Preparation of Immobilized Lipase Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Its Application in Ester Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
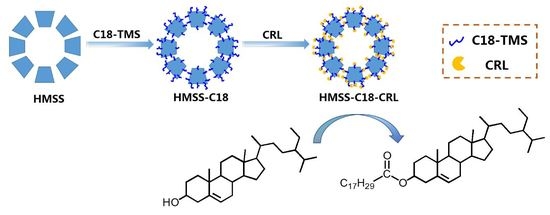
2.1. Characterizations of HMSS, HMSS-C18 and HMSS-C18-CRL
2.2. Evaluation of Immobilized CRLs with Different Hydrophobicities.
2.3. Enzymatic Esterification of Phytosterols with ALA in a Solvent-Free System
2.3.1. Effect of Temperature on the Degree of Esterification (DE)
2.3.2. Effect of Substrate Molar Ratio on DE
2.3.3. Effect of Enzyme Loading on DE
2.3.4. Response Surface Methodology Analysis.
2.4. Main Effects and Interactions between Parameters
2.5. Optimization and Model Verification
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of HMSS and Different Modified HMSS
3.3. Immobilization of CRL on HMSS with Different Surface Modifications
3.4. Lipase Activity Assay
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Effect of Temperature
3.7. Response Surface Methodology
3.8. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Phytosterols Esters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, K.; Ricco, R.; Doherty, C.M.; Styles, M.J.; Bell, S.; Kirby, N.; Mudie, S.; Haylock, D.; Hill, A.J.; Doonan, C.J. Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jesionowski, T.; Zdarta, J.; Krajewska, B. Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: A review. Adsorption 2014, 20, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.; Cooney, J.; Magner, E. Proteins in mesoporous silicates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 8582–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Jia, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, C. Hydrophobic surface induced activation of Pseudomonas cepacia lipase immobilized into mesoporous silica. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12016–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vescovi, V.; Giordano, R.L.; Mendes, A.A.; Tardioli, P.W. Immobilized lipases on functionalized silicaparticles as potential biocatalysts for thesynthesis of fructose oleate in an organic solvent/water system. Molecules 2017, 22, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasescu, C.; Preda, S.; Rusu, A.; Culita, D.; Zaharescu, M. Tubular and Spherical SiO2 Obtained by Sol Gel Method for Lipase Immobilization and Enzymatic Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Mendes, A.; Lafuente, R.; Tardioli, P.; Giordano, R. Performance of different immobilized lipases in the syntheses of short- and long-chain carboxylic acid esters by esterification reactions in organic media. Molecules 2018, 23, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanova, S.; Zarevucka, M.; Bousa, D.; Pumera, M.; Sofer, Z. Graphene oxide immobilized enzymes show high thermal and solvent stability. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5852–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.; Park, S. Dual-Surface Functionalization of metal-organic frameworks for enhancing the catalytic activity of Candida antarctica Lipase B in polar organic media. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Fu, C.W.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.A.; Wang, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Xiao, F.S.; Ma, S. Pore environment control and enhanced performance of enzymes infiltrated in covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 140, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.T.; Li, X.S.; Fu, X.M.; Wu, J.Y.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Electrospinning-based synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous silica fiber for lab-in-syringe enrichment of plasma peptides. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9980–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.S.; Pan, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.F.; Guo, L.; Feng, Y.Q. Preparation of titanium-grafted magnetic mesoporous silica for the enrichment of endogenous serum phosphopeptides. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1315, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wu, J.H.; Liu, J.F.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. Improved methodology for assaying brassinosteroids in plant tissues using magnetic hydrophilic material for both extraction and derivatization. Plant. Methods 2014, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.T.; He, X.M.; Cai, B.D.; Wang, H.; Ding, J.; Yuan, B.F.; Feng, Y.Q. In-syringe dispersive solid phase extraction: A novel format for electrospun fiber based microextraction. Analyst 2014, 139, 6266–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magner, E. Immobilisation of enzymes on mesoporous silicate materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, M.; Kostrov, X. Immobilization of enzymes on porous silicas—Benefits and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6277–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Yin, Y. Self-Templating approaches to hollow nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2018, e1802349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, N.; Yu, X. Improved Performance of Magnetic Cross-Linked Lipase Aggregates by Interfacial Activation: A Robust and Magnetically Recyclable Biocatalyst for Transesterification of Jatropha Oil. Molecules 2017, 22, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, M.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; Strounina, E.; Gu, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Yu, C. Tailoring mesoporous-silica nanoparticles for robust immobilization of lipase and biocatalysis. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, J.M.R.; Haust, H.L.; Connell, W.F. Magnitude of the Hypocholesterolemic Effect of Dietary Sitosterol in Man. J. Nutr. 1964, 83, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritchevsky, D.; Chen, S.C. Phytosterols—health benefits and potential concerns: A review. Nutr. Res. 2005, 25, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Cabral, J.M. Phytosterols: Applications and recovery methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2335–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Akoh, C.C. Modeling and optimization of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of phytosteryl esters of oleic acid by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, W.E. α-Linolenic acid in health and disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Q.; Huang, F.; Wei, F.; Zheng, M.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, C. Chemical synthesis of phytosterol esters of polyunsaturated fatty acids with ideal oxidative stability. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.S.; Ma, Y.; Pan, X.X.; Li, J.J.; Wang, M.G.; Yang, Y.B.; Jia, C.S.; Zhang, X.M.; Feng, B. Efficient Solvent-Free Synthesis of Phytostanyl Esters in the Presence of Acid-Surfactant-Combined Catalyst. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9763–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.M.; Lu, Y.; Huang, F.H.; Wang, L.; Guo, P.M.; Feng, Y.Q.; Deng, Q.C. Lipase Immobilization on Hyper-Cross-Linked Polymer-Coated Silica for Biocatalytic Synthesis of Phytosterol Esters with Controllable Fatty Acid Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.M.; Dong, L.; Lu, Y.; Guo, P.M.; Deng, Q.C.; Li, W.L.; Feng, Y.Q.; Huang, F.H. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on magnetic poly(allyl glycidyl ether-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) polymer microsphere for synthesis of phytosterol esters of unsaturated fatty acids. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 74, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.M.; Lu, Y.; Dong, L.; Guo, P.M.; Deng, Q.C.; Li, W.L.; Feng, Y.Q.; Huang, F.H. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on hydrophobic/strong cation-exchange functional silica particles for biocatalytic synthesis of phytosterol esters. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 115, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temocin, Z. Covalent immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase on aldehyde functionalized hydrophobic support and the application for synthesis of oleic acid ester. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1618–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhul, B.; Tan, T. Enzymatic synthesizing of phytosterol oleic esters. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari Krishna, S.; Karanth, N.G. Lipases and lipase-catalyzed esterification reactions in nonaqueous media. Catal. Rev. 2002, 44, 499–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Li, X.S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Q.A.; Guo, L.; Feng, Y.Q. Titania coated magnetic mesoporous hollow silica microspheres: Fabrication and application to selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9031–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiton, M.; Boncel, S.; Janas, D.; Chrobok, A. Highly active nanobiocatalyst from lipase noncovalently immobilized on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for Baeyer–Villiger synthesis of lactones. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, D.S.; Zhao, T.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.H. Synthesis of phytosteryl ester containing pinolenic acid in a solvent-free system using immobilized Candida rugosa lipase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8934–8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, M.; Kawakami, K. Enhancement of Rhizopus oryzae lipase activity immobilized on alkyl-functionalized spherical mesocellular foam: Influence of alkyl chain length. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, M.; Shi, J.; Tang, H.; Deng, Q.; Huang, F.; Luo, D. Enzymatic preparation of “functional oil” rich in feruloylated structured lipids with solvent-free ultrasound pretreatment. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, J.B.; Xu, X.; Mu, H. Process optimization using response surface design and pilot plant production of dietary diacylglycerols by lipase-catalyzed glycerolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7059–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamgui, H.; Miled, N.; Reba, A.; Karra chaabouni, M.; Gargouri, Y. Production of mono-olein by immobilized staphylococcus simulans lipase in a solvent-free system: Optimization by response surface methodology. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, N.; Soo Peng, K.; Long, K.; Chin-Ping, T.; Yusoff, M.S.A.; Oi-Ming, L. Modeling and optimization of lipozyme RM IM-Catalyzed esterification of medium- and long-Chain triacyglycerols (MLCT) using response surface methodology. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 5, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhu, J.; Huang, F.; Xiang, X.; Shi, J.; Deng, Q.; Ma, F.; Feng, Y. Enzymatic deacidification of the rice bran oil and simultaneous preparation of phytosterol esters-enriched functional oil catalyzed by immobilized lipase arrays. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 70073–70079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrelo, G.; Torres, C.F.; Senorans, F.J.; Blanco, R.M.; Reglero, G. Solvent-free preparation of phytosteryl esters with fatty acids from butterfat in equimolecular conditions in the presence of a lipase from Candida rugosa. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |










| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMSS-C18 | 399 | 1.49 | 12.0 |
| HMSS-C18-CRL | 260 | 1.06 | 11.9 |
| Run | Independent Variables | Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E a | T a | M a | Experimental | Predicted | |
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 42.96 ± 3.04 b | 42.49 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 67.40 ± 2.71 | 66.83 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 68.36 ± 0.41 | 67.88 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 80.33 ± 0.15 | 79.75 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 57.75 ± 2.58 | 57.94 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 79.69 ± 0.06 | 79.78 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 85.26 ± 0.44 | 85.45 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 86.72 ± 0.16 | 86.80 |
| 9 | −1.68 | 0 | 0 | 59.66 ± 0.59 | 59.82 |
| 10 | 1.68 | 0 | 0 | 84.40 ± 0.27 | 84.79 |
| 11 | 0 | −1.68 | 0 | 50.85 ± 8.72 | 51.13 |
| 12 | 0 | 1.68 | 0 | 87.28 ± 0.04 | 87.55 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1.68 | 60.78 ± 9.21 | 61.84 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1.68 | 84.64 ± 0.42 | 84.13 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.05±0.13 | 82.74 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 81.56 ± 0.41 | 82.74 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82.86 ± 0.24 | 82.74 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82.39 ± 0.27 | 82.74 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 83.95 ± 0.08 | 82.74 |
| Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3357.74 | 11 | 305.25 | 355.18 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 6.02 | 7 | 0.86 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 2.92 | 3 | 0.97 | 1.26 | 0.3999 |
| Pure Error | 3.09 | 4 | 0.77 |
| Independent Variables | Symbol | Coded Variable Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.68 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 1.68 | ||
| Reaction time (min) | T | 10.0 | 30.3 | 60.0 | 89.7 | 110.0 |
| Enzyme load (%) | E | 5.0 | 9.1 | 15.0 | 20.9 | 25.0 |
| Molar ratio | M | 1.0 | 2.2 | 4.0 | 5.8 | 7.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Jiang, M.-Y.; Shi, J.; Zheng, M.-M.; Huang, F.-H. Preparation of Immobilized Lipase Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Its Application in Ester Synthesis. Molecules 2019, 24, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030395
Dong Z, Jiang M-Y, Shi J, Zheng M-M, Huang F-H. Preparation of Immobilized Lipase Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Its Application in Ester Synthesis. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030395
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zhe, Meng-Ying Jiang, Jie Shi, Ming-Ming Zheng, and Feng-Hong Huang. 2019. "Preparation of Immobilized Lipase Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Its Application in Ester Synthesis" Molecules 24, no. 3: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030395
APA StyleDong, Z., Jiang, M. -Y., Shi, J., Zheng, M. -M., & Huang, F. -H. (2019). Preparation of Immobilized Lipase Based on Hollow Mesoporous Silica Spheres and Its Application in Ester Synthesis. Molecules, 24(3), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030395