Be Aware of Aggregators in the Search for Potential Human ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
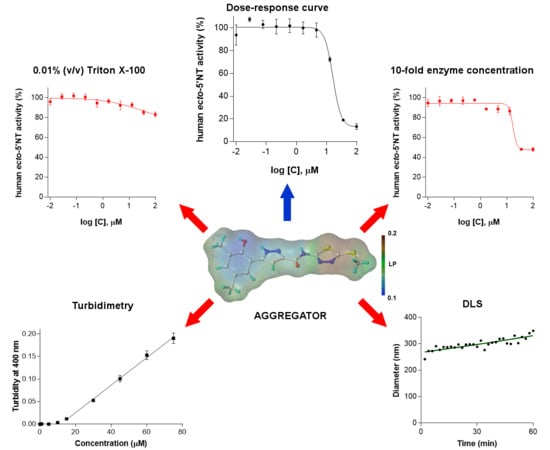
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, B.Y.; Shoichet, B.K. A detergent-based assay for the detection of promiscuous inhibitors. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, R.S.; Simeonov, A.; Jadhav, A.; Eidam, O.; Mott, B.T.; Keiser, M.J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Maloney, D.J.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Complementarity between a docking and a high-throughput screen in discovering new cruzain inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4891–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scior, T.; Bender, A.; Tresadern, G.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Martínez-Mayorga, K.; Langer, T.; Cuanalo-Contreras, K.; Agrafiotis, D.K. Recognizing pitfalls in virtual screening: A critical review. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvezzi, A.; Queiroz, R.F.; De Rezende, L.; Augusto, O.; Amaral, A.T. Do MPO inhibitors selected by virtual screening. Mol. Inform. 2011, 30, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Duan, D.; Torosyan, H.; Doak, A.K.; Ziebart, K.T.; Sterling, T.; Tumanian, G.; Shoichet, B.K. An Aggregation Advisor for Ligand Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7076–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malvezzi, A.; de Rezende, L.; Izidoro, M.A.; Cezari, M.H.S.; Juliano, L.; Amaral, A.T.d. Uncovering false positives on a virtual screening search for cruzain inhibitors. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, S.L.; Shoichet, B.K. Kinase inhibitors: Not just for kinases anymore. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, C.; Bertozzi, C.; Georg, G.I.; Kiessling, L.; Lindsley, C.; Liotta, D.; Merz, K.M.; Schepartz, A.; Wang, S. The Ecstasy and Agony of Assay Interference Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2165–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baell, J.; Walters, M.A. Chemistry: Chemical con artists foil drug discovery. Nature 2014, 513, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGovern, S.L.; Helfand, B.T.; Feng, B.; Shoichet, B.K. A specific mechanism of nonspecific inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Ursu, O.; Lipinski, C.A.; Sklar, L.A.; Oprea, T.I.; Bologa, C.G. Badapple: Promiscuity patterns from noisy evidence. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidler, J.; McGovern, S.L.; Doman, T.N.; Shoichet, B.K. Identification and prediction of promiscuous aggregating inhibitors among known drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4477–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.Y.; Shelat, A.; Doman, T.N.; Guy, R.K.; Shoichet, B.K. High-throughput assays for promiscuous inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateen, R.; Ali, M.M.; Hoare, T. A printable hydrogel microarray for drug screening avoids false positives associated with promiscuous aggregating inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 602, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, L.F.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Effects of synthetic lipids on solubilization and colloid stability of hydrophobic drugs. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 258, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliete, G.L.; Luciano, R.G.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A. Stable Indomethacin Dispersions in Water from Drug, Ethanol, Cationic Lipid and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2016, 4, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coan, K.E.D.; Shoichet, B.K. Stoichiometry and Physical Chemistry of Promiscuous Aggregate-Based Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9606–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoichet, B.K. Interpreting Steep Dose-Response Curves in Early Inhibitor Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7274–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGovern, S.L.; Caselli, E.; Grigorieff, N.; Shoichet, B.K. A common mechanism underlying promiscuous inhibitors from virtual and high-throughput screening. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaoglu, K.; Simconov, A.; Irwin, J.J.; Nelson, M.E.; Feng, B.; Thomas, C.J.; Cancian, L.; Costi, M.P.; Maltby, D.A.; Jadhav, A.; et al. Comprehensive mechanistic analysis of hits from high-throughput and docking screens against β-lactamase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassano, M.F.; Doak, A.K.; Roth, B.L.; Shoichet, B.K. Colloidal aggregation causes inhibition of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2406–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohjala, L.; Tammela, P. Aggregating behavior of phenolic compounds—A source of false bioassay results? Molecules 2012, 17, 10774–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alturki, M.S.; Fuanta, N.R.; Jarrard, M.A.; Hobrath, J.V.; Goodwin, D.C.; Rants′o, T.A.; Calderón, A.I. A multifaceted approach to identify non-specific enzyme inhibition: Application to Mycobacterium tuberculosis shikimate kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Doak, A.K.; Nedyalkova, L.; Shoichet, B.K. Colloidal Aggregation and the in Vitro Activity of Traditional Chinese Medicines. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, H.; Zebisch, M.; Sträter, N. Cellular function and molecular structure of ecto-nucleotidases. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 437–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Haskó, G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stagg, J.; Beavis, P.A.; Divisekera, U.; Liu, M.C.P.; Möller, A.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73-Deficient mice are resistant to carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, J.; Divisekera, U.; McLaughlin, N.; Sharkey, J.; Pommey, S.; Denoyer, D.; Dwyer, K.M.; Smyth, M.J. Anti-CD73 antibody therapy inhibits breast tumor growth and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loi, S.; Pommey, S.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Beavis, P.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J.; Stagg, J. CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11091–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cappellari, A.R.; Rockenbach, L.; Dietrich, F.; Clarimundo, V.; Glaser, T.; Braganhol, E.; Abujamra, A.L.; Roesler, R.; Ulrich, H. Oliveira Battastini, A.M. Characterization of Ectonucleotidases in Human Medulloblastoma Cell Lines: Ecto-5′NT/CD73 in Metastasis as Potential Prognostic Factor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, A.R.; Pillat, M.M.; Souza, H.D.N.; Dietrich, F.; Oliveira, F.H.; Figueiró, F.; Abujamra, A.L.; Roesler, R.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; et al. Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Overexpression Reduces Tumor Growth in a Xenograph Medulloblastoma Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flögel, U.; Burghoff, S.; Van Lent, P.L.E.M.; Temme, S.; Galbarz, L.; Ding, Z.; El-Tayeb, A.; Huels, S.; Bönner, F.; Borg, N.; et al. Selective activation of adenosine A2A receptors on immune cells by a CD73-dependent prodrug suppresses joint inflammation in experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paletta-Silva, R.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Adenosine and Immune Imbalance in Visceral Leishmaniasis: The Possible Role of Ectonucleotidases. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 2012, 650874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo-Abrahão, T.; Cosentino-Gomes, D.; Gomes, M.T.; Alviano, D.S.; Alviano, C.S.; Lopes, A.H.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Biochemical properties of Candida parapsilosis ecto-5′-nucleotidase and the possible role of adenosine in macrophage interaction. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 317, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chuang-Smith, O.N.; Frank, K.L.; Guenther, B.D.; Kern, M.; Schlievert, P.M.; Herzberg, M.C. Ecto-5′-Nucleotidase: A Candidate Virulence Factor in Streptococcus sanguinis Experimental Endocarditis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Solini, A. P2 receptors: New potential players in atherosclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, A.B.; Cronstein, B.N. Regulation of foam cells by adenosine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, M.L.; Henn, M.; Köhler, D.; Kloor, D.; Mittelbronn, M.; Gorzolla, I.C.; Stahl, G.L.; Eltzschig, H.K. Role of extracellular nucleotide phosphohydrolysis in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2784–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Mir, G.; McGeachy, M.J. CD73 is expressed by inflammatory Th17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis but does not limit differentiation or pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Xu, X.; Qiao, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, F.; Gao, G.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of NT5E/CD73 expression and its prognostic significance in distinct types of cancers. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braganhol, E.; Tamajusuku, A.S.K.; Bernardi, A.; Wink, M.R.; Battastini, A.M.O. Ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73 inhibition by quercetin in the human U138MG glioma cell line. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2007, 1770, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripphausen, P.; Freundlieb, M.; Brunschweiger, A.; Zimmermann, H.; Müller, C.E.; Bajorath, J. Virtual Screening Identifies Novel Sulfonamide Inhibitors of ecto-5′-Nucleotidase. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6576–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baqi, Y.; Lee, S.; Iqbal, J.; Ripphausen, P.; Lehr, A.; Scheiff, A.B.; Zimmermann, H.; Bajorath, J.; Müller, C.E. Development of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Based on an Anthraquinone Scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Saeed, A.; Raza, R.; Matin, A.; Hameed, A.; Furtmann, N.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Bajorath, J. Identification of sulfonic acids as efficient ecto-5′-nucleotidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 70, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, S.; Freundlieb, M.; Pippel, J.; Meyer, A.; Abdelrahman, A.; Fiene, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Zimmermann, H.; Yegutkin, G.G.; Sträter, N.; et al. α,β-Methylene-ADP (AOPCP) Derivatives and Analogues: Development of Potent and Selective ecto-5′-Nucleotidase (CD73) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6248–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rashida, M.; Batool, G.; Sattar, A.; Ejaz, S.A.; Khan, S.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Hameed, A.; Iqbal, J. 2-Alkoxy-3-(sulfonylarylaminomethylene)-chroman-4-ones as potent and selective inhibitors of ectonucleotidases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 115, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Ejaz, S.A.; Shehzad, M.; Hassan, S.; al-Rashida, M.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Iqbal, J. 3-(5-(Benzylideneamino)thiazol-3-yl)-2H-chromen-2-ones: A new class of alkaline phosphatase and ecto-5′-nucleotidase inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21026–21036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimova, R.; Fontanel, S.; Lionne, C.; Jordheim, L.P.; Peyrottes, S.; Chaloin, L. Identification of allosteric inhibitors of the ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) targeting the dimer interface. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiró, F.; Mendes, F.B.; Corbelini, P.F.; Janarelli, F.; Jandrey, E.H.F.; Russowsky, D.; Eifler-Lima, V.L.; Battastini, A.M.O. A monastrol-derived compound, LaSOM 63, inhibits ecto-5′-nucleotidase/CD73 activity and induces apoptotic cell death of glioma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, K.; Zebisch, M.; Pippel, J.; El-Tayeb, A.; Müller, C.E.; Sträter, N. Crystal structure of the human ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73): Insights into the regulation of purinergic signaling. Structure 2012, 20, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A Free Database of Commercially Available Compounds for Virtual Screening ZINC—A Free Database of Commercially Available Compounds for Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced Protein-Ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of physicochemical parameters by atomic contributions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M.; Delfert, D.; Junger, K.D. A direct colorimetric assay for Ca2+ -stimulated ATPase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1986, 157, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Jirovsky, D.; Lee, S.Y.; Zimmermann, H.; Müller, C.E. Capillary electrophoresis-based nanoscale assays for monitoring ecto-5′-nucleotidase activity and inhibition in preparations of recombinant enzyme and melanoma cell membranes. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freundlieb, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Müller, C.E. A new, sensitive ecto-5′-nucleotidase assay for compound screening. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 446, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channar, P.A.; Shah, S.J.A.; Hassan, S.; Nisa, Z.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Bajorath, J.; Saeed, A.; Iqbal, J. Isonicotinohydrazones as inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase and ecto-5′-nucleotidase. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the protein databank and cambridge structural database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 11, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved Protein—Ligand Docking Using GOLD. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2003, 623, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servos, J.; Reiländer, H.; Zimmermann, H. Catalytically active soluble ecto-5′-nucleotidase purified after heterologous expression as a tool for drug screening. Drug Dev. Res. 1998, 276, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, E.; Morrison, I. Particle Size Distribution from Analysis of Quasieletric Light Scattering Data. In Measurements of Suspended Particles by Quasielastic Light Scattering; Dahneke, B.E., Ed.; Willey-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 199–236. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples (small amounts) of the compounds are available from the authors. |






| Compound (ID) | Structure | Molecular Weight (g·mol−1) | cLogP 1 | IC50 (µM) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A |  | 331.28 | 2.4 | 82.9 ± 1.1 |
| B |  | 354.36 | 4.2 | 1.9 ± 1.0 |
| C |  | 361.45 | 3.6 | 16.3 ± 1.1 |
| D |  | 414.46 | 4.5 | 2.2 ± 1.2 |
| Compound (ID) | Structure | Previously Reported Aggregator (Structure) | Tanimoto Similarity Index Value (%) 1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A |  |  | 72 | [2] |
| B |  |  | 72 | [2] |
| C |  | n.s.2 | ||
| D |  |  | 81 | [2] |
| Compound (ID) | cLogP 1 | Estimated Solubility (µM) 2 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2.4 | 79.1 |
| B | 4.2 | 8.8 |
| C | 3.6 | 11.7 |
| D | 4.5 | < 0.5 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viviani, L.G.; Piccirillo, E.; Cheffer, A.; De Rezende, L.; Ulrich, H.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Amaral, A.T.-d. Be Aware of Aggregators in the Search for Potential Human ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081876
Viviani LG, Piccirillo E, Cheffer A, De Rezende L, Ulrich H, Carmona-Ribeiro AM, Amaral AT-d. Be Aware of Aggregators in the Search for Potential Human ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081876
Chicago/Turabian StyleViviani, Lucas G., Erika Piccirillo, Arquimedes Cheffer, Leandro De Rezende, Henning Ulrich, Ana Maria Carmona-Ribeiro, and Antonia T.-do Amaral. 2018. "Be Aware of Aggregators in the Search for Potential Human ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Inhibitors" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081876
APA StyleViviani, L. G., Piccirillo, E., Cheffer, A., De Rezende, L., Ulrich, H., Carmona-Ribeiro, A. M., & Amaral, A. T. -d. (2018). Be Aware of Aggregators in the Search for Potential Human ecto-5′-Nucleotidase Inhibitors. Molecules, 23(8), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081876