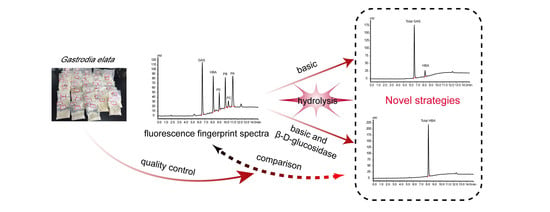
Novel Strategies Using Total Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin, or Total Gastrodigenin for Quality Control of Gastrodia elata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development of the Method
2.2. Quality Evaluation by Pharmacopoeia Indices
2.3. Quality Evaluation by Multi-Markers
2.4. TGH-B Strategy by Total GAS and HBA
2.5. TG-BE Strategy by Total HBA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Preparation of Standard Solution and Extract of G. elata
4.4. Hydrolysis
4.4.1. Base Hydrolysis
4.4.2. Base-Enzymatic Hydrolysis
4.5. Analytical Method Validation
4.5.1. Linearity and LOQ
4.5.2. Precision and Trueness
4.5.3. Recovery of Extraction and Matrix Effect
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, G.B.; Zhao, T.; Muna, S.S.; Jin, H.M.; Park, J.I.; Jo, K.S.; Lee, B.H.; Chae, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; et al. Therapeutic potential of Gastrodia elata Blume for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teong, I.W.J.; Ko, A.A.R.; Li, M.; Heese, K.; Liang, W. Gastrodia elata decreases isoprenaline potency and enhances spontaneous phasic activity in the rat detrusor. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, A.; Ramachandran, U.; Sundaramurthi, H.; Mishra, M.; Sze, S.K.; Hu, J.-M.; Feng, Z.W.; Heese, K. Gastrodia elata Blume (tianma) mobilizes neuro-protective capacities. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, E.K.; Jeon, H.J.; Lim, E.J.; Jung, H.J.; Park, E.H. Anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities of Gastrodia elata Blume. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Chiang, S.Y.; Cheng, K.S.; Lin, Y.H.; Tang, N.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Pon, C.Z.; Hsieh, C.T. Anticonvulsive and free radical scavenging activities of Gastrodia elata Bl. in kainic acid-treated rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2001, 29, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Tang, N.Y.; Chiang, S.Y.; Hsieh, C.T.; Lin, J.G. Anticonvulsive and free radical scavenging actions of two herbs, Uncaria rhynchophylla (MIQ) Jack and Gastrodia elata BL., in kainic acid-treated rats. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kim, I.S.; More, S.V.; Kim, B.W.; Bahk, Y.Y.; Choi, D.K. Gastrodin Protects Apoptotic Dopaminergic Neurons in a Toxin-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 514095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hao, X.W.; Yu, L.; Zhang, P.; Cao, W.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhu, D.L. Gastrodin causes vasodilation by activating KATP channels in vascular smooth muscles via PKA-dependent signaling pathway. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2017, 37, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.D.; Zhou, H.Y.; Sui, Y.P.; Du, X.L.; Wang, W.; Dai, L.; Sui, F.; Huo, H.R.; Jiang, T.L. The rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume—An ethnopharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; Lai, Y.S.; Lu, K.H.; Lin, S.H.; Liao, L.Y.; Ho, C.T.; Sheen, L.Y. Method development and validation for the high-performance liquid chromatography assay of gastrodin in water extracts from different sources of Gastrodia elata Blume. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.W.; Yang, T.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Su, H.W.; Xiang, M.X. Gastrodin stimulates anticancer immune response and represses transplanted H22 hepatic ascitic tumor cell growth: Involvement of NF-kappa B signaling activation in CD4+T cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 269, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.L.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.X.; Cheng, M.C.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, H.B. Comparative pharmacokinetics of gastrodin in rats after intragastric administration of free gastrodin, parishin and Gastrodia elata extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 176, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.L.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.X.; Cheng, M.C.; Xiao, H.B. Pharmacokinetic study of Gastrodia elata in rats. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8903–8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.T. Review: Drug therapy in Chinese traditional medicine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, H.B.; Liang, X.M.; Wei, L.X. Identification of phenolics and nucleoside derivatives in Gastrodia elata by HPLC-UV-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Y.R.; Liu, Y.C.; Hau, J.P.; Wen, K.C.; Lin, J.H.; Huang, W.F. Determination of parishin, parishins B and C in Gastrodiae rhizoma by HPLC. J. Food Drug Anal. 1995, 3, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.K.; Cao, Q.E.; Xiang, Y.Q.; Hu, Z.D. Identification and determination of active components in Gastrodia elata BL. by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 849, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Kang, R.-X.; Shi, J.-G.; Liu, G.-T.; Zhang, J.-J. NHBA isolated from Gastrodia elata exerts sedative and hypnotic effects in sodium pentobarbital-treated mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschke, M.W.; van Oijen, A.E.V.; Koerbel, C.; Scheuer, C.; Menger, M.D. 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol: A novel inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis and growth. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.K.; Chern, Y.J.; Fang, J.M.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, W.P.; Lin, Y.L. Neuroprotective principles from Gastrodia elata. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.J.; Whang, W.K.; Kim, S.; Bach, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Nguyen, X.K.T.; Nguyen, T.T.L.; Jung, B.D.; Yamada, K.; Nabeshima, T.; et al. Parishin C Attenuates Phencyclidine-Induced Schizophrenia-Like Psychosis in Mice: Involvements of 5-HT1A Receptor. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 113, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.S.; Zhao, J.; Zhen, W.P.; Zhao, Y. Neuroprotective effect of 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol against transient focal cerebral ischemia via anti-apoptosis in rats. Brain Res. 2010, 1308, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Choi, D.-K.; Jung, H.J. Neuroprotective Effects of Vanillyl Alcohol in Gastrodia elata Blume Through Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Anti-Apoptotic Activity in Toxin-Induced Dopaminergic MN9D Cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 5349–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.F.; Du, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.L.; Ma, X.D.; Zhou, P.; Li, P.; Li, H.J. Efficient Discovery of Quality Control Markers for Gastrodia elata Tuber by Fingerprint-Efficacy Relationship Modelling. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 28, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Studies on Chemical Constituents and Quality Control of Gastrodia elata; Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Dalian, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.D.; Fan, Y.X.; Jin, C.C.; Wang, F.; Xin, G.Z.; Li, P.; Li, H.J. Specific targeted quantification combined with non-targeted metabolite profiling for quality evaluation of Gastrodia elata tubers from different geographical origins and cultivars. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1450, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Qian, C.; Tang, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y. Chemical fingerprint technique and its application in the classification and quality assessment of the Gastrodia tuber. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 16746–16756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.X.; Feng, G.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhong, L.; Wu, C.J.; Wan, J. Origin discrimination and quality evaluation of Gastrodiae rhizoma (Orchidaceae) by high-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprint. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Menghini, L.; Malatesta, L.; De Luca, E.; Bellagamba, G.; Uysal, S.; Aktumsek, A.; Locatelli, M. Comparative study of biological activities and multicomponent pattern of two wild Turkish species: Asphodeline anatolica and Potentilla speciosa. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Healthcare (EDQM). European Pharmacopoeia, 8th ed.; EDQM: Strasbourg, France, 2014; pp. 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.L.; Wang, L.; Cheng, M.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Xiao, H.B. Rapid and sensitive analysis of parishin and its metabolites in rat plasma using ultra high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 973, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.J.; Liu, X.X.; Cheng, M.C.; Xiao, H.B. Analysis of the metabolic profile of parishin by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, S. A novel dereplication strategy for the identification of two new trace compounds in the extract of Gastrodia elata using UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 988, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.W.; Zou, Y.J.; Mo, Q.Z. Kinetic aspects of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of 3H-gastrodin in rats. Acta Pharm. Sinica 1985, 20, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Tsai, T.H. Pharmacokinetics of gastrodin and its metabolite p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in rat blood, brain and bile by microdialysis coupled to LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, G.S.; Zeng, S. Distribution and metabolism of gastrodin in rat brain. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.J.; Park, S.K.; Hwang, I.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Jung, S.J.; Baek, N.I.; Lee, H.Y.; Won, M.H.; et al. Gastrodin decreases immunoreactivities of gamma-aminobutyric acid shunt enzymes in the hippocampus of seizure-sensitive gerbils. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 71, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Chen, F. Preparative isolation and purification of gastrodin from the Chinese medicinal plant Gastrodia elata by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1052, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Tsai, T.R.; Tsai, T.H. Analysis of brain distribution and biliary excretion of a nutrient supplement, gastrodin, in rat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 590, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of all extracts are available from the authors. |




| Compounds | Precision and Trueness (n = 5) | Linearity | LOQ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (μg/mL) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |||||||
| Mean ± SD | RSD (%) | RE (%) | Mean ± SD | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ||||
| GAS | 0.2 | 0.19 ± 0 | 0.94 | −5.05 | 0.18 ± 0 | 3.37 | −6.67 | y = 9.12 × 105x + 6.69 × 104 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.18 ± 0 | 0.20 | −1.70 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.85 | −3.50 | |||
| 6 | 5.97 ± 0.02 | 0.36 | −0.46 | 5.86 ± 0.11 | 1.89 | −2.37 | |||
| HBA | 0.2 | 0.22 ± 0 | 0.20 | 9.58 | 0.21 ± 0 | 2.27 | 6.55 | y = 2.07 × 106x − 7.44 × 104 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.19 ± 0 | 0.29 | −0.48 | 1.16 ± 0.03 | 2.41 | −3.08 | |||
| 6 | 5.97 ± 0.01 | 0.18 | −0.47 | 5.75 ± 0.14 | 2.42 | −4.10 | |||
| PE | 0.2 | 0.17 ± 0 | 3.55 | −14.97 | 0.17 ± 0 | 3.00 | −14.77 | y = 1.65 × 105x − 6.01 × 103 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | 1.41 | −8.64 | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 2.95 | −12.02 | |||
| 6 | 5.60 ± 0.03 | 0.46 | −6.73 | 5.45 ± 0.11 | 2.10 | −9.11 | |||
| PB | 0.2 | 0.17 ± 0 | 5.10 | −14.16 | 0.17 ± 0 | 2.33 | −13.19 | y = 2.16 × 105x + 5.31 × 103 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.09 ± 0.02 | 1.91 | −9.10 | 1.07 ± 0.02 | 2.31 | −10.54 | |||
| 6 | 5.71 ± 0.04 | 0.75 | −4.85 | 5.71 ± 0.09 | 1.56 | −4.83 | |||
| PC | 0.2 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 8.52 | −9.00 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 11.44 | 6.43 | y = 1.77 × 105x + 5.64 × 103 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.12 ± 0.02 | 1.79 | −6.81 | 1.10 ± 0.01 | 1.00 | −8.57 | |||
| 6 | 5.77 ± 0.03 | 0.50 | −3.82 | 5.72 ± 0.12 | 0.02 | −4.65 | |||
| PA | 0.2 | 0.19 ± 0 | 5.11 | −4.88 | 0.17 ± 0 | 1.48 | −12.72 | y = 1.98 × 105x + 5.10 × 103 | 0.5 |
| 1.2 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 1.56 | −7.88 | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 3.36 | −12.36 | |||
| 6 | 5.38 ± 0.01 | 0.22 | −10.26 | 5.39 ± 0.16 | 3.01 | −10.24 | |||
| Compound | Origin (μg/mL) | Spiked (μg/mL) | Determined (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | Matrix Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAS | 0.7021 | 0.5 | 1.1785 ± 0.0108 | 95.28 ± 2.16 | 94.88 ± 0.02 |
| HBA | 0.1361 | 0.5 | 0.5970 ± 0.0199 | 92.20 ± 3.98 | 97.63 ± 0.62 |
| PE | 1.2966 | 0.5 | 1.8479 ± 0.0065 | 110.27 ± 1.29 | 101.93 ± 0.75 |
| PB | 2.3254 | 0.5 | 2.9022 ± 0.1082 | 114.98 ± 20.96 | 100.79 ± 0.17 |
| PC | 0.6598 | 0.5 | 1.1573 ± 0.0605 | 99.52 ± 12.11 | 106.79 ± 1.63 |
| PA | 2.6140 | 0.5 | 3.1205 ± 0.0574 | 101.32 ± 11.47 | 103.84 ± 1.07 |
| Content (%) | GAS | HBA | GAS + HBA | PE | PB | PC | PA | Sum of Six Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yunnan | 0.356 ± 0.172 | 0.093 ± 0.056 | 0.449 | 0.856 ± 0.226 | 0.725 ± 0.204 | 0.196 ± 0.072 | 1.475 ± 0.448 | 3.700 |
| Sichuan | 0.378 ± 0.231 | 0.097 ± 0.062 | 0.475 | 0.620 ± 0.166 | 0.540 ± 0.158 | 0.128 ± 0.040 | 0.930 ± 0.455 | 2.693 |
| Anhui | 0.485 ± 0.174 | 0.056 ± 0.042 | 0.541 | 0.583 ± 0.076 | 0.546 ± 0.113 | 0.131 ± 0.034 | 1.015 ± 0.552 | 2.815 |
| Zhejiang | 0.410 ± 0.288 | 0.070 ± 0.030 | 0.480 | 0.619 ± 0.181 | 0.541 ± 0.150 | 0.128 ± 0.042 | 1.269 ± 0.701 | 3.037 |
| Guizhou | 0.353 ± 0.102 | 0.044 ± 0.016 | 0.397 | 0.544 ± 0.167 | 0.439 ± 0.164 | 0.127 ± 0.037 | 0.768 ± 0.338 | 2.274 |
| Jilin | 0.283 ± 0.170 | 0.092 ± 0.043 | 0.375 | 0.832 ± 0.143 | 0.561 ± 0.191 | 0.134 ± 0.049 | 0.990 ± 0.678 | 2.891 |
| Shanxi | 0.279 ± 0.040 | 0.080 ± 0.024 | 0.359 | 0.614 ± 0.076 | 0.569 ± 0.072 | 0.148 ± 0.014 | 1.085 ± 0.156 | 2.774 |
| Xizang | 0.478 ± 0.161 | 0.062 ± 0.030 | 0.540 | 0.799 ± 0.135 | 0.681 ± 0.043 | 0.127 ± 0.021 | 1.256 ± 0.252 | 3.402 |
| Strategy | Marker | Order of Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacopoeia | GAS and HBA or single GAS | Anhui > Xizang > Zhejiang > Sichuan > Yunnan > Guizhou > Jilin > Shanxi |
| Multi-markers | GAS, HBA, PE, PB, PC and PA | Yunnan > Xizang > Zhejiang > Jilin > Anhui > Shanxi > Sichuan > Guizhou |
| TGH-B | Total GAS, HBA | Xizang > Zhejiang > Yunnan > Anhui > Jilin > Sichuan > Shanxi > Guizhou |
| TH-BE | Total HBA | Xizang > Zhejiang > Yunnan > Anhui > Jilin > Sichuan > Shanxi > Guizhou |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, B. Novel Strategies Using Total Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin, or Total Gastrodigenin for Quality Control of Gastrodia elata. Molecules 2018, 23, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020270
Tang C, Wu B, Wu J, Zhang Z, Yu B. Novel Strategies Using Total Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin, or Total Gastrodigenin for Quality Control of Gastrodia elata. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chunlan, Bingchu Wu, Jinyi Wu, Zheng Zhang, and Bocheng Yu. 2018. "Novel Strategies Using Total Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin, or Total Gastrodigenin for Quality Control of Gastrodia elata" Molecules 23, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020270
APA StyleTang, C., Wu, B., Wu, J., Zhang, Z., & Yu, B. (2018). Novel Strategies Using Total Gastrodin and Gastrodigenin, or Total Gastrodigenin for Quality Control of Gastrodia elata. Molecules, 23(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020270