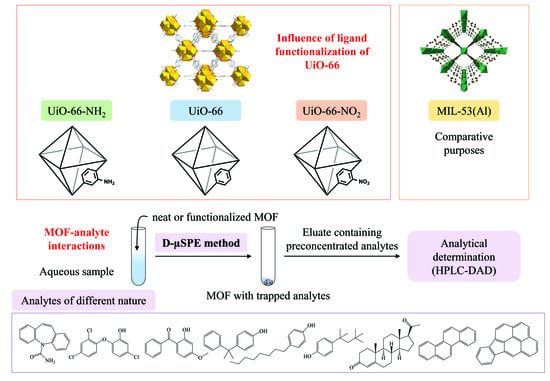
Influence of Ligand Functionalization of UiO-66-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks When Used as Sorbents in Dispersive Solid-Phase Analytical Microextraction for Different Aqueous Organic Pollutants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MOFs
2.3. Instruments and Equipment
2.4. Dispersive Miniaturized Solid-Phase Extraction Procedure (D-µSPE)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromatographic Method
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Studied MOFs
3.3. Screening of MOFs as Sorbents in D-µSPE-HPLC-DAD
3.4. Optimization of the D-µSPE-HPLC-DAD Method Using UiO-66-NO2
3.5. Influence of the UiO-66 Ligand Functionalization in the Overall Efficiency of the D-µSPE-HPLC-DAD Method
3.6. Quality Analytical Parameters of the Optimized D-µSPE-HPLC-DAD Method
3.7. Analysis of Wastewaters and Tap Water Samples Using the Optimized D-µSPE-HPLC-DAD Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaghi, O.M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Ockwig, N.W.; Chae, H.K.; Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 2003, 423, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranchemontagne, D.J.; Mendoza-Cortés, J.L.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Secondary building units, nets and bonding in the chemistry of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1257–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenecker, P.M.; Carson, C.G.; Jasuja, H.; Flemming, C.J.J.; Walton, K.S. Effect of water adsorption on retention of structure and surface area of metal-organic frameworks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6513–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Vallcorba, O.; Afonso, A.M.; Pasán, J. A green metal-organic framework to monitor water contaminants. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31304–31310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Demir, N.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, K. Applications of water stable metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5107–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Metal-organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerinck, T.; Bueno-Perez, R.; Vermoortele, F.; De Vos, D.E.; Calero, S.; Baron, G.V.; Denayer, J.F.M. Understanding hydrocarbon adsorption in the UiO-66 metal-organic framework: Separation of (un)saturated linear, branched, cyclic adsorbates, including stereoisomers. J. Phys. Chem. 2013, 117, 12567–12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragon, F.; Campo, B.; Yang, Q.; Martineau, C.; Wiersum, A.D.; Lago, A.; Guillerm, V.; Hemsley, C.; Eubank, J.F.; Vishnuvarthan, M.; et al. Acid-functionalized UiO-66(Zr) MOFs and their evolution after intra-framework cross-linking: Structural features and sorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3294–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Vaesen, S.; Ragon, F.; Wiersum, A.D.; Wu, D.; Lago, A.; Devic, T.; Martineau, C.; Taulelle, F.; Llewellyn, P.L.; et al. A water stable metal-organic framework with optimal features for CO2 capture. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2013, 52, 10316–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Chen, Q.; Lü, M.; Liu, X. Adsorption behavior of rhodamine B on UiO-66. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 22, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Rafique, U.; Davies, R.P. Investigations on post-synthetically modified UiO-66-NH2 for the adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 221, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirio, S.; Shih, Y.H.; Hsiao, S.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, H.T.; Liu, W.L.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, H.Y. Monitoring the effect of different metal centers in metal-organic frameworks and their adsorption of aromatic molecules using experimental and simulation studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 14044–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Are metal-organic frameworks able to provide a new generation of solid-phase microextraction coatings?—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; González-Hernández, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Afonso, A.M. Metal-organic frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Fernández, I.; González-Hernández, P.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Pino, V. The rise of metal-organic frameworks in analytical chemistry. In Handbook of Smart Materials in Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; De la Guardia, M., Esteve-Turrillas, F.A., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 463–502. [Google Scholar]
- Maya, F.; Cabello, C.P.; Frizzarin, R.M.; Estela, J.M.; Palomino, G.T.; Cerdà, V. Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.; Yan, X.P. MOF-5 metal-organic framework as sorbent for in-field sampling and preconcentration in combination with thermal desorption GC/MS for determination of atmospheric formaldehyde. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rui, M.; Lu, G. Recent applications of metal-organic frameworks in sample pretreatment. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Hernández-Borges, J. Dispersive solid-phase extraction. In Analytical Separation Science, 1st ed.; Anderson, J.L., Berthod, A., Pino, V., Stalcup, A.M., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 1525–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Szczepańska, N.; de la Guardia, M.; Namieśnik, J. Miniaturized solid-phase extraction techniques. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Xie, S.; Quan, H.; Luo, X.; Guo, L. Adsorption behaviors of organic micropollutants on zirconium metal-organic framework UiO-66: Analysis of surface interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41043–41054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; López-Hernández, I.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M. Insights in the analytical performance of neat metal-organic frameworks in the determination of pollutants of different nature from waters using dispersive miniaturized solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography. Talanta 2018, 179, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandiah, M.; Nilsen, M.H.; Usseglio, S.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Tilset, M.; Larabi, C.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Bonino, F.; Lillerud, K.P. Synthesis and stability of tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6632–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, Z.H.; Abid, H.R.; Sun, H.; Shang, J.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. Effects of -NO2 and -NH2 functional groups in mixed-linker Zr-based MOFs on gas adsorption of CO2 and CH4. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J.; Brown, Z.J.; Colón, Y.J.; Siu, P.W.; Scheidt, K.A.; Snurr, R.Q.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9449–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Férey, G. A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Ayala, J.H.; Pasán, J.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M. The metal-organic framework HKUST-1 as efficient sorbent in a vortex-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of parabens from environmental waters, cosmetic creams and human urine. Talanta 2015, 139, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, H.; Walton, K.S.; Sholl, D.S. Computational screening of functionalized UiO-66 materials for selective contaminant removal from air. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 20396–20406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Dou, Y.; Xie, L.H.; Rutledge, W.; Li, J.R.; Zhou, H.C. Zr-based metal-organic frameworks: Design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2327–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.; Liu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Z. Selectivity adsorptive mechanism of different nitrophenols on UiO-66 and UiO-66-NH2 in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.M.; Petit, C. Towards the use of metal-organic frameworks for water reuse: A review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22484–22506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, A.; Samanta, P.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. Guest-responsive metal-organic frameworks as scaffolds for separation and sensing applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2457–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Ahmed, I.; Seo, P.W.; Jhung, S.H. UiO-66 metal-organic framework with free carboxylic acid: Versatile adsorbents via H-bond for both aqueous and nonaqueous phases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27394–27402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, A.; Forse, A.C.; Whiterspoon, V.J.; Reimer, J.A. NMR spectroscopy reveals adsorbate binding sites in the metal-organic framework UiO-66(Zr). J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8295–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Yan, X.-P. Exploring reverse shape selectivity and molecular sieving effect of metal-organic framework UIO-66 coated capillary column for gas chromatographic separation. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1257, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Jhung, S.H. Applications of metal-organic frameworks in adsorption/separation processes via hydrogen bonding interactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Afonso, A.M. Ionic liquids in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |



| MOF | Structure (Detailed Functionalization for UiO-66) | Metal (mg) | Ligand (mg) | Solvent (mL) | Modulator/mL | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66 |  | Zr4+ (233) | terephthalic acid (246) | DMF (15) | HCl (37%, v/v)/1 | 95 |
| UiO-66-NH2 |  | Zr4+ (233) | 2-aminoterephthalic acid (271) | DMF (15) | HCl (37%, v/v)/1 | 78 |
| UiO-66-NO2 |  | Zr4+ (233) | 2-nitroterephthalic acid (317) | DMF (15) | HCl (37%, v/v)/1 | 97 |
| MIL-53(Al) |  | Al3+ (1300) | terephthalic acid (288) | H2O (15) | - | 45 |
| Analyte | Calibration Range (μg·L−1) | R | sy/x a | Slope ± SD b | LOD (ng·L−1) | LOQ (ng·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine | 0.05–5.74 | 0.9989 | 0.27 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 5.0 | 16.7 |
| 4-Cumylphenol | 0.80–5.74 | 0.9966 | 0.11 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 90 | 300 |
| Progesterone | 0.01–5.74 | 0.9980 | 0.99 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 2.4 | 8.00 |
| Benzophenone-3 | 0.05–5.74 | 0.9991 | 0.38 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 4.5 | 15.0 |
| Triclosan | 0.50–5.00 | 0.9982 | 0.17 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 30 | 100 |
| 4-tert-Octylphenol | 0.50–4.00 | 0.9995 | 0.09 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 90 | 300 |
| 4-Octylphenol | 0.10–5.00 | 0.9998 | 0.10 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 15 | 50.0 |
| Chrysene | 0.01–5.74 | 0.9984 | 4.8 | 37 ± 2 | 1.5 | 5.00 |
| Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene | 0.01–5.74 | 0.9986 | 1.6 | 13 ± 1 | 1.5 | 5.00 |
| Analyte | Spiked Level 1 (1.50 µg·L−1) | Spiked Level 2 (4.50 µg·L−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER a (%) | RR b (%) | Inter-Day RSD c (%) | Intra-Day RSD Range d (%) | ER a (%) | RR b (%) | Inter-Day RSD c (%) | Intra-Day RSD Range d (%) | |
| Cbz | 22.0 | 99.4 | 14 | 1.0–12 | 15.6 | 100 | 8.8 | 6.9–11 |
| CuP | 35.2 | 126 | 9.3 | 4.7–8.3 | 21.1 | 100 | 9.6 | 5.4–6.7 |
| Pg | 51.0 | 111 | 4.1 | 3.3–4.4 | 42.8 | 88.8 | 6.7 | 3.2–4.8 |
| BP-3 | 29.2 | 112 | 9.4 | 3.2–7.7 | 25.7 | 91.9 | 8.1 | 2.6–3.6 |
| Tr | 40.8 | 95.0 | 8.2 | 5.4–9.5 | 43.0 | 104 | 9.7 | 5.6–8.9 |
| t-OP | 53.5 | 118 | 7.2 | 4.1–8.2 | 45.7 | 102 | 5.7 | 2.5–3.7 |
| OP | 69.6 | 102 | 7.5 | 6.1–9.5 | 63.9 | 90.5 | 4.3 | 1.2–2.4 |
| Chy | 39.4 | 109 | 5.5 | 2.0–7.4 | 43.8 | 127 | 8.7 | 3.3–9.6 |
| Ind | 27.1 | 87.3 | 9.1 | 4.1–8.4 | 24.3 | 79.2 | 6.3 | 2.9–5.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taima-Mancera, I.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M.; Lago, A.B.; Pino, V. Influence of Ligand Functionalization of UiO-66-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks When Used as Sorbents in Dispersive Solid-Phase Analytical Microextraction for Different Aqueous Organic Pollutants. Molecules 2018, 23, 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112869
Taima-Mancera I, Rocío-Bautista P, Pasán J, Ayala JH, Ruiz-Pérez C, Afonso AM, Lago AB, Pino V. Influence of Ligand Functionalization of UiO-66-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks When Used as Sorbents in Dispersive Solid-Phase Analytical Microextraction for Different Aqueous Organic Pollutants. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112869
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaima-Mancera, Iván, Priscilla Rocío-Bautista, Jorge Pasán, Juan H. Ayala, Catalina Ruiz-Pérez, Ana M. Afonso, Ana B. Lago, and Verónica Pino. 2018. "Influence of Ligand Functionalization of UiO-66-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks When Used as Sorbents in Dispersive Solid-Phase Analytical Microextraction for Different Aqueous Organic Pollutants" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112869
APA StyleTaima-Mancera, I., Rocío-Bautista, P., Pasán, J., Ayala, J. H., Ruiz-Pérez, C., Afonso, A. M., Lago, A. B., & Pino, V. (2018). Influence of Ligand Functionalization of UiO-66-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks When Used as Sorbents in Dispersive Solid-Phase Analytical Microextraction for Different Aqueous Organic Pollutants. Molecules, 23(11), 2869. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112869