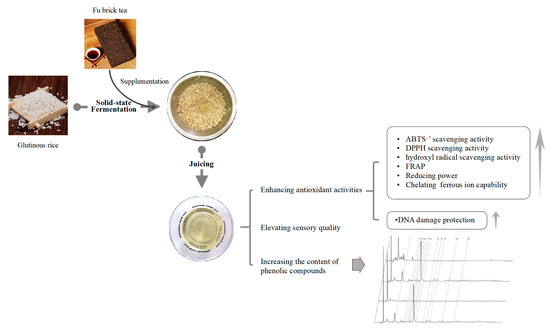
Increased Phenolic Content and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Glutinous Rice Supplemented with Fu Brick Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the Supplementation of FBT to produce FGR-FBT
2.2. Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Total Phenolic Content
2.4. HPLC Analysis of Phenolic Compounds
2.5. Antioxidant Activities
2.5.1. ABTS·+ and DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activities
2.5.2. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power and Reducing Power
2.5.3. Chelating Capability of Fe2+ and Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging Activity
2.6. Inhibition of Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Supercoiled Plasmid DNA Strand Breakage
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Solid-State Fermentation of Glutinous Rice
3.3. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
3.4. Preparation of Extracts by Different Solvents
3.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Contents
3.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Major Phenolic Compounds
3.7. Antioxidant Activities Evaluation
3.7.1. Assay for DPPH Radical-Scavenging Activity
3.7.2. Assay for ABTS·+-Scavenging Activity
3.7.3. Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
3.7.4. Reducing Power Assay
3.7.5. Evaluation of Ferrous Ion Chelating Activity
3.7.6. Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging Assay
3.8. Assessment of Supercoiled Plasmid DNA Strand Breakage Inhibition
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.-z.; Zhou, Y.-b.; Ling, T.-j.; Wan, X.-c. Chinese dark teas: Postfermentation, chemistry and biological activities. Food Res. Inter. 2013, 53, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Dong, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z. Rapid sensing of total theaflavins content in black tea using a portable electronic tongue system coupled to efficient variables selection algorithms. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 75, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.Y.; Mi, Y.S.; Liu, Z.G.; Fan, R.; Qiao, Q.L.; Sun, Y.L.; Ren, B.; Liu, X.B. Dietary tea polyphenols ameliorate metabolic syndrome and memory impairment via circadian clock related mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods. 2017, 34, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.H.; Ryan, E.P.; Huang, J.N.; Liu, Z.H.; Weir, T.L.; Snook, R.L.; Ryan, T.P. Fermented Camellia sinensis, Fu Zhuan Tea, regulates hyperlipidemia and transcription factors involved in lipid catabolism. Food Res. Inter. 2011, 44, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (Poly)phenolics in Human Health: Structures, Bioavailability, and Evidence of Protective Effects Against Chronic Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.E.; Lee, S.; Singh, D.; Jang, E.S.; Shin, H.W.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, C.H. Time-resolved comparative metabolomes for Koji fermentation with brown-, white-, and giant embryo-rice. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, T.; Kumari, A.; Banerjee, R. Enrichment of phenolics and free radical scavenging property of wheat koji prepared with two filamentous fungi. Bioresource Tech. 2009, 100, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xia, Y.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Tao, L.R.; Yu, J.S.; Ai, L.Z. Effects of boiling, ultra-high temperature and high hydrostatic pressure on free amino acids, flavor characteristics and sensory profiles in Chinese rice wine. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.B.; Wu, Z.Z.; Long, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.M.; Jin, Z.Y.; Jiao, A.Q. Improved bioaccessibility of phenolics and antioxidant activity of glutinous rice and its fermented Chinese rice wine by simultaneous extrusion and enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Funct. Foods. 2015, 17, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindes, M.M.M.; Cardoso, V.L.; Reis, M.H.M.; Boffito, D.C. Maximisation of the polyphenols extraction yield from green tea leaves and sequential clarification. J. Food Eng. 2019, 241, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananingsih, V.K.; Sharma, A.; Zhou, W.B. Green tea catechins during food processing and storage: A review on stability and detection. Food Res. Inter. 2013, 50, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Xia, Y.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Yu, J.S.; Ai, L.Z. Effect of mixed yeast starter on volatile flavor compounds in Chinese rice wine during different brewing stages. Lwt-Food Sci Technol. 2017, 78, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xue, D. Enhancement of antioxidant activity of Radix Puerariae and red yeast rice by mixed fermentation with Monascus purpureus. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.P.; Xiao, Y.; Rui, X.; Xu, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Dong, M.S. Fu brick tea extract supplementation enhanced probiotic viability and antioxidant activity of tofu under simulated gastrointestinal digestion condition. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103668–103682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Sakulnak, R.; Wang, S.A. Effect of black tea on antioxidant, textural, and sensory properties of Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.Y.; Shah, N.P.; Wang, M.F.; Lui, W.Y.; Corke, H. Fermentation alters antioxidant capacity and polyphenol distribution in selected edible legumes. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2016, 51, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Zhai, F.H.; Li, X.X.; Cao, J.L.; Han, J.R. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of buckwheat fermented by three strains of Agaricus. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 73, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, F.; Mao, L.C.; Pan, X. Antioxidant activities of five Chinese rice wines and the involvement of phenolic compounds. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, S.J.; Shyu, Y.T. Antioxidant properties of certain cereals as affected by food-grade bacteria fermentation. J. Biosci Bioeng. 2014, 117, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Lee, R.P.; Huang, J.J.; Yang, J.P.; Henning, S.M.; Hong, X.T.; Heber, D.; Li, Z.P. Quantification of bioactive constituents and antioxidant activity of Chinese yellow wine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Ma, Z.Z.; Tu, P.F. Comparison of the Chemical Constituents of Aged Pu-erh Tea, Ripened Pu-erh Tea, and Other Teas Using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8754–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieber, K. The Impact of Coffee on Health. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, E.S.; Slettenaar, M.; Van der Meer, N.; Transler, C.; Jans, L.; Quadt, F.; Berry, M. Differential contributions of theobromine and caffeine on mood, psychomotor performance and blood pressure. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Han, J.; Sun, D. Temperature- and pH-induced effects on the volumetric properties and refractive indices for two promising cancer preventive agents being protocatechuic acid and protocatechualdehyde. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedara, I.A.; Fasina, O.B.; Ayeni, M.F.; Ajayi, O.M.; Farombi, E.O. Protocatechuic acid ameliorates neurobehavioral deficits via suppression of oxidative damage, inflammation, caspase-3 and acetylcholinesterase activities in diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y.L.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Dong, M.S. Enhanced total phenolic and isoflavone aglycone content, antioxidant activity and DNA damage protection of soybeans processed by solid state fermentation with Rhizopus oligosporus RT-3. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29741–29756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.L.; Miao, J.Q.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Rui, X.; Dong, M.S. Solid-State Bioprocessing with Cordyceps militaris Enhanced Antioxidant Activity and DNA Damage Protection of Red Beans (Phaseolus angularis). Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, M.F. Does Impairment of Energy-Metabolism Result in Excitotoxic Neuronal Death in Neurodegenerative Illnesses. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 31, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Oniszczuk, A.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M. An attempt to elucidate the role of iron and zinc ions in development of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Hu, B.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of chemical property, cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick teas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, J. Physicochemical and sensory properties of fresh noodles fortified with ground linseed (Linum usitatissimum). LWT 2019, 101, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Hou, G.G.; Sun, J.; Wan, X.; Dubat, A. Effect of green tea powder on the quality attributes and antioxidant activity of whole-wheat flour pan bread. LWT-Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 79, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnopp, A.R.; Oliveira, K.G.; de Andrade, E.F.; Postingher, B.M.; Granato, D. Optimization of an organic yogurt based on sensorial, nutritional, and functional perspectives. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.; Jeewanthi, R.K.C.; Park, E.H.; Paik, H.D. Short communication: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of Cheddar-type cheese fortified with Inula britannica extract. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albishi, T.; John, J.A.; Al-Khalifa, A.S.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and DNA scission inhibitory activities of phenolic compounds in selected onion and potato varieties. J. Funct. Foods. 2013, 5, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.-N.; Ma, C.-L.; Qi, Z.; Ma, C.-M. Simultaneous quantification of ten constituents of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge using UHPLC-MS methods and evaluation of their radical scavenging, DNA scission protective, and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Daugelaite, J.; Shahidi, F. DNA scission and LDL cholesterol oxidation inhibition and antioxidant activities of Bael (Aegle marmelos) flower extracts. J. Tradit. Complem. Med. 2018, 8, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, B.K.; Park, K.J. Chemical and sensory profiles of makgeolli, Korean commercial rice wine, from descriptive, chemical, and volatile compound analyses. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.H.; Tian, H.X.; Ma, X. Characterization of Chinese rice wine taste attributes using liquid chromatographic analysis, sensory evaluation, and an electronic tongue. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 997, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamidele, P.; Fasogbon, M.B. Chemical and antioxidant properties of snake tomato (Trichosanthes cucumerina) juice and Pineapple (Ananas comosus) juice blends and their changes during storage. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Yuan, B.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Wu, X.; Rakariyatham, K.; Zhong, L.; Han, Y.H.; Kimatu, B.M.; Yang, W.J. Polyphenols-rich extract from Pleurotus eryngii with growth inhibitory of HCT116 colon cancer cells and anti-inflammatory function in RAW264.7 cells. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, F.H.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.R. Nutritional components and antioxidant properties of seven kinds of cereals fermented by the basidiomycete Agaricus blazei. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.H.; Jiang, M.; Rui, X.; Dong, M.S. Structural elucidation and antioxidant activities of exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 102, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |




| Control | FGR-0.5%FBT | FGR-1%FBT | FGR-2%FBT | FGR-3%FBT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Lightness | 9.00 ± 0.00 a | 7.30 ± 0.56 b | 6.85 ± 0.59 bc | 6.35 ± 0.81 c | 5.65 ± 0.84 d |
| Color | 2.00 ± 0.63 d | 4.75 ± 0.87 c | 6.15 ± 0.59 b | 7.15 ± 0.59 a | 7.80 ± 0.64 a | |
| Turbidity | 6.90 ± 0.49 a | 7.05 ± 0.52 a | 7.10 ± 0.66 a | 7.40 ± 0.44 a | 7.20 ± 0.56 a | |
| Aroma/flavor | Alcohol | 8.10 ± 0.37 a | 7.85 ± 0.55 ab | 7.75 ± 0.46 ab | 7.70 ± 0.46 ab | 7.40 ± 0.62 b |
| Acid | 7.75 ± 0.40 a | 7.50 ± 0.55 ab | 7.10 ± 0.66 bc | 6.65 ± 0.74 c | 5.55 ± 0.72 d | |
| Tea | 0.00 ± 0.00 e | 5.35 ± 0.90 d | 6.90 ± 0.58 c | 7.55 ± 0.52 b | 8.30 ± 0.40 a | |
| Cereal | 8.30 ± 0.40 a | 8.35 ± 0.39 a | 7.30 ± 0.51 b | 6.40 ± 0.70 c | 5.20 ± 0.98 d | |
| Taste/mouth-feel | Sweet | 8.05 ± 0.27 a | 7.80 ± 0.46 ab | 7.25 ± 0.46 b | 6.15 ± 0.71 c | 4.90 ± 0.83 d |
| Sour | 6.95 ± 0.52 a | 6.60 ± 0.54 ab | 6.50 ± 0.45 ab | 6.25 ± 0.46 bc | 5.95 ± 0.52 c | |
| Bitter | 0.75 ± 0.60 d | 1.30 ± 0.46 d | 3.35 ± 0.63 c | 4.45 ± 0.57 b | 6.40 ± 0.92 a | |
| Astringency | 2.60 ± 0.54 d | 2.80 ± 0.75 d | 3.80 ± 0.75 c | 4.90 ± 0.83 b | 6.65 ± 0.71 a | |
| Aftertaste | 3.95 ± 0.72 e | 5.00 ± 0.67 d | 5.80 ± 0.78 c | 7.25 ± 0.75 a | 6.40 ± 0.54 b | |
| Irritant | 5.45 ± 0.61 a | 5.25 ± 0.81 a | 5.00 ± 0.63 a | 4.90 ± 0.50 a | 4.70 ± 0.51 a | |
| Basic texture | Full body | 7.30 ± 0.40 a | 7.10 ± 0.49 ab | 7.00 ± 0.50 ab | 6.70 ± 0.40 bc | 6.30 ± 0.40 c |
| Granular sensor | 1.20 ± 0.33 d | 1.55 ± 0.47 d | 3.50 ± 0.45 c | 4.65 ± 0.63 b | 6.50 ± 0.84 a | |
| Continuation | 4.25 ± 0.46 c | 4.55 ± 0.47 c | 5.60 ± 0.54 b | 7.40 ± 0.77 a | 7.05 ± 0.73 a |
| Compounds | FGR-FBT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Extracts | Hydroalcoholic Extracts | ||
| 1 | GA | 77.47 ± 0.33 b | 81.30 ± 0.31 a |
| 2 | GC | 255.97 ± 1.71 b | 269.81 ± 2.77 a |
| 3 | Tb | 9.80 ± 0.07 a | 4.64 ± 0.17 b |
| 4 | DbA | 2.62 ± 0.12 a | 2.81 ± 0.13 a |
| 5 | Tp | 1.42 ± 0.02 a | 1.43 ± 0.03 a |
| 6 | EGC | 28.95 ± 0.14 b | 38.88 ± 0.72 a |
| 7 | Dbd | 13.18 ± 0.04 a | 13.25 ± 0.10 a |
| 8 | Caffeine | 272.46 ± 0.13 a | 267.06 ± 0.54 b |
| 9 | C | 9.09 ± 0.20 b | 26.35 ± 1.15 a |
| 10 | CA | 0.46 ± 0.03 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 b |
| 11 | EC | 119.71 ± 1.72 b | 152.98 ± 1.41 a |
| 12 | EGCG | 46.31 ± 0.17 b | 48.76 ± 0.39 a |
| 13 | GCG | 41.81 ± 0.06 b | 45.85 ± 0.67 a |
| 14 | ECG | 7.76 ± 0.07 b | 8.31 ± 0.22 a |
| FGR-FBT | FGR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Extracts | Hydroalcoholic Extracts | Water Extracts | Hydroalcoholic Extracts | |
| ABTS·+ | 30.67 ± 0.29 c | 10.75 ± 0.24 d | 257.71 ± 4.82 a | 224.55 ± 3.63 b |
| DPPH | 17.26 ± 0.30 c | 15.97 ± 0.21 d | 132.75 ± 3.09 a | 114.83 ± 4.43 b |
| FRAP | 26.61 ± 2.43 c | 13.23 ± 1.87 d | 351.67 ± 26.62 a | 319.04 ± 32.92 b |
| Reducing power | 265.61 ± 10.69 b | 126.42 ± 3.83 c | 1654.89 ± 24.26 a | 1648.89 ± 8.19 a |
| Fe2+ chelating * | 498.43 ± 13.75 d | 705.47 ± 55.92 c | 1679.88 ± 67.05 b | 1893.39 ± 64.13 a |
| ·OH * | 969.79 ± 17.49 a | 292.19 ± 4.03 b | nd | nd |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Hu, W.; Zhou, S.; Tu, C.; Xia, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, M. Increased Phenolic Content and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Glutinous Rice Supplemented with Fu Brick Tea. Molecules 2019, 24, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040671
Xu X, Hu W, Zhou S, Tu C, Xia X, Zhang J, Dong M. Increased Phenolic Content and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Glutinous Rice Supplemented with Fu Brick Tea. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040671
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiao, Wenxiu Hu, Siduo Zhou, Chuanhai Tu, Xiudong Xia, Juanmei Zhang, and Mingsheng Dong. 2019. "Increased Phenolic Content and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Glutinous Rice Supplemented with Fu Brick Tea" Molecules 24, no. 4: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040671
APA StyleXu, X., Hu, W., Zhou, S., Tu, C., Xia, X., Zhang, J., & Dong, M. (2019). Increased Phenolic Content and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity in Fermented Glutinous Rice Supplemented with Fu Brick Tea. Molecules, 24(4), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040671