Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
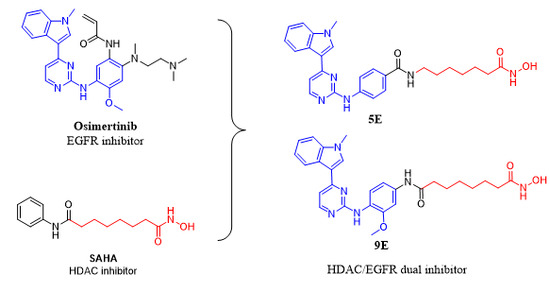
2.1. Compound Design
2.2. Chemistry
2.3. In Vitro HDAC and EGFR Inhibitory Assay
2.4. In Vitro Antiproliferation Assay
2.5. Kinase Selectivity Profile
2.6. LSD1 and BRD4 Assay
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Materials and Methods
3.1.2. Methyl 4-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) pyrimidin-2-yl) amino) benzoate (2)
3.1.3. 4-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) pyrimidin-2-yl) amino) benzoic acid (3)
3.1.4. General Procedure for Preparation of 4A–4E
3.1.5. General Procedure for Preparation of 5A–5E
3.1.6. N-(2-aminophenyl)-4-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) pyrimidin-2-yl)amino) benzamide (10B)
3.1.7. N-(2-methoxy-4-nitrophenyl)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) pyrimidin-2-amine (6)
3.1.8. 2-methoxy-N1-(4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) pyrimidin-2-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine (7)
3.1.9. General Procedure for Preparation of 8A and 8B
3.1.10. General Procedure for Preparation of 8C–8E
3.1.11. General Procedure for Preparation of 9A–9D
3.1.12. General Procedure for Preparation of 9C and 9E
3.2. Biological Materials and Methods
3.2.1. In Vitro HDACs Inhibition Fluorescent Assay
3.2.2. In Vitro EGFR Inhibition
3.2.3. In Vitro Anti-Proliferative Assay
3.2.4. Kinases Inhibition Assay
3.2.5. LSD1 Inhibition Assay
3.2.6. BRD4 Inhibition Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeVita, V.T.; Chu, E. A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8643–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Mishra, L.; Li, S. EMT, CTCs and CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10697–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T.; Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favoni, R.E.; De Cupis, A. The role of polypeptide growth factors in human carcinomas: New targets for a novel pharmacological approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 179–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.R.; Jänne, P.A. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Lu, W.; Chen, G.; Cheng, F.; Su, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Pang, X. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases Sensitizes EGFR-TKI-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Erlotinib In Vitro and In Vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3608–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaltriti, M.; Baselga, J. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Pathway: A Model for Targeted Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5268–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.J.; Gibson, K.H.; Grundy, W.; Godfrey, A.A.; Barlow, J.J.; Healy, M.P.; Woodburn, J.R. Studies leading to the identification of ZD1839 (Iressa™): An orally active, selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeted to the treatment of cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.D.; Barbacci, E.G.; Iwata, K.K.; Arnold, L.; Boman, B.; Cunningham, A.; Diorio, C.; Doty, J.; Morin, M.J.; Moyer, M.P. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Shen, X.; Wang, D.; Xie, G.; Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Hu, Y.; He, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Icotinib (BPI-2009H), a novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, displays potent efficacy in preclinical studies. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M. Phase III Study of Afatinib or Cisplatin Plus Pemetrexed in Patients With Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma WithEGFRMutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.-Y.; Wu, Y.-L. Novel agents and strategies for overcoming EGFR TKIs resistance. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Yuan, X.; Tian, Y.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, G.; Wu, K. Non-invasive approaches to monitor EGFR-TKI treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Ding, P.N.; Lord, S.J.; Inoue, A.; Zhou, C. Impact of specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations and clinical characteristics on outcomes after treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: A metaanalysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of Tumor Specimens at the Time of Acquired Resistance to EGFR TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Gettinger, S.; Akhavanfard, S.; Temel, J.; Vernovsky, K.; Lanuti, M.; Mino-Kenudson, M. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar]
- Finlay, M.R.V.; Anderton, M.; Ashton, S.; Ballard, P.; Bethel, P.A.; Box, M.R.; Bradbury, R.H.; Brown, S.J.; Butterworth, S.; Campbell, A. Discovery of a Potent and Selective EGFR Inhibitor (AZD9291) of Both Sensitizing and T790M Resistance Mutations That Spares the Wild Type Form of the Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8249–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Pawara, R.; Ansari, A.; Surana, S. Recent updates on third generation EGFR inhibitors and emergence of fourth generation EGFR inhibitors to combat C797S resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.W.; Wu, M.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chen, C.C. HDAC Inhibition Decreases the Expression of EGFR in Colorectal Cancer Cells. PLoS One 2011, 6, e1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amila, S.; Kenneth, J.O.; Derek, J.R. Combination Therapy with Histone Deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witta, S.E.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Yoshida, K. ErbB-3 expression is associated with E-cadherin and their coexpression restores response to gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greve, G.; Schiffmann, I.; Pfeifer, D.; Pantic, M.; Schüler, J.; Lübbert, M. The pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat acts as a sensitizer for erlotinib activity in EGFR-mutated and -wildtype non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, F.; Lin, Z.; Shi, L.; Liu, T.; Yu, D.; Wu, G.; Huang, A. Antitumor effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer lines in vitro and in vivo. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2018, 29, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, K.; Feng, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Guo, C.; Xia, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Epigenetic therapy potential of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on invasive human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 68768–68780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeannot, V.; Busser, B.; VanWonterghem, L.; Michallet, S.; Ferroudj, S.; Cokol, M.; Coll, J.-L.; Öztürk, M.; Hurbin, A. Synergistic activity of vorinostat combined with gefitinib but not with sorafenib in mutant KRAS human non-small cell lung cancers and hepatocarcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6843–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anighoro, A.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.-U. Polypharmacology–Foe or Friend? J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8955–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, L.; Dallavalle, S.; Zunino, F. Perspectives in the development of hybrid bifunctional antitumour agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 96, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.G.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, W.B.; Liao, D.F. Designing multi-targeted agents: An emerging anticancer drug discovery paradigm. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.; Liang, X.; Huang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Chou, C.J.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of Novel Pazopanib-Based HDAC and VEGFR Dual Inhibitors Targeting Cancer Epigenetics and Angiogenesis Simultaneously. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5304–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, M.; Zheng, L.; Wang, F.; Yan, W.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; He, J. Discovery of Novel Dual Histone Deacetylase and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Target Inhibitors as a Promising Strategy for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Dong, G.; Wu, S.; Fang, K.; Miao, Z.; Wang, W.; Sheng, C. Small Molecules Simultaneously Inhibiting p53-Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2) Interaction and Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Discovery of Novel Multitargeting Antitumor Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7245–7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zang, J.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Huang, M.; Geng, M.; Chou, J.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Xu, W.; et al. Discovery of Novel Janus Kinase (JAK) and Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Dual Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3783–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Zhai, H.-X.; Wang, J.; Forrester, J.; Qu, H.; Yin, L.; Lai, C.-J.; Bao, R.; Qian, C. Discovery of 7-(4-(3-Ethynylphenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yloxy)-N-hydroxyheptanamide (CUDC-101) as a Potent Multi-Acting HDAC, EGFR, and HER2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, D.A.E.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.V.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J. AZD9291, an Irreversible EGFR TKI, Overcomes T790M-Mediated Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lan, F.; Matson, C.; Mulligan, P.; Whetstine, J.R.; Cole, P.A.; Casero, R.A.; Shi, Y. Histone Demethylation Mediated by the Nuclear Amine Oxidase Homolog LSD1. Cell 2004, 119, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyata, N. Lysine Demethylases Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8236–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-R.; Suo, F.-Z.; Hu, B.; Guo, Y.-J.; Fu, D.-J.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Identification of osimertinib (AZD9291) as a lysine specific demethylase 1 inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, P.; Müller, S.; O’Mahony, A.; Fedorov, O.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Hunt, J.P.; Lasater, E.A.; Pallares, G.; Picaud, S.; Wells, C. Dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitors for rationally designed polypharmacology. Nat. Methods 2014, 10, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Becker, A.; Berndt, N.; Schönbrunn, E.; Olesen, S.H.; Martin, M.P.; Georg, G.I.; Ember, S.W.J. Acetyl-lysine binding site of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) interacts with diverse kinase inhibitors. ACS Chem. Boil. 2014, 9, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Schönbrunn, E.; Martin, M.P.; Olesen, S.H.; Georg, G.I. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor dinaciclib interacts with the acetyl-lysine recognition site of bromodomains. ACS Chem. Boil. 2013, 8, 2360–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Inks, E.S.; Li, X.; Hou, J.; Chou, C.J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W. Discovery of the First N-Hydroxycinnamamide-Based Histone Deacetylase 1/3 Dual Inhibitors with Potent Oral Antitumor Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3324–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Duan, Y.C.; Ma, J.L.; Xu, R.M.; Zi, X.; Lv, W.L.; Wang, M.M.; Ye, X.W.; Zhu, X.; Mobley, D.; et al. Triazole–Dithiocarbamate Based Selective Lysine Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) Inactivators Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Growth, Invasion, and Migration. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8543–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 5B, 5E, 9C, 9E, 10A are available from the authors. |







| Compound | R | X | Y | HDAC IC50 (μM) a | EGFR (T790M) Inhibition Rate at 1 μM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5A | H |  |  | 1 | 36% |
| 5B | H |  |  | 1 | 34% |
| 5C | H |  |  | 0.462 | 42% |
| 5D | H |  |  | 0.023 | 35% |
| 5E | H |  |  | 0.105 | 44% |
| 10A | H | / |  | 1 | 41% |
| 10B | H | / |  | 10 | 40% |
| 9A |  |  |  | 1 | 38% |
| 9B |  |  |  | 1 | 37% |
| 9C |  |  |  | 0.397 | 12% |
| 9D |  |  |  | 0.121 | 13% |
| 9E |  |  |  | 0.085 | 15% |
| SAHA | 0.178 | ND b | |||
| AZD9291 | N.D. b | IC50 = 1.4 nM |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) a | |
|---|---|---|
| EGFR (WT) | EGFR (T790M) | |
| 5E | 3.2 | 1.2 |
| 9E | 5.7 | 5.0 |
| AZD9291 | 0.0022 | 0.0014 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HeLa | MDA-MB-231 | MDA-MB-468 | HT-29 | KG-1 | PC-3 | |
| 5D | 3.56 | 4.06 | 1.16 | 0.66 | 2.94 | 1.47 | ND |
| 5E | 2.40 | 2.79 | 0.66 | 0.33 | 1.99 | 0.52 | 2.25 |
| 9D | 5.11 | 5.64 | 3.69 | 1.07 | 4.13 | 3.62 | 5.45 |
| 9E | 2.19 | 1.85 | 0.60 | 0.23 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 3.39 |
| AZD9291 | 1.97 | 3.27 | 3.54 | 1.30 | 0.87 | 0.53 | 1.23 |
| SAHA | 2.13 | 2.71 | 5.18 | 0.95 | 2.82 | 1.59 | 10 |
| LSD1 Inhibition Rate at 10 μM a | BRD4 Inhibition Rate at 1 μM a | |
|---|---|---|
| 9E | 13% | 0% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Yin, H.; Zhao, C.; Cao, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132407
Dong H, Yin H, Zhao C, Cao J, Xu W, Zhang Y. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132407
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Hang, Hao Yin, Chunlong Zhao, Jiangying Cao, Wenfang Xu, and Yingjie Zhang. 2019. "Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132407
APA StyleDong, H., Yin, H., Zhao, C., Cao, J., Xu, W., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Osimertinib-Based HDAC and EGFR Dual Inhibitors. Molecules, 24(13), 2407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132407