Interaction between Saikosaponin D, Paeoniflorin, and Human Serum Albumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SSD- and PF-Induced Conformational Changes in HSA
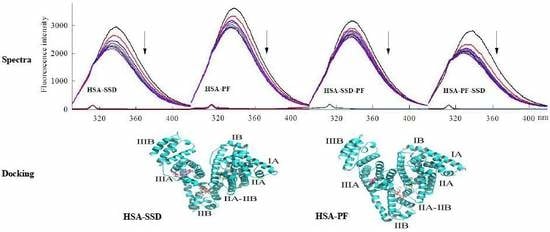
2.1.1. Fluorescence Spectra
2.1.2. Circular Dichroism Studies
2.2. Fluorescence Quenching of HSA by SSD and PF
2.3. Static Quenching of HSA Induced by SSD and PF
2.4. Binding Constants, Sites and Forces
2.4.1. Binding Constants and Numbers of Binding Sites
2.4.2. Identification of SSD or PF Binding Sites
2.4.3. Binding Forces between HSA and SSD/PF
2.5. Energy Transfer Resulting from HSA-SSD and HSA-PF Interaction
2.6. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Absorbance Measurements
3.3. Fluorescence Spectra
3.4. Correction of the Internal Filter
3.5. CD Spectra
3.6. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zunszain, P.A.; Ghuman, J.; Komatsu, T.; Tsuchida, E.; Curry, S. Crystal structural analysis of human serum albumin complexed with hemin and fatty acid. BMC. Struct. Biol. 2003, 3, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curry, S.; Mandelkow, H.; Brick, P.; Franks, N. Crystal structure of human serum albumin complexed with fatty acid reveals an asymmetric distribution of binding sites. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, W.; Sokolowska, M.; Kurowska, E.; Faller, P. Binding of transition metal ions to albumin: Sites, affinities and rates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5444–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. A systematic review of the active saikosaponins and extracts isolated from Radix Bupleuri and their applications. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 620–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Ni, J. Radix bupleuri: A review of traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7597596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, K.; Chu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yan, X.; Ma, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, C. UFLC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic studies of six saikosaponins in rat plasma after oral administration of bupleurum dropping pills. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 124, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.N.; Yuan, Z.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Yan, R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Liao, M.; Chen, J.X. Saikosaponin a and its epimer saikosaponin d exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Guo, X.T.; Chen, J.W.; Zhao, Y.; Cong, X.; Jiang, Z.L.; Cao, R.F.; Cui, K.; Gao, S.S.; Tian, W.R. Saikosaponin-D attenuates heat stress-induced oxidative damage in LLC-PK1 cells by increasing the expression of anti-oxidant enzymes and HSP72. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Wang, T.; Shen, H.; Siow, Y.; Choy, P.; Gong, Y. Saikosaponin-d attenuates the development of liver fibrosis by preventing hepatocyte injury. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, S.S.; Wang, B.F.; Cheng, Y.A.; Song, P.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, Z.F. Inhibitory effects of saikosaponin-d on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.F.; Huang, S.J.; Huang, C.C.; Liu, P.S.; Lin, K.I.; Liu, C.W.; Hsieh, W.C.; Shiu, L.Y.; Chen, C.H. Saikosaponin d induces cell death through caspase-3-dependent, caspase-3-independent and mitochondrial pathways in mammalian hepatic stellate cells. BMC. Cancer 2016, 16, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Bi, K.; Guo, D. Determination of paeoniflorin in rat plasma by a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method coupled with solid-phase extraction. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Xiao, X.; Guo, D.; Mo, L.; Bu, C.; Ye, W.; Den, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, X. Protective effects of paeoniflorin against AOPP-induced oxidative injury in HUVECs by blocking the ROS-HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Shan, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HIF-1alpha through mTOR-dependent pathway. Fitoterapia 2014, 99, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Chu, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, W.; Yi, J.; Gao, Y. Beneficial effects of paeoniflorin on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat diet in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44819–44829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Shen, H. Protective effects of paeoniflorin on TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway and apoptosis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kang, Y.; Cao, J. Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on the conformation and activity of bovine serum albumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 159, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastukhov, A.V.; Levchenko, L.A.; Sadkov, A.P. Spectroscopic study on binding of rutin to human serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 842, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Hyodo, S.; Taguchi, K.; Nishi, K.; Yamaotsu, N.; Hirono, S.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Seo, H.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Long chain fatty acids alter the interactive binding of ligands to the two principal drug binding sites of human serum albumin. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, A.M.; Abdelhameed, A.S. A spectroscopic approach to investigate the molecular interactions between the newly approved irreversible ErbB blocker “Afatinib” and bovine serum albumin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Qin, Q.; Chang, M.; Li, S.; Shi, X.; Xu, G. Molecular interaction study of flavonoids with human serum albumin using native mass spectrometry and molecular modeling. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Duan, J.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Meng, A.; Shi, J. Insight into the binding interaction of kaempferol-7-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside with human serum albumin by multiple fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular modeling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3619–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, K.; Alam, P.; Khan, R.H.; Rauf, A. Synthesis, characterization and interaction studies of 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives of fatty acid with human serum albumin (HSA): A combined multi-spectroscopic and molecular docking study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Hu, Y.X.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.; Ai, H.X.; Liu, H.S. Study on the interaction of paeoniflorin with human serum albumin (HSA) by spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wang, H.M.; Niu, Q.X.; Ye, D.Y.; Liang, G.W. Binding between saikosaponin C and human serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular docking. Molecules 2016, 21, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudlarek, A.; Pentak, D.; Ploch, A.; Pozycka, J.; Maciazek-Jurczyk, M. Effect of temperature on tolbutamide binding to glycated serum albumin. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X.H. Investigation of the interaction between berberine and human serum albumin. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y. Determination of binding domains of paeonol on immobilized human serum albumin by high-performance affinity chromatography. Se Pu 2010, 28, 688–692. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.H.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.J. Intermolecular interaction of prednisolone with bovine serum albumin: Spectroscopic and molecular docking methods. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 15, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, A.S.; Bakheit, A.H.; Almutairi, F.M.; AlRabiah, H.; Kadi, A.A. Biophysical and in silico studies of the interaction between the anti-viral agents acyclovir and penciclovir, and human serum albumin. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Yuan, H.; Liu, M.; Hu, J. 1H-NMR study of the effect of acetonitrile on the interaction of ibuprofen with human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A. Clinical utility of free drug monitoring. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, P. Investigation of the inter-action between bovine serum albumin with paeoniforin and loganin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2010, 30, 6–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Binding of paeonol to human serum albumin: A hybrid spectroscopic approach and conformational study. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1976, 12, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rimac, H.; Dufour, C.; Debeljak, Z.; Zorc, B.; Bojic, M. Warfarin and flavonoids do not share the same binding region in binding to the IIA subdomain of human serum albumin. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Chuang, V.T.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Albumin-drug interaction and its clinical implication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 5435–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kokot, S. Spectrometric and voltammetric studies of the interaction between quercetin and bovine serum albumin using warfarin as site marker with the aid of chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, P.M.; Martins, M.A.P.; Castilho, R.O. Review on mechanisms and interactions in concomitant use of herbs and warfarin therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martino, M.; Chiarugi, A.; Boner, A.; Montini, G.; De’Angelis, G.L. Working towards an appropriate use of ibuprofen in children: An evidence-based appraisal. Drugs 2017, 77, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, B.Y.; Mo, J.F.; Wong, V.K. Autophagic effects of chaihu (dried roots of bupleurum chinense DC or bupleurum scorzoneraefolium WILD). Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Li, W.; Wang, L.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.X.; Huang, B.; Gao, X.M. Varieties, functions and clinical applications of chishao and baishao: A literature review. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2013, 38, 3595–3601. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronina, T.; Strugala, P.; Poplonski, J.; Wloch, A.; Sordon, S.; Bartmanska, A.; Huszcza, E. The influence of glycosylation of natural and synthetic prenylated flavonoids on binding to human serum albumin and inhibition of cyclooxygenases COX-1 and COX-2. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Pan, H.; Shen, T.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Di, X.; Wang, S. Interaction of flavonoids from Woodwardia unigemmata with bovine serum albumin (BSA): Application of spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling methods. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; He, L.L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ye, X.; Jing, J.J.; Zhang, J.F.; Gao, M.; Wang, X. Spectroscopic investigation on the food components-drug interaction: The influence of flavonoids on the affinity of nifedipine to human serum albumin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stryer, L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1978, 47, 819–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Kim, S.; Nallet, J.P.; Nepveu, F. Interactions between antimalarial indolone-N-oxide derivatives and human serum albumin. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB Protein Data Bank—Structure Summary. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2BXE (accessed on 30 November 2017).
Sample Availability: Not Available. |










| Type | Binding | Detection | Shift and Its Range (nm) | Quenching (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary | HSA-SSD | λex = 280 nm | Left shift 5, 338–333 | 26.55 |
| Δλ = 15 nm | No shift | 7.43 | ||
| Δλ = 60 nm | Left shift 2, 279–277 | 24.34 | ||
| HSA-PF | λex = 280 nm | Left shift 3, 337–334 | 19.42 | |
| Δλ = 15 nm | No shift | 8.29 | ||
| Δλ = 60 nm | Left shift 2, 279–277 | 17.66 | ||
| Terniary | HSA-PF-SSD | λex = 280 nm | Left shift 13, 339–326 | 28.63 |
| HSA-SSD-PF | λex = 280 nm | Left shift 3, 336–333 | 18.19 | |
| Tyrosine | Tyr-SSD | Δλ = 15 nm | No shift | 2.82 |
| Tyr-PF | Δλ = 15 nm | No shift | 4.31 | |
| Tryptophan | Trp-SSD | Δλ = 60 nm | No shift | 12.82 |
| Trp-PF | Δλ = 60 nm | No shift | 10.38 |
| Binding | Ratio | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA | 52.7 | 7.3 | 10.9 | 29.3 | |
| HSA-SSD | 1:1 | 46.3 | 9.0 | 16.9 | 27.8 |
| HSA-PF | 1:1 | 55.6 | 6.5 | 9.1 | 25.2 |
| HSA-PF-SSD | 1:1:1 | 66.4 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 20.1 |
| Binding | Fluorescence | T (°C) | Detection | Kq (L·mol−1·s−1) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-SSD | Conventional | 20 | λex = 280 nm | 1.6 × 1015 | 0.998 |
| 30 | λex = 280 nm | 1.1 × 1015 | 0.996 | ||
| Synchronous | 20 | Δλ = 15 nm | 4.3 × 1014 | 0.991 | |
| 20 | Δλ = 60 nm | 1.3 × 1015 | 0.994 | ||
| 30 | Δλ = 15 nm | 3.5 × 1014 | 0.993 | ||
| 30 | Δλ = 60 nm | 1.1 × 1015 | 0.991 | ||
| HSA-PF | Conventional | 20 | λex = 280 nm | 1.3 × 1015 | 0.995 |
| 30 | λex = 280 nm | 1.1 × 1015 | 0.993 | ||
| Synchronous | 20 | Δλ = 15 nm | 7.5 × 1013 | 0.992 | |
| 20 | Δλ = 60 nm | 7.0 × 1013 | 0.992 | ||
| 30 | Δλ = 15 nm | 3.2 × 1014 | 0.994 | ||
| 30 | Δλ = 60 nm | 5.8 × 1014 | 0.995 | ||
| HSA-PF-SSD | Conventional | 20 | λex = 280 nm | 8.5 × 1014 | 0.992 |
| 30 | λex = 280 nm | 7.3 × 1014 | 0.994 | ||
| HSA-SSD-PF | Conventional | 20 | λex = 280 nm | 5.9 × 1014 | 0.992 |
| 30 | λex = 280 nm | 6.8 × 1014 | 0.993 |
| Binding | T (°C) | Ka (mol·L−1) ± SD | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-SSD | 20 | 6.54 × 103 ± 0.146 | 0.525 | 0.998 |
| 30 | 8.28 × 102 ± 0.015 | 0.464 | 0.998 | |
| HSA-PF-SSD | 20 | 2.46 × 103 ± 0.138 | 0.497 | 0.996 |
| 30 | 0.95 × 102 ± 0.121 | 0.230 | 0.996 | |
| HSA-PF | 20 | 7.39 × 104 ± 0.174 | 0.736 | 0.998 |
| 30 | 4.43 × 103 ± 0.019 | 0.482 | 0.995 | |
| HSA-SSD-PF | 20 | 9.58 × 102 ± 0.024 | 0.324 | 0.992 |
| 30 | 3.24 × 102 ± 0.031 | 0.263 | 0.991 |
| Drug | °C | Ka | n | ΔG | ΔS | ΔH | Reaction System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | 25 | 3.56 × 104 | 0.62 | −21.0 | 103.5 | 4.1 | 10–70 μM PF, 10 μM BSA, pH7.4 Tris-HCL | [34] |
| 37 | 3.78 × 104 | 0.61 | −22.0 | |||||
| PF | 15 | 1.91 × 103 | 0.91 | −18.1 | 28.2 | −10.0 | 2.5–12.5 μM PF, 10 μM BHSA, pH7.4 Tris-HCL | [24] |
| 37 | 1.42 × 103 | 0.89 | −18.7 | |||||
| Paeonol | 10 | 1.58 × 104 | 1.01 | −22.7 | 88.7 | 2.4 | 10–70 μM paenol, 1 μM BHSA, pH7.4 Tris-HCL | [35] |
| 40 | 9.68 × 102 | 0.84 | −17.9 | 64.9 | ||||
| Paeonol | 4 | 1.33 × 104 | - | −22.0 | −6.3 | −23.8 | pH7.4 PBS | [28] |
| 37 | 3.55 × 103 | - | −21.8 | |||||
| SSC | 26 | 3.72 × 103 | 0.79 | −20.34 | −90.3 | −47.3 | 1–15 μM PF, 2 μM BHSA, pH7.4 PBS | [26] |
| Fixed | Binding | Shift and Range (nm) | Quenching (%) | Ka (mol·L−1) ± SD | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe | HSA-SSD | Left shift 5, 338–333 | 26.55 | 6.54 × 103 ± 0.146 | 0.525 | 0.998 |
| HSA-War-SSD | Left 5, 337–332 | 29.93 | 3.18 ± 0.016 | 0.224 | 0.995 | |
| HSA-Ibu-SSD | Left 5, 338–333 | 26.12 | 8.42 ± 0.025 | 0.177 | 0.992 | |
| HSA-PF | Left shift 3, 337–334 | 19.42 | 7.39 × 104 ± 0.174 | 0.736 | 0.998 | |
| HSA-War-PF | Left 3, 338–335 | 18.57 | 3.45 ± 0.036 | 0.277 | 0.997 | |
| HSA-Ibu-PF | Left 2, 336–334 | 16.09 | 7.86 ± 0.039 | 0.382 | 0.994 | |
| SSD/PF | HSA-War | Left 3, 338–335 | 19.07 | 2.54 × 102 ± 0.899 | 0.389 | 0.996 |
| HSA-PF-War | Left 4, 340–336 | 14.78 | 4.11 × 105 ± 3.420 | 0.716 | 0.997 | |
| HSA-SSD-War | Left 4, 339–335 | 17.00 | 9.72 × 102 ± 0.448 | 0.469 | 0.996 | |
| HSA-Ibu | Left 3, 338–335 | 17.07 | 4.10 × 102 ± 0.169 | 0.448 | 0.992 | |
| HSA-SSD-Ibu | Left 1, 335–334 | 17.08 | 7.21 × 103 ± 0.368 | 0.520 | 0.994 | |
| HSA-PF-Ibu | Left 3, 338–335 | 19.36 | 4.2 × 105 ± 0.034 | 0.638 | 0.992 |
| Binding | T (°C) | ΔG (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS (J·mol−1·K−1) | ΔH (kJ·mol−1) | J (cm3·L·mol−1) | R0 (nm) | E (J) | r (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-SSD | 20 | −19.33 | −314.92 | −111.60 | 1.03 × 10−14 | 2.50 | 0.24 | 3.00 |
| 23 | −17.44 | 1.03 × 10−14 | 2.47 | 0.21 | 3.07 | |||
| 27 | −16.45 | 1.04 × 10−14 | 2.06 | 0.13 | 2.83 | |||
| 30 | −16.18 | 1.04 × 10−14 | 2.47 | 0.27 | 2.92 | |||
| HSA-PF | 20 | −27.64 | −1201.16 | −379.58 | 1.88 × 10−15 | 1.86 | 0.05 | 2.27 |
| 23 | −22.19 | 1.91 × 10−15 | 2.02 | 0.08 | 3.02 | |||
| 27 | −21.29 | 1.91 × 10−15 | 2.05 | 0.12 | 2.85 | |||
| 30 | −15.63 | 1.92 × 10−15 | 1.86 | 0.23 | 2.27 |
| Site | Amino Acid Residue | Atoms * | Bond Length | Trp or Tyr around the Pocket | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | Site I | Lys199 | CH2OH (7) | 2.9 Å | Tyr150 Tyr452 |
| Trp214 | CH2CH2OH (24) | 3.4 Å | |||
| Arg218 | CH2OH (35) | 2.5 Å | |||
| Glu292 | CH2OH (36) | 2.6 Å | |||
| Site II | Asn391 | CH2CH2OH (24) | 2.3 Å | Trp214 | |
| Arg410 | CH2OH (34) | 3.1 Å | |||
| IIA-IIB | Arg209 | CH2CH2OH (37) | 3.3 Å | ||
| PF | Site I | Lys199 | O (21) | 2.9 Å | Tyr150 Trp214 |
| Lys199 | O (27) | 3.0 Å | |||
| Arg257 | O (14) | 3.4 Å | |||
| Arg218 | CH2OH (25) | 2.3 Å | |||
| Ala291 | CH2OH (23) | 2.4 Å | |||
| Glu292 | O (10) | 2.9 Å | |||
| Site II | Asn391 | O (14) | 3.2 Å | Trp214 | |
| Asn391 | CH2OH (23) | 2.5 Å | |||
| Lys414 | O (27) | 3.5 Å | |||
| IIA-IIB | Arg209 | CH2OH (24) | 2.2 Å | Tyr411 | |
| Glu354 | CH2CH2OH (26) | 2.0 Å |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, G.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.-M.; Pan, X.-Y.; Chen, P.-H.; Niu, Q.-X. Interaction between Saikosaponin D, Paeoniflorin, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules 2018, 23, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020249
Liang G-W, Chen Y-C, Wang Y, Wang H-M, Pan X-Y, Chen P-H, Niu Q-X. Interaction between Saikosaponin D, Paeoniflorin, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Guo-Wu, Yi-Cun Chen, Yi Wang, Hong-Mei Wang, Xiang-Yu Pan, Pei-Hong Chen, and Qing-Xia Niu. 2018. "Interaction between Saikosaponin D, Paeoniflorin, and Human Serum Albumin" Molecules 23, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020249
APA StyleLiang, G. -W., Chen, Y. -C., Wang, Y., Wang, H. -M., Pan, X. -Y., Chen, P. -H., & Niu, Q. -X. (2018). Interaction between Saikosaponin D, Paeoniflorin, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules, 23(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020249