Echinacoside Isolated from Cistanche tubulosa Putatively Stimulates Growth Hormone Secretion via Activation of the Ghrelin Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
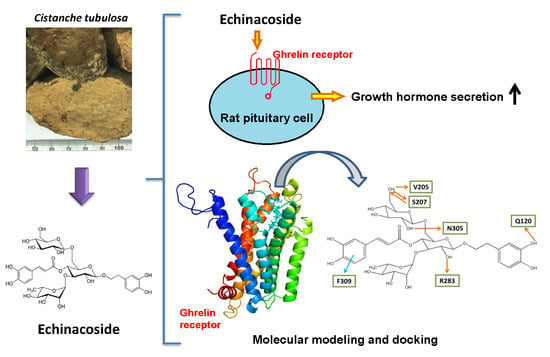
2.1. Separation and Identification of Three Major Phenylethanol Glycosides in the Water Extract of Two Cistanche Species
2.2. Effect of Echinacoside on the Induction of Growth Hormone Secretion in Rat Pituitary Cells
2.3. Molecular Docking of Echinacoside, Tubuloside A, and Acteoside to the Ghrelin Receptor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Plant Materials
4.2. HPLC/UV and LC−MSn Analyses of the Water Extraction of Cistanche spp.
4.3. Isolation of Echinacoside
4.4. Animals
4.5. Primary Pituitary Cell Culture
4.6. Growth Hormone Secretion Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Homology Modeling and Docking
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W. Cistanche deserticola YC Ma, “Desert ginseng”: A review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 1123–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Yang, M.; Deng, B.; Kirby, M.G.; Zhang, X. Cistanche tubulosa ethanol extract mediates rat sex hormone levels by induction of testicular steroidgenic enzymes. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Chun, Y.; Jack, C.; Kao, S.T.; Tsai, F.J.; Liu, H.P. Molecular pathways related to the longevity promotion and cognitive improvement of Cistanche tubulosa in Drosophila. Phytomedicine 2017, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Lin, H.C.; Su, M.H. Reversal by aqueous extracts of Cistanche tubulosa from behavioral deficits in Alzheimer’s disease-like rat model: Relevance for amyloid deposition and central neurotransmitter function. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, G.D.; Liu, C.Q. Research on the effect of phenylethanoid glycosides (PEG) of the Cistanche deserticola on anti-aging in aged mice induced by D-galactose. Zhong Yao Cai 2008, 31, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.F. Analysis of chemical constituents in Cistanche species. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Wang, C.; Wu, G. Cistanche total glycosides on the influence of the vascular dementia rats learning and memory and the mechanism research. Chin. Herb. Med. 2005, 36, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Chen, W.; Qi, D.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, P. Echinacoside promotes bone regeneration by increasing OPG/RANKL ratio in MC3T3-E1 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, H.; Tanaka, J.; Takahara, Y.; Takemoto, K.; Shan, S.J.; Su, M.H. The hypocholesterolemic effects of Cistanche tubulosa extract, a Chinese traditional crude medicine, in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J. Effect of echinacoside on kidney fibrosis by inhibition of TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway in the db/db mice model of diabetic nephropathy. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 2813–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.T.; Gu, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, H.X.; Liu, X. Anti-hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Cistanche tubulosa in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.X.; Ma, H.H.; Ding, H.; Li, W.W.; Zhu, M. Preliminary optimization of a Chinese herbal medicine formula based on the neuroprotective effects in a rat model of rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zigman, J.M.; Jones, J.E.; Lee, C.E.; Saper, C.B.; Elmquist, J.K. Expression of ghrelin receptor mRNA in the rat and the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 528–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, T.R.; Tong, J.; Datta, R.; Culler, M.; Tschop, M.H. Ghrelin in the regulation of body weight and metabolism. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 31, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudman, D.; Feller, A.G.; Nagraj, H.S.; Gergans, G.A.; Lalitha, P.Y.; Goldberg, A.F.; Schlenker, R.A.; Cohn, L.; Rudman, I.W.; Mattson, D.E. Effects of human growth hormone in men over 60 years old. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Bravata, D.M.; Olkin, I.; Nayak, S.; Roberts, B.; Garber, A.M.; Hoffman, A.R. Systematic review: The safety and efficacy of growth hormone in the healthy elderly. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 146, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, R.; Bonelli, L.; Marinazzo, E.; Ghigo, E.; Arvat, E. Growth hormone treatment in human ageing: Benefits and risks. Hormones 2008, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, F.R. Growth hormone in the aging male. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, C.I.; Lin, Y.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, M.R.; Lee, V.S.; Tzen, J.T.C. Teaghrelins, unique acylated flavonoid tetraglycosides in Chin-shin oolong tea, are putative oral agonists of the ghrelin receptor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5085–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.K.; Lo, Y.H.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, T.Y.; Tzen, J.T.C. Identification of biosynthetic intermediates of teaghrelins and teaghrelinlike compounds in oolong teas, and their molecular docking to the ghrelin receptor. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.K.; Chung, T.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Lo, Y.H.; Lin, N.H.; Kuo, P.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Tzen, J.T.C. Ginkgoghrelins, unique acylated flavonoid diglycosides in Folium Ginkgo, stimulate growth hormone secretion via activation of the ghrelin receptor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Mavis, B.Y.; Liu, E.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Song, X.; Fu, F.; Gao, X. Structural characterisation and identification of phenylethanoid glycosides from Cistanches deserticola YC Ma by UHPLC/ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Ma, Z. Quantitative analysis of Cistanches Herba using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection and high-resolution mass spectrometry combined with chemometric methods. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.; Kim, H.G.; Hwang, L.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Chung, H.; Oh, M.S.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of ghrelin in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease by blocking microglial activation. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, S.J.; Isabelle, O.M.; Hupbach, A.; Tu, M.T.; Buss, C.; Walker, D.; Pruessner, J.; Mcewen, B.S. Beyond the stress concept: Allostatic load-A developmental biological and cognitive perspective. In Developmental Psychopathology: Volume Two: Developmental Neuroscience; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 578–628. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, M.; Rizvi, A.A.; Sudar, E.; Soskic, S.; Obradovic, M.; Montalto, G.; Boutjdir, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Isenovic, E.R. A review of the cardiovascular and anti-atherogenic effects of ghrelin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 4953–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, B.; Lang, M.; Brandt, E.; Bach, A.; Howard, A.; Frimurer, T.M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.; Schwartz, T.W. Ghrelin receptor inverse agonists: Identification of an active peptide core and its interaction epitopes on the receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Matsubara, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kangawa, K.; Sakai, T. Regulational effect of ghrelin on growth hormone secretion from perifused rat anterior pituitary cells. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Chung, T.Y.; Lin, N.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, M.R.; Chou, C.C.; Tzen, J.T.C. Emoghrelin, a unique emodin derivative in Heshouwu, stimulates growth hormone secretion via activation of the ghrelin receptor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukhametzianov, R.; Warne, T.; Edwards, P.C.; Serrano-Vega, M.J.; Leslie, A.G.; Tate, C.G.; Schertler, G.F. Two distinct conformations of helix 6 observed in antagonist-bound structures of a beta1-adrenergic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8228–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Zhang, C.; Lyons, J.A.; Holl, R.; Aragao, D.; Arlow, D.H.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Choi, H.J.; Devree, B.T.; Sunahara, R.K.; et al. Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-beta(2) adrenoceptor complex. Nature 2011, 469, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM—A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Sample of echinacoside is available from the authors. |






| Compound | Energy (kJ mol−1) | Van der Waals’ Force (kJ mol−1) | H Bond (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Echinacoside | −132.35 | −111.82 | −20.53 |
| Tubuloside A | −122.88 | −103.93 | −18.95 |
| Acteoside | −120.35 | −93.65 | −26.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-J.; Chien, M.-Y.; Lin, N.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Tzen, J.T.C. Echinacoside Isolated from Cistanche tubulosa Putatively Stimulates Growth Hormone Secretion via Activation of the Ghrelin Receptor. Molecules 2019, 24, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040720
Wu C-J, Chien M-Y, Lin N-H, Lin Y-C, Chen W-Y, Chen C-H, Tzen JTC. Echinacoside Isolated from Cistanche tubulosa Putatively Stimulates Growth Hormone Secretion via Activation of the Ghrelin Receptor. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040720
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chieh-Ju, Mei-Yin Chien, Nan-Hei Lin, Yi-Chiao Lin, Wen-Ying Chen, Chao-Hsiang Chen, and Jason T. C. Tzen. 2019. "Echinacoside Isolated from Cistanche tubulosa Putatively Stimulates Growth Hormone Secretion via Activation of the Ghrelin Receptor" Molecules 24, no. 4: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040720
APA StyleWu, C. -J., Chien, M. -Y., Lin, N. -H., Lin, Y. -C., Chen, W. -Y., Chen, C. -H., & Tzen, J. T. C. (2019). Echinacoside Isolated from Cistanche tubulosa Putatively Stimulates Growth Hormone Secretion via Activation of the Ghrelin Receptor. Molecules, 24(4), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040720