Potential of Cellulose Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid as Biosorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
2.2. Dye Adsorption
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
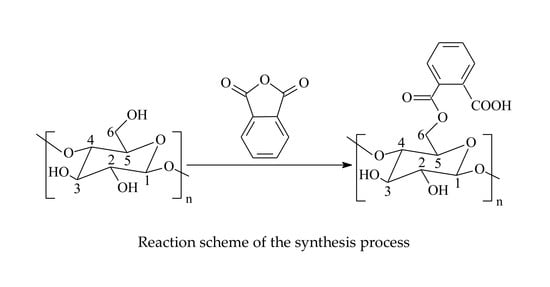
3.2. Modification of Cellulose
3.3. Determination of Carboxyl Groups Incorporated in Cellulose
3.4. Zero Point of Charge (pHpzc)
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Dye Adsorption
3.6.1. Effect of pH
3.6.2. Effect of Time
3.6.3. Effect of Dye Concentration and Temperature
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruan, C.; Strømme, M.; Lindh, J. Preparation of porous 2,3-dialdehyde cellulose beads crosslinked with chitosan and their application in adsorption of Congo red dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.S.; Lima, L.C.B.; Silva, F.C.; Matos, J.M.E.; Santos, M.R.M.C.; Santos Júnior, L.S.; Sousa, K.S.; Silva Filho, E.C. Dye anionic sorption in aqueous solution onto a cellulose surface chemically modified with aminoethanethiol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J. Adsorption of C.I. Reactive Red 228 dye from aqueous solution by modified cellulose from flax shive: Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 42, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Dinh, D.M.; Hsieh, Y. Adsorption and desorption of cationic malachite green dye on cellulose nanofibril aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.C.; Silva, M.M.F.; Lima, L.C.B.; Osajima, J.A.; Silva Filho, E.C. Integrating chloroethyl phosphate with biopolymer cellulose and assessing their potential for absorbing brilliant green dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, E.; Min, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pang, L.; Ma, T. Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Min, Y.; Qiao, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, E.; Ma, T. Improved removal of malachite green from aqueous solution using chemically modified cellulose by anhydride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, H.; Dash, S.; Ghorai, S.; Pal, S.; Sarkar, A. SBA-16: Application for the removal of neutral, cationic, and anionic dyes from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Jin, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z. Enhanced malachite green removal from aqueous solution by citric acid modified rice straw. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, F.; Saygili, H.; Saygili, G.A.; Koyuncu, F. Decolorisation of aqueous crystal violet solution by a new nanoporous carbon: Equilibrium and kinetic approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3375–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A. Adsorption of methylene blue onto Platanus orientalis leaf powder: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A. W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.S.; Lima, L.C.B.; Ferreira, F.J.L.; Silva, M.S.; Osajima, J.A.; Bezerra, R.D.S.; Silva Filho, E.C. Sorption of the anionic reactive red RB dye in cellulose: Assessment of kinetic, thermodynamic, and equilibrium data. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, R.D.S.; Morais, A.I.S.; Osajima, J.A.; Nunes, L.C.C.; Silva Filho, E.C. Development of new phosphated cellulose for application as an efficient biomaterial for the incorporation/release of amitriptyline. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Filho, E.C.; Melo, J.C. P.; Airoldi, C. Preparation of ethylenediamine-anchored cellulose and determination of thermochemical data for the interaction between cations and basic centers at the solid/liquid interface. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2842–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.P.; Santana, S.A.A.; Bezerra, C.W.B.; Silva, H.A.S.; Melo, J.C.P.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Airoldi, C. Copper sorption from aqueous solutions and sugar cane spirits by chemically modified babassu coconut (Orbignya speciosa) mesocarp. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Mankotia, D.; Chauhan, G.S. Crosslinked cellulose dialdehyde for congo red removal from its aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.P.; Santana, S.A.A.; Bezerra, C.W.B.; Silva, H.A.S.; Chaves, J.A.P.; Melo, J.C.P.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Airoldi, C. Kinetics and thermodynamics of textile dye adsorption from aqueous solutions using babassu coconut mesocarp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, J.C.P.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Santana, S.A.A.; Airoldi, C. Exploring the favorable ion-exchange ability of phthalylated cellulose biopolymer using thermodynamic data. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Filho, E.C.; Silva, L.S.; Lima, L.C.B.; Santos Junior, L.S.; Santos, M.R.M.C.; Matos, J.M.E.; Airoldi, C. Thermodynamic data of 6-(4′-aminobutylamino)-6-deoxycellulose sorbent for cation removal from aqueous solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.A. Introduction to Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Broks Cole: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E., Jr.; Conrad, C.M. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Ramamurthi, V.; Sivanesan, S. Modeling the mechanism involved during the sorption of methylene blue onto fly ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jin, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, T. Heavy metal ions and organic dyes removal from water by cellulose modified with maleic anhydride. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoruelo, L.M.; Marqués, M.D.; Díaz, F.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Cordero, T. Lignin-based activated carbons as adsorbents for crystal violet removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2012, 31, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Saha, P.D. Adsorption of crystal violet from aqueous solution onto NaOH-modified rice husk. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, W.; Kan, X.; Dong, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Cheng, R. Sorption of methylene blue by carboxymethyl cellulose and reuse process in a secondary sorption. Colloid Surf. A 2011, 380, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, C.; Tompkins, F.C. Kinetics of adsorption and desorption and the Elovich equation. Process Saf. Environ. 1970, 21, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.C.; Mouta, R.; Junior, M.C.C.; Santana, S.A.A.; Silva, H.A.S.; Bezerra, C.W.B. Chitosan-edible oil based materials as upgraded adsorbents for textile dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 15, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Uber die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys. Chim. 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Gurgel, L.V.A.; Freitas, R.P.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) from aqueous single metal solutions by sugarcane bagasse and mercerized sugarcane bagasse chemically modified with succinic anhydride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.R.; Rodrigues, J.A.V.; Adarme, O.F.H.; Melo, T.M.S.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Gil, L.F. Optimization of cellulose and sugarcane bagasse oxidation: Application for adsorptive removal of crystal violet and auramine-O from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 494, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, J.; Ma, T. Adsorption of cationic dyes on a cellulose-based multicarboxyl adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, G.O. Removal of methylene blue and crystal violet from aqueous solutions by palm kernel fiber. Desalination 2011, 272, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Gao, M.; Chang, J.; Ma, H. Adsorption properties of crosslinking carboxymethyl cellulose grafting dimethyldiallylammonium chloride for cationic and anionic dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 20, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Tian, Y. Removal of malachite green and crystal violet cationic dyes from aqueous solution using activated sintering process red mud. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 93, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Q.; Lei, T.; Negulescu, I.I. Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium studies for methylene blue dye by partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite hydrogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 251, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |




| Adsorbent | pH | Dye | qe,exp (mg g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Elovich Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe,cal (mg g−1) | R2 | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe,cal (mg g−1) | h (mg g−1 min−1) | R2 | α (mg g−1 min−1) | β (g mg−1) | R2 | ||||
| Cel | 7.0 | CV | 24.7470 | 0.0328 | 24.5225 | 0.9815 | 0.0014 | 28.7321 | 1.1557 | 0.9879 | 3.3022 | 0.1788 | 0.9829 |
| 8.0 | MB | 9.6460 | 0.0201 | 10.2337 | 0.9892 | 0.0016 | 12.8901 | 0.2658 | 0.9861 | 0.5198 | 0.3359 | 0.9818 | |
| PhCel | 6.0 | CV | 34.8730 | 0.0460 | 34.1093 | 0.9795 | 0.0019 | 37.9294 | 2.7334 | 0.9838 | 18.6190 | 0.1769 | 0.9741 |
| 8.0 | MB | 41.7840 | 0.0262 | 43.5332 | 0.9845 | 0.0005 | 53.2477 | 1.4177 | 0.9661 | 2.8421 | 0.0823 | 0.9512 | |
| Adsorbent | pH | Dye | Temperature (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | RL | R2 | nf | Kf (L g−1) | R2 | AT (L mg−1) | bT (J mol−1) | R2 | ||||
| Cel | 7.0 | CV | 298 | 27.1985 | 0.1403 | 0.1336 | 0.9844 | 3.5521 | 7.8022 | 0.9648 | 1.9197 | 110.1706 | 0.9843 |
| 308 | 26.6632 | 0.1354 | 0.1696 | 0.9700 | 3.7394 | 8.0199 | 0.9541 | 2.6169 | 151.0012 | 0.9690 | |||
| 318 | 27.0856 | 0.1166 | 0.1538 | 0.9784 | 3.4158 | 7.2187 | 0.9637 | 1.7727 | 166.9936 | 0.9783 | |||
| Cel | 8.0 | MB | 298 | 12.0854 | 0.0671 | 0.2193 | 0.9909 | 2.7744 | 2.1758 | 0.9615 | 0.6367 | 216.2711 | 0.9863 |
| 308 | 14.3716 | 0.0549 | 0.2446 | 0.9886 | 2.4717 | 2.0835 | 0.9558 | 0.5589 | 228.1585 | 0.9811 | |||
| 318 | 14.1790 | 0.0731 | 0.2240 | 0.9910 | 2.7743 | 2.6760 | 0.9604 | 0.7447 | 278.4868 | 0.9857 | |||
| PhCel | 6.0 | CV | 298 | 37.5097 | 0.2686 | 0.1067 | 0.9682 | 4.0826 | 13.6859 | 0.9666 | 7.6652 | 96.5475 | 0.9790 |
| 308 | 37.1611 | 0.2677 | 0.0881 | 0.9637 | 4.0281 | 13.4287 | 0.9820 | 9.8824 | 126.9822 | 0.9840 | |||
| 318 | 43.2401 | 0.0696 | 0.2596 | 0.9805 | 2.4657 | 6.8735 | 0.9849 | 1.1053 | 103.9071 | 0.9699 | |||
| PhCel | 8.0 | MB | 298 | 52.2047 | 0.1590 | 0.1885 | 0.9256 | 3.5962 | 16.0065 | 0.8550 | 1.7601 | 53.5470 | 0.8930 |
| 308 | 56.9999 | 0.0847 | 0.2935 | 0.9448 | 2.4163 | 9.4411 | 0.8712 | 0.6308 | 51.7234 | 0.9418 | |||
| 318 | 55.0383 | 0.1428 | 0.3313 | 0.9567 | 2.8477 | 12.7742 | 0.8709 | 1.2046 | 69.4659 | 0.9360 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dos Santos Silva, L.; De Oliveira Carvalho, J.; De Sousa Bezerra, R.D.; Da Silva, M.S.; Ferreira, F.J.L.; Osajima, J.A.; Da Silva Filho, E.C. Potential of Cellulose Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid as Biosorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2018, 23, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040743
Dos Santos Silva L, De Oliveira Carvalho J, De Sousa Bezerra RD, Da Silva MS, Ferreira FJL, Osajima JA, Da Silva Filho EC. Potential of Cellulose Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid as Biosorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution. Molecules. 2018; 23(4):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040743
Chicago/Turabian StyleDos Santos Silva, Lucinaldo, Jhonatam De Oliveira Carvalho, Roosevelt Delano De Sousa Bezerra, Mateus Soares Da Silva, Francisco José Lustosa Ferreira, Josy Anteveli Osajima, and Edson Cavalcanti Da Silva Filho. 2018. "Potential of Cellulose Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid as Biosorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution" Molecules 23, no. 4: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040743
APA StyleDos Santos Silva, L., De Oliveira Carvalho, J., De Sousa Bezerra, R. D., Da Silva, M. S., Ferreira, F. J. L., Osajima, J. A., & Da Silva Filho, E. C. (2018). Potential of Cellulose Functionalized with Carboxylic Acid as Biosorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solution. Molecules, 23(4), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040743