Transepithelial Transport Characteristics of the Cholesterol- Lowing Soybean Peptide, WGAPSL, in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cytotoxicity in Caco-2 Cells
2.2. Peptides Stability
2.3. Transepithelial Absorption of WGAPSL through Cell Culture Model
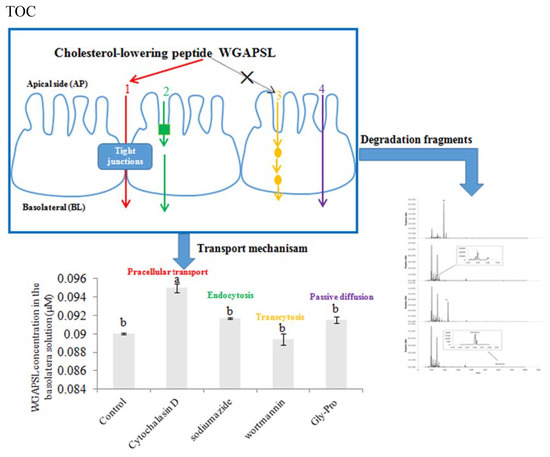
2.4. Effects of Various Inhibitors on Peptide Transport
2.5. Peptide Degradation Fragments in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Caco-2 Cells Culture
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.4. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
3.5. Transport Experiments
3.6. LC-MS Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaboorani, A.; Riedl, B.; Blanchet, P.; Fellin, M.; Hosseinaei, O.; Wang, S. Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC): A renewable nano-material for polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesive. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgers, A.R.; Conradi, R.A.; Burton, P.S. Caco-2 cell monolayers as a model for drug transport across the intestinal mucosa. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.J.; Kanai, Y.; Nussberger, S.; Ganapathy, V.; Leibach, F.H.; Romero, M.F.; Singh, S.K.; Boron, W.F.; Hediger, M.A. Expression cloning of a mammalian proton-coupled oligopeptide transporter. Nature 1994, 368, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aito-Inoue, M.; Lackeyram, D.; Fan, M.Z.; Sato, K.; Mine, Y. Transport of a tripeptide, Gly-Pro-Hyp, across the porcine intestinal brush-border membrane. J. Pept. Sci. 2007, 13, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Transport of egg white ACE-inhibitory peptide, Gln-Ile-Gly-Leu-Phe, in human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers with cytoprotective effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, L.; Li, S. Transport of Val-Leu-Pro-Val-Pro in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cell monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regazzo, D.; Mollé, D.; Gabai, G.; Tomé, D.; Dupont, D.; Leonil, J.; Boutrou, R. The (193–209) 17-residues peptide of bovine β-casein is transported through Caco-2 monolayer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Geissler, S.; Zwarg, M.; Knütter, I.; Markwardt, F.; Brandsch, M. The bioactive dipeptide anserine is transported by human proton-coupled peptide transporters. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.; Dávalos, A.; Manso, M.A.; De, L.P.G.; Lasunción, M.A.; Lópezfandiño, R. Transepithelial transport across Caco-2 cell monolayers of antihypertensive egg-derived peptides. PepT1-mediated flux of Tyr-Pro-Ile. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1507–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, M.; Tsunogai, M.; Arai, S. Transepithelial Transport of Oligopeptides in the Human Intestinal Cell, Caco-2. Peptides 1997, 18, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Even, R.; Lovati, M.R. Soybean protein diet and plasma cholesterol: From therapy to molecular mechanisms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 676, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveille, G.A.; Fisher, H. Plasma cholesterol in growing chicken as influenced by dietary protein and fat. Exp. Biol. Med. 1958, 98, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, J.S.; Kimpton, W.G.; Nestel, P.J. The effect of dietary casein and soy protein on cholesterol and very low density lipoprotein metabolism in the rat. Atherosclerosis 1984, 52, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Miwa, K.; Eto, M.; Kuzuya, Y.; Hori, G.; Yamamoto, K. Soy protein peptic hydrolysate with bound phospholipids decreases micellar solubility and cholesterol absorption in rats and Caco-2 Cells. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Masaoka, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hasegawa, M.; Watanabe, K. Egg ovomucin attenuates hypercholesterolemia in rats and inhibits cholesterol absorption in Caco-2 cells. Lipids 2002, 37, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Shoemaker, C.F. Preparation of hypocholesterol peptides from soy protein and their hypocholesterolemic effect in mice. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Shoemaker, C.F. Fractionation and identification of a novel hypocholesterolemic peptide derived from soy protein Alcalase hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 756–762. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Bartley, G.E.; Zhang, H.; Jing, W.; Fagerquist, C.K.; Zhong, F.; Yokoyama, W. Peptides identified in soybean protein increase plasma cholesterol in mice on hypercholesterolemic diets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8389–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Sleisenger, M.H. Studies on the properties of peptide hydrolases in the brush-border and soluble fractions of small intestinal mucosa of rat and man. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Enzymol. 1974, 370, 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, B.M. Overview of pepsin-like aspartic peptidases. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2001, 25, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Gupta, N.; Smith, R.D.; Pevzner, P.A. Does trypsin cut before proline. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 7, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sienkiewiczszłapka, E.; Jarmołowska, B.; Krawczuk, S.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Bielikowicz, K. Transport of bovine milk-derived opioid peptides across a Caco-2 monolayer. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltz, M.; Cerstiaens, A.; Meensel, A.V.; Mols, R.; Pijl, P.C.V.D.; Duchateau, G.S.M.J.E.; Augustijns, P. The angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory tripeptides Ile-Pro-Pro and Val-Pro-Pro show increasing permeabilities with increasing physiological relevance of absorption models. Peptides 2008, 29, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artursson, P.; Palm, K.; Luthman, K. Caco-2 monolayers in experimental and theoretical predictions of drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejjani, S.; Wu, J. Transport of IRW, an Ovotransferrin-Derived Antihypertensive Peptide, in Human Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Qin, Z. Transepithelial transport characteristics of the antihypertensive peptide, Lys-Val-Leu-Pro-Val-Pro, in human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, A.; Del Mar Contreras, M.; Ramos, M.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Stability to gastrointestinal enzymes and structure–activity relationship of β-casein-peptides with antihypertensive properties. Peptides 2009, 30, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwan, M.; Jarmołowska, B.; Bielikowicz, K.; Kostyra, E.; Kostyra, H.; Kaczmarski, M. Transport of micro-opioid receptor agonists and antagonist peptides across Caco-2 monolayer. Peptides 2008, 29, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-Originating ACE Inhibitors, Including Antihypertensive Peptides, as Preventive Food Components in Blood Pressure Reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Transport of Antihypertensive Peptide RVPSL, Ovotransferrin 328–332, in Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8143–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, X.R.; Meng, Y.; Jing, W. Soluble dietary fiber from Qing Ke (highland barley) brewers spent grain could alter the intestinal cholesterol efflux in Caco-2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, A.; Dávalos, A.; Lasunción, M.A.; Ramos, M.; Recio, I. Bioavailability of the antihypertensive peptide LHLPLP: Transepithelial flux of HLPLP. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound WGAPSL are available from the authors. |








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J. Transepithelial Transport Characteristics of the Cholesterol- Lowing Soybean Peptide, WGAPSL, in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Molecules 2019, 24, 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152843
Zhang H, Duan Y, Feng Y, Wang J. Transepithelial Transport Characteristics of the Cholesterol- Lowing Soybean Peptide, WGAPSL, in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152843
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huijuan, Yawen Duan, Yulin Feng, and Jing Wang. 2019. "Transepithelial Transport Characteristics of the Cholesterol- Lowing Soybean Peptide, WGAPSL, in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152843
APA StyleZhang, H., Duan, Y., Feng, Y., & Wang, J. (2019). Transepithelial Transport Characteristics of the Cholesterol- Lowing Soybean Peptide, WGAPSL, in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. Molecules, 24(15), 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152843