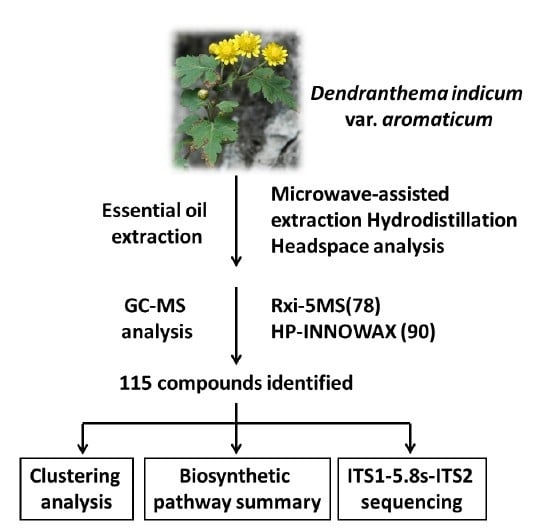
GC-MS Analysis of the Composition of the Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum Var. Aromaticum Using Three Extraction Methods and Two Columns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compound Identification
2.2. Comparative Analysis of Compound Categories
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Two Columns Using Three Extraction Methods
2.4. Clustering Analysis Using Top Ten Compositions with Reported Results
2.5. ITS1-5.8s-ITS2 Sequencing
2.6. Biosynthetic Pathway Summary of Main Composition
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Reagents
4.3. DNA Extraction, ITS Amplification, Electrophoresis and Sequencing
4.4. Preparation of Volatile Oils
4.4.1. Hydrodistillation (HD) Extraction
4.4.2. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
4.4.3. Headspace (HS) Extraction
4.5. Apparatus and Analytical Conditions
4.6. Clustering of Essential Oil Compositions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.H.; Zhang, S.F. A new variety of Dendranthema Gaertn. from Shennongjia of Hubei. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1983, 1, 237–238. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.H.; Zhang, S.F. The investigation on geographical distribution, ecological habit and storage quantity on a new resource plant of Hubei, Dendranthema indicum (L.) Des Monl. var. aromaticum. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1983, 1, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.J.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, K.T.; Yan, Y.J.; Li, X.U.; Liu, Y. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Mechanism of Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum var. aromaticum. J. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lv, P.; Pan, N.; Huang, L.; Zhang, R.; Lu, J.Q. Analysis on volatile components of Dendranthema indicum from three different habitats by SPME-GC/MS. J. Hubei Univ. Chin. Med. 2012, 14, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Z.; Yue, S.; Dan, L.; Bing, C.; Guo, Y.L. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds from Dendranthema indicum var aromaticum by Headspace Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Accurate Mass Measurement. Anal. Lett. 2010, 43, 2297–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, B.; Christen, P. Recent extraction techniques for natural products: Microwave-assisted extraction and pressurised solvent extraction. Phytochem. Anal. 2002, 13, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.M.; Raghavan, G.S.V.; Ngadi, M.; Wang, N. Microwave power control strategies on the drying process I. Development and evaluation of new microwave drying system. J. Food Eng. 2006, 76, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Lv, J.S.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, J.Y. GC-MS Determination of Volatile Components of Flowers of White Clove. Phys. Test Chem. Anal. 2009, 45, 1174–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.Q.; Li, J. Chemical constituents in volatile oil from the flos of Dendranthema indicum var. aromaticum var. nov. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2002, 27, 598–599. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Q. Analysis on aroma compositions in flowers, stems and leaves of Chrysanthemun indicum var. aromaticum. J. Northwest A&F Univ. 2014, 14, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Huang, L.; Rong, L.; Wu, Z.; Yu, S.G.; Fang, N.B. Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds from the Bud and Flower of Dendranthema indicum var. aromaticum by Static Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2011, 50, 4266–4268. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y.; Gao, H.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.R. Analysis of chemical composition of Chrysanthemum indicum flowers by GC/MS and HPLC. J. Med. Plant Res. 2010, 4, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.D.; Ying, Y.; Zou, G.L. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Chrysanthemum indicum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wan, Q.; Guo, Y.P.; Abbott, R.J.; Rao, G.Y. Should I stay or should I go: Biogeographic and evolutionary history of a polyploid complex (Chrysanthemum indicum complex) in response to Pleistocene climate change in China. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.J.; Hall, D.E. Identification of Genes in Thujaplicata Foliar Terpenoid Defenses. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/kegg/ (accessed on 20 August 2017).
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.J.; Croteau, R. Biosynthesis of aromatic monoterpenes: Conversion of γ-terpinene to p-cymene and thymol in Thymus vulgaris, L. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 187, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Gang, D.R. Suites of terpene synthases explain differential terpenoid production in ginger and turmeric tissues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Harada, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Okamoto, S.; Hirase, S.; Tanaka, Y. Isolation and functional characterization of a β-eudesmol synthase, a new sesquiterpene synthase from Zingiber zerumbet Smith. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Peng, G.P. Progress in studies on oplopanones. Nat. Prod. Res. 2001, 14, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoiea Committee. China Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Part IV; pp. 203–204. [Google Scholar]
- Pripdeevech, P.; Wongpornchai, S.; Marriott, P.J. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of volatile constituents in Thai vetiver root oils obtained by using different extraction methods. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIST: National Institute of Standards and Technologies, Mass Spectra Libraries. Available online: http://www.sisweb.com/software/nist-gc-library.htm (accessed on 26 August 2017).
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Rxi-5MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| HD | MAE | HS | |
| No. | 63 | 48 | 64 |
| Top ten comp. | α-Thujone (21.63%) | Neointermedeol (16.19%) | α-Thujone (39.3%) |
| Neointermedeol (12.6%) | α-Thujone (15.88%) | β-Thujone (16.52%) | |
| β-Thujone (9.53%) | β-Thujone (6.49%) | Sabinyl acetate (7.52%) | |
| cis-Sabinol (5.13%) | Sabinyl acetate (5.83%) | Isothujol (3.31%) | |
| Sabinyl acetate (5.13%) | (Z)-Tibetinspiroether (3.31%) | β-Caryophyllene (3.09%) | |
| Isothujol (2.64%) | Cubebol (3.28%) | (+)-cis-Sabinol (2.75%) | |
| β-Caryophyllene (2.58%) | Camphor (2.66%) | Camphor (2.36%) | |
| (-)-Caryophyllene oxide (2.36%) | β-Eudesmol (2.38%) | (-)-Neointermedeol (2.13%) | |
| (+)-Borneol (2.33%) | Modhephene (2.12%) | (+)-Borneol (1.72%) | |
| Modhephene (2.05%) | (E)-Tibetinspiroether (1.83) | β-Phellandrene (1.56%) | |
| HP-INNOWAX | |||
| HD | MAE | HS | |
| No. | 59 | 35 | 48 |
| Top ten comp. | α-Thujone (16.75%) | Neointermedeol (19.41%) | α-Thujone (37.05%) |
| (-)-Neointermedeol(15.02%) | α-Thujone (12.01%) | β-Thujone (16.91%) | |
| β-Thujone (7.72%) | β-Eudesmol (5.4%) | Sabinyl acetate (7.7%) | |
| cis-Sabinol (6.33%) | β-Thujone (5.01%) | cis-Sabinol (5.74%) | |
| β-Eudesmol (4.61%) | Sabinyl acetate (4.81%) | Neointermedeol (4.32%) | |
| Sabinyl acetate (4.58%) | Epicubebol (3.74%) | Camphor (3.68%) | |
| (+)-Borneol(2.56%) | Caryophylladienol I (2.82%) | (+)-Borneol (2.99%) | |
| Caryophylladienol I (2.44%) | Camphor (2.26%) | Epicubebol (1.70%) | |
| (-)-Caryophyllene oxide (2.29%) | (+)-Borneol (2.22%) | β-Eudesmol (1.32%) | |
| Thujylalkohol (2.14%) | Benzyl benzoate (1.96%) | Bornyl acetate (1.29%) | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, S.; Chang, J.; Zong, Y.; Hu, G.; Jia, J. GC-MS Analysis of the Composition of the Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum Var. Aromaticum Using Three Extraction Methods and Two Columns. Molecules 2018, 23, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030576
Fan S, Chang J, Zong Y, Hu G, Jia J. GC-MS Analysis of the Composition of the Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum Var. Aromaticum Using Three Extraction Methods and Two Columns. Molecules. 2018; 23(3):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030576
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Sanpeng, Jin Chang, Yufeng Zong, Gaosheng Hu, and Jingming Jia. 2018. "GC-MS Analysis of the Composition of the Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum Var. Aromaticum Using Three Extraction Methods and Two Columns" Molecules 23, no. 3: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030576
APA StyleFan, S., Chang, J., Zong, Y., Hu, G., & Jia, J. (2018). GC-MS Analysis of the Composition of the Essential Oil from Dendranthema indicum Var. Aromaticum Using Three Extraction Methods and Two Columns. Molecules, 23(3), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030576