Cyclodextrin-Enabled Polymer Composites for Packaging †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Cyclodextrins Used for Packaging
- They are semi-natural products; produced from a renewable natural material, starch, by a relatively simple enzymatic conversion.
- Their prices are low enough (in case of BCD < 10 USD/kg) to be acceptable for most industrial purposes.
- They are versatile in complexation of various molecules, and change important properties of the complexed substances significantly. The beneficiary effects of so called “molecular encapsulation” are widely utilized in industrial products, technologies, and analytical methods [4].
- The parent CDs are non-toxic taken orally and can be consumed by humans as ingredients of drugs, foods, or cosmetics.
- The diffusion and volatility (in the case of volatile substances) of the included guest can decrease strongly.
- The complexed substances, even gaseous substances can be entrapped in a carbohydrate matrix forming a microcrystalline or amorphous powder.
- The complexed substance can be effectively protected against heat decomposition, oxidation and any other type of reaction, except against those with the hydroxyl groups of cyclodextrin, or reactions catalyzed by them.
- The carbohydrate wrapping around the guest molecule makes the complex hydrophilic, easily wetted and rapidly soluble.
1.2. Polymer Packaging/Carrier Materials
- satisfactory tear strength,
- flexibility,
- low permeability for gases (O2, CO2), and low or higher permeability for water depending on the entrapped product,
- reduced UV-light transmission,
- low if any release of undesired components like monomers, softeners, plasticizers, etc.,
- appropriate compatibility with additives, such as pigments, antioxidants, or cyclodextrin complexes.
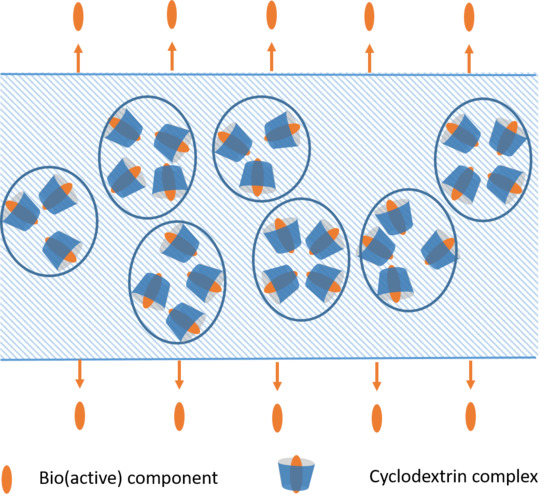
1.3. Incorporation of (Bio)active Components
2. Cyclodextrin Complexes in Packaging Materials: Films, Laminates, Containers
2.1. Fragrant Films
2.2. Antimicrobial Packaging Materials
2.3. Insecticidal Films
2.4. Colored Plastics
2.5. UV-filter, Anticorrosive, Antistatic Films
- If the entrapped product is UV sensitive, the packaging material should contain some of the well-known, widely used UV filters, such as sodium 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonate, 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone, or 2,2′,4,4′-tetrahydrobenzophenone [70].
- Complexation of plastic additives, such as antistatic agents and UV-absorbers with cyclodextrins and their incorporation into plastics results in products of longer durability [94].
- Antistatic polypropylene extruded films were prepared by mixing the resin pellets with cyclodextrin complexes of antistatic agents [95]. Stretch-resistant and aging-resistant plastic films were produced by adding hydroxypropyl β-CD to polyvinyl chloride–polystyrene mixture containing UV filters, antibacterial agents and plant oil [96].
- Nickel-cyclohexyl-ammonium nitrite/β-CD complex mixed with polyethylene pellets was blow-molten into a corrosion inhibiting film [97]. Rust preventing films are produced by incorporating volatile corrosion inhibitor, such as dicyclohexyl ammonium nitrite, hexamethylenetetramine or benztriazole, into thermoplastic resin, such as polypropylene, polyethylene, ethylene-vinylacetate copolymer and poly(vinyl chloride) [98].
2.6. Miscellaneous
3. Empty Cyclodextrins as Penetration Barriers in Packaging Films
4. Conclusions
- The loss (decomposition, volatilization etc.) of these biologically active substances at the necessary high temperature during production can be reduced. The dry cyclodextrin complexes of these substances are generally stable up to the thermal degradation temperature of the cyclodextrin (220 to 250 °C).
- The incorporation of cyclodextrin-complexed (bio)active substances into the polymer matrix do not reduce their chemical stability.
- Preparing such packaging materials, relatively small amount of the (bio)active components are distributed evenly over a large surface, to exert their effects on the surface of the packaged goods either by direct contact, or in the gas-phase within the closed package. The prerequisite of effective blending of cyclodextrin-complexed actives into the polymer phase is the compatibility of the components: less apolar polymers and less polar cyclodextrin derivatives can be successfully blended.
- The release of the complexed and polymer-incorporated (bio)active substances depends on the hydrophobicity of the matrix, permeation of water into the polymer, particle size of the complex incorporated, temperature, presence of other hydrophilic components, etc. The release must be slow to avoid the permeation of significant fraction of the (bio)active component into the packaged goods. This can be tuned by applying proper cyclodextrins.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szejtli, J. Cyclodextrin Technology; Kluwer: Dordrecht, Germany, 1988; ISBN 90-277-2314-1. [Google Scholar]
- Szejtli, J. Utilization of cyclodextrins in industrial products and processes. J. Mater. Chem. 1997, 7, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J.; Osa, T. Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry; Volume 3: Cyclodextrins; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1996; ISBN 0-08-042715-4. [Google Scholar]
- Szejtli, J. Cyclodextrins and Inclusion Complexes; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 1982; ISBN 963-05-2850-9. [Google Scholar]
- Szejtli, J. Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem. Revs. 1998, 98, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J. Cyclodextrins in the textile industry. Starch 2003, 55, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J. Medicinal applications of cyclodextrins. Med. Res. Rev. 1994, 14, 353–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenyvesi, E.; Vikmon, M.; Szente, L. Cyclodextrins in food technology and human nutrition: Benefits and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1981–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, K.; Binello, A.; Lawson, D.; Jicsinszky, L.; Cravotto, G. Recent applications of cyclodextrins as food additives and in food processing. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 9, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortense, A.; Agualar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Dusemund, B.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Leblanc, J.-C.; et al. Re-evaluation of β-cyclodextrin (E-459) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Yoshida, H. Cyclodextrin-Containing Polyester Polymer and Process for Producing the Same. PCT Pat. Appl. WO2006115211, 18 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Plackett, D.V.; Holm, V.K.; Johansen, P.; Ndoni, S.; Nielsen, P.V.; Sipilainen-Malm, T.; Soedergaard, A.; Verstichel, S. Characterization of l-polylactide and l-polylactide-polycaprolactone co-polymer films for use in cheese-packaging applications. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2006, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.J.; Auras, R.; Almenar, E. Preparation and characterization of blends made of poly(l-lactic acid) and beta-cyclodextrin: Improvement of the blend properties by using a masterbatch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.J.; Merkel, C.; Auras, R.; Almenar, E. Development and characterization of antimicrobial poly(l-lactic acid) containing trans-2-hexenal trapped in cyclodextrins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koontz, J.L.; Marcy, J.E. Controlled release of active ingredients from polymer food packaging by molecular encapsulation with cyclodextrins. Polym. Preprints (Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Polym. Chem.) 2007, 48, 742. [Google Scholar]
- Poverenov, E.; Granit, R.; Gabai, S. Encapsulation and controlled release of antifungal propionic acid utilizing biodegradable active films based on natural polymers. Eur. Res. Technol. 2013, 237, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Oikawa, T.; Fukaya, S.; Torii, M.; Fukushima, Y. Antimicrobial Film. JP Pat. Appl. JPH0692842, 5 April 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Suda, T. Product Containing Chlatrate Compound. JP Pat. Appl. JPH0441438, 12 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, M.; Kashikura, A.; Saeki, T.; Hirota, T.; Ozaki, S.; Kawakubo, H. Antimicrobial Water-Absorbing Sheet. JP Pat. Appl. JPH1189548, 6 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Saeki, T.; Shirakawa, K. Antibacterial Egg Container. JP Patent JPH08310577, 26 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Saeki, T.; Shirakawa, K. Antibacterial Resin Film. JP Pat. Appl. JPH08282741, 29 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki, T. Antibacterial Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Film. JP Pat. Appl. JPH11116756, 27 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Mokwena, K. The potential of triacetyl-β-cyclodextrin and its inclusion complex with AITC for LDPE film extrusion. In Proceedings of the 18th IAPR World Packaging Conference, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 17–21 June 2012; pp. 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Plackett, D.; Ghanbari-Siahkali, A.; Szente, L. Behavior of alpha- and beta-cyclodextrin-encapsulated allyl isothiocyanate as slow-release additives in polylactide-co-polycaprolactone films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2850–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, Y. Packaging Materials. JP Patent JPS6136361, 21 February 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoine, N.; Givord, C.; Tabary, N.; Desloges, I.; Martel, B.; Bras, J. Elaboration of a new antibacterial bio-nano-material for food-packaging by synergistic action of cyclodextrin and microfibrillated cellulose. IFSET 2014, 26, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, L.; López-Carballo, G.; Hernández-Muñoz, P.; Catalá, R.; Gavara, R. Antimicrobial packaging of chicken fillets based on the release of carvacrol from chitosan/cyclodextrin films. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 188, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, D.O.; Tabary, N.; Martel, B.; Gandini, A.; Belgacem, N.; Bras, J. Controlled release of carvacrol and curcumin: Bio-based food packaging by synergism action of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanocrystals and cyclodextrin. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, E.; Fukukita, T. Antifogging Resin Sheet. JP Pat. Appl. JP2004137426, 13 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Kai, S. Antibacterial Insecticidal Thermoplastic Composition and Its Molded Articles. JP Pat. Appl. JPH07207165, 8 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzano, M.; Barolo, C.; Buscaino, R.; D’Agostino, G.; Ferri, A.; Sangermano, M.; Pisano, R. Controlled atmosphere in food packaging using ethylene−α-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes dispersed in photocured acrylic films. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sui, S.; Ference, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, K. Antimicrobial and mechanical properties of β-cyclodextrin inclusion with essential oils in chitosan films. J Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8914–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munhuweyi, K.; Caleb, O.J.; van Reenen, A.J.; Opara, U.L. Physical and antifungal properties of β-cyclodextrin microcapsules and nanofibre films containing cinnamon and oregano essential oils. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Wen, P.; Yang, H.; Li, N.; Lou, W.J.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H. Enhancement of the antimicrobial activity of cinnamon essential oil-loaded electrospun nanofilm by the incorporation of lysozyme. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.H.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.J.; Lou, W.Y.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H. Fabrication of electrospun polylactic acid nanofilm incorporating cinnamon essential oil/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antimicrobial packaging. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias Antunes, M.; da Silva Dannenberg, G.; Fiorentini, Â.M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Lim, L.T.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Antimicrobial electrospun ultrafine fibers from zein containing eucalyptus essential oil/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Furui, K.I. Multilayer Structure for Packaging. JP Pat. Appl. JPH03215031, 20 September 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaee, M.; Askari, G.; Emam Djomeh, Z.; Salami, M. Effect of organic additives on physiochemical properties and anti-oxidant release from chitosan-gelatin composite films to fatty food simulant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibanai, I.; Horikoshoi, K.; Nakamura, N. Fragrant Synthetic Resin Product and Method of Producing the Same. U.S. Patent US4356115, 26 October 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kayaci, F.; Sen, H.S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Functional electrospun polymeric nanofibers incorporating geraniol-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: High thermal stability and enhanced durability of geraniol. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, S.; Saga, K.; Imai, T. Freshness-Preserving Packaging Material for Fruit and Vegetable and Freshness Preservation Using the Same. JP Pat. Appl. JPH0616990, 25 January 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Imakura, H.; Yamada, Y.; Fukazawa, R. Packaging Film, Material for Keeping Freshness of Food and Freshness-Keeping Method. JP Pat. Appl. JPH04325069, 13 November 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Karatsu, M.; Imakura, H.; Fukazawa, R. Antifungal Stretch Film for Food Packaging. JP Pat. Appl. JPH04359028, 11 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Karatsu, M.; Imakura, H.; Fukazawa, R. Antifungal Stretch Film for Food Packaging. JP Pat. Appl. JPH04359029, 11 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fukazawa, R.; Tamayama, M.; Kodama, S. Prevention of Additional Ripening and Aging of Vegetable and Fruit. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01211446, 24 August 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Tanaka, R. Thermoplastic Resin Composition. JP Pat. Appl. JPH111624, 6 January 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara, T. Case for Keeping Freshness of Vegetable and Fruit. JP Patent JP2002281894, 2 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Atsuta, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Okabe, T.; Otomo, Y.; Saito, K. Tacky Tape or Sheet for Preventing Mold, Microorganism and Insect of Vegetable, Fruit or the Like. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01153601, 15 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, T.; Yashiki, I. Antibacterial Plastic Film and Manufacture Thereof. JP Pat. Appl. JPH06191562, 12 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tachika, S. Method for Keeping Food Fresh. JP Pat. Appl. JPH06336265, 6 December 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tachika, S. Antibacterial Base Material and Bag for Food Packaging. JP Pat. Appl. JPH07108641, 25 April 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li., D. Package Material for Candied Fruits on Stick and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent CN106360667, 1 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu, T.; Imazu, R.; Hayamizu, S.; Yamamura, Y. Method for Preserving Food with Cyclodextrin Clathrate Compound. JP Pat. Appl. JPH03224437, 3 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Tsunoda, H.; Mita, K. Production of Food Juice Drink Put in Container. JP Pat. Appl. JPS62171661, 28 July 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Fuenmayor, C.A.; Mascheroni, E.; Cosio, M.S.; Piergiovanni, L.; Benedetti, S.; Ortenzi, M.; Schiraldi, A.; Mannino, S. Encapsulation of R(+)-limonene in edible electrospun nanofibers. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallardo, S.; De Vito, V.; Malinconoico, M.; Volpe, M.G.; Santagata, G.; Di Lorenzio, M.L. Poly(butylene succinate)-based composites containing β-cyclodextrin/d-limonene inclusion complex. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostansek, E.C. Delivery Systems Comprising Cyclopropenes Enclosed in a Packaging Material. U.S. Patent US2002058592, 16 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Neoh, T.L.; Ariyanto, H.D.; Menéndez Galvan, P.; Yoshii, H. Controlled release of 1-methylcyclopropene from its functionalised electrospun fibres under constant and linearly ramped humidity. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Contr. Expos. Risk Assessm. 2017, 34, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, B. Cellulose sulfate based film with slow-release antimicrobial properties prepared by incorporation of mustard essential oil and b -cyclodextrin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, R.L.; Rodríguez, F.J.; Guarda, A.; Galotto, M.J.; Bruna, J.E.; Fávaro Perez, M.A.; Souza, F.R.; Padula, M. Application of β-cyclodextrin/2-nonanone inclusion complex as active agent to design of antimicrobial packaging films for control of Botrytis cinerea. Food Bioproc. Technol. 2017, 10, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Komatsu, K. Coating for Food Packaging, Food Packaging Container Using the Same. JP Pat. Appl. JP2017210584, 30 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hochin, N. Pull Resin Film Sandwiched between Laver and Rice Ball (Onigiri) Therefrom. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01257435, 13 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Bai, M.; Lin, L. Plasma-treated poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers containing tea tree oil/beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for antibacterial packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F. Antibacterial Packaging Film Material and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent CN106479196, 8 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating thymol/cyclodextrin-inclusion complex for food packaging. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koontz, J.L.; Marcy, J.E.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Duncan, S.E.; Long, T.E.; Moffitt, R.D. Polymer processing and characterization of LLDPE films loaded with alpha-tocopherol, quercetin, and their cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siro, I.; Fenyvesi, E.; Szente, L.; De Meulenaer, B.; Devlieghere, F.; Orgovanyi, J.; Senyi, J.; Barta, J. Release of alpha-tocopherol from antioxidative low-density polyethylene film into fatty food simulant: Influence of complexation in beta-cyclodextrin. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aytac, Z.; Keskin, N.O.S.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant α-tocopherol/γ-cyclodextrin-inclusion complex encapsulated polylactic acid electrospun nanofibrous web for food packaging. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Umu, O.C.O.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial electrospun poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanofibrous webs incorporating triclosan/cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isozaki, T.; Sato, K. Ultraviolet Light-Impermeable Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Packaging Films. JP Pat. Appl. JPH11116757, 27 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ozaki, S.; Kawakubo, H. Antimicrobial Films for Food Packaging. JP Pat. Appl. JPH11276135, 12 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Beaverson, N.; Wood, W.E. Barrier Material Comprising Nanosize Metal Particles. PCT Pat. Appl. WO2003025067, 27 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, S.; Masuda, H.; Matsuda, M.; Kitano, H. Fragrant Cured Resin Film. JP Patent JPS6445471, 17 February 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, L.; Yao, J. Tea-Fragrant Fully-Degradable Film and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent CN104892996, 9 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shibanai, I. Synthetic Resin Product Containing Compound Included in Cyclodextrin and Process for the Production of the Same. U.S. Patent US4725657, 16 February 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara, N.; Takaku, H.; Oku, S.; Kogure, Y. Production of Transparent Perfumed Plastic Article. JP Pat. Appl. JPS63265926, 2 November 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shibauchi, I. Manufacture of Artificial Leather Having Smell. JP Patent JPS6099079, 1 June 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Shibanai, I. Process for the Preparation of Odored Synthetic Leather. U.S. Patent US4725633, 16 February 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Shibauchi, I. Synthetic Resin Product Containing Guest Material Included in Cyclodextrin and Its Production. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01225644, 8 September 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Chikahisa, N.; Cho, S. Warming Bag. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01280457, 10 November 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, S.; Masuda, H.; Matsuda, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuda, H. Aromatic Recording Card. JP Patent JPS6444792, 17 February 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, S.; Ukon, M. Garbage Bag Protected from Crow. JP Pat. Appl. JP2007223781, 6 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Balogh, K.; Fenyvesi, É.; Makk, J.; Márialigeti, K.; Sényi, J.M.; Siró, I.; Orgoványi, J.; Otta, K.; Szente, L. Cyclodextrin complexes of natural antimicrobial compounds in active packaging. In Proceedings of the 14th International Cyclodextrins Symposium, Kyoto, Japan, 8–11 May 2008; pp. 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Lugo, A.C.; Lim, L.T. Controlled release of allyl isothiocyanate using soy protein and poly(lactic acid) electrospun fibers. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.Y.; Signal, F.A.; Campion, S.H.; Motion, R.L. Citronella as an insect repellent in food packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4633–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibauchi, I. Production of Insecticidal Film. JP Pat. Appl. JPS61137803, 25 June 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Shibauchi, I. Production of Insect-Repellent and Insecticidal Film. JP Pat. Appl. JPS6165805, 4 April 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizuka, Y. Plastic Material. JP Pat. Appl. JPH01149884, 12 June 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Akasaka, M.; Shibata, T.; Ochiai, H. Moth-Proofing Fiber. JP Pat. Appl. JPH0359178, 14 March 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shibauchi, I.; Nakamura, K. Production of Concentrated Pellet for Synthetic Resin. JP Patent JPS60192729, 1 October 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Enmanji, K.; Yamazaki, I. Dye Laser. JP Pat. Appl. JPH06125150, 6 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, C.; Melzig, M.; Weigang, U. Photochromic Plastic Article. Eur. Patent EP1099743, 16 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, M.; Kim, Y.T.; Tonelli, A.; Whang, H.S. Cyclodextrin inclusion complex formation with butylated hydroxytoluene and its application in polyethylene film. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikahisa, N.; Cho, S. Plastic Additive. JP Pat. Appl. JPS6323939, 1 February 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Oku, S. Production of Resin Product Having Antistatic Property. JP Pat. Appl. JPH0333131, 13 February 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Stretch-Resistant and Aging-Resistant Plastic Film. CN Patent CN107522976, 29 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shibauchi, I. Production of Rustproof Material. JP Pat. Appl. JPS61291984, 22 December 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Shibanai, I.; Nakamura, K. Rust Preventive Method and Producing the Same. U.S. Patent US4677177, 30 June 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mascheroni, E.; Fuenmayor, C.A.; Cosio, M.S.; Di Silvestro, G.; Piergiovanni, L.; Mannino, S.; Schiraldi, A. Encapsulation of volatiles in nanofibrous polysaccharide membranes for humidity-triggered release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, W. Edible Chewing Gum Packaging Film. CN Patent CN105400213, 16 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss, J.H.; Watkins, C.B.; Sanchez, D.G. Release of 1-methylcyclopropene from heat-pressed polymer films. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E330–E334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J.; Kuduk, W.J. Maturation or Ripening Inhibitor Release from Polymer, Fiber, Film, Sheet or Packaging. CA Patent CA2692211, 13 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzi, L.C.; Bazzano, M.; Sangermano, M.; Pisano, R. Inclusion complexes dispersed in polystyrene-based labels for fruit ripening on demand. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstichel, S.; De Wilde, B.; Fenyvesi, É.; Szejtli, J. Investigation of the aerobic biodegradability of several types of cyclodextrins in a laboratory-controlled composting test. J. Polym. Environ. 2004, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, R.P.; Allenza, P.; Schollmeyer, J.; Oltman, H.D. Biodegradable Polymeric Materials and Articles Fabricated Therefrom. PCT Int. Appl. WO9106601, 16 May 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Monforton, R.J.; Popa, M.A.; Plank, D.W.; Devries, J.W. Oil-Resistant Packaging. CA Patent CA2578580, 17 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fujishiro, T.; Nakamura, N.; Matsuzawa, M. Method for Making Laminated Film for Meat. JP Patent JPS54142282, 6 November 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Beaverson, N.J.; Wood, W.E. Beverage Bottle Polymer which Resists Elution of Water-Solubles—Comprising a Thermoplastic Containing Sufficient of a Modified Cyclo-Dextrin to Absorb Materials that Could Be Extracted by a Beverage. PCT Int. Appl. WO9730122, 21 August 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. Packaging System Comprising Cellulosic Web with a Permeant Barrier or Contaminant Trap. U.S. Patent US5985772, 16 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E. Improved aroma barrier properties in food packaging with cyclodextrins. In Proceedings of the 10th International Cyclodextrin Symposium, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 21–24 May 2000; pp. 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. Sealing Element for Vessel or Container Closures Having Improved Barrier Properties. U.S. Patent US2003207056, 6 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Asslisi, C. Active Packaging of Ground Coffee Using Cyclodextrin-Containing Cellophane Films. Master’s Thesis, Corvinus University, Budapest, Hungary, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. Malodor Absorente Polymer and Fiber. Eur Patent EP2414450, 8 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-de-Dicastillo, C.; Gallur, M.; Catala, R.; Gavara, R.; Hernandez-Munoz, P. Immobilization of beta-cyclodextrin in ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer for active food packaging applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-de-Dicastillo, C.; Jorda, M.; Catala, R.; Gavara, R.; Hernandez-Munoz, P. Development of active polyvinyl alcohol/beta-cyclodextrin composites to scavenge undesirable food components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11026–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-de-Dicastillo, C.; Catalá, R.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Food applications of active packaging EVOH films containing cyclodextrins for the preferential scavenging of undesirable compounds. J. Food Eng. 2011, 104, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, W.E.; Erickson, R.A. Packaging Material Such as Film, Fiber, Woven and Nonwoven Fabric with Adsorbancy. PCT Pat. Appl. WO2011041479, 7 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ikenotani, M. Laminated Packaging Material. JP Pat. Appl. JP2007083619, 5 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. Packaging Materials Having Improved Barrier Properties. PCT Pat. Appl. WO2003016148, 18 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. A Barrier Material Comprising a Thermoplastic and a Compatible Cyclodextrin Derivative. PCT Pat. Appl. WO1996000260, 4 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, W.E.; Beaverson, N.J. Cellulosic Web with a Contaminant Barrier or Trap. PCT Pat. Appl. WO1997033044, 12 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, S.J.; Kwak, S.Y. Encapsulation of beta-cyclodextrin by in situ polymerization with vinyl chloride leading to suppressing the migration of endocrine disrupting phthalate plasticizer. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesi, E.; Balogh, K.; Siro, I.; Orgovanyi, J.; Senyi, J.M.; Otta, K.; Szente, L. Permeability and release properties of cyclodextrin-containing poly(vinyl chloride) and polyethylene films. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, M. Packaging Material. JP Pat. Appl. JPH10151710, 9 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Welle, F.; Maurer, A. Method for Reducing Perceptible Disturbing Odor in the Treatment of Plastic Materials with Ionizing Rays. Eur. Pat. Appl. EP1206390, 22 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.Y.; Chung, J.W.; Kwak, S.Y. Reduced migration from flexible poly(vinyl chloride) of a plasticizer containing beta-cyclodextrin derivative. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7522–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.B. Production of Cyclodextrin Derivative-Containing Flexible PVC Compositions with Suppressed Plasticizer Migration. PCT Pat. Appl. WO2007066839, 14 June 2007. [Google Scholar]




| Active Guest | CD | Carrier Material | Carrier Form | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| allyl isothiocyanate | CD | poly(ethylene-terephthalate)/poly(ethylene vinyl acetate) | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [17] |
| β-CD | polyethylene | tray | antibacterial packaging for raw tuna | [18] | |
| natural pulp | sheet | water-absorbing antimicrobial sheet e.g., for raw tuna | [19] | ||
| poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [20,21,22] | ||
| triacetyl β-CD | polyethylene | film | antimicrobial | [23] | |
| β-CD | poly(lactic acid) | film, container | antimicrobial packaging for cheese | [12,24] | |
| bromo-cinnamaldehyde | CD | polyethylene | film | antimicrobial or rust proof | [25] |
| carvacrol | β-CD | microfibrillated cellulose | paper | antibacterial packaging | [26] |
| chitosan | film | antimicrobial packaging for chicken filet | [27] | ||
| HPBCD | oxidized cellulose | film | prolonged release | [28] | |
| catechins | CD | styrene copolymers | film | antibacterial activity and antifogging | [29] |
| cedar leaf oil | CD | thermoplastic resins | container | antibacterial and worm-repellent | [30] |
| ethylene | α-CD | poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate | film | controlled ripening by controlled release of ethylene | [31] |
| essential oil | β-CD | chitosan | film | antibacterial packaging | [32] |
| chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | antifungal electrospun nanofibers | [33] | ||
| poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | antimicrobial electrospun nanofilm | [34] | ||
| poly(lactic acid) | film | antimicrobial electrospun nanofilm | [35] | ||
| zein | membrane | antimicrobial electrospun composite | [36] | ||
| FeSO4 | γ-CD | polypropylene | bottle | oxygen barrier | [37] |
| gallic acid | β-CD | chitosan | film | antioxidant for fatty food | [38] |
| geraniol | α-CD | polyethylene | cups, brushes | long-lasting fragrance | [39] |
| γ-CD | poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | prolonged durability | [40] | |
| hinokitiol | β-CD | packaging material | printing ink | freshness preservation | [41] |
| polyethylene | film | fruit, vegetable antifungal packaging | [42] | ||
| polyethylene/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [43] | ||
| polypropylene/polybutene | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [44] | ||
| paper, cloth | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [45] | ||
| CD | thermoplastic resin | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [46] | |
| polyolefins | packaging case | antimicrobial food pack | [47] | ||
| packaging container | adhesive tape | antimicrobial and insect repellent | [48] | ||
| iodine | β-CD | Et-cellulose polypropylene cloth | film | sea food | [11] |
| isocyanate/terpene | CD | polystyrene | film | antimicrobial food packaging | [49] |
| wrapping material | vacuum packaging material | antimicrobial food packaging | [50] | ||
| polyester/vinylidene chloride/polyurethane | bag of permeable wall | antimicrobial food packaging | [51] | ||
| starch, methyl cellulose | packaging material | edible antimicrobial packaging for candied fruits | [52] | ||
| packaging material | coating | antimicrobial food packaging | [53] | ||
| limonene | β-CD | polyester/Al/polyethylene | container, film | orange juice, flavor improvement | [54] |
| pullalan | electrospun nanofibers | active food packaging | [55] | ||
| poly(butylene succinate) | compression molded composite films | antimicrobial food packaging | [56] | ||
| methyl-cyclopropene | α-CD | poly(vinyl alcohol) | film cardboard or plastic container, wood box | prolonged plant life and delayed ripening by inhibiting ethylene response | [57] |
| polystyrene | fiber mat | humidity-triggered release | [58] | ||
| mustard oil | β-CD | cellulose sulfate | film | antimicrobial edible films and coatings | [59] |
| 2-nonanone | β-CD | poly(lactic acid), polyethylene | film | antibacterial packaging | [60] |
| polyphenols, terpenes | CD | crosslinked polyethylene | coating | antibacterial, fungicide, deodorizing effect | [61] |
| rapeseed oil | β-CD | polypropylene | film | to separate moist/dry components of pre-packed foods (rice) | [62] |
| tea tree oil | β-CD | poly(ethylene oxide) | nanofiber film | antibacterial packaging | [63] |
| thyme oil | β-CD | alginate, caseate | film | antibacterial packaging | [64] |
| thymol | γ-CD | zein | nanofibrous web | antibacterial food packaging | [65] |
| α-tocopherol | β-CD | polyethylene | film | long-lasting antioxidant effects | [66,67] |
| γ-CD | poly(lactic acid) | nanofibrous web | food packaging for meat | [68] | |
| trans-2-hexanal | β-CD | poly(lactic acid) | sheet | antimicrobial food packaging | [14] |
| triclosan | β-CD, γ-CD | poly(lactic acid) | nanofibrous webs | antibacterial packaging | [69] |
| UV-filter | β-CD/HPBCD | poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | UV-light impermeable pack | [70] |
| volatile microbicides | CD | polyethylene, coated | film | antimicrobial food pack | [71] |
| zinc nanoparticles | triacetyl α-, β-, γ-CD | matrix-material | - | barrier material in food packaging | [72] |
| CD | Carrier Material | Carrier Form | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | polyester | beverage bottle | sorption of materials that could be extracted by the beverage | [108] |
| CD | non-woven cellulose web or thermoplastic polymer | fiber web, coating or laminate | permeants/contaminants traps | [109] |
| CD | thermoplastic paperboard | packaging material | barrier for permeation of volatiles | [110] |
| CD | thermoplastic polymer | sealing element, polymer liner for bottles | barrier | [111] |
| CD | cellulose acetate | membrane | aroma-preserving packaging of roasted, ground coffee | [112] |
| β-CD | polyethylene | film | elimination of development of undesired odor, discoloration | [113] |
| β-CD | ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer, poly(vinyl alcohol) | film | sorption of cholesterol | [114,115,116] |
| β-CD | poly(ethylenimine) | adsorption of unwanted substances | [117] | |
| α-, β-, γ-CD | polyethylene | coating | trap for odorous components of resins and adhesives | [118] |
| α-, β-, γ-CD derivatives | matrix material | barrier material in food packaging, diapers | [119] | |
| CD derivative | thermoplastic resin | film | aroma barrier | [120] |
| β-CD trimethyl-silylether | coatings on paperboard | film | for trapping environmental contaminants | [121] |
| β-CD silylated | poly(vinyl chloride) | - | reduced migration of plasticizer | [122] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szente, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Cyclodextrin-Enabled Polymer Composites for Packaging. Molecules 2018, 23, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071556
Szente L, Fenyvesi É. Cyclodextrin-Enabled Polymer Composites for Packaging. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071556
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzente, Lajos, and Éva Fenyvesi. 2018. "Cyclodextrin-Enabled Polymer Composites for Packaging" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071556
APA StyleSzente, L., & Fenyvesi, É. (2018). Cyclodextrin-Enabled Polymer Composites for Packaging. Molecules, 23(7), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071556