Heme Oxygenase-1 is a Key Molecule Underlying Differential Response of TW-37-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparative Analysis of Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of TW-37 in Human MEC Cell Lines
2.2. Target Profiling Related to Differential Response of Human MEC Cells to TW-37
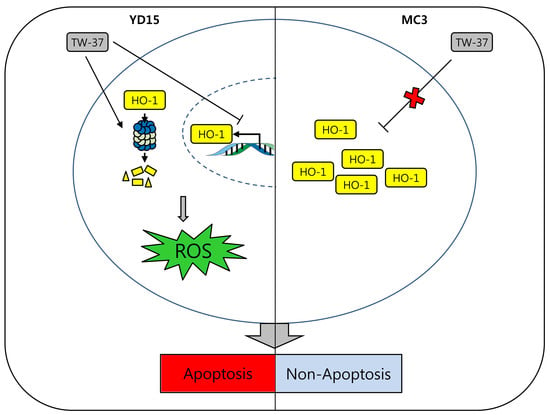
2.3. Role of HO-1 in Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis Upon TW-37 Treatment
2.4. Role of Intracellular ROS Generation in TW-37-Induced Apoptosis
2.5. Transcriptional and Post-Translational Regulation of HO-1 by TW-37
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Trypan Blue Exclusion Assay
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. DAPI Staining
4.6. Annexin V/PI Double Staining
4.7. Analysis of the Sub-G1 Population
4.8. Human Apoptosis Array
4.9. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
4.10. Construction of Overexpression Vectors and Transient Transfection
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ettl, T.; Schwarz-Furlan, S.; Gosau, M.; Reichert, T.E. Salivary gland carcinomas. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 16, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisanti, S.; Amoroso, V.; Buglione, M.; Rosati, A.; Gatta, R.; Pizzocaro, C.; Ferrari, V.D.; Marini, G. Cetuximab in the treatment of metastatic mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands: A case report and review of literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2008, 2, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.J.; Ahn, C.H.; Yang, I.H.; Won, D.H.; Jin, B.; Cho, N.P.; Hong, S.D.; Shin, J.A.; Cho, S.D. Apoptosis induced by methanol extract of Potentilla discolor in human mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells through STAT3/PUMA signaling axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5258–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.S.; Oh, S.; Jang, B.; Yu, H.J.; Shin, J.A.; Cho, N.P.; Yang, I.H.; Won, D.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Hong, S.D.; et al. Silymarin and its active component silibinin act as novel therapeutic alternatives for salivary gland cancer by targeting the ERK1/2-Bim signaling cascade. Cell Oncol. (Dordr.) 2017, 40, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.H.; Reynolds, C.P. Bcl-2 inhibitors: Targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogler, M. Targeting BCL2-Proteins for the Treatment of Solid Tumours. Adv. Med. 2014, 2014, 943648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Marcellus, R.C.; Roulston, A.; Watson, M.; Serfass, L.; Murthy Madiraju, S.R.; Goulet, D.; Viallet, J.; Belec, L.; Billot, X.; et al. Small molecule obatoclax (GX15-070) antagonizes MCL-1 and overcomes MCL-1-mediated resistance to apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19512–19517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tse, C.; Shoemaker, A.R.; Adickes, J.; Anderson, M.G.; Chen, J.; Jin, S.; Johnson, E.F.; Marsh, K.C.; Mitten, M.J.; Nimmer, P.; et al. ABT-263: A potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3421–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labi, V.; Grespi, F.; Baumgartner, F.; Villunger, A. Targeting the Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis pathway by BH3 mimetics: A breakthrough in anticancer therapy? Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.M.; Goustin, A.S.; Aboukameel, A.; Chen, B.; Banerjee, S.; Wang, G.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Wang, S.; Al-Katib, A. Preclinical studies of TW-37, a new nonpeptidic small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, in diffuse large cell lymphoma xenograft model reveal drug action on both Bcl-2 and Mcl-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Ding, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, C.; Liang, H. The preclinical analysis of TW-37 as a potential anti-colorectal cancer cell agent. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Azmi, A.S.; Ahmad, A.; Banerjee, S.; Wang, S.; Sarkar, F.H.; Mohammad, R.M. TW-37, a small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer: Involvement of Notch-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Wang, Z.; Burikhanov, R.; Rangnekar, V.M.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Sarkar, F.H.; Mohammad, R.M. Critical role of prostate apoptosis response-4 in determining the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to small-molecule inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varadarajan, S.; Vogler, M.; Butterworth, M.; Dinsdale, D.; Walensky, L.D.; Cohen, G.M. Evaluation and critical assessment of putative MCL-1 inhibitors. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skommer, J.; Brittain, T. Extended survival of SH-SY5Y cells following overexpression of Lys67Glu neuroglobin is associated with stabilization of DeltapsiM. Cytometry A 2012, 81, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Chiang, M.T.; Chau, L.Y. Ubiquitin-proteasome system mediates heme oxygenase-1 degradation through endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2008, 1783, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortso, M.D.; Andersen, M.H. The expression, function and targeting of haem oxygenase-1 in cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2014, 14, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, K.D.; Tonegawa, S. Reduced stress defense in heme oxygenase 1-deficient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10925–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayerhofer, M.; Florian, S.; Krauth, M.T.; Aichberger, K.J.; Bilban, M.; Marculescu, R.; Printz, D.; Fritsch, G.; Wagner, O.; Selzer, E.; et al. Identification of heme oxygenase-1 as a novel BCR/ABL-dependent survival factor in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3148–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberat, P.O.; Dambrauskas, Z.; Gulbinas, A.; Giese, T.; Giese, N.; Kunzli, B.; Autschbach, F.; Meuer, S.; Buchler, M.W.; Friess, H. Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 increases responsiveness of pancreatic cancer cells to anticancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Was, H.; Cichon, T.; Smolarczyk, R.; Rudnicka, D.; Stopa, M.; Chevalier, C.; Leger, J.J.; Lackowska, B.; Grochot, A.; Bojkowska, K.; et al. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 in murine melanoma: Increased proliferation and viability of tumor cells, decreased survival of mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2181–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Wen, X.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wan, H.; Chen, F.; Nie, X. Oxysophocarpine Retards the Growth and Metastasis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting the Nrf2/HO-1 Axis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.H.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Upregulation of VEGF by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 via heme oxygenase-1 and ERK1/2 signaling in MCF-7 cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1090, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, S.A.; Zaitseva, L.; Bowles, K.M.; Rushworth, S.A.; Macewan, D.J. Protection of acute myeloid leukaemia cells from apoptosis induced by front-line chemotherapeutics is mediated by haem oxygenase-1. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chau, L.Y. Heme oxygenase-1: Emerging target of cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Fang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, S. Crucial role of heme oxygenase-1 in the sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cell line Kasumi-1 to ursolic acid. Anticancer Drugs 2014, 25, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Ma, D.; Wang, P.; Cao, L.; Lu, T.; Fang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. Potential crosstalk of the interleukin-6-heme oxygenase-1-dependent mechanism involved in resistance to lenalidomide in multiple myeloma cells. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.H.; Lan, W.M.; Chau, L.Y. TRC8 suppresses tumorigenesis through targeting heme oxygenase-1 for ubiquitination and degradation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunzo, J.; Andrieu, C.; Baylot, V.; So, A.; Rocchi, P. Hsp27 as a therapeutic target in cancers. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, L.; Yang, T.; Jiang, J.; Li, P. Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) Increases chemosensitivity to paclitaxel by increasing production of reactive oxygen species in human ovarian cancer cells (HO8910). J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, P.; Fang, M.; Wu, M.; Liu, T. Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-dependent upregulation of death receptor 5 in human esophageal cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 352, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Fu, D.; Li, Y.; Zi, X.; Liu, H.M.; et al. A novel chalcone derivative S17 induces apoptosis through ROS dependent DR5 up-regulation in gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilshara, M.G.; Jayasooriya, R.; Molagoda, I.M.N.; Jeong, J.W.; Lee, S.; Park, S.R.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Silibinin sensitizes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by upregulating DR5 through ROS-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress-Ca(2+)-CaMKII-Sp1 pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10324–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.O.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, G.Y. Guggulsterone sensitizes hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through the induction of CHOP-dependent DR5: Involvement of ROS-dependent ER-stress. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, I.-H.; Ahn, C.-H.; Cho, N.-P.; Jin, B.; Lee, W.; Jung, Y.C.; Hong, S.D.; Shin, J.-A.; Cho, S.-D. Heme Oxygenase-1 is a Key Molecule Underlying Differential Response of TW-37-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091700
Yang I-H, Ahn C-H, Cho N-P, Jin B, Lee W, Jung YC, Hong SD, Shin J-A, Cho S-D. Heme Oxygenase-1 is a Key Molecule Underlying Differential Response of TW-37-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Cells. Molecules. 2019; 24(9):1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091700
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, In-Hyoung, Chi-Hyun Ahn, Nam-Pyo Cho, Bohwan Jin, WonWoo Lee, Yun Chan Jung, Seong Doo Hong, Ji-Ae Shin, and Sung-Dae Cho. 2019. "Heme Oxygenase-1 is a Key Molecule Underlying Differential Response of TW-37-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Cells" Molecules 24, no. 9: 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091700
APA StyleYang, I. -H., Ahn, C. -H., Cho, N. -P., Jin, B., Lee, W., Jung, Y. C., Hong, S. D., Shin, J. -A., & Cho, S. -D. (2019). Heme Oxygenase-1 is a Key Molecule Underlying Differential Response of TW-37-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Cells. Molecules, 24(9), 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091700