First Report on a Solvent-Free Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes with an Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
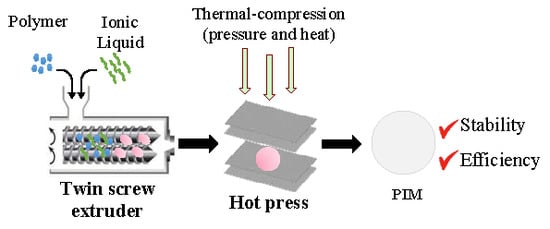
2.1. Preparation of Polymeric Membranes
2.2. Membrane Characterization
2.3. Stability Studies
2.4. Testing Membranes Efficiency: Cr(VI) Extraction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solutions
3.2. PIM Preparation
3.3. Membrane Characterization
3.4. Membrane Stability Studies
3.5. Cr(VI) Extraction Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pabby, A.K.; Rizvi, S.S.H.; Sastre, A.M. Handbook of Membrane Separations: Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Biotechnological Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gardas, R.L.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Group contribution methods for the prediction of thermophysical and transport properties of ionic liquids. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 1274–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Feng, S.; Li, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X. Recent development of ionic liquid membranes. Green Energy Environ. 2016, 1, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs) in chemical analysis—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 987, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Alvarez, A.; Matamoros, V.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Development of polymer Inclusion membranes for the extraction of antibiotics from environmental waters. Procedia Eng. 2012, 44, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Matamoros, V.; Kolev, S.D.; Fontàs, C. Development of a polymer inclusion membrane (PIM) for the preconcentration of antibiotics in environmental water samples. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 492, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, N.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Selective transport and removal of Cd from chloride solutions by polymer inclusion membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 318, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, L.; Mornane, P.; Potter, I.; Perera, J.; Cattrall, R.; Kolev, S. Extraction and transport of metal ions and small organic compounds using polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs). J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 281, 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, J.-P.; Virtanen, P.; Sjöholm, R. Aliquat 336®—a versatile and affordable cation source for an entirely new family of hydrophobic ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O.’Bryan, Y.; Cattrall, R.W.; Truong, Y.B.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Kolev, S.D. The use of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) for the preparation of polymer inclusion membranes. Application to the extraction of thiocyanate. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 510, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O.’Bryan, Y.; Truong, Y.B.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Kolev, S.D. Electrospun polystyrene/Aliquat 336 for preconcentration and determination of thiocyanate in flow analysis. Electrospinning 2017, 1, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kebiche-Senhadji, O.; Tingry, S.; Seta, P.; Benamor, M. Selective extraction of Cr(VI) over metallic species by polymer inclusion membrane (PIM) using anion (Aliquat 336) as carrier. Desalination 2010, 258, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blitz-Raith, A.H.; Paimin, R.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Separation of cobalt(II) from nickel(II) by solid-phase extraction into Aliquat 336 chloride immobilized in poly(vinyl chloride). Talanta 2007, 71, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontàs, C.; Tayeb, R.; Tingry, S.; Hidalgo, M.; Seta, P. Transport of platinum(IV) through supported liquid membrane (SLM) and polymeric plasticized membrane (PPM). J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 263, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Fontàs, C.; Matamoros, V.; Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Development of a polymer inclusion membrane-based passive sampler for monitoring of sulfamethoxazole in natural waters. Minimizing the effect of the flow pattern of the aquatic system. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Panigrahi, A.; Murakami, Y.; Kondo, K. Effect of ammonium- and phosphonium-based ionic liquids on the separation of lactic acid by supported ionic liquid membranes (SILMs). Membranes (Basel) 2011, 1, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Insa, S.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E. A new extraction phase based on a polymer inclusion membrane for the detection of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and cyprodinil in natural water samples. Talanta 2018, 185, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güell, R.; Anticó, E.; Kolev, S.D.; Benavente, J.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Development and characterization of polymer inclusion membranes for the separation and speciation of inorganic As species. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 383, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontàs, C.; Vera, R.; Batalla, A.; Kolev, S.D.; Anticó, E. A novel low-cost detection method for screening of arsenic in groundwater. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11682–11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontàs, C.; Queralt, I.; Hidalgo, M. Novel and selective procedure for Cr(VI) determination by X-ray fluorescence analysis after membrane concentration. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Bai, L.; Gao, H.; Deng, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S. Pebax-based composite membranes with high gas transport properties enhanced by ionic liquids for CO2 separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6422–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi Estahbanati, E.; Omidkhah, M.; Ebadi Amooghin, A. Preparation and characterization of novel Ionic liquid/Pebax membranes for efficient CO2/light gases separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Marino, T.; Simone, S.; Di Nicolò, E.; Li, X.M.; He, T.; Tornaghi, S.; Drioli, E. Towards non-toxic solvents for membrane preparation: A review. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayfun, U.; Dogan, M.; Bayramli, E. Effect of Surface Modification of Rice Straw on Mechanical and Flow Properties of TPU-Based Green Composites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, S.; Diban, N.; Urtiaga, A. Hydrolytic degradation and mechanical stability of poly(ε-Caprolactone)/reduced graphene oxide membranes as scaffolds for in vitro neural tissue regeneration. Membranes (Basel) 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmeyer, F.W. Textbook of Polymer Science, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ocampo, A.L.; Aguilar, J.C.; Rodríguez de San Miguel, E.; Monroy, M.; Roquero, P.; de Gyves, J. Novel proton-conducting polymer inclusion membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 326, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.S.; Walker, J.O.; Lamb, J.D. Permeability and durability effects of cellulose polymer variation in polymer inclusion membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 229, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagaya, S.; Ryokan, Y.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Stability studies of poly(vinyl chloride)-based polymer inclusion membranes containing Aliquat 336 as a carrier. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 101, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Gelde, L.; Anticó, E.; Martínez de Yuso, M.V.; Benavente, J.; Fontàs, C. Tuning physicochemical, electrochemical and transport characteristics of polymer inclusion membrane by varying the counter-anion of the ionic liquid Aliquat 336. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Sánchez-González, S.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Urtiaga, A. Facile fabrication of poly(ε-caprolactone)/graphene oxide membranes for bioreactors in tissue engineering. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 540, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güell, R.; Anticó, E.; Salvadó, V.; Fontàs, C. Efficient hollow fiber supported liquid membrane system for the removal and preconcentration of Cr(VI) at trace levels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Anticó, E.; Fontàs, C. The Use of a Polymer Inclusion Membrane for Arsenate Determination in Groundwater. Water 2018, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Fise, E. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Membrane Composition (w/w) | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 70% CAP–30% Aliquat 336 | Brownish and fragile |
| 70% CAB–30% Aliquat 336 | Oily, slightly translucent and fragile |
| 70% PCL–30% Aliquat 336 | Non-oily, whitish, translucent and flexible |
| 70% TPU–30% Aliquat 336 | Non-oily, whitish, translucent and flexible |
| Membrane | Elements | Theoretical (%) | Found (%) (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70% TPU–30% Aliquat336 | N | 1.4 | 1.72 (0.04) |
| C | 68 | 67.17 (0.02) | |
| H | 10.4 | 11.1 (0.2) | |
| 70% PCL–30% Aliquat336 | N | 1.03 | 1.1 (0.2) |
| C | 64.2 | 64.4 (0.2) | |
| H | 9.6 | 9.6 (0.2) |
| Polymer | Chemical Structure | Melting Point (°C) | Processing Temperature (°C) |
| CAP |  | 188–210 | 220 |
| CAB |  | 130–160 | 140 |
| PCL |  | 58–60 | 100 |
| TPU | Hard segment (4%): Soft segment (96%):  | 80–84 | 130 |
| IL | Chemical Structure | Melting point (°C) | Processing Temperature (°C) |
| Aliquat 336 |  | Liquid at room temperature | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vera, R.; Anticó, E.; Eguiazábal, J.I.; Aranburu, N.; Fontàs, C. First Report on a Solvent-Free Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes with an Ionic Liquid. Molecules 2019, 24, 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101845
Vera R, Anticó E, Eguiazábal JI, Aranburu N, Fontàs C. First Report on a Solvent-Free Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes with an Ionic Liquid. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101845
Chicago/Turabian StyleVera, Ruben, Enriqueta Anticó, José Ignacio Eguiazábal, Nora Aranburu, and Clàudia Fontàs. 2019. "First Report on a Solvent-Free Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes with an Ionic Liquid" Molecules 24, no. 10: 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101845
APA StyleVera, R., Anticó, E., Eguiazábal, J. I., Aranburu, N., & Fontàs, C. (2019). First Report on a Solvent-Free Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes with an Ionic Liquid. Molecules, 24(10), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101845