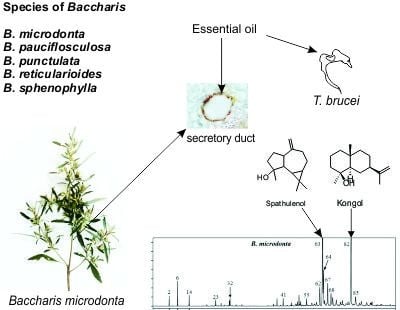
Essential Oils of Five Baccharis Species: Investigations on the Chemical Composition and Biological Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Yield and Chemical Composition of Essential Oils
2.2. Antimalarial Activity
2.3. Antitrypanosomal Activity
2.4. Insecticidal Studies with Bed Bugs
2.5. Secretory Structures
2.6. Identification of the Samples by DNA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Extraction of Essential Oil (EO)
3.3. Chemicals
3.4. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) Analysis
3.5. Antimalarial Activity
3.6. Antitrypanosomal Activity
3.7. Insecticidal Studies against Bed Bugs
3.8. Microscopic Procedure
3.9. DNA Extraction, PCR, Sequencing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heiden, G.; Schneider, A. Baccharis. In Lista de Espécies da Flora do Brasil; Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Budel, J.M.; Matzenbacher, N.I.; Duarte, M.R. Genus Baccharis (Asteraceae): A Review of Chemical and Pharmacological Studies; Studium Press LLC: Houston, TX, USA, 2008; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos Campos, F.; Bressan, J.; Godoy Jasinski, V.C.; Zuccolotto, T.; da Silva, L.E.; Bonancio Cerqueira, L. Baccharis (Asteraceae): Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budel, J.M.; Raman, V.; Monteiro, L.M.; Almeida, V.P.; Bobek, V.B.; Heiden, G.; Takeda, I.J.M.; Khan, I.A. Foliar anatomy and microscopy of six Brazilian species of Baccharis (Asteraceae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, M.J.; Bermejo, P. Baccharis (Compositae): A review update. Arkivoc 2007, 7, 76–96. [Google Scholar]
- Simões-Pires, C.A.; Debenedetti, S.; Spegazzini, E.; Mentz, L.A.; Matzenbacher, N.I.; Limberger, R.P.; Henriques, A.T. Investigation of the essential oil from eight species of Baccharis belonging to sect. Caulopterae (Asteraceae, Astereae): A taxonomic approach. Plant Syst. Evol. 2005, 253, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budel, J.M.; Duarte, M.R.; Döll-Boscardin, P.M.; Farago, P.V.; Matzenbacher, N.I.; Sartoratto, A.; Sales Maia, B.H.L.N. Composition of essential oils and secretory structures of Baccharis anomala, B. megapotamica and B. ochracea. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retta, D.; Gattuso, M.; Gattuso, S.; Di Leo Lira, P.; van Baren, C.; Bandoni, A. Volatile constituents of five Baccharis Species from Northeastern Argentina. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreiros, M.O.; Pawlowski, Â.; Zini, C.A.; Soares, G.L.G.; Motta, A.S.; Frazzon, A.P.G. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of Baccharis psiadioides essential oil against antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecalis strains. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, W.H.; Bizzo, H.R.; Gama, P.E.; Alviano, C.S.; Salimena, F.R.G.; Alviano, D.S.; Leitão, S.G. Essential oil constituents from high altitude Brazilian species with antimicrobial activity: Baccharis parvidentata Malag., Hyptis monticola Mart. ex Benth. and Lippia origanoides Kunth. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2017, 29, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florão, A.; Budel, J.M.; Duarte, M.R.; Marcondes, A.; Rodrigues, R.A.F.; Rodrigues, M.V.N.; Santos, C.A.M.; Weffort-Santos, A.M. Essential oils from Baccharis species (Asteraceae) have anti-inflammatory effects for human cells. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarezo, E.; Rosales, J.; Morocho, V.; Cartuche, L.; Guaya, D.; Ojeda-Riascos, S.; Armijos, C.; González, S. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil of Baccharis obtusifolia Kunth from Loja, Ecuador. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2015, 27, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho, A.C.N.; de Souza, E.B.; Rocha, M.F.G.; Albuquerque, M.R.J.R.; Bandeira, P.N.; dos Santos, H.S.; de Paula Cavalcante, C.S.; Oliveira, S.S.; Aragão, P.R.; de Morais, S.M.; et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant, antifungal and hemolytic activities of essential oil from Baccharis trinervis (Lam.) Pers. (Asteraceae). Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 84, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, R.N.; Rehder, V.L.; Santos Oliveira, A.S.; Junior, I.M.; de Carvalho, J.E.; de Ruiz, A.L.; Jeraldo Vde, L.; Linhares, A.X.; Allegretti, S.M. Schistosoma mansoni: In vitro schistosomicidal activity of essential oil of Baccharis trimera (less) DC. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botas, G.; Cruz, R.; de Almeida, F.; Duarte, J.; Araújo, R.; Souto, R.; Ferreira, R.; Carvalho, J.; Santos, M.; Rocha, L.; et al. Baccharis reticularia DC. and Limonene Nanoemulsions: Promising Larvicidal Agents for Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Control. Molecules 2017, 22, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.B.; Kanunfre, C.C.; Farago, P.V.; Borsato, D.M.; Budel, J.M.; de Noronha Sales Maia, B.H.L.; Campesatto, E.A.; Sartoratto, A.; Miguel, M.D.; Miguel, O.G. Cytotoxic mechanism of Baccharis milleflora (Less.) DC. essential oil. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 42, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, C.; Anesini, C. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Argentinean medicinal plants. Fitoterapia 1994, 65, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, V.C.G.; Bristot, D.; Pires, C.L.; Toyama, M.H.; Romoff, P.; Pena, M.J.; Favero, O.A.; Toyama, D.O. Evaluation of Extracts and Partitions from Aerial Parts of Baccharis microdonta on Enzymatic Activity, Pro-Inflammatory and Myotoxic Activities Induced by Secretory Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu. Toxicon 2012, 60, 208–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesini, C.; Perez, C. Screening of plants used in Argentine folk medicine for antimicrobial activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1993, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budel, J.M.; Wang, M.; Raman, V.; Zhao, J.; Khan, S.I.; Rehman, J.U.; Monteiro, L.M.; Heiden, G.; Farago, P.V.; Khan, I.A. Chemical Composition of Essential oils, biological activity and secretory structures of species of Baccharis from Brazil. In Proceedings of the American Society of Pharmacognosy Annual Meeting, Lexington, KY, USA, 21–25 July 2018; pp. 78–79. [Google Scholar]
- Malizia, R.A.; Cardell, D.A.; Molli, J.S.; González, S.; Guerra, P.E.; Grau, R.J. Volatile Constituents of Leaf Oils from the Genus Baccharis. Part II: Baccharis obovata Hooker et Arnott and B. salicifolia (Ruiz et Pav.) Pers. Species from Argentina. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2005, 17, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.H.G.; Romoff, P.; Fávero, O.A.; Soares, M.G.; Baraldi, P.T.; Corrêa, A.G.; Souza, F.O. Composição química dos óleos essenciais das folhas de seis espécies do gênero Baccharis de “Campos de Altitude” da mata atlântica paulista. Quím. Nov. 2008, 31, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schossler, P.; Schneider, G.L.; Wunsch, D.; Soares, G.L.G.; Zini, C.A. Volatile compounds of Baccharis punctulata, Baccharis dracunculifolia and Eupatorium laevigatum obtained using solid phase microextraction and hydrodistillation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2009, 20, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbo-Neto, L.; Lopes, N.P. Plantas medicinais: Fatores de influência no conteúdo de metabólitos secundários. Quím. Nov. 2007, 30, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, B.; Vendruscolo, R.G.; Wagner, R.; Menezes, C.R.; Barin, C.S.; Giacomelli, S.R.; Budel, J.M.; Barin, J.S. Effect of grinding method on the analysis of essential oil from Baccharis articulata (Lam.) Pers. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayuri, V.A.; Romoff, P.; Fávero, O.A.; Ferreira, M.J.P.; Lago, J.H.G.; Buturi, F.O.S. Chemical Composition, Seasonal Variation, and Biosynthetic Considerations of Essential Oils from Baccharis microdonta and B. elaeagnoides (Asteraceae). Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 2771–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulle, C.C.; Raman, V.; Oliveira, A.V.G.; Maia, B.H.L.N.S.; Meneghetti, E.K.; Flores, T.B.; Farago, P.V.; Khan, I.A.; Budel, J.M. Anatomy and volatile oil chemistry of Eucalyptus saligna cultivated in South Brazil. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, J.S.; Karuppayil, S.M. A status review on the medicinal properties of essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.G.; Oliveira, A.P.; Ribeiro, E.A.N.; Claudino, F.S.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Lima, J.T.; Bonjardin, L.R.; Ribeiro, L.A.A.; Quintas-Júnior, L.J.; Santos, M.R.V. Atividade farmacológica de monoterpenos. In Farmacognosia: Coletânea Científica; Souza, G.H.B., Mello, J.C.P., Lopes, N.P., Eds.; UFOP: Ouro Preto, Brazil, 2012; pp. 219–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bogo, C.A.; de Andrade, M.H.; de Paula, J.P.; Farago, P.V.; Döll-Boscardin, P.M.; Budel, J.M. Comparative analysis of essential oils of Baccharis L.: A review. Revis. Strict. Sensu 2016, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, V.B.; Vargas, R.M.F.; Minteguiaga, M.; Umpiérrez, N.; Dellacassa, E.; Cassel, E. Evaluation of the key odorants of Baccharis anomala DC. essential oil: New applications for known products. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis Lage, T.C.; Montanari, R.M.; Fernandes, S.A.; de Oliveira Monteiro, C.M.; de Oliveira Souza Senra, T.; Zeringota, V.; da Silva Matos, R.; Daemon, E. Chemical composition and acaricidal activity of the essential oil of Baccharis dracunculifolia De Candole (1836) and its constituents nerolidol and limonene on larvae and engorged females of Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 148, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minteguiaga, M.; Umpiérrez, N.; Xavier, V.; Lucas, A.; Mondin, C.; Fariña, L.; Cassel, E.; Dellacassa, E. Recent Findings in the Chemistry of Odorants from Four Baccharis Species and Their Impact as Chemical Markers. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdelas, R.R.; López, S.; Lima, B.; Feresin, G.E.; Zygadlo, J.; Zacchino, S.; López, M.L.; Tapia, A.; Freile, M.L. Chemical composition, anti-insect and antimicrobial activity of Baccharis darwinii essential oil from Argentina, Patagonia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 40, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minteguiaga, M.; Mercado, M.I.; Ponessa, G.I.; Catalán, C.A.N.; Dellacassa, E. Morphoanatomy and essential oil analysis of Baccharis trimera (Less.) DC. (Asteraceae) from Uruguay. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minteguiaga, M.; González, A.; Cassel, E.; Umpierrez, N.; Fariña, L.; Dellacassa, E. Volatile Constituents from Baccharis spp. L. (Asteraceae): Chemical Support for the Conservation of Threatened Species in Uruguay. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, N. Gas chromatographic retention indices of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes on methyl silicon and Carbowax 20M phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 503, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Filho, A.A.; Resende, D.O.; Fukui, M.J.; Santos, F.F.; Pauletti, P.M.; Cunha, W.R.; Silva, M.L.; Gregorio, L.E.; Bastos, J.K.; Nanayakkara, N.P. In vitro antileishmanial, antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activities of phenolics and triterpenoids from Baccharis dracunculifolia DC. (Asteraceae). Fitoterapia 2009, 80, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, V.; Sauvain, M.; Bourdy, G.; Arrazola, S.; Callapa, J.; Ruiz, G.; Choque, J.; Deharo, E. A search for natural bioactive compounds in Bolivia through a multidisciplinary approach. Part III. Evaluation Of the antimalarial activity of plants used by Altenos Indians. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 71, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpoviessi, S.; Bero, J.; Agbani, P.; Gbaguidi, F.; Kpadonou-Kpoviessi, B.; Sinsin, B.; Accrombessi, G.; Frederich, M.; Moudachirou, M.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Chemical composition, cytotoxicity and in vitro antitrypanosomal and antiplasmodial activity of the essential oils of four Cymbopogon species from Benin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Cavadas, C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L.; do Céu Sousa, M. In vitro susceptibility of Trypanosoma brucei brucei to selected essential oils and their major components. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 190, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas Júnior, C. Terpenos com atividade inseticida: Uma alternativa para o controle químico de insetos. Quím. Nov. 2003, 26, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.F.; Moore, S.J. Plant-based insect repellents: A review of their efficacy, development and testing. Malar. J. 2011, 10, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.K.; Cardoso, M.G.; Moraes, J.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; Rodrigues, V.G.; Guimarães, L.G.L. Chemical composition and fumigant effect of essentialoil of Lippia sidoides Cham. and monoterpenes against Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2011, 35, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, O.; Salatino, A. Função e evolução de óleos essenciais e de suas estruturas secretoras. Ciênc. Cul. 1987, 39, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Budel, J.M.; Paula, J.P.; Santos, V.L.P.; Franco, C.R.C.; Farago, P.V.; Duarte, M.R. Pharmacobotanical study of Baccharis pentaptera. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobek, V.B.; Heiden, G.; Oliveira, C.F.; Almeida, V.P.; Paula, J.P.; Farago, P.V.; Nakashima, T.; Budel, J.M. Comparative analytical micrographs of vassouras (Baccharis, Asteraceae). Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinar, L.A. Las especies de Baccharis (Compositae) de Argentina Central. In Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Fisicas y Naturales; Universidad Nacional de Córdoba: Córdoba, Argentina, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Techen, N.; Parveen, I.; Pan, Z.; Khan, I.A. DNA barcoding of medicinal plant material for identification. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ANVISA. Farmacopeia Brasileira; ANVISA (Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária): Brasília, Brasil, 2010.
- Kesselmans, R.P.W.; Wijnberg, J.B.P.A.; de Groot, A.; van Beek, T.A. Chromatographic and Spectroscopic Data of All Stereoisomers of Eudesm-11-en-4-ol. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1992, 4, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Khan, S.I.; Beena; Rajalakshmi, G.; Kumaradhas, P.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity and cytotoxicity of substituted 3,6-diphenyl-[1,2,4,5]tetraoxanes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5632–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makler, M.T.; Hinrichs, D.J. Measurement of the Lactate Dehydrogenase Activity of Plasmodium falciparum as an Assessment of Parasitemia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Jacob, M.; Walker, L.; Tekwani, B. Screening North American plant extracts in vitro against Trypanosoma brucei for discovery of new antitrypanosomal drug leads. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, C.; Cuadrillero, C.; Vilella, D. Maintenance of a laboratory colony of Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) using an artificial feeding technique. J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.; Miller, D. Insecticide Resistance in Eggs and First Instars of the Bed Bug, Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Insects 2015, 6, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, C.R.; Goertzen, L.R.; Heuvel, B.V.; Francisco-Ortega, J.; Jansen, R.K. The Complete External Transcribed Spacer of 18S26S-rDNA: Amplification and Phylogenetic Utility at Low Taxonomic Levels in Asteraceae and Closely Allied Families. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2000, 14, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Taberlet, P.; Gielly, L.; Pautou, G.; Bouvet, J. Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1991, 17, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.B. Four primer pairs for the amplification of chloroplast intergenic regions with intraspecific variation. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| No. | RRI a | RI Lit b | RRI c | RI Lit d | Compound Name | Peak Area % e | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. microdonta | B. pauciflosculosa | B. punctulata | B. reticularioides | B. sphenophylla | ID | |||||||||||
| NC | PC | NC | PC | NC | PC | NC | PC | NC | PC | |||||||
| 1 | 937 | 924 | 1019 | 1038 | α-Thujene | - | - | 3.42 | 2.94 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.89 | 1.18 | 0.54 | 0.37 | MS, RI |
| 2 | 942 | 932 | 1014 | 1036 | α-Pinene | 0.72 | 0.73 | 10.45 | 9.44 | 3.55 | 3.15 | 24.50 | 24.78 | 10.74 | 8.04 | tR, MS, RI |
| 3 | 954 | 946 | 1050 | 1083 | Camphene f | - | - | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.30 | tR, MS, RI |
| 4 | 950 | 953 | 1109 | - | Thuja-2,4(10)-diene | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.91 | 3.65 | 0.12 | 0.09 | MS, RI |
| 5 | 973 | 969 | 1105 | 1130 | Sabinene f | - | - | 2.75 | 2.62 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.39 | 0.85 | 3.82 | 3.18 | tR, MS, RI |
| 6 | 976 | 974 | 1089 | 1124 | β-Pinene | 2.24 | 2.33 | 18.33 | 16.50 | 4.95 | 4.41 | 7.68 | 9.24 | 15.24 | 13.17 | tR, MS, RI |
| 7 | 988 | 988 | 1156 | 1156 | β-Myrcene | - | - | 3.65 | 2.76 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.67 | 0.57 | tR, MS, RI |
| 8 | 1001 | 1002 | 1151 | 1177 | α-Phellandrene | - | - | - | - | 0.33 | 0.11 | - | - | - | - | tR, MS, RI |
| 9 | 1003 | 1008 | - | 1141 | δ-(3)-Carene | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.99 | 0.82 | tR, MS, RI |
| 10 | 1010 | 1014 | 1198 | 1188 | α-Terpinene | - | - | 0.19 | - | 0.10 | - | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.64 | tR, MS, RI |
| 11 | 1018 | 1020 | 1271 | 1272 | p-Cymene | - | - | 0.82 | 1.24 | 3.44 | 1.94 | 3.18 | 3.27 | 1.31 | 1.79 | tR, MS, RI |
| 12 | 1021 | 1024 | 1189 | 1206 | Limonene f | 1.12 | 1.14 | 18.77 | 14.99 | 11.35 | 9.77 | 2.47 | 2.75 | 14.33 | 11.81 | tR, MS, RI |
| 13 | 1040 | 1044 | 1254 | 1250 | trans-β-Ocimene | - | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.08 | - | - | MS, RI |
| 14 | 1049 | 1054 | 1243 | 1251 | γ-Terpinene | - | - | 0.31 | - | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 1.03 | 0.41 | tR, MS, RI |
| 15 | 1074 | 1086 | 1267 | 1287 | Terpinolene f | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.37 | 0.18 | tR, MS, RI |
| 16 | 1079 | 1089 | 1462 | - | p-Cymenene | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.85 | 1.01 | 0.11 | 0.12 | MS, RI |
| 17 | 1092 | 1095 | 1593 | 1506 | Linalool f | 0.14 | - | 0.41 | 0.57 | 0.31 | 0.37 | - | - | 0.15 | 0.22 | tR, MS, RI |
| 18 | 1106 | 1101 | 1449 | - | Thujone f | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.52 | 0.55 | - | - | tR, MS, RI |
| 19 | 1115 | 1122 | 1518 | - | α-Campholenal | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.63 | 2.38 | - | - | MS, RI |
| 20 | 1124 | 1135 | 1607 | - | Nopinone | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.38 | 0.42 | - | - | MS, RI |
| 21 | 1127 | 1135 | 1695 | - | trans-Pinocarveol | 0.73 | 1.23 | 0.41 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.37 | 4.44 | 6.84 | 0.79 | 1.23 | tR, MS, RI |
| 22 | 1133 | 1140 | 1700 | - | trans-Verbenol | - | - | 0.10 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.94 | 0.61 | 0.11 | - | MS, RI |
| 23 | 1138 | - | 1706 | - | Unknown 1 [m/z 94 (100%), 79 (89.9%), 59 (79.7%), 91 (51.7%)] | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.12 | 2.10 | - | - | MS |
| 24 | 1148 | 1160 | 1597 | - | Pinocarvone f | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 1.03 | 0.27 | 0.34 | tR, MS, RI |
| 25 | 1161 | - | 1769 | - | α-Phellandren-8-ol | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.60 | 3.72 | 0.15 | 0.03 | MS |
| 26 | 1168 | 1174 | 1643 | 1628 | Terpinene-4-ol f | - | - | 1.19 | 1.23 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 1.34 | 1.29 | 3.10 | 3.45 | tR, MS, RI |
| 27 | 1176 | 1179 | 1882 | 1846 | p-Cymene-8-ol | - | - | 0.11 | 0.17 | - | - | 0.83 | 1.16 | 0.21 | 0.32 | MS, RI |
| 28 | 1181 | 1195 | 1659 | - | Myrtenal f | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 2.14 | 3.25 | 0.53 | 0.62 | tR, MS, RI |
| 29 | 1184 | 1186 | 1740 | 1731 | α-Terpineol | 0.97 | 0.65 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 4.82 | 0.61 | 1.85 | 1.42 | tR, MS, RI |
| 30 | 1193 | 1204 | 1737 | 1733 | Verbenone f | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.95 | 2.65 | - | - | tR, MS, RI |
| 31 | 1208 | 1225 | 1850 | 1820 | cis-Carveol | 0.15 | - | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 1.19 | 1.15 | 0.27 | 0.38 | MS, RI |
| 32 | 1231 | 1239 | 1765 | 1715 | Carvone f | 0.17 | - | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.22 | 0.31 | MS, RI |
| 33 | 1235 | - | 1867 | - | 2-Carene-4-ol | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.32 | 0.17 | - | - | MS |
| 34 | 1271 | 1284 | 1615 | 1599 | Bornyl acetate f | - | - | - | - | 1.32 | 1.04 | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.09 | tR, MS, RI |
| 35 | 1356 | 1374 | 1515 | 1493 | α-Copaene | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.33 | - | - | - | - | 0.26 | 0.34 | MS, RI |
| 36 | 1370 | 1389 | 1621 | 1591 | β-Elemene | 0.87 | 1.10 | 0.41 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.53 | - | - | 0.23 | - | MS, RI |
| 37 | 1395 | 1417 | 1624 | 1617 | β-Caryophyllene | 0.97 | 0.92 | 1.80 | 1.55 | 3.35 | 2.76 | - | - | 3.61 | 3.46 | tR, MS, RI |
| 38 | 1427 | 1437 | 1707 | 1672 | α-Humulene | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.19 | - | 0.42 | 0.41 | - | - | 0.31 | 0.12 | tR, MS, RI |
| 39 | 1447 | 1478 | 1720 | 1692 | γ-Muurolene | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.54 | - | - | 0.27 | 0.47 | MS, RI |
| 40 | 1451 | 1484 | 1737 | 1712 | Germacrene-D | 0.64 | 0.41 | 2.56 | 0.68 | 3.63 | 2.48 | - | - | 1.44 | 0.80 | MS, RI |
| 41 | 1458 | 1489 | 1746 | 1756 | β-Selinene | 1.35 | 1.23 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.21 | MS, RI |
| 42 | 1460 | 1496 | 1725 | - | Ledenef | - | - | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.13 | - | - | 0.17 | 0.14 | tR, MS, RI |
| 43 | 1464 | 1500 | 1761 | 1744 | Bicyclogermacrene f | - | - | 1.25 | 0.01 | 3.10 | 2.85 | - | - | 0.48 | 0.05 | MS, RI |
| 44 | 1464 | 1498 | 1751 | 1729 | α-Selinene | 0.58 | 0.48 | - | - | - | - | - | MS, RI | |||
| 45 | 1469 | 1500 | 1756 | 1730 | α-Muurolene | 0.14 | - | 0.63 | 0.73 | 0.26 | 0.27 | - | - | 0.29 | 0.26 | MS, RI |
| 46 | 1480 | 1505 | 1705 | 1745 | β-Bisabolene | - | - | - | - | 1.18 | 0.78 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 47 | 1488 | 1522 | 1787 | 1761 | δ-Cadinene | 1.00 | 1.17 | 2.74 | 1.96 | 1.13 | 1.35 | 0.28 | 1.04 | 0.79 | 1.52 | MS, RI |
| 48 | 1509 | 1544 | 1930 | 1916 | α-Calacorene | 0.78 | 0.37 | - | - | - | - | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.21 | MS, RI |
| 49 | 1520 | 1548 | 2080 | 2078 | Elemol f | - | - | 0.12 | - | 1.02 | 1.09 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 50 | 1537 | 1561 | 2051 | 2044 | (E)-Nerolidol | - | - | 0.43 | 0.60 | 0.13 | 0.30 | - | - | 0.17 | 0.17 | MS, RI |
| 51 | 1540 | 1567 | 1942 | 1931 | Palustrol f | 3.23 | 3.22 | - | - | 0.13 | - | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 52 | 1551 | 1577 | 2114 | 2153 | Spathulenol f | 22.74 | 24.19 | 9.53 | 12.18 | 9.96 | 11.66 | 5.52 | 2.70 | 13.15 | 14.92 | tR, MS, RI |
| 53 | 1555 | 1582 | 1987 | 1966 | Caryophyllene oxide f | 6.84 | 7.47 | 2.11 | 3.44 | 5.30 | 6.01 | 1.37 | 1.34 | 5.34 | 6.78 | tR, MS, RI |
| 54 | 1559 | 1590 | 2128 | - | Globulol | 0.59 | 0.69 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.36 | 0.32 | MS, RI |
| 55 | 1571 | 1592 | 2080 | 2112 | Viridiflorol f | 4.36 | 4.90 | 1.81 | 2.69 | - | - | - | - | 1.66 | 2.01 | tR, MS, RI |
| 56 | 1585 | 1602 | 2031 | - | Ledol f | 2.38 | 2.55 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 57 | 1622 | 1627 | 2063 | 2037 | 1-epi-Cubenol | 1.03 | 0.57 | 0.38 | 0.39 | - | - | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 58 | 1625 | 1630 | - | - | γ-Eudesmol | - | - | - | - | 1.09 | 1.65 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 59 | 1630 | - | - | - | Unknown 2 [m/z 119 (100%), 105 (92.9%), 91 (90.2%), 93 (79.5%)] | 1.37 | 1.22 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MS |
| 60 | 1633 | 1638 | 2094 | - | epi-α-Cadinol | 0.18 | 0.38 | - | - | 1.95 | 2.09 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 61 | 1644 | 1644 | 2151 | 2150 | δ-Cadinol | 0.42 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.26 | 0.64 | 2.64 | 1.56 | 2.27 | 2.03 | MS, RI |
| 62 | 1647 | 1640 | 2164 | - | epi-α-Muurolol | 0.19 | - | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.27 | 0.33 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 63 | 1659 | 1649 | 2196 | 2248 | β-Eudesmol | - | - | - | - | 0.64 | 1.65 | - | - | - | - | tR, MS, RI |
| 64 | 1661 | 1656 | 2120 | - | α-Bisabolol oxide B | - | - | - | - | 1.17 | 0.47 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 65 | 1662 | 1652 | 2200 | 2224 | α-Cadinol | - | - | 1.44 | 2.08 | - | - | 1.36 | 0.46 | 1.49 | 2.10 | MS, RI |
| 66 | 1665 | - | 2214 | - | Kongol | 22.22 | 20.09 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | tR, MS |
| 67 | 1672 | 1675 | 2209 | 2203 | Cadalene | - | - | - | - | 1.34 | 1.32 | - | - | - | - | MS, RI |
| 68 | 1697 | - | 2278 | - | Murolan-3,9(11)-diene-10-peroxy | 0.54 | 0.64 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | MS |
| 69 | 1705 | - | 2292 | - | (1R,7S,E)-7-Isopropyl-4,10-dimethylenecyclodec-5-enol | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.39 | 0.28 | - | - | - | - | 0.42 | 0.46 | MS |
| 70 | 1708 | 1685 | 2190 | 2022 | α-Bisabolol | - | - | - | - | 23.63 | 20.72 | - | - | - | - | tR, MS, RI |
| Compounds identified (%) | 58.33 | 52.63 | 77.36 | 67.27 | 77.96 | 73.33 | 74.50 | 66.66 | 76.66 | 69.84 | ||||||
| Monoterpenoids hydrocarbons | 6.67 | 5.26 | 20.75 | 16.36 | 22.03 | 20.00 | 27.45 | 24.56 | 25.00 | 23.81 | ||||||
| Oxygenated monoterpenoids | 10.00 | 7.02 | 16.98 | 16.36 | 15.26 | 15.00 | 33.33 | 29.82 | 18.33 | 15.87 | ||||||
| Sesquiterpenoids hydrocarbons | 18.33 | 17.54 | 20.75 | 18.19 | 18.64 | 18.33 | 5.88 | 5.26 | 20.00 | 17.46 | ||||||
| Oxygenated sesquiterpenoids | 23.33 | 22.81 | 18.88 | 16.36 | 22.03 | 20.00 | 7.84 | 7.02 | 13.33 | 12.70 | ||||||
| Sample Name | P. falciparum (D6 Clone) | P. falciparum (W2 Clone) | Cytotoxicity (Vero Cells) IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | IC50 (µg/mL) | SI | ||
| B. microdonta | 14.75 ± 3.80 | 2.4 | 23.93 ± 4.64 | 1.5 | 35.80 ± 7.29 |
| B. pauciflosculosa | 10.90 ± 0.98 | >4.3 | 14.20 ± 1.08 | >3.3 | NC |
| B. punctulata | 17.26 ± 0.83 | 2.2 | 19.73 ± 4.11 | 1.9 | 37.81 ± 6.36 |
| B. reticularioides | 20.32 ± 4.37 | >2.3 | 34.35 ± 10.15 | >1.4 | NC |
| B. sphenophylla | 27.58 ± 1.64 | >1.7 | 32.53 ± 16.5 | >1.5 | NC |
| Chloroquine | 0.014 | >17 | 0.117 | >2 | NC |
| Artemisinin | 0.004 | >31.8 | 0.003 | >71.3 | NC |
| Sample Name | IC50 (µg/mL) * | IC90 (µg/mL) * |
|---|---|---|
| B. microdonta | 1.688 ± 0.354 | 2.683 ± 0.123 |
| B. pauciflosculosa | 0.306 ± 0.056 | 0.516 ± 0.043 |
| B. punctulata | 1.054 ± 0.211 | 1.969 ± 0.201 |
| B. reticularioides | 0.955 ± 0.121 | 2.484 ± 0.165 |
| B. sphenophylla | 1.143 ± 0.113 | 2.378 ± 0.201 |
| Pentamidine | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.011 ± 0.002 |
| α-Difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) | 5.506 ± 0.412 | 12.052 ± 0.613 |
| Lowest Kp Distance (ITS) | Lowest Kp Distance (trnL-trnF) | Lowest Kp Distance (ETS) | Lowest Kp Distance (psbA-trnH) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Species Match | Value | Species Match | Value | Species Match | Value | Species Match(es) | Value | |||
| B. pa. | B. pa | 0.000 | B. il | 0.000 | B. pa | 0.003 | B. pa | B. il | B. re | B. sp | 0.004 |
| B. re | B. re | 0.000 | B. il | 0.001 | B. re | 0.001 | B. pa | B. il | B. re | 0.000 | |
| B. mi | B. mi | 0.001 | B. mi | 0.000 | NA | B. mi | 0.000 | ||||
| B. pu | B. pu | 0.006 | B. pu | 0.000 | NA | B. pu | 0.000 | ||||
| B. sp | B. sp | 0.000 | B. il | 0.004 | NA | B. pa | B. il | B. re | 0.000 | ||
| Genomic Regions | Sequence in 5′-3′ | Source | TM | Extension Time at 72 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETS1f | CTTTTTGTGCATAATGTATATATAGGGGG | Linder et al. [58] | 45 °C | 60 s |
| 18S-2L | TGACTACTGGCAGGATCAACCAG | |||
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | White et al. [59] | 52 °C | 30 s |
| ITS5 | GGAAGTAAAAGTCGTAACAAGG | |||
| trnL-F-trnC | CGAAATCGGTAGACGCTACG | Taberlet et al. [60] | 52 °C | 60 s |
| trnL-F-trnF | ATTTGAACTGGTGACACGAG | |||
| psbA | CGAAGCTCCATCTACAAATGG | Hamilton et al. [61] | 56 °C | 30 s |
| trnH (GUG) | ACTGCCTTGATCCACTTGGC |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budel, J.M.; Wang, M.; Raman, V.; Zhao, J.; Khan, S.I.; Rehman, J.U.; Techen, N.; Tekwani, B.; Monteiro, L.M.; Heiden, G.; et al. Essential Oils of Five Baccharis Species: Investigations on the Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102620
Budel JM, Wang M, Raman V, Zhao J, Khan SI, Rehman JU, Techen N, Tekwani B, Monteiro LM, Heiden G, et al. Essential Oils of Five Baccharis Species: Investigations on the Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102620
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudel, Jane M., Mei Wang, Vijayasankar Raman, Jianping Zhao, Shabana I. Khan, Junaid U. Rehman, Natascha Techen, Babu Tekwani, Luciane M. Monteiro, Gustavo Heiden, and et al. 2018. "Essential Oils of Five Baccharis Species: Investigations on the Chemical Composition and Biological Activities" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102620
APA StyleBudel, J. M., Wang, M., Raman, V., Zhao, J., Khan, S. I., Rehman, J. U., Techen, N., Tekwani, B., Monteiro, L. M., Heiden, G., Takeda, I. J. M., Farago, P. V., & Khan, I. A. (2018). Essential Oils of Five Baccharis Species: Investigations on the Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. Molecules, 23(10), 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102620