Computer-Aided Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Transcriptional Activity of TLX (NR2E1) Nuclear Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Virtual Screening
2.2. Expression of TLX in PCa Cell Lines
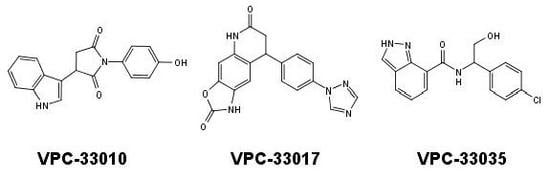
2.3. In Vitro Screening (Luciferase Reporter Assay)
2.4. Binding Mode Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Protein Structure Preparation
3.2. Docking
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Chemicals and Antibodies
3.5. Plasmids and Constructs
3.6. Transcriptional Assay
3.7. Quantitative RT-PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oprea, T.I.; Bologa, C.G.; Brunak, S.; Campbell, A.; Gan, G.N.; Gaulton, A.; Gomez, S.M.; Guha, R.; Hersey, A.; Holmes, J.; et al. Unexplored therapeutic opportunities in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Germain, P.; Staels, B.; Dacquet, C.; Spedding, M.; Laudet, V. Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.T.; McKeown, M.; Evans, R.M.; Umesono, K. Relationship between Drosophila gap gene tailless and a vertebrate nuclear receptor Tlx. Nature 1994, 370, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strecker, T.R.; Merriam, J.R.; Lengyel, J.A. Graded requirement for the zygotic terminal gene, tailless, in the brain and tail region of the Drosophila embryo. Development 1988, 102, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.K.; Belz, T.; Bock, D.; Takacs, A.; Wu, H.; Lichter, P.; Chai, M.; Schutz, G. The nuclear receptor tailless is required for neurogenesis in the adult subventricular zone. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 2473–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monaghan, A.P.; Bock, D.; Gass, P.; Schwager, A.; Wolfer, D.P.; Lipp, H.P.; Schutz, G. Defective limbic system in mice lacking the tailless gene. Nature 1997, 390, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Kuznicki, K.; Wu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Bock, D.; Schutz, G.; Vranich, N.; Monaghan, A.P. The Tlx gene regulates the timing of neurogenesis in the cortex. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8333–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, T.; Uemura, A.; Dezawa, M.; Yu, R.T.; Ide, C.; Nishikawa, S.; Honda, Y.; Tanabe, Y.; Tanabe, T. Tlx, an orphan nuclear receptor, regulates cell numbers and astrocyte development in the developing retina. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8124–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zou, Y.; Yu, R.T.; Gage, F.H.; Evans, R.M. Nuclear receptor TLX prevents retinal dystrophy and recruits the corepressor atrophin1. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, R.T.; Chiang, M.Y.; Tanabe, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Yasuda, K.; Evans, R.M.; Umesono, K. The orphan nuclear receptor Tlx regulates Pax2 and is essential for vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2621–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Chichung Lie, D.; Taupin, P.; Nakashima, K.; Ray, J.; Yu, R.T.; Gage, F.H.; Evans, R.M. Expression and function of orphan nuclear receptor TLX in adult neural stem cells. Nature 2004, 427, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.K.; Wang, Y.; Belz, T.; Bock, D.; Takacs, A.; Radlwimmer, B.; Barbus, S.; Reifenberger, G.; Lichter, P.; Schutz, G. The nuclear receptor tailless induces long-term neural stem cell expansion and brain tumor initiation. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Q.; Yang, S.; Ye, P.; Tian, E.; Sun, G.; Zhou, J.; Sun, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Murai, K.; et al. Downregulation of TLX induces TET3 expression and inhibits glioblastoma stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavali, P.L.; Saini, R.K.; Zhai, Q.; Vizlin-Hodzic, D.; Venkatabalasubramanian, S.; Hayashi, A.; Johansson, E.; Zeng, Z.J.; Mohlin, S.; Pahlman, S.; et al. TLX activates MMP-2, promotes self-renewal of tumor spheres in neuroblastoma and correlates with poor patient survival. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.J.; Johansson, E.; Hayashi, A.; Chavali, P.L.; Akrap, N.; Yoshida, T.; Kohno, K.; Izumi, H.; Funa, K. TLX controls angiogenesis through interaction with the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Biol. Open 2012, 1, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murai, K.; Sun, G.; Ye, P.; Tian, E.; Yang, S.; Cui, Q.; Sun, G.; Trinh, D.; Sun, O.; Hong, T.; et al. The TLX-miR-219 cascade regulates neural stem cell proliferation in neurodevelopment and schizophrenia iPSC model. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.A.; McGhee, K.A.; Leach, S.; Bonaguro, R.; Maclean, A.; Aguirre-Hernandez, R.; Abrahams, B.S.; Coccaro, E.F.; Hodgins, S.; Turecki, G.; et al. Initial association of NR2E1 with bipolar disorder and identification of candidate mutations in bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and aggression through resequencing. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2008, 147, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Deng, H.; Dai, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, X.; Ma, P.; Cheng, J. Nr2e1 deficiency augments palmitate-induced oxidative stress in beta cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9648769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Deng, H.; He, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, Q.; Xue, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Xu, Y. The relationship between NR2E1 and subclinical inflammation in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.L.; Patel, H.; Remenyi, J.; Banerji, C.R.; Lai, C.F.; Periyasamy, M.; Lombardo, Y.; Busonero, C.; Ottaviani, S.; Passey, A.; et al. Expression profiling of nuclear receptors in breast cancer identifies TLX as a mediator of growth and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21685–21703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Yu, S.; Jia, L.; Zou, C.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, L.; Wong, K.B.; Ng, C.F.; Chan, F.L. Orphan nuclear receptor TLX functions as a potent suppressor of oncogene-induced senescence in prostate cancer via its transcriptional co-regulation of the CDKN1A (p21(WAF1) (/) (CIP1)) and SIRT1 genes. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Ng, C.F.; Teoh, J.Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chan, F.L. Nuclear receptor profiling in prostatospheroids and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; You, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Cai, G.; Xu, Z.; Zou, C.; Wang, F.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor TLX contributes to androgen insensitivity in castration-resistant prostate cancer via its repression of androgen receptor transcription. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3340–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Rajan, H.; Pitman, J.L.; McKeown, M.; Tsai, C.C. Histone deacetylase-associating Atrophin proteins are nuclear receptor corepressors. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, A.; Takezawa, S.; Schule, R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kato, S. Transrepressive function of TLX requires the histone demethylase LSD1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3995–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Yu, R.T.; Evans, R.M.; Shi, Y. Orphan nuclear receptor TLX recruits histone deacetylases to repress transcription and regulate neural stem cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15282–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estruch, S.B.; Buzon, V.; Carbo, L.R.; Schorova, L.; Luders, J.; Estebanez-Perpina, E. The oncoprotein BCL11A binds to orphan nuclear receptor TLX and potentiates its transrepressive function. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 37963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Ye, P.; Zhao, C.; Yu, R.T.; Gage, F.H.; Evans, R.M.; Shi, Y. Orphan nuclear receptor TLX activates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling to stimulate neural stem cell proliferation and self-renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Zeng, Z.J.; Lakshminarasimhan, P.; Yang, W.; Uemura, A.; Nishikawa, S.; Moshiri, A.; Tajima, N.; Agren, H.; et al. TLX activates MASH1 for induction of neuronal lineage commitment of adult hippocampal neuroprogenitors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2010, 45, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benod, C.; Villagomez, R.; Filgueira, C.S.; Hwang, P.K.; Leonard, P.G.; Poncet-Montange, G.; Rajagopalan, S.; Fletterick, R.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Webb, P. The human orphan nuclear receptor tailless (TLX, NR2E1) is druggable. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 99440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, A.E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J.R.; Schweppe, K.W.; Thijssen, J.H. Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46 (Suppl. 1), S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- iCSS ToxCast Dashboard Version 1.0. Built on August 3rd, 2015.iCSS ToxCast Dashboard Version 1.0. Data Source—Toxcast_Dashboard_v2 for ToxCast and Tox21 Assay Annotations and Data. Available online: https://actor.epa.gov/dashboard/ (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Chemical Computing Group ULC: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2018.
- Zhi, X.; Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; Searose-Xu, K.; Zhang, C.L.; Tsai, C.C.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Structural basis for corepressor assembly by the orphan nuclear receptor TLX. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, T.; Irwin, J.J. ZINC 15—Ligand discovery for everyone. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-1: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FRED 3.2.0.2: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM. Available online: http://www.eyesopen.com (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- McGann, M. FRED pose prediction and virtual screening accuracy. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, M.A.; Totrov, M.; Abagyan, R. Docking and scoring with ICM: The benchmarking results and strategies for improvement. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, J.W.; Case, D.A. Force fields for protein simulations. Adv. Protein Chem. 2003, 66, 27–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagorce, D.; Sperandio, O.; Galons, H.; Miteva, M.A.; Villoutreix, B.O. FAF-Drugs2: Free ADME/tox filtering tool to assist drug discovery and chemical biology projects. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.R.; Walkinshaw, M.D. Consensus docking: Improving the reliability of docking in a virtual screening context. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMEGA 2.5.1.4: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM. Available online: http://www.eyesopen.com (accessed on 1 September 2018).
- Hawkins, P.C.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| Compound ID | Compound Structure | % Inhibition of 3XTAE-LUC Reporter (DU145) at 35 µM | % Inhibition of LUC Reporter (PC3M) at 35 µM |
|---|---|---|---|
| VPC-33009 |  | 46 ± 9 | 44 ± 2 |
| VPC-33010 |  | 50 ± 9 | −9 ± 5 |
| VPC-33017 |  | 43 ± 13 | −2.5 ± 6 |
| VPC-33035 |  | 48 ± 12 | 12 ± 4 |
| VPC-33040 |  | 52 ± 17 | 15 ± 4 |
| VPC-33087 |  | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dueva, E.; Singh, K.; Kalyta, A.; LeBlanc, E.; Rennie, P.S.; Cherkasov, A. Computer-Aided Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Transcriptional Activity of TLX (NR2E1) Nuclear Receptor. Molecules 2018, 23, 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112967
Dueva E, Singh K, Kalyta A, LeBlanc E, Rennie PS, Cherkasov A. Computer-Aided Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Transcriptional Activity of TLX (NR2E1) Nuclear Receptor. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112967
Chicago/Turabian StyleDueva, Evgenia, Kriti Singh, Anastasia Kalyta, Eric LeBlanc, Paul S. Rennie, and Artem Cherkasov. 2018. "Computer-Aided Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Transcriptional Activity of TLX (NR2E1) Nuclear Receptor" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112967
APA StyleDueva, E., Singh, K., Kalyta, A., LeBlanc, E., Rennie, P. S., & Cherkasov, A. (2018). Computer-Aided Discovery of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Transcriptional Activity of TLX (NR2E1) Nuclear Receptor. Molecules, 23(11), 2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112967