A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
- 5′-cy5-(CH2)6-aaa-aaa-aaa-aaa-aaa-aaa-gat-cgg-gtg-tgg-gtg-gcg-taa-agg-gag-cat-cgg-aca-3′
- cDNA: 5′-biotin-(CH2)6-aaa-aaa-tgt-ccg-atg-ctc-cct-tta-cgc-cac-cca-cac-ccg-atc-3′
- probe 2: 5′-biotin-(CH2)6-ttt-ttt-ttt-ttt-ttt-ttt-3′
2.2. Preparation of Streptavidin-Biotin-DNA Probe Conjugates
2.3. Fabrication of Aptamer-Based Strips
2.4. OTA Detection
2.5. Strip Sensitivity and Specificity Detection
2.6. Applications of Test Strips to Samples
3. Results and Discussion
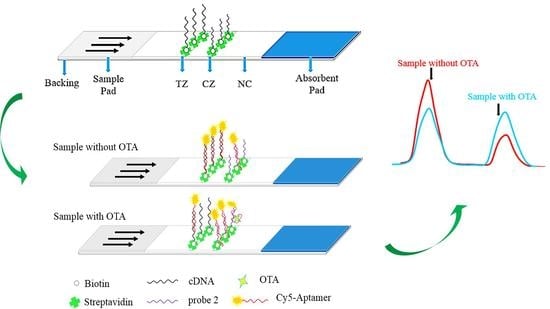
3.1. Concept and Aptasensor Mechanism
3.2. Optimization of the Aptamer Concentration
3.3. Effect of pH Value of the Running Buffer on the Strip Sensor Performance
3.4. Sensitivity and Specificity
3.5. Practical Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scott, P.M.; Walbeek, W.V.; Kennedy, B.; Anyeti, D. Mycotoxins (ochhratoxin A, citrinin, and sterigmatocystin) and toxigenic fungi in grains and other agricultural products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1972, 20, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, K.; Wang, X.L.; Zhi, H.W.; Sun, B.G.; Li, X.T. Identification and safety evaluation of a product from the biodegradation of Ochratoxin A by an Aspergillus strain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzo, M.; Piemontese, L.; Gambacorta, L.; Zivoli, R.; Longobardi, F. Food Coloring Agents and Plant Food Supplements Derived from Vitis vinifera: A New Source of Human Exposure to Ochratoxin A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3609–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvano, F.; Albanese, D.; Pilloton, R.; Di Matteo, M. A highly sensitive impedimetric label free immunosensor for Ochratoxin measurement in cocoa beans. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, C.; Biermaier, B.; Gross, M.; Schwaiger, K.; Gareis, M. Ochratoxin A in brewer’s yeast used as food supplement. Mycotoxin Res. 2016, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, J.N.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Xing, F.G.; Dai, X.F.; Liu, Y. Mycotoxin detection—Recent trends at global level. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2265–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Apaliya, M.T.; Mahunu, G.K.; Chen, L.L.; Li, W.H. Control of Ochratoxin A-producing fungi in grape berry by microbial antagonists: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.Y.F.; Renaud, J.B.; McDowell, T.; Seifert, K.A.; Yeung, K.K.C.; Sumarah, M.W. Diversity of Mycotoxin-Producing Black Aspergilli in Canadian Vineyards. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toman, J.; Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Grosse, Y.; Dvorak, V.; Roubal, T.; Neuchlova, L. The Occurrence of Ochratoxin A in White and Parboiled Rice. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Kong, W.J.; Hu, Y.C.; Yang, M.H.; Huang, L.Q.; Zhao, M.; Ouyang, Z. Aptamer-affinity column clean-up coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection for the rapid determination of Ochratoxin A in ginger powder. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouati, A.; Yang, C.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Aptamers: A Promising Tool for Ochratoxin A Detection in Food Analysis. Toxins 2013, 5, 1988–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.Z.; Zheng, J.J.; Luo, Y.B.; Zhao, C.H.; Hao, J.R.; Li, X.H.; Huang, K.L.; Xu, W.T. Lipid Rafts Disruption Increases Ochratoxin A Cytotoxicity to Hepatocytes. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Gan, F.; Xue, H.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, D.; Khan, A.Z.; Chen, X.X.; Huang, K.H. Nephropathy and hepatopathy in weaned piglets provoked by natural Ochratoxin A and involved mechanisms. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koszegi, T.; Poor, M. Ochratoxin A: Molecular Interactions, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Prevention at the Molecular Level. Toxins 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.S.J.; El-Nezami, H. Maternal-Fetal Cancer Risk Assessment of Ochratoxin A during Pregnancy. Toxins 2016, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Xing, F.G.; Dai, X.F.; Liu, Y. Recent mycotoxin survey data and advanced mycotoxin detection techniques reported from China: A review. Food Addit. Contam. A 2015, 32, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savastano, M.L.; Losito, I.; Pati, S. Rapid and automatable determination of Ochratoxin A in wine based on microextraction by packed sorbent followed by HPLC-FLD. Food Control 2016, 68, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; La Torre, G.L.; Potorti, A.G.; Saitta, M.; Alfa, M.; Dugo, G. Organic wine safety: UPLC-FLD determination of Ochratoxin A in Southern Italy wines from organic, farming and winemaking. Food Control 2016, 59, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wen, J.; Kong, W.J.; Liu, Q.T.; Luo, H.L.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.H. Simultaneous determination of four aflatoxins and Ochratoxin A in ginger after inoculation with fungi by ultra-fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 Years of Research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.W.; Yoshinari, T.; Layne, J.; Chan, S.H. Multi-Mycotoxin Screening Reveals Separate Occurrence of Aflatoxins and Ochratoxin A in Asian Rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3104–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.Q.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, X.L.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.H. Phage-free peptide ELISA for Ochratoxin A detection based on biotinylated mimotope as a competing antigen. Talanta 2016, 146, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Suryoprabowo, S.; Li, A.; Kuang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. A gold nanoparticle-based semi-quantitative and quantitative ultrasensitive paper sensor for the detection of twenty mycotoxins. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5245–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.R.G.; Ramadas, D.; Chu, V.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Conde, J.P.; Viana, A.S.; Cascalheira, A.C. An ultrarapid and regenerable microfluidic immunoassay coupled with integrated photosensors for point-of-use detection of Ochratoxin A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, C.T.L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasena, S.D. Aptamers: An Emerging Class of Molecules That Rival Antibodies in Diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.Y.; Deng, H.P.; Su, Y.; He, L.; Wang, R.B.; Tong, G.S.; He, D.N.; Zhu, X.Y. Aptamer-Functionalized and Backbone Redox-Responsive Hyperbranched Polymer for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarczewska, M.; Górski, Ł.; Malinowska, E. Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensors as potential tools for clinical diagnostics. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3861–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.C.; Wang, A.; Ye, K.M.; Jin, S. A RNA-DNA Hybrid Aptamer for Nanoparticle-Based Prostate Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilgu, M.; Ray, J.; Bendickson, L.; Wang, T.J.; Geraskin, I.M.; Kraus, G.A.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M. Light-up and FRET aptamer reporters; evaluating their applications for imaging transcription in eukaryotic cells. Methods 2016, 98, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Chen, N.D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, K.M.; Li, W.S.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.J.; Fang, H.M. A simple label-free aptamer-based method for C-reactive protein detection. Anal. Methods-UK 2016, 8, 4177–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, A. Ultrasensitive detection of lead(II) using a turn-on probe based on the use of an aptamer and a water-soluble fluorescent perylene probe. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, C.H.; Fang, Z.Z.; Bai, W.H.; Yan, M.M.; Zhu, C.; Chen, A.L. Aptamer based photometric assay for the antibiotic sulfadimethoxine based on the inhibition and reactivation of the peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnous, K.; Danesh, N.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Lavaee, P.; Taghdisi, S.M. Aptamer based fluorometric acetamiprid assay using three kinds of nanoparticles for powerful signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong Won, J.; Choi, J.W.; Min, J. Micro-fluidic chip platform for the characterization of breast cancer cells using aptamer-assisted immunohistochemistry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunniger, T.; Felbinger, C.; Wessels, H.; Mast, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Schefer, A.; Martlbauer, E.; Paschke-Kratzin, A.; Fischer, M. Food Targeting: A Real-Time PCR Assay Targeting 165 rDNA for Direct Quantification of Alicyclobacillus spp. Spores after Aptamer-Based Enrichment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.P.; Wang, D.F.; Lin, Z.Y.; Qiu, B.; Liu, M.H.; Guo, L.H.; Chen, G.N. Disassembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for colorimetric detection of Ochratoxin A. Anal. Methods-UK 2015, 7, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.; Tominaga, J.; Tan, S.C.; Tang, T.H. Assays for aptamer-based platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Qian, J.; Yang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, K. Amplified impedimetric aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles covalently bound graphene sheet for the picomolar detection of Ochratoxin A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 806, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanante, G.; Mishra, R.K.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Sensitive analytical performance of folding based biosensor using methylene blue tagged aptamers. Talanta 2016, 153, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Istamboulie, G.; Marty, J.L. Sensitive quantitation of Ochratoxin A in cocoa beans using differential pulse voltammetry based aptasensor. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Qian, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, Q.; Hao, N.; Wang, C.K.; Dong, X.Y.; Huang, X.Y. Colorimetric aptasensing of Ochratoxin A using Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles as signal indicator and magnetic separator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, L. A simple and rapid biosensor for Ochratoxin A based on a structure-switching signaling aptamer. Food Control 2012, 25, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.; Mishra, R.K.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Sharma, V.; Munoz, R.; Marty, J.L. Portable and low cost fluorescence set-up for in-situ screening of Ochratoxin A. Talanta 2016, 159, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.-B.; Mun, H.; Joung, H.-A.; Ofori, J.A.; Chung, D.-H.; Kim, M.-G. Chemiluminescence competitive aptamer assay for the detection of Aflatoxin B1 in corn samples. Food Control 2014, 36, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z. A luminescence resonance energy transfer based aptasensor for the mycotoxin Ochratoxin A using upconversion nanoparticles and gold nanorods. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.N.; Daud, M. Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: A literature review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.L.; Yang, S.M. Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.M.; Mao, Y.P.; Fang, Z.Y.; Lu, X.W.; Zeng, L.W. A sensitive lateral flow biosensor for Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection based on aptamer mediated strand displacement amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, M.; Strych, U.; Kim, J.; Goux, H.; Dhamane, S.; Poongavanam, M.V.; Hagstrom, A.E.V.; Kourentzi, K.; Conrad, J.C.; Willson, R.C. Aptamer-Phage Reporters for Ultrasensitive Lateral Flow Assays. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11660–11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.Y.; Wen, W.; Zhang, X.H.; Gu, H.S.; Wang, S.F. Visual detection of thrombin using a strip biosensor through aptamer-cleavage reaction with enzyme catalytic amplification. Analyst 2015, 140, 7710–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, M.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Bai, W.; Chen, A. A sandwich dipstick assay for ATP detection based on split aptamer fragments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4151–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.; Fung, D.Y.C.; Yang, X.; Renrong, L.; Xiong, Y. Development of a colloidal gold strip for rapid detection of Ochratoxin A with mimotope peptide. Food Control 2009, 20, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Giraudi, G.; Biagioli, F.; Passini, C.; Baggiani, C. A lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid detection of Ochratoxin A in wine and grape must. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11491–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. An aptamer-based chromatographic strip assay for sensitive toxin semi-quantitative detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3059–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Fluorescent strip sensor for rapid determination of toxins. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1574–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, S. Development of Nanogold-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of Ochratoxin A in Buffer Systems. J. Nonsci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 7245–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Suryoprabowo, S.; Song, S.; Kuang, H. Development of an immunochromatographic test strip for the detection of Ochratoxin A in red wine. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Xing, G.X.; Yang, J.F.; Wang, F.Y.; Deng, R.G.; Zhang, G.P.; Hu, X.F.; Zhang, Y. Development of an immunochromatographic test strip for simultaneous qualitative and quantitative detection of Ochratoxin A and zearalenone in cereal. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3673–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.L.; Kong, W.J.; Dou, X.W.; Zhao, M.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, M.H. An aptamer based lateral flow strip for on-site rapid detection of Ochratoxin A in Astragalus membranaceus. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1022, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Giovannoli, C.; Passini, C.; Baggiani, C. Increased sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassay for Ochratoxin A through silver enhancement. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9859–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Aguado, J.A.; Penner, G. Determination of Ochratoxin A with a DNA Aptamer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10456–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Spiked (ng·mL−1) | Detected (ng·mL−1) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.00 | 3.14 ± 0.47 | 104.67 | 6.40 |
| 10.00 | 9.64 ± 1.15 | 96.40 | 4.80 |
| 30.00 | 29.17 ± 2.73 | 97.23 | 5.10 |
| Method | Range (ng·mL−1) | LOD (ng·mL−1) | Sample | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody-strip | - | 10 | PBS buffer | [58] |
| Antibody-strip | 1.00–6.00 | 0.77 | cereal | [60] |
| Antibody-strip | - | 10 | corn, wheat | [54] |
| Antibody-strip | - | 1 | wine, grape must | [55] |
| Antibody-strip | - | 0.9 | wine, grape must | [62] |
| Antibody-strip | - | 0.5 | wed wine | [59] |
| Apatamer-strip | 0.5–2.5 | 0.18 | red wine | [56] |
| Apatamer-strip | 0.5–25 | 0.5 | Astragalus membranaceus | [61] |
| Aptamer-strip | 0.10–10.00 | 1.90 | - | [57] |
| Aptamer-strip | 1.00–1000.00 | 0.40 | corn | Present |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, A. A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples. Molecules 2018, 23, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020291
Zhang G, Zhu C, Huang Y, Yan J, Chen A. A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020291
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guilan, Chao Zhu, Yafei Huang, Jiao Yan, and Ailiang Chen. 2018. "A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples" Molecules 23, no. 2: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020291
APA StyleZhang, G., Zhu, C., Huang, Y., Yan, J., & Chen, A. (2018). A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples. Molecules, 23(2), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020291