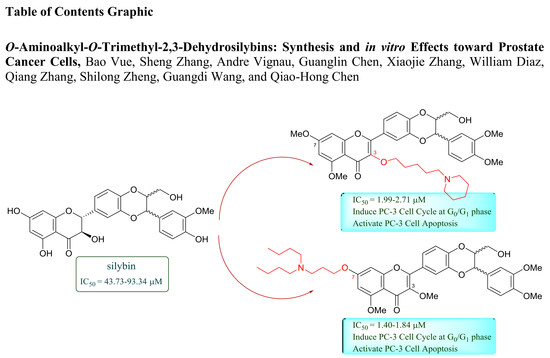
O-Aminoalkyl-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and In Vitro Effects Towards Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Synthesis of 7-O-Aminoalkyl-3,5,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins (9–14)
2.1.2. Synthesis of 3-O-Aminoalkyl-5,7,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins (20–45)
2.1.3. Structure Determination
2.2. Antiproliferative Activity towards Prostate Cancer Cell Lines and Structure-Activity Relationships
2.3. Antiproliferative Activity towards MCF 10A and PWR-1E Non-Neoplastic Human Epithelial Cell Lines
2.4. Cell Cycle Regulation and Cell Apoptosis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Synthesis of 7-O-Benzylsilybin (5)
3.3. Synthesis of 7-O-Benzyl-3,5,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybin (6)
3.4. Synthesis of 3,5,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybin (7)
3.5. Synthesis of 7-O-(3′-Bromo)Propyl-3,5,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybin (8)
3.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 7-O-(N,N-Dialkylamino)Propyl-3,5,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins
3.7. Synthesis of 5,7,20-O-Trimethylsilybin (15)
3.8. Synthesis of 5,7,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybin (16)
3.9. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 3-O-Bromoalkyl-5,7,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins (17–19)
3.10. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 3-O-(Alkylamino)Alkyl-5,7,20-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins
3.11. Cell Culture
3.12. WST-1 Cell Proliferation Assay
3.13. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.14. F2N12S and SYTOX AADvanced Double Staining Assay
3.15. Statistical Analysis:
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, N.-C.; Graf, T.N.; Sparacino, C.M.; Wani, M.C.; Wall, M.E. Complete isolation and characterization of silybins and isosilybins from milk thistle (Silybum marianum). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabio, G.D.; Romanucci, V.; Marino, C.D.; De Napoli, L.; Zarrelli, A. A rapid and simple chromatographic separation of diastereomers of silibinin and their oxidation to produce 2,3-dehydrosilybin enantiomers in an optically pure form. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althagafy, H.S.; Meza-Avina, M.E.; Oberlies, N.H.; Croatt, M.P. Mechanistic study of the biomimetic synthesis of flavonolignan diastereoisomers in milk thistle. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7594–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelter, A.; Haensel, R. The structure of silybin (Silybum substance E6), the first flavonolignan. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, D.J.; Shaw, H.S.; Oberlies, N.H. Milk thistle nomenclature: Why it matters in cancer research and pharmacokinetic studies. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, D.J.; Crowe, T.; Sokhansanj, S.; Wahab, J.; Barl, B. Milk thistle, Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn., flower head development and associated marker compound profile. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2002, 10, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Capasso, R.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Milk thistle in liver diseases: Past, present, future. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, D.; Vavrikova, E.; Cvak, L.; Kren, V. Chemistry of silybin. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flora, K.; Hahn, M.; Rosen, H.; Benner, K. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Katiyar, S.K.; Lundgren, D.W.; Mukhtar, H. Inhibitory effect of silymarin, an anti-hepatotoxic flavonoid, on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced epidermal ornithine decarboxylase activity and mRNA in SENCAR mice. Carcinogenesis 1994, 15, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri-Chatterjee, M.; Katiyar, S.K.; Mohan, R.R.; Agarwal, R. A flavonoid antioxidant, silymarin, affords exceptionally high protection against tumor promotion in the SENCAR mouse skin tumorigenesis model. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C.; Ichikawa, H.; Singh, R.P.; Aggarwal, B.B. Anticancer potential of silymarin: From bench to bed side. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 4457–4498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vue, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.-H. Flavonoids with therapeutic potential in prostate cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1205–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis-Searles, P.R.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kim, N.-C.; Graf, T.N.; Oberlies, N.H.; Wani, M.C.; Wall, M.E.; Agarwal, R.; Kroll, D.J. Milk thistle and prostate cancer: Differential effects of pure flavonolignans from Silybum marianum on antiproliferative end points in human prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4448–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vue, B.; Chen, Q.-H. The potential of flavonolignans in prostate cancer management. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 3925–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, T.W.; Gustafson, D.L.; Su, L.J.; Zirrolli, J.A.; Crighton, F.; Harrison, G.S.; Pierson, A.S.; Agarwal, R.; Glode, L.M. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of silybin-phytosome in prostate cancer patients. Invest. New Drugs 2007, 25, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Duan, C.; Jia, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Hao, L.; et al. In vitro antitumor activity of silybin nanosuspension in PC-3 cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 307, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sy-Cordero, A.A.; Graf, T.N.; Runyon, S.P.; Wani, M.C.; Kroll, D.J.; Agarwal, R.; Brantley, S.J.; Paine, M.F.; Polyak, S.J.; Oberlies, N.H. Enhanced bioactivity of silybin B methylation products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, C.; Wadhwa, R.; Deep, G.; Biedermann, D.; Gazak, R.; Kren, V.; Agarwal, R. Anti-cancer efficacy of silybin derivatives – A structure-activity relationship. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanucci, V.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R.; Pannecouque, C.; Iuliano, M.; De Tommaso, G.; Caruso, T.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Silibinin phosphodiester glycol-conjugates: Synthesis, redox behavior and biological investigations. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.X.; Huang, K.X.; Li, H.B.; Gong, J.X.; Wang, F.; Feng, Y.B.; Tao, Q.F.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, X.K.; Wu, X.M.; et al. Design, synthesis, and examination of neuron protective properties of alkenylated and amidated dehydro-silybin derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7732–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivannan, E.; Amawi, H.; Hussein, N.; Karthikeyan, C.; Fetcenko, A.; Narayana Moorthy, N.S.H.; Trivedi, P.; Tiwari, A.K. Design and discovery of silybin analogues as antiproliferative compounds using a ring disjunctive – Based, natural product lead optimization approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 133, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vue, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Parisis, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, Q.-H. Silibinin derivatives as anti-prostate cancer agents: Synthesis and cell-based evaluations. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Vue, B.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X.; Lee, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, Q.-H. 3-O-Alkyl-2,3-dehydrosilibinins: Two synthetic approaches and in vitro effects toward prostate cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3226–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fabio, G.; Romanucci, V.; De Nisco, M.; Pedatella, S.; Di Marino, C.; Zarrelli, A. Microwave-assisted oxidation of silibinin: A simple and preparative method for the synthesis of improved radical scavengers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6279–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazak, R.; Svobodova, A.; Psotova, J.; Sedmera, P.; Prikrylova, V.; Walterova, D.; Kren, V. Oxidized derivatives of silybin and their antiradical and antioxidant activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 5677–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrelli, A.; Sgambato, A.; Petito, V.; De Napoli, L.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G. New C-23 modified of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of antioxidant properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4389–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzubak, P.; Hajduch, M.; Gazak, R.; Svobodova, A.; Psotova, J.; Walterova, D.; Sedmera, P.; Kren, V. New derivatives of silybin and 2,3-dehydrosilybin and their cytotoxic and P-glycoprotein modulatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3793–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psyzkova, M.; Biler, M.; Biedermann, D.; Valentova, K.; Kuzma, M.; Vrba, J.; Ulrichova, J.; Sokolova, R.; Mojovic, M.; Popovic-Bijelic, A.; et al. Flavonolignan 2,3-dehydroderivatives: Preparation, antiradical and cytoprotective activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 90, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vue, B.; Zhang, X.; Lee, T.; Nandini, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, Q.-H. 5- or/and 20-O-Alkyl-2,3-dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and biological profiles on prostate cancer cell models. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4845–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.; Bhatia, N.; Condon, M.S.; Bosland, M.C.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of silibinin in rat prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2002, 53, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, X.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin decreases prostate-specific antigen with cell growth inhibition via G1 arrest, leading to differentiation of prostate carcinoma cells: Implications for prostate cancer intervention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7490–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deep, G.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, C.; Kroll, D.J.; Agarwal, R. Silymarin and silibinin cause G1 and G2-M cell cycle arrest via distinct circuitries in human prostate cancer PC3 cells: A comparison of flavone silibinin with flavanolignan mixture silymarin. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Deep, G.; Blouin, M.-J.; Pollak, M.N.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin suppresses in vivo growth of human prostate carcinoma PC-3 tumor xenograft. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 9–14 and 20–45 are available from the authors. |





| Compound | IC50 (µM) a | IC50 (Silibinin)/IC50(Derivative) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-3 b | DU145 c | LNCaP d | PC-3b | DU145 c | LNCaP d | |
| Docetaxel | 0.0019 ± 0.0006 | 0.0012 ± 0.0003 | 0.0002 ± 0.0001 | - | - | - |
| Silibinin | 72.65 ± 3.15 | 93.34 ± 13.67 | 43.73 ± 10.90 | - | - | - |
| 2 [23] | 9.45 ± 0.56 | 11.48 ± 1.42 | 3.09 ± 1.30 | 8 | 8 | 14 |
| 3 [24] | 3.25 ± 0.31 | 7.59 ± 0.66 | 2.58 ± 0.07 | 22 | 12 | 17 |
| 4 [24] | 1.71 ± 0.45 | 11.04 ± 0.68 | 2.07 ± 0.18 | 42 | 8 | 21 |
| 8 | 26.09 ± 3.58 | 11.47 ± 2.38 | 5.71 ± 2.13 | 3 | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 42.64 ± 6.61 | 39.64 ± 9.49 | 12.08 ± 1.81 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 10 | 9.92 ± 0.43 | 8.62 ± 0.32 | 7.49 ± 0.16 | 7 | 11 | 6 |
| 11 | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 1.84 ± 0.14 | 1.82 ± 0.14 | 52 | 51 | 24 |
| 12 | 25.05 ± 1.00 | 19.59 ± 0.47 | 11.00 ± 0.99 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| 13 | 26.47 ± 1.00 | 45.10 ± 11.53 | 12.72 ± 6.28 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 14 | 25.65 ± 3.39 | 19.42 ± 0.88 | 16.35 ± 3.47 | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| 19 | 5.76 ± 1.36 | 8.13 ± 0.42 | 5.19 ± 2.08 | 13 | 11 | 8 |
| 20 | 9.09 ± 1.48 | 32.71 ± 5.32 | 20.69 ± 5.34 | 8 | 3 | 2 |
| 21 | 5.15 ± 2.13 | 9.97 ± 3.34 | 5.13 ± 0.89 | 14 | 9 | 9 |
| 22 | 3.47 ± 2.23 | 6.73 ± 0.45 | 5.07 ± 0.52 | 21 | 14 | 9 |
| 23 | 5.16 ± 0.94 | 9.21 ± 0.37 | 3.09 ± 0.15 | 14 | 10 | 14 |
| 24 | 5.76 ± 1.36 | 8.18 ± 0.42 | 5.19 ± 2.08 | 11 | 8 | 13 |
| 25 | 6.41 ± 0.40 | 6.64 ± 0.54 | 6.33 ± 0.34 | 11 | 14 | 7 |
| 26 | 2.03 ± 0.69 | 8.39 ± 1.38 | 3.89 ± 0.54 | 36 | 11 | 11 |
| 27 | 3.77 ± 0.41 | 5.39 ± 0.53 | 4.02 ± 1.55 | 19 | 17 | 11 |
| 28 | 3.30 ± 0.86 | 5.78 ± 1.36 | 2.70 ± 0.47 | 22 | 16 | 16 |
| 29 | 2.73 ± 0.12 | 2.51 ± 0.04 | 2.21 ± 0.17 | 27 | 37 | 20 |
| 30 | 3.77 ± 0.41 | 3.07 ± 0.51 | 3.84 ± 0.51 | 19 | 30 | 11 |
| 31 | 2.84 ± 0.10 | 2.85 ± 0.23 | 2.51 ± 0.31 | 26 | 33 | 17 |
| 32 | 2.86 ± 0.79 | 14.12 ± 2.79 | 5.89 ± 0.30 | 25 | 7 | 7 |
| 33 | 7.49 ± 1.98 | 19.84 ± 2.38 | 8.06 ± 1.44 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| 34 | 2.95 ± 0.76 | 5.90 ± 1.30 | 3.92 ± 1.67 | 25 | 16 | 11 |
| 35 | 2.37 ± 0.70 | 7.26 ± 1.12 | 2.28 ± 0.42 | 31 | 13 | 19 |
| 36 | 24.09 ± 10.55 | 66.96 ± 13.65 | 27.30 ± 5.42 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 37 | 2.71 ± 0.23 | 2.69 ± 0.03 | 1.99 ± 0.23 | 27 | 35 | 22 |
| 38 | 2.94 ± 0.13 | 10.60 ± 0.63 | 1.74 ± 0.97 | 25 | 9 | 25 |
| 39 | 3.49 ± 0.24 | 6.36 ± 0.37 | 2.84 ± 0.22 | 21 | 15 | 15 |
| 40 | 2.72 ± 0.08 | 3.06 ± 0.13 | 2.23 ± 0.18 | 27 | 31 | 20 |
| 41 | 9.98 ± 4.94 | >50 | 11.41 ± 5.91 | 7 | <2 | 4 |
| 42 | 5.30 ± 0.66 | 6.85 ± 0.77 | 4.58 ± 1.77 | 14 | 14 | 10 |
| 43 | 7.87 ± 1.47 | 48.12 ± 16.27 | 14.39 ± 7.49 | 9 | 2 | 3 |
| 44 | 8.45 ± 2.89 | 18.57 ± 7.67 | 12.80 ± 7.80 | 9 | 5 | 3 |
| 45 | 4.72 ± 0.88 | 8.59 ± 2.23 | 5.66 ± 0.44 | 15 | 11 | 8 |
| Compound | IC50 (µM) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-3 | DU145 | LNCaP | MCF 10A | PWR-1E | |
| Silibinin | 72.65 ± 3.15 | 93.34 ± 13.67 | 43.73 ± 10.90 | 23.84 ± 0.96 | 20.45 ± 4.09 |
| 11 | 1.40 ± 0.17 | 1.84 ± 0.14 | 1.82 ± 0.14 | >50 | >50 |
| 29 | 2.73 ± 0.12 | 2.51 ± 0.04 | 2.21 ± 0.17 | <5 | <5 |
| 31 | 2.84 ± 0.10 | 2.85 ± 0.23 | 2.51 ± 0.31 | <5 | <5 |
| 37 | 2.71 ± 0.23 | 2.69 ± 0.03 | 1.99 ± 0.23 | <5 | <5 |
| 40 | 2.72 ± 0.08 | 3.06 ± 0.13 | 2.23 ± 0.18 | <5 | <5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vue, B.; Zhang, S.; Vignau, A.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Diaz, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, Q.-H. O-Aminoalkyl-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and In Vitro Effects Towards Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123142
Vue B, Zhang S, Vignau A, Chen G, Zhang X, Diaz W, Zhang Q, Zheng S, Wang G, Chen Q-H. O-Aminoalkyl-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and In Vitro Effects Towards Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123142
Chicago/Turabian StyleVue, Bao, Sheng Zhang, Andre Vignau, Guanglin Chen, Xiaojie Zhang, William Diaz, Qiang Zhang, Shilong Zheng, Guangdi Wang, and Qiao-Hong Chen. 2018. "O-Aminoalkyl-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and In Vitro Effects Towards Prostate Cancer Cells" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123142
APA StyleVue, B., Zhang, S., Vignau, A., Chen, G., Zhang, X., Diaz, W., Zhang, Q., Zheng, S., Wang, G., & Chen, Q. -H. (2018). O-Aminoalkyl-O-Trimethyl-2,3-Dehydrosilybins: Synthesis and In Vitro Effects Towards Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules, 23(12), 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123142