Antifungal Activities of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Amphiphilic Kanamycins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fungal Growth Inhibition by 4″,6″-Disubstituted AKs
2.2. Analysis of Correlation Between MIC and cLogD
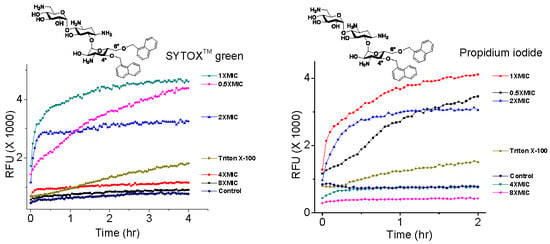
2.3. Plasma Membrane Permeabilization by 4″,6″-Disubstituted Kanamycins
2.4. Effect of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Kanamycins on the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Levitz, S.M. Tackling human fungal infections. Science 2012, 336, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong-James, D.; Meintjes, G.; Brown, G.D. A neglected epidemic: Fungal infections in HIV/AIDS. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutcher, J.D. The discovery and development of amphotericin b. Chest 1968, 54, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovick, R.; Gold, W.; Pagano, J.F.; Stout, H.A. Amphotericins a and b, antifungal antibiotics produced by a streptomycete. I. In vitro studies. Antibiot. Annu. 1955, 3, 579–586. [Google Scholar]
- Lyman, C.A.; Walsh, T.J. Systemically administered antifungal agents. Drugs 1992, 44, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.A.; Hewson, K. Synthesis of potential anticancer agents. X. 2-fluoroadenosine1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.K.; Fosso, M.Y.; Green, K.D.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Amphiphilic tobramycin analogues as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4861–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolley, D.W. Some biological effects produced by benzimidazole and their reversal by purines. J. Biol. Chem. 1944, 152, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Tracking Candida auris | Candida auris | Fungal Diseases | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/candida-auris/tracking-c-auris.html (accessed on 13 April 2019).
- Chandrika, N.T.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Comprehensive review of chemical strategies for the preparation of new aminoglycosides and their biological activities. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1189–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chiang, F.-I.; Wu, L.; Czyryca, P.G.; Li, D.; Chang, C.-W.T. Surprising alteration of antibacterial activity of 5′′-modified neomycin against resistant bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7563–7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Antibacterial activities of aminoglycoside antibiotics-derived cationic amphiphiles. Polyol-modified neomycin b-, kanamycin a-, amikacin-, and neamine-based amphiphiles with potent broad spectrum antibacterial activity. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3626–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.T.; Takemoto, J.Y. Antifungal amphiphilic aminoglycosides. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, Y.P.; AlFindee, M.N.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. Antifungal amphiphilic kanamycins: New life for an old drug. MedChemComm 2018, 9, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-W.T.; Fosso, M.; Kawasaki, Y.; Shrestha, S.; Bensaci, M.F.; Wang, J.; Evans, C.K.; Takemoto, J.Y. Antibacterial to antifungal conversion of neamine aminoglycosides through alkyl modification. Strategy for reviving old drugs into agrofungicides. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-W.T.; Takemoto, J. Aminoglycosides: Synthesis and Use as Antifungals. U.S. Patent US 13/316,720; U.S. Patent US8865665 B2, 21 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fosso, M.; AlFindee, M.N.; Zhang, Q.; Nziko, V.d.P.N.; Kawasaki, Y.; Shrestha, S.K.; Bearss, J.; Gregory, R.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. Structure–activity relationships for antibacterial to antifungal conversion of kanamycin to amphiphilic analogues. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 4398–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosso, M.Y.; Shrestha, S.K.; Green, K.D.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. Synthesis and bioactivities of kanamycin b-derived cationic amphiphiles. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9124–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, Q.Z.; Benhamou, R.I.; Herzog, I.M.; Ben Baruch, B.; Fridman, M. Cationic amphiphiles induce macromolecule denaturation and organelle decomposition in pathogenic yeast. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16391–16395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbuch, K.B.; Benhamou, R.I.; Levin, L.; Stein, R.; Fridman, M. Increased degree of unsaturation in the lipid of antifungal cationic amphiphiles facilitates selective fungal cell disruption. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salta, J.; Benhamou, R.I.; Herzog, I.M.; Fridman, M. Tuning the effects of bacterial membrane permeability through photo-isomerization of antimicrobial cationic amphiphiles. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12724–12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFindee, M.N.; Subedi, Y.P.; Fiori, M.C.; Krishnan, S.; Kjellgren, A.; Altenberg, G.A.; Chang, C.-W.T. Inhibition of connexin hemichannels by new amphiphilic aminoglycosides without antibiotic activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellgren, A.; Fiori, M.C.; AlFindee, M.N.; Subedi, Y.P.; Krishnan, S.; Chang, C.-W.T.; Altenberg, G.A. Inhibition of connexion hemichannels by new aminoglycosides without antibiotic activity. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 250a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, Y.P.; Roberts, P.; Grilley, M.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. Development of fungal selective amphiphilic kanamycin: Cost-effective synthesis and use of fluorescent analogs for mode of action investigation. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, J.P.; Baker, C.; Kawasaki, Y.; Subedi, Y.P.; de Paul, N.N.V.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. Synthesis and bioactivity investigation of quinone-based dimeric cationic triazolium amphiphiles selective against resistant fungal and bacterial pathogens. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, J.P.; Subedi, Y.P.; Chen, L.; Chang, C.-W.T. A mode of action study of cationic anthraquinone analogs: A new class of highly potent anticancer agents. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Jin Oh, H.; Kim, M.J.; Pun, N.T.; Magar, T.B.T.; Bist, G.; Choi, H.; Park, P.-H.; Lee, E.-S. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship study of halogen containing 2-benzylidene-1-indanone derivatives for inhibition of lps-stimulated ros production in raw 264.7 macrophages. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 133, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFindee, M.N.; Zhang, Q.; Subedi, Y.P.; Shrestha, J.P.; Kawasaki, Y.; Grilley, M.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. One-step synthesis of carbohydrate esters as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 9, 11, K20 and FG08 are available from the authors. |









| Compound | cLogD | Strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| 1 | −10.32 | 32–64 | 256 | 256 | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| 2 | −9.81 | 256 | 256 | >256 | 32 | 64 | 64 |
| 3 | −8.88 | 64–128 | >256 | 256 | 8 | 16 | 32 |
| 4 | −9.53 | 16–32 | 32–64 | 32–64 | 4 | 8 | 16 |
| 5 | −8.77 | 16–32 | 64 | 128 | 4–8 | 8 | 8 |
| 6 | −7.81 | 4–16 | 32–64 | 64 | 2–4 | 8 | 8 |
| 7 | −7.81 | 4−8 | 128 | 128 | 8–16 | 4 | 8 |
| 8 | −6.44 | 2–8 | 128–256 | 256 | 8–16 | 4 | 2–4 |
| 9 | −9.36 | 32 | 32 | 16–32 | 8–16 | 8 | 8 |
| 10 | −8.57 | 32 | ND | 8–16 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 11 | −7.78 | 16 | ND | 128 | 8–16 | 8 | 8–16 |
| 12 | −6.99 | ND | 8 | 16–32 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 13 | −1.44 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 256 | >256 |
| K20 | −11.62 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 8–16 | 8 | 16 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfindee, M.N.; Subedi, Y.P.; Grilley, M.M.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Chang, C.-W.T. Antifungal Activities of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Amphiphilic Kanamycins. Molecules 2019, 24, 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101882
Alfindee MN, Subedi YP, Grilley MM, Takemoto JY, Chang C-WT. Antifungal Activities of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Amphiphilic Kanamycins. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101882
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfindee, Madher N., Yagya P. Subedi, Michelle M. Grilley, Jon Y. Takemoto, and Cheng-Wei T. Chang. 2019. "Antifungal Activities of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Amphiphilic Kanamycins" Molecules 24, no. 10: 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101882
APA StyleAlfindee, M. N., Subedi, Y. P., Grilley, M. M., Takemoto, J. Y., & Chang, C. -W. T. (2019). Antifungal Activities of 4″,6″-Disubstituted Amphiphilic Kanamycins. Molecules, 24(10), 1882. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101882