Identification of Bis-Cyclic Guanidines as Antiplasmodial Compounds from Positional Scanning Mixture-Based Libraries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. P. falciparum Culture and Antiplasmodial Activity Assay
3.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
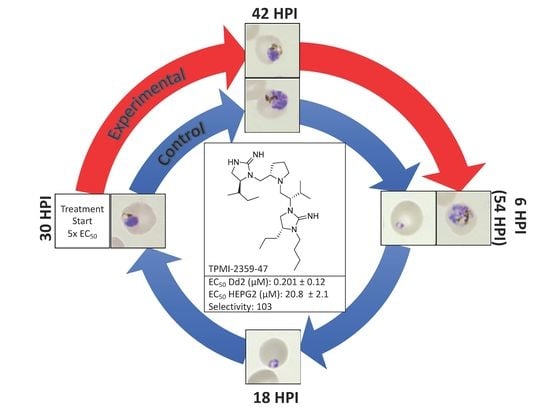
3.3. Stage-Specific Inhibition Assays
3.4. Mouse Plasma Stability of Compound TPI 2539-47
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESI-MS | electron spray ionization mass spectrometry |
| 1H-NMR | H-nuclear magnetic resonance |
| 13C-NMR | C (isotope 13)-nuclear magnetic resonance |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
| RP-HPLC | reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| HF | hydrogen fluoride |
References
- Murray, C.J.; Rosenfeld, L.C.; Lim, S.S.; Andrews, K.G.; Foreman, K.J.; Haring, D.; Fullman, N.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Lopez, A.D. Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, B.T.; Mehlotra, R.K. Expanding the Antimalarial Drug Arsenal-Now, But How? Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 681–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W. WHO urges the phasing out of artemisinin based monotherapy for malaria to reduce resistance. BMJ 2011, 342, d2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, E.A.; Dhorda, M.; Fairhurst, R.M.; Amaratunga, C.; Lim, P.; Suon, S.; Sreng, S.; Anderson, J.M.; Mao, S.; Sam, B.; et al. Spread of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.; Vederas, J.C. Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science 2009, 325, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, R.J.; Pontavornpinyo, W.; Saralamba, S.; Aguas, R.; Yeung, S.; Dondorp, AM.; Day, NP.; White, N.J.; White, L.J. The last man standing is the most resistant: Eliminating artemisinin-resistant malaria in Cambodia. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Yeung, S.; White, L.; Nguon, C.; Day, N.P.; Socheat, D.; von Seidlein, L. Artemisinin resistance: Current status and scenarios for containment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Nosten, F.; Yi, P.; Das, D.; Phyo, A.P.; Tarning, J.; Lwin, K.M.; Ariey, F.; Hanpithakpong, W.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, D.H.; Macarron, R. Enhancements of screening collections to address areas of unmet medical need: An industry perspective. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazato, K.; Wang, Y.; Kobayashi, N. Viral infectious disease and natural products with antiviral activity. Drug Discov. Ther. 2007, 1, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Vallejo, F.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Houghten, R.A.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Expanding the medicinally relevant chemical space with compound libraries. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Appel, J.R.; Dooley, C.T.; Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M.; Yu, Y.; Maggiora, G.M.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; et al. Strategies for the use of mixture-based synthetic combinatorial libraries: scaffold ranking, direct testing in vivo, and enhanced deconvolution by computational methods. J. Comb. Chem. 2008, 10, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Franco, J.L.; Martinez-Mayorga, K.; Bender, A.; Marin, R.M.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Pinilla, C.; Houghten, R.A. Characterization of activity landscapes using 2D and 3D similarity methods: consensus activity cliffs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Franco, J.L.; Martinez-Mayorga, K.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C. Visualization of the Chemical Space in Drug Discovery. Curr. Comput-Aid. Drug 2008, 4, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Villanueva, J.; Santos, R.; Hernandez-Campos, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Castillo, R.; Medina-Franco, J.L. Towards a systematic characterization of the antiprotozoal activity landscape of benzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7380–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C.; Appel, J.R.; Blondelle, S.E.; Dooley, C.T.; Eichler, J.; Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M. Mixture-based synthetic combinatorial libraries. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3743–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, T.N.; Paguio, M.; Gligorijevic, B.; Seudieu, C.; Kosar, A.D.; Davidson, E.; Roepe, P.D. Novel, rapid, and inexpensive cell-based quantification of antimalarial drug efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1807–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.D.; Dennull, R.A.; Gerena, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, M.; Roncal, N.E.; Waters, N.C. Assessment and continued validation of the malaria SYBR green I-based fluorescence assay for use in malaria drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilkstein, M.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kelly, J.X.; Wilairat, P.; Riscoe, M. Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.G.; Appel, J.R.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Edwards, B.S.; Sklar, L.A.; Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C. The mathematics of a successful deconvolution: a quantitative assessment of mixture-based combinatorial libraries screened against two formylpeptide receptors. Molecules 2013, 18, 6408–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.G.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Dooley, C.T.; Pinilla, C.; Appel, J.R.; Houghten, R.A. Use and implications of the harmonic mean model on mixtures for basic research and drug discovery. ACS Comb. Sci. 2011, 13, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minond, D.; Cudic, M.; Bionda, N.; Giulianotti, M.; Maida, L.; Houghten, R.A.; Fields, G.B. Discovery of novel inhibitors of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 17 (ADAM17) using glycosylated and non-glycosylated substrates. J. Biolog. Chem. 2012, 287, 36473–36487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, H.; Debevec, G.; Santos, R.G.; Houghten, R.A.; Da-vis, J.C.; Nefzi, A.; Lemmon, V.P.; Bixby, J.L.; Giulianotti, M.A. Scaffold Ranking and Positional Scanning Identify Novel Neu-rite Outgrowth Promoters with Nanomolar Potency. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Madegowda, M.; Nefzi, A.; Houghten, R.A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Rosen, B.P. Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Human As(III) S-Adenosylmethionine Methyltrans-ferase (AS3MT). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilley, K.J.; Giulianotti, M.; Dooley, C.T.; Nefzi, A.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Houghten, R.A. Identification of two novel, potent, low-liability antinociceptive compounds from the direct in vivo screening of a large mixture-based combinatorial library. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla, C.; Appel, J.R.; Blanc, P.; Houghten, R.A. Rapid identification of high affinity peptide ligands using positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biotechniques 1992, 13, 901–905. [Google Scholar]
- Houghten, R.A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: Specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5131–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rideout, M.C.; Boldt, J.L.; Vahi-Ferguson, G.; Salamon, P.; Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M.; Giulianotti, M.; Pinilla, C.; Segall, A.M. Potent antimicrobial small molecules screened as inhibitors of tyrosine recombinases and Holliday junction-resolving enzymes. Mol. Divers. 2011, 15, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulianotti, M.A.; Vesely, B.A.; Azhari, A.; Souza, A.; La-Voi, T.; Houghten, R.A.; Kyle, D.E.; Leahy, J.W. Identification of a Hit Series of Antileishmanial Compounds through the Use of Mixture-Based Libraries. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleeman, R.M.; LaVoi, T.; Santos, R.G.; Morales, A.; Nefzi, A.; Welmaker, G.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Giulianotti, M.; Houghten, R.A.; Shaw, L.N. Combinatorial libraries as a tool for the discovery of novel, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents target-ing the ESKAPE pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3340–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensler, M.E.; Bernstein, G.; Nizet, V.; Nefzi, A. Pyrrolidine bis-cyclic guanidines with antimicrobial activity against drug resistant gram positive pathogens identified from a mixture-based combinatorial library. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5073–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, J.; Cutrona, K.J.; Kaufman, B.A.; Figueroa, D.M.; Elmore, D.E. Role of Arginine and Lysine in the Antimicrobial Mechanism of Histone-derived Antimicrobial Peptides. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3915–3920. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rice, A.; Wereszczynski, J. Probing the disparate effects of arginine and lysine residues on antimicrobial peptide/bilayer asso-ciation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 859, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Macedonio, G.; Stefanucci, A.; Costante, R.; Carradori, S.; Cataldi, V.; Di Giulio, M.; Cellini, L.; Silvestri, R.; Giordano, C.; et al. Ar-ginine- and Lysine-rich Peptides: Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2018, 15, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fahem, A.; Albericio, F. Peptide Coupling Reagents, More than a Letter Soup. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6557–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeur, E.; Bradley, M. Amide bond formation: Beyond the myth of coupling reagents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 606–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riester, D.; Wiesmüller, K.-H.; Stoll, D.; Kuhn, R. Racemization of Amino Acids in Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis Investigated by Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2361–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostresh, J.M.; Schoner, C.S.; Hamashin, V.T.; Nefzi, A.; Meyer, J.-P.; Houghten, R.A. Solid-phase synthesis of trisubsti-tuted bicyclic guanidines via cyclization of reduced N-acylated dipeptides. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 8622–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manku, S.; Laplante, C.; Kopac, D.; Chan, T.; Hall, D.G. A mild and general solid-phase method for the synthesis of chiral polyamines. Solution studies on the cleavage of borane-amine intermediates from the reduction of secondary amides. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribaut, C.; Berry, A.; Chevalley, S.; Reybier, K.; Morlais, I.; Parzy, D.; Nepveu, F.; Benoit-Vical, F.; Valentin, A. Concentration and purification by magnetic separation of the erythrocytic stages of all human Plasmodium species. Malar. J. 2008, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambros, C.; Vanderberg, J.P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, A.; Gorgette, O.; Mercereau-Puijalon, O.; Barale, J.C. Screening and evaluation of inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum merozoite egress and invasion using cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 923, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.W.; Langer, C.; Goodman, C.D.; McFadden, G.I.; Beeson, J.G. Defining the timing of action of antimalarial drugs against Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamo, F.J.; Sanz, L.M.; Vidal, J.; de Cozar, C.; Alvarez, E.; Lavandera, J.L.; Vanderwall, D.E.; Green, D.V.; Kumar, V.; Hasan, S.; et al. Thousands of chemical starting points for antimalarial lead identification. Nature 2010, 465, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perry, D.L., Jr.; Roberts, B.F.; Debevec, G.; Michaels, H.A.; Chakrabarti, D.; Nefzi, A. Identification of Bis-Cyclic Guanidines as Antiplasmodial Compounds from Positional Scanning Mixture-Based Libraries. Molecules 2019, 24, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061100
Perry DL Jr., Roberts BF, Debevec G, Michaels HA, Chakrabarti D, Nefzi A. Identification of Bis-Cyclic Guanidines as Antiplasmodial Compounds from Positional Scanning Mixture-Based Libraries. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061100
Chicago/Turabian StylePerry, David L., Jr., Bracken F. Roberts, Ginamarie Debevec, Heather A. Michaels, Debopam Chakrabarti, and Adel Nefzi. 2019. "Identification of Bis-Cyclic Guanidines as Antiplasmodial Compounds from Positional Scanning Mixture-Based Libraries" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061100
APA StylePerry, D. L., Jr., Roberts, B. F., Debevec, G., Michaels, H. A., Chakrabarti, D., & Nefzi, A. (2019). Identification of Bis-Cyclic Guanidines as Antiplasmodial Compounds from Positional Scanning Mixture-Based Libraries. Molecules, 24(6), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061100