Preclinical Evaluation of Radiolabeled Peptides for PET Imaging of Glioblastoma Multiforme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Radiolabeling of Studied Peptides
2.2. In Vitro Characterization
2.3. In Vitro Uptake
2.4. In Vivo Stability of 68Ga-Peptides
2.5. Ex Vivo Biodistribution
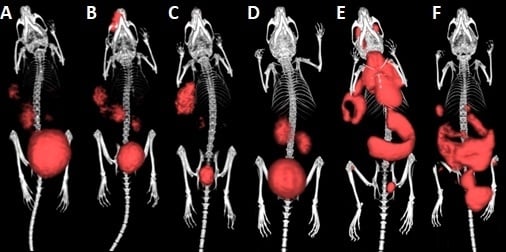
2.6. µPET/CT Imaging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Radiolabeling and in Vitro Characterization of Studied Peptides
4.2.1. Stability in the Presence of Competing Metal
4.2.2. Stability in the Presence of Competing Chelator
4.2.3. Stability in Physiological pH
4.2.4. Plasma Stability
4.2.5. Determination of Partition Coefficient (Log P)
4.2.6. Plasma Protein Binding
4.2.7. Determination of Metabolic Stability in Vivo
4.3. Cell Culture and Cell Uptake Assay
4.4. Tumor Xenografts
4.5. Ex Vivo Biodistribution
4.6. µPET/CT Imaging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladomersky, E.; Scholtens, D.M.; Kocherginsky, M.; Hibler, E.A.; Bartom, E.T.; Otto-Meyer, S.; Zhai, L.; Lauing, K.L.; Choi, J.; Sosman, J.A.; et al. The Coincidence Between Increasing Age, Immunosuppression, and the Incidence of Patients With Glioblastoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Oborski, M.J.; Hwang, M.; Lieberman, F.S.; Mountz, J.M. Malignant gliomas: current perspectives in diagnosis, treatment, and early response assessment using advanced quantitative imaging methods. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frosina, G. Positron emission tomography of high-grade gliomas. J. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 127, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosina, G. Non-routine tracers for PET imaging of high-grade glioma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 3253–3260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W. Clinical Applications of PET in Brain Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Ji, N.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Kang, P.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. 68Ga-PRGD2 PET/CT in the Evaluation of Glioma: A Prospective Study. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3923–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnell, O.; Krebs, B.; Wagner, E.; Romagna, A.; Beer, A.J.; Grau, S.J.; Thon, N.; Goetz, C.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Tonn, J.C.; et al. Expression of integrin alphavbeta3 in gliomas correlates with tumor grade and is not restricted to tumor vasculature. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.M.; Annala, M.; Chua, C.Y.X.; Dunlap, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Hugen, N.; Moore, L.M.; Cogdell, D.; Hu, L.; Nykter, M.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2-driven glioma progression is prevented by blocking a clinically significant integrin, integrin-linked kinase, and NF-κB network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3475–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Reichart, F.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M.; Weinmüller, M.; Räder, A.; Steiger, K.; Kessler, H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubner, R.; Weber, W.A.; Beer, A.J.; Vabuliene, E.; Reim, D.; Sarbia, M.; Becker, K.F.; Goebel, M.; Hein, R.; Wester, H.J.; et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated alphavbeta3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Chen, K.; Chen, X. (68)Ga-labeled multimeric RGD peptides for microPET imaging of integrin alpha(v)beta (3) expression. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knetsch, P.A.; Petrik, M.; Griessinger, C.M.; Rangger, C.; Fani, M.; Kesenheimer, C.; Von Guggenberg, E.; Pichler, B.J.; Virgolini, I.; Decristoforo, C.; et al. [68Ga]NODAGA-RGD for imaging αvβ3 integrin expression. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubner, R.; Kuhnast, B.; Mang, C.; Weber, W.A.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M. [18F]Galacto-RGD: Synthesis, Radiolabeling, Metabolic Stability, and Radiation Dose Estimates. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangger, C.; Helbok, A.; Sosabowski, J.; Kremser, C.; Koehler, G.; Prassl, R.; Andreae, F.; Virgolini, I.J.; Von Guggenberg, E.; Decristoforo, C.; et al. Tumor targeting and imaging with dual-peptide conjugated multifunctional liposomal nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4659–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brahm, C.G.; Hollander, M.W.D.; Enting, R.H.; De Groot, J.C.; Solouki, A.M.; Dunnen, W.F.A.D.; Heesters, M.A.A.M.; Wagemakers, M.; Verheul, H.M.W.; De Vries, E.G.E.; et al. Serial FLT PET imaging to discriminate between true progression and pseudoprogression in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a long-term follow-up study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R.; Esteban, F.; Redondo, M. The substance P/NK-1 receptor system: NK-1 receptor antagonists as anti-cancer drugs. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isal, S.; Pierson, J.; Imbert, L.; Clement, A.; Collet, C.; Pinel, S.; Veran, N.; Reinhard, A.; Poussier, S.; Gauchotte, G.; et al. PET imaging of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD, as compared with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, in experimental rodent models of engrafted glioblastoma. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-López, P.D.; Riñones-Mena, E.; Corrales-García, E.M. Treatment-related changes in glioblastoma: A review on the controversies in response assessment criteria and the concepts of true progression, pseudoprogression, pseudoresponse and radionecrosis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, P.; Stavrinou, P.; Lipke, K.; Bauer, E.; Ceccon, G.; Werner, J.; Neumaier, B.; Fink, G.; Shah, N.; Langen, K.; et al. FET PET reveals considerable spatial differences in tumour burden compared to conventional MRI in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. 57. Jahrestag. der Dtsch. Ges. für Nukl. 2019, 58, V54. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Van Der Gucht, A.; Pomoni, A.; Jreige, M.; Allemann, P.; Prior, J.O. 68Ga-NODAGA-RGDyK PET/CT Imaging in Esophageal Cancer: First-in-Human Imaging. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e491–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Franssen, G.M.; Petrik, M.; Laverman, P.; Summer, D.; Rangger, C.; Haubner, R.; Haas, H.; Decristoforo, C. Comparison of Ga-68-Labeled Fusarinine C-Based Multivalent RGD Conjugates and [68Ga]NODAGA-RGD—In Vivo Imaging Studies in Human Xenograft Tumors. Mol. Imaging Boil. 2016, 18, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Shen, L. Integrin αvβ3 receptor targeting PET/MRI dual-modal imaging probe based on the 64Cu labeled manganese ferrite nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 186, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, C.; Rozenblum-Beddok, L.; Nataf, V.; Merabtene, F.; Prignon, A.; Talbot, J.N. [68Ga]RGD Versus [18F]FDG PET Imaging in Monitoring Treatment Response of a Mouse Model of Human Glioblastoma Tumor with Bevacizumab and/or Temozolomide. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, J.S.; Jeong, J.M. Angiogenesis Imaging Using 68Ga-RGD PET/CT: Therapeutic Implications. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 46, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Hou, Y.; Tohme, M.; Park, R.; Bading, J.R. MicroPET imaging of breast cancer alphav-integrin expression with 64Cu-labeled dimeric RGD peptides. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2004, 6, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, A.R.; Johnson, M.B.; Chauhan, V.S.; Moerdyk-Schauwecker, M.J.; Young, A.D.; Cooley, I.D.; Martinez, A.N.; Ramesh, G.; Philipp, M.T.; Marriott, I. Human microglia and astrocytes constitutively express the neurokinin-1 receptor and functionally respond to substance P. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Yan, Y.; Watzlowik, P.; Wester, H.J.; Chin, F.T.; Chen, X. 18F-abeled galacto and PEGylated RGD dimers for PET imaging of αvβ3 integrin expression. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2010, 12, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, S.; Erfani, M.; Beiki, D.; Daha, F.J.; Kobarfard, F.; Balalaie, S.; Fallahi, B. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of a new (99m)tc labeled substance p analogue as a potential tumor imaging agent. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rinne, P.; Silvola, J.M.U.; Hellberg, S.; Ståhle, M.; Liljenbäck, H.; Salomäki, H.; Koskinen, E.; Nuutinen, S.; Saukko, P.; Knuuti, J.; et al. Pharmacological Activation of the Melanocortin System Limits Plaque Inflammation and Ameliorates Vascular Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2014, 34, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, S.R.; Salem, K.; Jeffery, J.; Powers, G.L.; Yan, Y.; Shoghi, K.I.; Mahajan, A.M.; Fowler, A.M. Sex as a Biologic Variable in Preclinical Imaging Research: Initial Observations with 18F-FLT. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Zoete, V.; Alghisi, G.C.; Rüegg, C.; Michelin, O.; Prior, J.; Scapozza, L.; Seimbille, Y. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of a novel radioligand for αvβ3 integrin receptor imaging: [18F]FPPA-c(RGDfK). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6068–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.-L.; Li, M.; Zhang, R.-J.; Jiang, H.-J.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Pan, W.-B. Prediction of tumor biological characteristics in different colorectal cancer liver metastasis animal models using 18 F-FDG and 18 F-FLT. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2018, 17, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Hu, X.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Using RGD PET/CT in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, S.A.; Holzapfel, K.; Seidl, C.; Treiber, U.; Krause, B.J.; Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R. Characterization of choline uptake in prostate cancer cells following bicalutamide and docetaxel treatment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardeni, T.; Eckhaus, M.; Morris, H.D. Retro-orbital injections in mice. Lab Anim. 2011, 40, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





| The Peptide | Log P | Incubation Time | Plasma Protein Binding (%) | % Stability in 0.1 M FeCl3 | % Stability in 6 mM DTPA | % Stability in pH 7 | % Stability in Plasma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68Ga-DOTA-c(RGDfK) | −3.43 ± 0.11 | 30 min | 2.39 | 97.04 ± 1.24 | 99.39 ± 0.43 | 99.60 ± 0.23 | 99.23 ± 0.18 |
| 60 min | 2.65 | 96.76 ± 1.21 | 99.39 ± 0.54 | 99.51 ± 0.13 | 99.14 ± 0.19 | ||
| 120 min | 3.29 | 95.83 ± 1.04 | 99.06 ± 0.57 | 99.49 ± 0.20 | 98.81 ± 0.33 | ||
| 68Ga-NODAGA-c(RGDyK) | −3.05 ± 0.62 | 30 min | 2.74 | 99.24 ± 0.44 | 99.65 ± 0.07 | 99.82 ± 0.05 | 99.23 ± 0.18 |
| 60 min | 1.31 | 98.56 ± 0.60 | 99.20 ± 0.37 | 99.78 ± 0.12 | 99.14 ± 0.19 | ||
| 120 min | 3.21 | 98.94 ± 0.42 | 99.23 ± 0.32 | 99.72 ± 0.22 | 98.81 ± 0.33 | ||
| 68Ga-NODAGA-c(RGDyK)2 | −3.34 ± 0.13 | 30 min | 1.74 | 98.66 ± 0.82 | 99.39 ± 0.43 | 99.83 ± 0.11 | 99.51 ± 0.17 |
| 60 min | 1.89 | 99.22 ± 0.19 | 99.39 ± 0.54 | 99.74 ± 0.18 | 99.31 ± 0.11 | ||
| 120 min | 3.40 | 99.17 ± 0.18 | 99.06 ± 0.57 | 99.62 ± 0.21 | 99.02 ± 0.33 | ||
| 68Ga-DOTA-substance P | −3.03 ± 0.33 | 30 min | 22.35 | 88.4 | 73.4 | 98.2 | 98.2 |
| 60 min | 24.49 | 85.1 | 63.1 | 98.1 | 98.2 | ||
| 120 min | 29.21 | 78.8 | 56.1 | 98.1 | 98.0 |
| 68GA-DOTA-C(RGDFK) | 68GA-NODAGA-C(RGDYK) | 68GA-NODAGA-C(RGDYK)2 | 68GA-DOTA-SUBSTANCE P | 18F-FDG | 18F-FLT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | 30 min p.i. | 90 min p.i. | |
| Tumor to blood ration | 1.09 | 14.70 | 1.90 | 23.12 | 2.30 | 16.38 | 0.93 | 2.84 | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.10 | 2.36 |
| Tumor to muscle ration | 2.42 | 13.53 | 3.23 | 6.51 | 5.84 | 10.47 | 3.10 | 6.45 | 2.67 | 3.58 | 1.31 | 2.83 |
| Tumor to kidney ratio | 0.29 | 1.43 | 0.36 | 0.90 | 0.61 | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 1.01 | 2.21 | 0.76 | 1.79 |
| 68Ga-DOTA-c(RGDfK) | 68Ga-NODAGA-c(RGDyK) | 68Ga-NODAGA-c(RGDyK)2 | 68Ga-DOTA-Substance P | 18F-FDG | 18F-FLT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor to brain ratio | 4.70 | 4.00 | 4.14 | 4.25 | 0.64 | 4.58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novy, Z.; Stepankova, J.; Hola, M.; Flasarova, D.; Popper, M.; Petrik, M. Preclinical Evaluation of Radiolabeled Peptides for PET Imaging of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Molecules 2019, 24, 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132496
Novy Z, Stepankova J, Hola M, Flasarova D, Popper M, Petrik M. Preclinical Evaluation of Radiolabeled Peptides for PET Imaging of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132496
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovy, Zbynek, Jana Stepankova, Michaela Hola, Dominika Flasarova, Miroslav Popper, and Milos Petrik. 2019. "Preclinical Evaluation of Radiolabeled Peptides for PET Imaging of Glioblastoma Multiforme" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132496
APA StyleNovy, Z., Stepankova, J., Hola, M., Flasarova, D., Popper, M., & Petrik, M. (2019). Preclinical Evaluation of Radiolabeled Peptides for PET Imaging of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Molecules, 24(13), 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132496