Lidia Włodek. 2017. "Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur" Molecules 22, no. 3: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030388
APA StyleBilska-Wilkosz, A., Iciek, M., Kowalczyk-Pachel, D., Górny, M., Sokołowska-Jeżewicz, M., & Włodek, L. (2017). Lipoic Acid as a Possible Pharmacological Source of Hydrogen Sulfide/Sulfane Sulfur. Molecules, 22(3), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030388