Functional Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Capped with an Azo-Derivative: A Promising Colon Drug Delivery Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
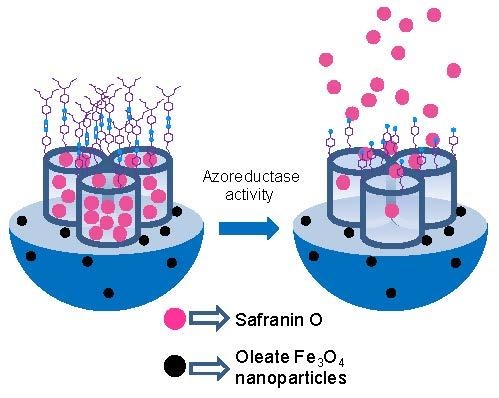
2.1. Synthesis of Gated Magnetic Micro-Sized Mesoporous Silica Particles
2.2. Characterization of the Prepared Materials
2.3. Cargo Release from S1
2.4. In Vitro Digestion Model Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Techniques
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Synthesis of Oleic Acid-coated Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
3.4. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Containing MNPs (S0)
3.5. Synthesis of 1b
3.6. Synthesis of 1d
3.7. Synthesis of 1f
3.8. Synthesis of 1
3.9. Synthesis of S1
3.10. Controlled Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Descalzo, A.B.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Hoffmann, K.; Rurack, K. The supramolecular chemistry of organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, C.; de la Torre, C.; Gorbe, M.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P. Gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of drugs in cancer cells. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A. Advances in microporous and mesoporous solids—Highlights of recent progress. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekaru, H.; Lu, J.; Tamanoi, F. Development of mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release capability for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 95, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart mesoporous silica nanocarriers for antitumoral therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.; Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Chemical synthesis and assembly of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, E.; Oroval, M.; Pascual, L.; Murguía, J.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Gated materials for on-command release of guest molecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doane, T.L.; Burda, C. The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis-Lorente, A.; Lozano-Torres, B.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Mesoporous silica materials for controlled delivery based on enzymes. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancenón, F.; Pascual, L.; Oroval, M.; Aznar, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Gated silica mesoporous materials in sensing applications. ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, C.; Climent, E.; Aznar, E.; Martánez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P.; Rurack, K. Towards chemical communication between gated nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llopis-Lorente, A.; Díez, P.; Sánchez, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Martínez-Ruíz, P.; Villalonga, R.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, J.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Engineering biomaterial-drug conjugates for local and sustained chemotherapeutic delivery. Bioconj. Chem. 2015, 26, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.K.; Rane, B.R.; Gujarathi, N.A. Developments in colon specific drug delivery systems—A review. Pharm. Sci. Monit. 2014, 5, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, D.; Singh, M.; Sharma, D.; Kaur, S. Emerging techniques and challenges in colon drug delivery systems. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, K.; Goswami, L.; Kothiyal, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A review on colon targeting drug delivery system: Novel approaches, anatomy and evaluation. Pharma. Innov. J. 2012, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lautenschläger, C.; Schmidt, C.; Fischer, D.; Stallmach, A. Drug delivery strategies in the therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 71, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, S.; Marks, E.; Schneider, J.J.; Keely, S. Advances in oral nano-delivery systems for colon targeted drug delivery in inflammatory bowel disease: Selective targeting to diseased versus healthy tissue. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V.R.; Kumria, R. Microbially triggered drug delivery to the colon. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, A. Microbially controlled drug delivery to the colon. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1990, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oroval, M.; Díez, P.; Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Villalonga, R.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Self-regulated glucose-sensitive neoglycoenzyme-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Fernández, A.; García-Laínez, G.; Ferrándiz, M.L.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Murguía, J.R.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Costero, A.M.; et al. Targeting inflammasome by the inhibition of caspase-1 activity using capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 248, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ultimo, A.; Giménez, C.; Bartovsky, P.; Aznar, E.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P.; Bernardo, A.R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Jiménez-Lara, A.M.; et al. Targeting innate immunity with dsRNA-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles promotes antitumor effects on breast cancer cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Amorós, P.; Cano, J.; Ruiz, E. Borate-driven gatelike scaffolding using mesoporous materials functionalised with saccharides. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringas, E.; Köysüren, O.; Quach, D.V.; Mahmoudi, M.; Aznar, E.; Roehling, J.D.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Stroeve, P. Triggered release in lipid bilayer-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles containing SPION using an alternating magnetic field. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, A.; Mondragón, L.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Costero, A.; Manguan-García, C.; Perona, R.; et al. Targeted cargo delivery in senescent cells using capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Torre, C.; Casanova, I.; Acosta, G.; Coll, C.; Moreno, M.J.; Albericio, F.; Aznar, E.; Mangues, R.; Royo, M.; Sancenón, F.; et al. Gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles using a double-role circular peptide for the controlled and target-preferential release of doxorubicin in CXCR4-expresing lymphoma cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, L.; Gómez-Cerezo, N.; Aznar, E.; Vivancos, J.L.; Sancenón, F.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Molecular gates in mesoporous bioactive glasses for the treatment of bone tumors and infection. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Gu, H. Synthesis and characterization of pore size-tunable magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haskouri, J.; Cabrera, S.; Caldés, M.; Alamo, J.; Beltrán, A.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P.; Beltrán, D. Ordered mesoporous materials: Composition and topology control through chemistry. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, N.; Agostini, A.; Mondragón, L.; Bernardos, A.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; et al. Enzyme-responsive silica mesoporous supports capped with azopyridinium salts for controlled delivery applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Esteve, E.; Ruiz-Rico, M.; de la Torre, C.; Villaescusa, L.A.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M.D.; Amorós, P.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Barat, J.M. Encapsulation of folic acid in different silica porous supports: A comparative study. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Moroz, E.; Castagner, B.; Leroux, J.C. Activatable cell penetrating peptide-peptide nucleic acid conjugate via reduction of azobenzene PEG chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Grammel, M.; Raghavan, A.S.; Charron, G.; Hang, H.C. Comparative analysis of cleavable azobenzene-based affinity tags for bioorthogonal chemical proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versantvoort, C.H.; Oomen, A.G.; Van de Kamp, E.; Rompelberg, C.J.; Sips, A.J. Applicability of an in vitro digestion model in assessing the bioaccessibility of mycotoxins from food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, A.G.; Rompelberg, C.J.; Bruil, M.A.; Dobbe, C.J.; Pereboom, D.P.; Sips, A.J. Development of an in vitro digestion model for estimating the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 44, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallingborg, J.; Christensen, L.A.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Rasmussen, S.N. Very low intraluminal colonic pH in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1993, 38, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Hada, R.; Nakajima, H.; Fukuda, S.; Munakata, A. Improved localizing method of radiopill in measurement of entire gastrointestinal pH profiles: Colonic luminal pH in normal subjects and patients with Crohn's disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |









| Solid | SBET (m2 g−1) | pore volume 1 (cm3 g−1) | pore size 1,2 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 1057 | 0.94 | 2.83 |
| S1 | 834 | 0.68 | - |
| Solid | Organic Content (g/g SiO2) | Azo Derivative (g/g SiO2) | Dye Release (µg/mg solid) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.0469 | 0.043 | 0.69 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teruel, A.H.; Coll, C.; Costero, A.M.; Ferri, D.; Parra, M.; Gaviña, P.; González-Álvarez, M.; Merino, V.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; et al. Functional Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Capped with an Azo-Derivative: A Promising Colon Drug Delivery Device. Molecules 2018, 23, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020375
Teruel AH, Coll C, Costero AM, Ferri D, Parra M, Gaviña P, González-Álvarez M, Merino V, Marcos MD, Martínez-Máñez R, et al. Functional Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Capped with an Azo-Derivative: A Promising Colon Drug Delivery Device. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeruel, Adrián H., Carmen Coll, Ana M. Costero, Daniel Ferri, Margarita Parra, Pablo Gaviña, Marta González-Álvarez, Virginia Merino, M. Dolores Marcos, Ramón Martínez-Máñez, and et al. 2018. "Functional Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Capped with an Azo-Derivative: A Promising Colon Drug Delivery Device" Molecules 23, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020375
APA StyleTeruel, A. H., Coll, C., Costero, A. M., Ferri, D., Parra, M., Gaviña, P., González-Álvarez, M., Merino, V., Marcos, M. D., Martínez-Máñez, R., & Sancenón, F. (2018). Functional Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Microparticles Capped with an Azo-Derivative: A Promising Colon Drug Delivery Device. Molecules, 23(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020375