Isolation and Identification of the Five Novel Flavonoids from Genipa americana Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction and TLC Analysis
2.2. UHPLC-DAD Characterization
2.3. HPLC-ESI-IT-MS/MS Characterization
2.4. Isolation of Major Compounds
2.5. Identification of the Isolated Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Extraction and TLC Characterization
3.3. UHPLC Characterization
3.4. HPLC-ESI-IT-MS/MS Characterization
3.5. Isolation of Major Compounds
3.6. Preparative HPLC Optimization and Analyses
3.7. MS/MS of Isolated Compounds
3.8. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) of Isolated Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbosa, M.R.; Zappi, D.; Taylor, C.; Cabral, E.; Jardim, J.G.; Pereira, M.S.; Calió, M.F.; Pessoa, M.C.R.; Salas, R.; Souza, E.B.; et al. Rubiaceae em Flora do Brasil 2020 em construção.Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro. Available online: http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/jabot/FichaPublicaTaxonUC/FichaPublicaTaxonUC.do?id=FB14045 (accessed on 8 March 2018).
- Martins, D.; Nunez, C.V. Secondary metabolites from rubiaceae species. Molecules 2015, 20, 13422–13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, O.A.; Couceiro, S.R.M.; Rezende, A.C.C.; Silva, M.D.S. Composition and richness of woody species in riparian forests in urban areas of Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. Landsc. Urban Plan 2016, 150, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Iwahashi, Y. Production of anti-tumor-promoting iridoid glucosides in Genipa americana and its cell cultures. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappi, D. Genipa in Lista de Espécies da Flora do Brasil. Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro. Available online: http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/jabot/floradobrasil/FB14045 (accessed on 22 November 2017).
- Almeida, E.R.; Almeida, E.; Almeida, E. Plantas Medicinais Brasileiras: Conhecimentos Populares e Científicos; Hemus: São Paulo, Brasil, 1993; pp. 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, R.P. Fruticultura Brasileira; Nobel: São Paulo, Brasil, 1982; pp. 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Agra, M.F.; Silva, K.N.; Basílio, I.J.L.D.; de Freitas, P.F.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M. Survey of medicinal plants used in the region Northeast of Brazil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2008, 18, 472–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mors, W.B.; Rizzini, C.T.; Pereira, N. Medicinal Plants of Brazil; Reference Publications, Inc.: Algonac, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Delprete, P.G.; Smith, L.B.; Klein, R.M. Rubiáceas. In Flora Ilustrada Catarinense; Reis, A., Ed.; Herbário Barbosa Rodrigues: Itajaí, Santa Catarina, Brizal, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.J.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, B.C.; Jin, C.; Lim, C.J.; Park, E.H. Antiinflammatory effects of genipin, an active principle of gardenia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 495, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.C.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, S.A.; Lim, S.; Park, E.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lim, C.J. Genipin-induced apoptosis in hepatoma cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species/c-Jun NH 2-terminal kinase dependent activation of mitochondrial pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, F.A.; Nery, P.S.; Morais-Costa, F.; de Faria Oliveira, N.J.; Martins, E.R.; Duarte, E.R. Efficacy of aqueous extracts of Genipa americana L. (Rubiaceae) in inhibiting larval development and eclosion of gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2014, 42, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, P.M.; De Salesi, P.M.; Simeoni, L.A.; Silva, E.C.; Silveira, D.; Magalhães, P.O. Inhibitory activity of α-amylase and α-glucosidase by plant extracts from the Brazilian cerrado. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonato, D.T.T.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Mota, M.R.L.; de Barros Silva, P.G.; Cunha, A.P.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Pereira, M.G.; Assreuy, A.M.S.; Chaves, E.M.C. The anticonvulsant effect of a polysaccharide-rich extract from Genipa americana leaves is mediated by GABA receptor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Ishimatsu, N.; Masuoka, C.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Okawa, M.; Kinjo, J.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T. Three new monoterpenoids from the fruit of Genipa americana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bentes, A.S.; Mercadante, A.Z. Influence of the stage of ripeness on the composition of iridoids and phenolic compounds in genipap (Genipa americana L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djerassi, C.; Gray, J.D.; Kincl, F. Isolation and characterization of genipin. J. Org. Chem. 1960, 25, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Ueno, M.; Masouka, C.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T. Iridoid glucosides from the fruit of Genipa americana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1342–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallent, W.H. Two new antibiotic cyclopentanoid monoterpenes of plant origin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1964, 20, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsua, H.; Yang, J.; Lin, S.; Linb, C. Comparisons of geniposidic acid and geniposide on antitumor and radioprotection after sublethal irradiation. Cancer Lett. 1997, 113, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnaccia, R.; Madyastha, K.M.; Tegtmeyer, E.; Coscia, C.J. Geniposidic acid, an iridoid glucoside from Genipa americana. Tetrahedron Lett. 1972, 50, 5125–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, C.F.; Jacob, M.R.; Clark, A.M.; Walker, L.A.; Nagle, D.G. Genipatriol, a new cycloartane triterpene from Genipa spruceana. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, J.S.F.; Medeiros, L.A.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Araújo, R.M.; Zucolotto, S.M. Iridoids from leaf extract of Genipa americana. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, R.E.; Miao, X.-S.; Metcalfe, C.D. A fragmentation study of a flavone triglycoside, kaempferol-3-O-robinoside-7-O-rhamnoside. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Bladt, S. Plant Drug Analysis: A Thin Layer Chromatography Atlas; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Omena, C.M.B.; Valentim, I.V.; Guedes, G.S.; Rabelo, L.A.; Mano, C.M.; Bechara, E.J.H.; Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; Trevisan, M.T.S.; Da Costa, J.G.; Ferreira, R.C.S.; et al. Antioxidant, anti-acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activities of ethanol extracts of peel, pulp and seeds of exotic Brazilian fruits. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroda, K.; Yagami, S.; Takama, R.; Fukushima, K. Distribution of coniferin in freeze-fixed stem of Ginkgo biloba L. by cryo-TOF-SIMS/SEM. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, H.; Jensen, S.R.; Nielsen, B.J. Iridoid glucosides from Asystasia bella. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3361–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, F.; Mao, C.; Li, L.; Cai, B.; Lu, T. Quality control and producing areas differentiation of Gardeniae Fructus for eight bioactive constituents by HPLC–DAD–ESI/MS. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xue, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C. Fragmentation patterns study of iridoid glycosides in Fructus Gardeniae by HPLC-Q/TOF-MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choze, R.; Delprete, P.G.; Lião, L.M. Chemotaxonomic significance of flavonoids, coumarins and triterpenes of Augusta longifolia (Spreng.) Rehder, Rubiaceae-Ixoroideae, with new insights about its systematic position within the family. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2010, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchen, J.; Bortl, L.; Huml, L.; Miksatkova, P.; Doskocil, I.; Marsik, P.; Villegas, P.P.P.; Flores, Y.B.; Damme, P.V.; Lojka, B.; et al. Phenolic composition, antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities of edible and medicinal plants from the Peruvian Amazon. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, W.K.; Omar, A.A.; Christensen, S.B. Isorhamnetin3-(2,6-dirhamnosylgalactoside)-7-rhamnoside and 3-(6-rhamnosylgalactoside)-7-rhamnoside from Rhazya stricta. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lo, R. Phenolic Compounds from the Leaf Extract of Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and Their Antimicrobial Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7272–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochado, C.D.O.; Almeida, A.P.; Barreto, B.P.; Costa, L.P.; Ribeiro, L.S.; Pereira, R.L.C.; Koatz, V.L.G.; Costa, S.S. Flavonol robinobiosides and rutinosides from Alternanthera brasiliana (Amaranthaceae) and their effects on lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, T.; Angenot, L. Six flavonol glycosides from leaves of Strychnos variabilis. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschi, C.A.; Pomilio, A.B. Isorhamnetin 3-O-robinobioside from Gomphrena martiana. J. Nat. Prod. 1982, 45, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, A.F.; Saad, H.E.A.; Hashish, N.E. Flavonol glycosides from Nitraria retusa. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Ahmed, I.; Jay, M.; Voirin, B. Flavonoid glycosides and an anthraquinone from Rumex chalepensis. Phytochemistry 1995, 39, 1211–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaouadji, M. Flavonol diglycosides from Blackstonia perfoliata. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.-C.; Lin, R.-D.; Lee, T.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Hsu, F.-L.; Lee, M.-H. The phenolic constituents and free radical scavenging activities of Gynura formosana Kiamnra. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos-Olea, R.S.; Borges, M.O.R.; Borges, A.C.R.; Freire, S.M.F.; Silveira, L.M.S.; Vilegas, W.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Oliveira, A.V.; Costa, J.L. Flavonoides de Calotropis procera R. Br. (Asclepiadaceae). Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2008, 10, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiklauri, L.K.; An, G.; Alania, M.D.; Kemertelidze, E.P.; Morris, M.E. Optimum HPLC parameters for simultaneous determination of robinin and kaempferol. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, N.C.; Elliott, P.C.; Kite, G.C.; Lewis, G.P. Flavonoid glycosides of the black locust tree, Robinia pseudoacacia (Leguminosae). Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asres, K.; Eder, U.; Bucar, F. Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity of extracts and compounds from the leaves of Melilotus elegans. Ethiop. Pharm. J. 2000, 18, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ghareeb, M.A.; Shoeb, H.A.; Madkour, H.M.F.; Refahy, L.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Saad, A.M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of flavonoidal compounds from Gmelina arborea Roxb. Global J. Pharm. 2014, 8, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, J.; Sghaier, M.B.; Skandrani, I.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. Isorhamnetin 3-O-robinobioside from Nitraria retusa leaves enhance antioxidant and antigenotoxic activity in human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
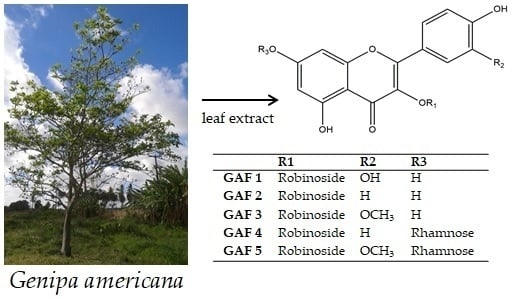
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds GAF 1, GAF 2, GAF 3, GAF 4 and GAF 5 are available from the authors. |


| R1 (position 3′) | R2 (position 2′′) | R3 (position 7′) | |
| GAF 1 | Robinoside | OH | H |
| GAF 2 | Robinoside | H | H |
| GAF 3 | Robinoside | OCH3 | H |
| GAF 4 | Robinoside | H | Rhamnose |
| GAF 5 | Robinoside | OCH3 | Rhamnose |
| Peak nº | Rt (min) | m/z | m/z MS2 | m/z MS3 | LC-DAD | Molecular Formula | Compound (MM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pos/Neg | Pos/Neg | Pos/Neg | λmax [nm] | ||||
| 1 | 5.2 a | -/342 | -/179 | -/- | - | C16H22O8 | Coniferin (342) |
| 2 | 24 b | 559/535, 571- | -/535 | 373, 210 | - | C22H32O15 | Asystasioside D (536) |
| 3 | 25.1 a | 397/373, 409 | 379, 217/210 | 172/166, 148, 122 | - | C16H22O10 | Geniposidic acid (374) |
| 4 | 26.1 a | -/357, 393 | -/194 | -/- | - | C16H25O9 | Tarenoside (358) |
| 5 | 26.9 b | -/375 | -/213 | -/169, 125 | - | C16H24O10 | Loganic acid (376) |
| 6 | 33.4 a,b | 355/353 | 162/190 | -/- | C16H18O9 | Chlorogenic acid (354) | |
| 7 | 48.8 a,b,c | 741/739- | 595/593 | 433, 287/285 | 266, 346 | C33H39O20 | Kaempferol-3-O-hexoside-deoxyhexoside-7-O-deoxyhexoside (740) |
| 8 | 50.1 a,b | 771/769 | 625, 463/623 | 317/315 | 255, 354 | C34H42O21 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-hexoside-deoxyhexoside-7-O-deoxyhexoside (770) |
| 9 | 51.4 a,b | 611/609- | 465/301 | 303/- | 255, 366 | C27H30O16 | Quercetin-3-O-hexoside-deoxyhexoside (610) |
| 10 | 51.7 b | -/515 | -/353, 190, 178 | -/- | - | C25H24O12 | 1,3-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (516) |
| 11 | 52 | 519, 373, 211/517, 371- | -/- | -/- | - | C22H30O14 | Teneoside A (518) |
| 12 | 53.9 a,b | 595/593 | 2834.7/449, 288 | -/- | 265, 355 | C27H30O16 | Kaempferol-3-O-hexoside-deoxyhexoside (594) |
| 13 | 55.2 a,b | 625/623 | 479/315 | 317/- | 255, 370 | C28H33O16 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-hexoside-deoxyhexoside (624) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, L.M.P.; Alves, J.S.F.; Da Silva Siqueira, E.M.; De Souza Neto, M.A.; Abreu, L.S.; Tavares, J.F.; Porto, D.L.; De Santis Ferreira, L.; Demarque, D.P.; Lopes, N.P.; et al. Isolation and Identification of the Five Novel Flavonoids from Genipa americana Leaves. Molecules 2018, 23, 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102521
Silva LMP, Alves JSF, Da Silva Siqueira EM, De Souza Neto MA, Abreu LS, Tavares JF, Porto DL, De Santis Ferreira L, Demarque DP, Lopes NP, et al. Isolation and Identification of the Five Novel Flavonoids from Genipa americana Leaves. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102521
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Larissa Marina Pereira, Jovelina Samara Ferreira Alves, Emerson Michell Da Silva Siqueira, Manoel André De Souza Neto, Lucas Silva Abreu, Josean Fechine Tavares, Dayanne Lopes Porto, Leandro De Santis Ferreira, Daniel Pecoraro Demarque, Norberto Peporine Lopes, and et al. 2018. "Isolation and Identification of the Five Novel Flavonoids from Genipa americana Leaves" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102521
APA StyleSilva, L. M. P., Alves, J. S. F., Da Silva Siqueira, E. M., De Souza Neto, M. A., Abreu, L. S., Tavares, J. F., Porto, D. L., De Santis Ferreira, L., Demarque, D. P., Lopes, N. P., Aragão, C. F. S., & Zucolotto, S. M. (2018). Isolation and Identification of the Five Novel Flavonoids from Genipa americana Leaves. Molecules, 23(10), 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102521