Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Triterpenoids as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Cirsium setosum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Structural Elucidation of the Three New Compounds
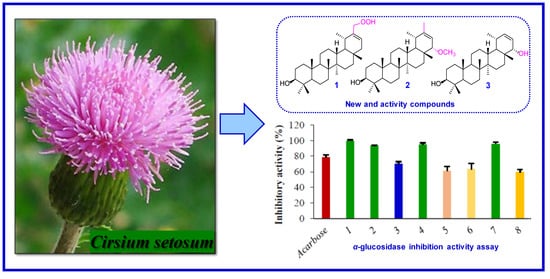
2.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of the Isolates
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. General Experimental Procedures
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. 3β-Hydroxy-30-hydroperoxy-20-taraxastene (1)
3.5. 3β-Hydroxy-22α-methoxy-20-taraxastene (2)
3.6. 30-Nor-3β,22α-dihydroxy-20-taraxastene (3)
3.7. 3β,22α-Dihydroxy-20-taraxastene (4)
3.8. 20-Taraxastene-3,22-dione (5)
3.9. 3β-Acetoxy-20-taraxasten-22-one (6)
3.10. 3β-Hydroxy-20-taraxasten-22-one (7)
3.11. 30-Nor-3β-hydroxy-20-taraxastene (8)
3.12. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect Assay
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.Y.; Yang, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, H.X. Research progress on Cirsium setosum. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.G.; Liu, W.M.; Sang, Z.P.; Li, J.; Li, Y.P.; Wen, R.R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.Q.; Feng, Z.W. Studies on flavonoids from Cirsium setosum. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 868–873. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.gnc.com/herbs-natural-remedies/herbs-f-n/milk-thistle/ (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Zhang, Z. Drink for treatment of type ii diabetes complicated hypertension and preparation method thereof. CN 104857372 A, 26 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M. Tea beverage for stabilizing blood pressure and its preparation method. CN 103891958 A, 2 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K. Corn stigma beverage with chrysanthemum fragrance for reducing cholesterol and preparation method thereof. CN 105942095 A, 21 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.Y. Health tea for preventing and treating frequent micturition. CN 103918842 A, 16 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, N.; Wei, W.D.; Wang, A.L.; Li, J.J.; Zheng, J.Q.; Shang, X.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Qi, Y. Four new taraxastane-type triterpenoic acids from Cirsium setosum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Li, L.L.; Yuan, Z.Z.; Wang, A.L.; Li, J.J.; Shang, X.Y. Isolation, purification and elucidation on steroils from Cirsium setosum (Willd.) MB. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H.; Cui, J.H.; Ding, A.W.J. Impact of Herba Cirsii extracts on hemorrhage, blood coagulation and experimental inflammation in Rats. Sichuan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2006, 24, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.H.; Zhao, J.B.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Jiang, J.G. Comparative extraction processes, volatile compounds analysis and antioxidant activities of essential oils from Cirsium japonicum Fisch. ex DC and Cirsium setosum (Willd.) M.Bieb. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhou, L.L. Analysis of chemical components of essential oils from Cirsium setosum and their antimicrobial and hemostatic activities. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 31, 604–610. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.Y. Traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating diabetes. CN 106166191 A, 30 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Y.Z.; Zhuo, Y.H. Chinese medicine preparation for treating diabetes mellitus and preparation method thereof. CN 105963582 A, 28 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.H. A yang-warming and yin-nourishing drug for treatment of diabetes and preparation method. CN 104606550 A, 13 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. A traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy. CN 105168534 A, 23 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.S. Chinese medicinal composition containing Lysimachia and Taraxacum and others for treating diabetes urinary tract infection. CN 101112594 A, 30 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Warashina, T.; Umehara, K.; Miyase, T. Constituents from the roots of Taraxacum platycarpum and their effect on proliferation of human skin fibroblasts. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Kuo, Y.H. Taraxastane-type triterpenes from the Aerial Roots of Ficus microcarpa. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Chaiang, Y.M. Five new taraxastane-type triterpenes from the Aerial Roots of Ficus microcarpa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Chang, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.H. Cytotoxic triterpenes from the aerial roots of Ficus microcarpa. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, H.; Kinzo, W. Sesquiterpene alcohols and triterpenoids from Liatris Microcephala. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 1457–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, P.H.; Nguyen, H.X.; Duong, T.T.T.; Tran, T.K.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Vu, T.K.T.; Vuong, H.C.; Phan, N.H.T.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Awale, S. α-Glucosidase inhibitory and cytotoxic taxane diterpenoids from the stem bark of Taxus wallichiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 5–8 are available from the authors. |




| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (mult, J, Hz) | δC (mult) | δH (mult, J, Hz) | δC (mult) | δH (mult, J, Hz) | δC (mult) | |
| 1 | (a) 0.99 (1H, m) (b) 1.71 (1H, m) | 39.2 | (a) 0.96 (1H, m) (b) 1.71 (1H, m) | 38.9 | 0.91 (1H, m) 1.69 (1H, m) | 38.7 |
| 2 | 1.89 (2H, m) | 28.3 | 1.60 (2H,m) | 27.5 | 1.59 (2H, m) | 27.4 |
| 3 | 3.47 (1H, dd, J = 6.3, 9.8 Hz) | 78.1 | 3.20 (1H, dd, J = 9.8, 2.8 Hz) | 79.2 | 3.17 (1H, dd, J = 5.0, 11.0 Hz) | 78.8 |
| 4 | 39.5 | 39.0 | 38.8 | |||
| 5 | 0.82 (1H, d, J = 10.0 Hz) | 55.8 | 0.70 (1H, br d, J = 10.0 Hz) | 55.5 | 0.66 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, 11.0 Hz) | 55.3 |
| 6 | (a) 1.41 (1H, m) (b) 1.56 (1H, m) | 18.7 | (a) 1.39 (1H, m) (b) 1.53 (1H, m) | 18.5 | (a) 1.36 (1H, m) (b) 1.50 (1H, m) | 18.3 |
| 7 | 1.40 (2H, m) | 34.6 | 1.40 (2H, m) | 34.4 | 1.37 (2H, m) | 34.3 |
| 8 | 41.3 | 41.2 | 41.0 | |||
| 9 | 1.33 (1H, br d, J =12.0 Hz) | 50.7 | 1.29 (1H, m) | 50.6 | 1.26 (1H, br s) | 50.2 |
| 10 | 37.4 | 37.3 | 37.1 | |||
| 11 | (a) 1.50 (1H, brd, J =11.8 Hz) (b) 1.33 (1H, brd, J =11.8 Hz) | 21.7 | (a) 1.28 (1H, m) (b) 1.54 (1H, m) | 21.8 | 1.26 (1H, m) 1.51 (1H, m) | 21.5 |
| 12 | 1.55 (2H, m) | 27.8 | 1.25 (2H, m) | 27.6 | 1.17 (H, m) 1.65 (1H, m) | 28.0 |
| 13 | 1.57 (1H, m) | 39.4 | 1.65 (1H, m) | 38.8 | 1.69 (1H, m) | 38.9 |
| 14 | 42.5 | 42.4 | 42.2 | |||
| 15 | (a) 0.99 (1H, m) (b) 1.76 (1H, m) | 27.3 | (a) 1.06 (1H, m) (b) 1.75 (1H, m) | 27.1 | (a) 1.06 (1H, m) (b) 1.73 (1H, m) | 26.6 |
| 16 | (a) 1.24 (1H, m) (b) 1.34 (1H, m) | 36.9 | (a) 0.94 (1H, m) (b) 2.00 (1H, dt, J = 4.0, 13.5 Hz) | 30.2 | (a) 0.93 (1H, m) (b) 1.97 (1H, dt, J =4.0, 13.5 Hz) | 30.1 |
| 17 | 34.9 | 38.5 | 38.3 | |||
| 18 | 1.15 (1H, m) | 48.7 | 1.50 (1H, m) | 41.7 | 1.35 (1H, m) | 40.5 |
| 19 | 2.22 (1H, m) | 32.5 | 1.56 (1H, m) | 36.9 | 1.76 (1H, m) | 32.8 |
| 20 | 141.1 | 145.9 | 5.62 (1H, dd, J = 3.3, 9.8 Hz) | 139.4 | ||
| 21 | 5.81 (1H, d, J = 6.5 Hz) | 124.3 | 5.59 (1H, d, J = 5.8 Hz) | 119.8 | 5.77 (1H, ddd, J = 1.8, 6.0, 9.8 Hz) | 124.6 |
| 22 | (a) 1.71 (1H, m) (b) 1.86 (1H, m) | 42.1 | 2.91 (1H, d, J = 5.8 Hz) | 82.9 | 3.30 (1H, d, J = 6.0 Hz) | 73.3 |
| 23 | 1.25 (3H, s) | 28.6 | 0.97 (3H, s) | 28.1 | 0.94 (3H, s) | 28.1 |
| 24 | 1.06 (3H, s) | 16.3 | 0.77 (3H, s) | 16.5 | 0.74 (3H, s) | 15.5 |
| 25 | 0.91 (3H, s) | 16.6 | 0.85 (3H, s) | 15.6 | 0.81 (3H, s) | 16.3 |
| 26 | 1.00 (3H, s) | 16.2 | 1.03 (3H, s) | 16.2 | 1.01 (3H, s) | 16.1 |
| 27 | 0.97 (3H, s) | 14.9 | 0.98 (3H, s) | 15.0 | 0.95 (3H, s) | 14.6 |
| 28 | 0.96 (3H, s) | 18.0 | 0.66 (3H, s) | 18.7 | 0.71 (3H, s) | 18.1 |
| 29 | 1.14 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz) | 22.6 | 1.01 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz) | 22.6 | 0.99 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz) | 24.1 |
| 30 | (a) 4.66 (1H, d, J = 11.5 Hz) (b) 4.91 (1H, d, J = 11.5 Hz) | 79.4 | 1.69 (3H, s) | 22.1 | ||
| OCH3 | 3.30 (3H, s) | 56.8 | ||||
| Compounds | Inhibition (%) | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.46 ± 1.04 | 18.34 ± 1.27 |
| 2 | 93.29 ± 0.74 | 26.98 ± 0.89 |
| 3 | 70.34 ± 2.73 | 44.62 ± 1.39 |
| 4 | 94.95 ± 1.67 | 17.49 ± 1.42 |
| 5 | 60.78 ± 5.81 | 68.90 ± 1.82 |
| 6 | 63.06 ± 7.44 | 54.16 ± 2.25 |
| 7 | 95.59 ± 2.34 | 22.67 ± 0.25 |
| 8 | 59.19 ± 3.81 | 80.07 ± 2.13 |
| Acarbose | 78.35 ± 3.41 | 42.52 ± 0.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Yue, J.; Yang, X.; Shang, X.; Lin, S. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Triterpenoids as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Cirsium setosum. Molecules 2019, 24, 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101844
Li X, Zhong X, Wang X, Li J, Liu J, Wang K, Yue J, Yang X, Shang X, Lin S. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Triterpenoids as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Cirsium setosum. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101844
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiuting, Xiangjian Zhong, Xin Wang, Jinjie Li, Jiachen Liu, Kaiqi Wang, Jianyu Yue, Ximiao Yang, Xiaoya Shang, and Sheng Lin. 2019. "Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Triterpenoids as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Cirsium setosum" Molecules 24, no. 10: 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101844
APA StyleLi, X., Zhong, X., Wang, X., Li, J., Liu, J., Wang, K., Yue, J., Yang, X., Shang, X., & Lin, S. (2019). Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Triterpenoids as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Cirsium setosum. Molecules, 24(10), 1844. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101844