Comparative Study of Aryl O-, C-, and S-Mannopyranosides as Potential Adhesion Inhibitors toward Uropathogenic E. coli FimH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
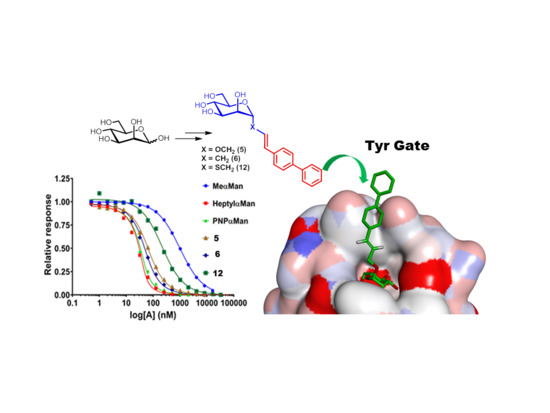
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Glycomimetic Synthesis
2.2. Structural and Conformational Analyses
2.3. Relative FimH Binding Affinity
3. Materials and Methods
SPR Solution Affinity of Ligands for the E. coli FimH Adhesin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adeyi, O.O.; Baris, E.; Jonas, O.B.; Irwin, A.; Berthe, F.C.J.; Le Gall, F.G.; Marquez, P.V.; Nikolic, I.A.; Plante, C.A.; Schneidman, M.; et al. Drug-resistant infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future. World Bank Rep. 2017, 2, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavifar, L.; Roy, R. Alternative therapeutic strategies to fight bacterial infections. Frontiers in Drug, Chem. Clin. Res. 2018, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, T.K.; Wong, C.-H. Carbohydrate-Based Antibiotics: A New Approach to Tackling the Problem of Resistance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, C.N.; Klein, R.D.; Schreiber, H.L.; Janetka, J.W.; Hultgren, S.J. Precision antimicrobial therapeutics: The path of least resistance? NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Abgottspon, D.; Wittwer, M.; Rabbani, S.; Herold, J.; Jiang, X.; Kleeb, S.; LUthi, C.; Scharenberg, M.; Bezencon, J. FimH Antagonists for the Oral Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections: From Design and Synthesis to in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8627–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebling, T.L. Urologic diseases in America project: Trends in resource use for urinary tract infections in men. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, M.E.; Gribaudo, G.; Maffei, M.E. UroPathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) infections: Virulence factors, bladder responses, antibiotic, and non-antibiotic antimicrobial strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Mo, W.-J.; Sebbel, P.; Min, G.; Neubert, T.A.; Glockshuber, R.; Wu, X.-R.; Sun, T.-T.; Kong, X.-P. Uroplakin Ia is the urothelial receptor for uropathogenic Escherichia coli: Evidence from in vitro FimH binding. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavifar, L.; Touaibia, M.; Roy, R. Development of Mannopyranoside Therapeutics against Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli Infections. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2937–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Hase, K. Glycoprotein 2 (GP2) grabbing the fimH+ bacteria into m cells for mucosal immunity. Gut. Microbes 2010, 1, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, C.; Hultgren, S. Adhesive Pili in UTI Pathogenesis and Drug Development. Pathogens 2016, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalopin, T.; Brissonnet, Y.; Sivignon, A.; Deniaud, D.; Cremet, L.; Barnich, N.; Bouckaert, J.; Gouin, S.G. Inhibition profiles of mono- and polyvalent FimH antagonists against 10 different Escherichia coli strains. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 11369–11375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.S.; Bouckaert, J.; Hung, D.; Pinkner, J.; Widberg, C.; DeFusco, A.; Auguste, C.G.; Strouse, R.; Langermann, S.; Waksman, G.; et al. Structure basis of tropism of Escherichia coli to the bladder during urinary tract infection. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurpel, D.J.; Beatson, S.A.; Totsika, M.; Petty, N.K.; Schembri, M.A. Chaperone-Usher Fimbriae of Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abgottspon, D.; Ernst, B. In vivo Evaluation of FimH Antagonists – A Novel Class of Antimicrobials for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection. Chimia 2012, 66, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mydock-McGrane, L.K.; Cusumano, Z.T.; Janetka, J.W. Mannose-derived FimH antagonists: A promising anti-virulence therapeutic strategy for urinary tract infections and Crohn’s disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touaibia, M.; Krammer, E.-M.; Shiao, T.C.; Yamakawa, N.; Wang, Q.; Glinschert, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mousavifar, L.; Maes, E.; Oscarson, S.; et al. Sites for Dynamic Protein-Carbohydrate Interactions of O- and C-Linked Mannosides on the E. coli FimH Adhesin. Molecules 2017, 22, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M.; Lindhorst, T.K. The bacterial lectin FimH, a target for drug discovery–Carbohydrate inhibitors of type 1 fimbriae-mediated bacterial adhesion. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 3583–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorta, D.A.; Sivignon, A.; Chalopin, T.; Dumych, T.I.; Roos, G.; Bilyy, R.O.; Deniaud, D.; Krammer, E.M.; de Ruyck, J.; Lensink, M.F.; et al. The Antiadhesive Strategy in Crohn′s Disease: Orally Active Mannosides to Decolonize Pathogenic Escherichia coli from the Gut. ChemBioChem. 2016, 17, 936–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavifar, L.; Vergoten, G.; Roy, R. Deciphering the conformation of C -linked α-D-mannopyranosides and their application toward the synthesis of low nanomolar E. Coli FimH ligands. Arkivoc. 2018, 7, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Pinkner, J.S.; Ford, B.; Obermann, R.; Nolan, W.; Wildman, S.A.; Hobbs, D.; Ellenberger, T.; Cusumano, C.K.; Hultgren, S.J.; et al. Structure-based drug design and optimization of mannoside bacterial fimH antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4779–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mydock-McGrane, L.; Cusumano, Z.; Han, Z.; Binkley, J.; Kostakioti, M.; Hannan, T.; Pinkner, J.S.; Klein, R.; Kalas, V.; Crowley, J.; et al. Antivirulence C-Mannosides as Antibiotic-Sparing, Oral Therapeutics for Urinary Tract Infections. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9390–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiege, B.; Rabbani, S.; Preston, R.C.; Jakob, R.P.; Zihlmann, P.; Schwardt, O.; Jiang, X.; Maier, T.; Ernst, B. The tyrosine gate of the bacterial lectin FimH: A conformational analysis by NMR spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography. ChemBioChem. 2015, 16, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, S.; Krammer, E.M.; Roos, G.; Zalewski, A.; Preston, R.; Eid, S.; Zihlmann, P.; Prévost, M.; Lensink, M.F.; Thompson, A.; et al. Mutation of Tyr137 of the universal Escherichia coli fimbrial adhesin FimH relaxes the tyrosine gate prior to mannose binding. IUCrJ 2017, 4, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivignon, A.; Yan, X.; Dorta, D.A.; Bonnet, R.; Bouckaert, J.; Fleury, E.; Bernard, J.; Gouin, S.G.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Barnich, N. Development of heptyl mannoside-based glycoconjugate antiadhesive compounds against adherent-invasive escherichia coli bacteria associated with crohn’s disease. MBio 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, C.N.; Klein, R.D.; Ruer, S.; Kau, A.L.; Schreiber, H.L.; Cusumano, Z.T.; Dodson, K.W.; Pinkner, J.S.; Fremont, D.H.; Janetka, J.W.; et al. Selective depletion of uropathogenic E. coli from the gut by a FimH antagonist. Nature 2017, 546, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomašic, T.; Rabbani, S.; Gobec, M.; Raščan, I.M.; Podlipnik, Č.; Ernst, B.; Anderluh, M. Branched a-D-mannopyranosides: A new class of potent FimH antagonists. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellens, A.; Lahmann, M.; Touaibia, M.; Vaucher, J.; Oscarson, S.; Roy, R.; Remaut, H.; Bouckaert, J. The tyrosine gate as a potential entropic lever in the receptor-binding site of the bacterial adhesin FimH. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4790–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, G.; Wellens, A.; Touaibia, M.; Yamakawa, N.; Geerlings, P.; Roy, R.; Wyns, L.; Bouckaert, J. Validation of reactivity descriptors to assess the aromatic stacking within the tyrosine gate of FimH. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Agnihotri, G.; Misra, A.K. Modified One-Pot Protocol for the Preparation of Thioglycosides from Unprotected Aldoses via S-Glycosyl Isothiouronium Salts. J. Carbohydr. Chem 2005, 24, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachamuthu, K.; Schmidt, R.R. Synthetic routes to thiooligosaccharides and thioglycopeptides. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 160–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrier, R.J.; Furneaux, R.H. Synthesis of 1,2-trans-Related 1-Thioglycoside Esters. Carbohydr. Res. 1976, 52, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crich, D.; Mataka, J.; Zakharov, L.N.; Rheingold, A.L.; Wink, D.J. Stereoselective Formation of Glycosyl Sulfoxides and Their Subsequent Equilibration: Ring Inversion of an r-Xylopyranosyl Sulfoxide Dependent on the Configuration at Sulfur. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6028–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominique, R.; Das, S.K.; Roy, R. Alkenyl O-and C-glycopyranoside homodimerization by olefin metathesis reaction. Chem. Commun. 1998, 2437–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Das, S.K. Recent applications of olefin metathesis and related reactions in carbohydrate chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2000, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruyck, J.; Lensink, M.F.; Bouckaert, J. Structures of C-mannosylated anti-adhesives bound to the type 1 fimbrial FimH adhesion. IUCrJ 2016, 3, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choumane, M.; Banchet, A.; Probst, N.; Gérard, S.; Plé, K.; Haudrechy, A. The synthesis of d-C-mannopyranosides. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2011, 14, 235–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.G.; Szolcsányi, P.; Koenig, S.G.; Paterson, D.E.; Isshiki, Y.; Vasella, A. Preparation of an advanced intermediate for the synthesis of stable analogues of guanofosfocin. Helv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwardt, O.; Rabbani, S.; Hartmann, M.; Abgottspon, D.; Wittwer, M.; Kleeb, S.; Zalewski, A.; Smieško, M.; Cutting, B.; Ernst, B. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of mannosyl triazoles as FimH antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6454–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, A.; Coslovi, A.; Doisneau, G.; Beau, J.M. An expeditious synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid α-C-glycosyl derivatives (“α-C-glycosides”) from the anomeric acetates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 19, 3145–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen W., L.; Tirado-Rives, J. Molecular modeling of organic and biomolecular systems using BOSS and MCPRO. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derreumaux, P.; Vergoten, G. A new spectroscopic molecular mechanics force field. Parameters for proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 102, 8586–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergoten, G.; Mazur, I.; Lagant, P.; Michalski, J.C.; Zanetta, J.P. The SPASIBA force field as an essential tool for studying the structure and dynamics of saccharides. Biochimie 2003, 85, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagant, P.; Nolde, D.; Stote, R.; Vergoten, G.; Karplus, M. Increasing normal modes analysis accuracy: The SPASIBA spectroscopic force field introduced into the CHARMM program. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2004, 108, 4019–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, J.; Berglund, J.; Schembri, M.; De Genst, E.; Cools, L.; Wuhrer, M.; Hung, C.S.; Pinkner, J.; Slättegård, R.; Zavialov, A. Receptor binding studies disclose a novel class of high-affinity inhibitors of the Escherichia coli FimH adhesion. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, L.M.; Hernáiz, M.J.; Martín-Pastor, M.; Skrydstrup, T.; Jiménez-Barbero, J. Conformation of glycomimetics in the free and protein-bound state: Structural and binding features of the C-glycosyl analogue of the core trisaccharide α-d-Man-(1 → 3)-[α-d-Man-(1 → 6)]-d-Man. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14940–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Alonso, C.M.; Díaz, D.; Berbis, M.Á.; Marcelo, F.; Cañada, J.; Jiménez-Barbero, J. Protein-carbohydrate interactions studied by NMR: From molecular recognition to drug design. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eris, D.; Preston, R.C.; Scharenberg, M.; Hulliger, F.; Abgottspon, D.; Pang, L.; Jiang, X.; Schwardt, O.; Ernst, B. The Conformational Variability of FimH: Which Conformation Represents the Therapeutic Target? ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crich, D.; Mataka, J.; Sun, S.; Lam, K.C.; Rheingold, A.L.; Win, D.J. Stereoselective sulfoxidation of α-mannopyranosyl thioglycosides: The exo-anomeric effect in action. Chem. Commun. 1998, 24, 2763–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Hung, C.S.; Pinkner, J.S.; Walker, J.N.; Cusumano, C.K.; Li, Z.; Bouckaert, J.; Gordon, J.I.; Hultgren, S.J. Positive selection identifies an in vivo role for FimH during urinary tract infection in addition to mannose binding. PNAS 2009, 106, 22439–22444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- André, S.; Cañada, F.J.; Shiao, T.C.; Largartera, L.; Diercks, T.; Bergeron-Brlek, M.; Papadopoulos, A.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Touaibia, M.; Solís Menéndez, D.M.; et al. Fuorinated Carbohydrates as Lectin Ligands: Biorelevant Sensors with Capacity to Monitor Anomer Affinity in 19F-NMR-Based Inhibitor Screening. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 4354–4364. [Google Scholar]
- de Mol, N.J. Affinity Constants for Small Molecules from SPR Competition Experiments. In Surface Plasmon Resonance; de Mol, N.J., Fischer, M.J.E., Eds.; Humana Press of Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 101–113. ISBN 9781607616696. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Compound | Kd (nM) | Relative Potency | ΔG° (kcal mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MeαMan (1) | 475.4 ± 5.7 | 1 | −8.62 |
| PNPαMan (2) | 4.21 ± 0.72 | 113 | −11.42 |
| HeptylαMan (3) | 2.37 ± 0.50 | 200 | −11.76 |
| 4 | 38.58 ± 0.11 | 12 | −10. 11 |
| 5 | 19.90 ± 1.22 | 24 | −10. 50 |
| 6 | 11.45 ± 0.63 | 42 | −10. 83 |
| 12 | 94.4± 6.2 | 5 | −9. 58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mousavifar, L.; Vergoten, G.; Charron, G.; Roy, R. Comparative Study of Aryl O-, C-, and S-Mannopyranosides as Potential Adhesion Inhibitors toward Uropathogenic E. coli FimH. Molecules 2019, 24, 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193566
Mousavifar L, Vergoten G, Charron G, Roy R. Comparative Study of Aryl O-, C-, and S-Mannopyranosides as Potential Adhesion Inhibitors toward Uropathogenic E. coli FimH. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193566
Chicago/Turabian StyleMousavifar, Leila, Gérard Vergoten, Guillaume Charron, and René Roy. 2019. "Comparative Study of Aryl O-, C-, and S-Mannopyranosides as Potential Adhesion Inhibitors toward Uropathogenic E. coli FimH" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193566
APA StyleMousavifar, L., Vergoten, G., Charron, G., & Roy, R. (2019). Comparative Study of Aryl O-, C-, and S-Mannopyranosides as Potential Adhesion Inhibitors toward Uropathogenic E. coli FimH. Molecules, 24(19), 3566. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193566