A Novel Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hybrid Silicon Wastewater Nano-Adsorbent Material and Its Adsorption Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Properties
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.6. Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
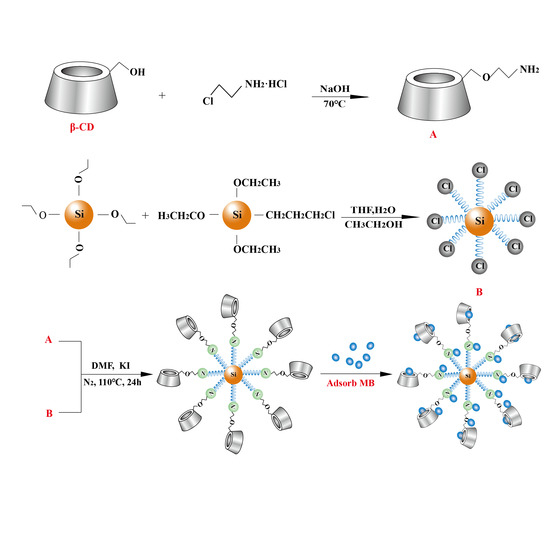
3.1. Preparation of 6-EA-β-CD
3.2. Preparation of Cl-Si
3.3. Preparation of 6-EA-β-CD-Si
3.4. Samples Characterization
3.5. Adsorption of Anionic Dyes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, E.; Min, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pang, L.; Ma, T. Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2015, 141 (Suppl. C), 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gai, L.; Ma, W.; Jiang, H.; Peng, X.; Zhao, L. Ultrasound-assisted catalytic degradation of methyl orange with Fe3O4/polyaniline in near neutral solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Stuckey, D.C. Bioaugmentation and its application in wastewater treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2015, 140 (Suppl. C), 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, N. Disinhibition of the ammonium nitrogen in autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion for sewage sludge by chemical precipitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169 (Suppl. C), 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, J.; Sikder, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Curcio, S.; Drioli, E. Remediation of textile effluents by membrane based treatment techniques: A state of the art review. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147 (Suppl. C), 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panić, V.V.; Šešlija, S.; Nešić, A.R.; Veličković, S.J. Adsorption of azo dyes on polymer materials. Hemijska Industrija 2013, 67, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouamid, M.; Ouahrani, M.R.; Bensaci, M.B. Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using date palm leaves. Energy Procedia 2013, 36 (Suppl. C), 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Feng, Y.L.; Guo, J.Z.; Bai, L.Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.J. An amorphous coordination polymer with high adsorption ability for anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2013, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, R.I.; El-Eswed, B.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.a.H. Adsorption characteristics of natural zeolites as solid adsorbents for phenol removal from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamics studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wei, Q.; Du, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, X.; Yan, L.; Yu, H. Removal of basic dyes (malachite green) from aqueous medium by adsorption onto amino functionalized graphenes in batch mode. Des. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Kitinya, J.; Onyango, M.S. Removal of Congo red from aqueous solution by two variants of calcium and iron based mixed oxide nano-particle agglomerates. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Afzali, D.; Taher, M.A.; Mostafavi, A.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of Safranin dye from aqueous solution using magnetic mesoporous clay: Optimization study. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212 (Suppl. C), 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Agricultural based activated carbons for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilkaya, B.; Tekinay, A.A. Comparative study and removal of Co and Ni (II) ions from aqueous solutions using fish bones. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2011, 3, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Ye, Q.; Lin, J.-M.; Yuan, J. Adsorption of environmental pollutants using magnetic hybrid nanoparticles modified with β-cyclodextrin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305 (Suppl. C), 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Ballav, N.; Maity, A.; Pillay, K. Competitive adsorption of ternary dye mixture using pine cone powder modified with β-cyclodextrin. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225 (Suppl. C), 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, H.; Motoyama, K.; Higashi, T. Potential Use of cyclodextrins as drug carriers and active pharmaceutical ingredients. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Shawon, Z.B.Z.; Tay, W.J.D.; Hidajat, K.; Uddin, M.S. Fe3O4/cyclodextrin polymer nanocomposites for selective heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. A novel method of synthesizing cyclodextrin grafted multiwall carbon nanotubes/iron oxides and its adsorption of organic pollutant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320 (Suppl. C), 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiasat, A.R.; Nazari, S. β-Cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as a novel magnetic microvessel and phase transfer catalyst: Synthesis and applications in nucleophilic substitution reaction of benzyl halides. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 76, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, K.; Gruba, E.; Bocian, W.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Enantioselective recognition of radezolid by cyclodextrin modified capillary electrokinetic chromatography and electronic circular dichroism. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 139 (Suppl. C), 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvets, O.; Belyakova, L. Synthesis, characterization and sorption properties of silica modified with some derivatives of β-cyclodextrin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283 (Suppl. C), 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Luo, X. Quaternary ammonium β-cyclodextrin-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbents for the treatment of dyeing wastewater: Synthesis and adsorption studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Hu, Y. Improved synthesis of graphene/β-cyclodextrin composite for highly efficient dye adsorption and removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242 (Suppl. C), 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, G.; Monge-Marcet, A.; Pleixats, R.; Parella, T.; Cattoën, X.; Man, M.W.C. Recyclable hybrid silica-based catalysts derived from Pd–NHC complexes for Suzuki, Heck and Sonogashira reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 3625–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akҫakoca Kumbasar, E.P.; Akduman, Ç.; Çay, A. Effects of β-cyclodextrin on selected properties of electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane nanofibres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104 (Suppl. C), 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; O’Dwyer, J.P.; Chang, V.S.; Granda, C.B.; Holtzapple, M.T. Structural features affecting biomass enzymatic digestibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3817–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.S.; Huang, W.Q.; Hu, J.L. Water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin polymer crosslinked by citric acid: Synthesis and adsorption properties toward phenol and methylene blue. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagöz, S.; Tay, T.; Ucar, S.; Erdem, M. Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6214–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, A.; Rafati, A.A. Preparation of silica mesoporous nanoparticles functionalized with β-cyclodextrin and its application for methylene blue removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dil, A.E.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Hajati, S.; Mehrabi, F.; Goudarzi, A. Preparation of nanomaterials for the ultrasound-enhanced removal of Pb2+ ions and malachite green dye: Chemometric optimization and modeling. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34 (Suppl. C), 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Ma, L.; Ren, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, C. Preparation of polyethersulfone-modified sepiolite hybrid particles for the removal of environmental toxins. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Yuzer, H.; Sabah, E.; Celik, M.S. Adsorption of cobalt from aqueous solutions onto sepiolite. Water Res. 2003, 37, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.N.; Almeida, C.A.P.; Debacher, N.A.; de Souza Sierra, M.M. Isotherm and thermodynamic data of adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto peat. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 982, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ping, Q.; Niu, M.; Shi, H.; Li, N. Kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption on diatomite treated with sodium hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.; Almawla, M.; Moubarak, E.; Alghoul, M.; Elrassy, H. Surface-functionalized silica aerogels and alcogels for methylene blue adsorption. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 6111–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Ao, Y.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of methylene blue by a magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290 (Suppl. C), 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, A.; Karaca, S.; Doğar, Ç.; Bayrak, R.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Yalçın, M. Determination of adsorptive properties of clay/water system: Methylene blue sorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherifi, H.; Fatiha, B.; Salah, H. Kinetic studies on the adsorption of methylene blue onto vegetal fiber activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282 (Suppl. C), 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |











| Material | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Hole Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-CD | 0.3445 | 0.0003 | 12.00 |
| 6-EA-β-CD | 0.3669 | 0.0002 | 10.80 |
| Cl-Si | 341.7485 | 0.2438 | 3.940 |
| 6-EA-β-CD-Si | 240.4112 | 0.3010 | 4.162 |
| C0 (mg/L) | Pseudo-first-order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-second-order Kinetic Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1/min−1 | Qe, cal/(mg/g) | R2 | K2/min−1 | Qe, cal/(mg/g) | R2 | Qe, exp/(mg/g) | |
| 20 | 0.0378 | 8.0776 | 0.9391 | 0.02 | 17.7305 | 0.9966 | 18.8629 |
| 35 | 0.064 | 13.2567 | 0.9387 | 0.0106 | 31.0559 | 0.9896 | 30.4405 |
| 50 | 0.2004 | 30.8674 | 0.9024 | 0.0075 | 42.7351 | 0.9931 | 39.122 |
| 75 | 0.0664 | 14.7508 | 0.9597 | 0.0051 | 43.8596 | 0.9993 | 43.233 |
| 100 | 0.1377 | 21.0774 | 0.9549 | 0.0034 | 54.3478 | 0.9994 | 51.4216 |
| T(K) | Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm | Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| 303 | 39.47 | 0.4790 | 0.9858 | 15.8433 | 2.8775 | 0.9927 |
| 313 | 39.21 | 0.3778 | 0.9825 | 12.4202 | 2.6749 | 0.9930 |
| 323 | 36.90 | 0.2691 | 0.9812 | 10.4340 | 2.6142 | 0.9903 |
| 333 | 36.36 | 0.1436 | 0.9707 | 6.5337 | 2.0669 | 0.9944 |
| Co (mg/L) | T (K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J·mol−1·K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 303 | −15.6178 | −19.3966 | −12.4710 |
| 313 | −15.4931 | |||
| 323 | −15.3684 | |||
| 333 | −15.2437 | |||
| 40 | 303 | −11.5930 | −14.616 | −9.9768 |
| 313 | −11.4933 | |||
| 323 | −11.3935 | |||
| 333 | −11.2937 |
| Adsorbents | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Isotherm | Adsorption Capacity, Qm (mg/g) | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sodium hydroxide | 31.35 | Langmuir | 27.86 | – | [36] |
| phenyl-functionalized silica materials | − | Sips | 33.7 | 8 | [37] |
| magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube | – | Langmuir | 24.88 | 7 | [38] |
| clay | 30 | Freundlich | 6.3 | – | [39] |
| activated carbon from waste biomass | 240.02 | Langmuir | 16.43 | 6 | [30] |
| vegetal fiber activated carbons | – | – | 33.7 | 10 | [40] |
| cyclodextrin-functionalized hybrid silicon | 240 | Freundlich | 39.47 | 8 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Qiu, C.; Fan, H.; Bai, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J. A Novel Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hybrid Silicon Wastewater Nano-Adsorbent Material and Its Adsorption Properties. Molecules 2018, 23, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061485
Li J, Qiu C, Fan H, Bai Y, Jin Z, Wang J. A Novel Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hybrid Silicon Wastewater Nano-Adsorbent Material and Its Adsorption Properties. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061485
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jing, Chao Qiu, Haoran Fan, Yuxiang Bai, Zhengyu Jin, and Jinpeng Wang. 2018. "A Novel Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hybrid Silicon Wastewater Nano-Adsorbent Material and Its Adsorption Properties" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061485
APA StyleLi, J., Qiu, C., Fan, H., Bai, Y., Jin, Z., & Wang, J. (2018). A Novel Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Hybrid Silicon Wastewater Nano-Adsorbent Material and Its Adsorption Properties. Molecules, 23(6), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061485