Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Development of the HPLC-UV-ELSD Quantitative Method
2.1.1. Optimization of the HPLC Condition
2.1.2. Optimization of the Extraction Method
2.2. Comparing UV and ELSD in Quantitative Determination of Saponins in PV
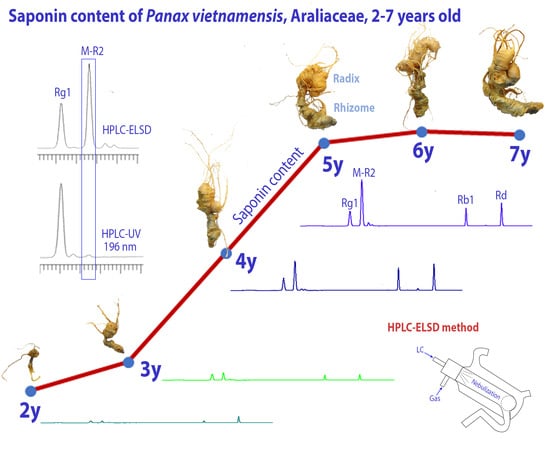
2.3. Growth Characteristics of the Underground Parts of PV with Age
2.4. Saponin Contents in the PV Radix at Different Ages
2.5. Saponins Contents in the PV Rhizome at Different Ages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrument
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Sample Preparation
3.2.2. HPLC Analysis
3.2.3. Calibration Curve
3.2.4. Validation
3.2.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, M.D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 2010–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Kasai, R.; Ohtani, K.; Ito, A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese Ginseng, Panax vietnamensis HA et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Kasai, R.; Ohtani, K.; Ito, A.; Nham, N.T.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. collected in central Vietnam. III. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K.; Nham, N.T.; Tanaka, O. New dammarane saponins from Vietnamese ginseng. In Studies in Plant Science; Chong-Ren, Y., Osamu, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Kunming, China, 1999; Volume 6, pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, N.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H. In vitro antioxidant activity of Vietnamese ginseng saponin and its components. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quan, T.L.; Adnyana, I.K.; Tezuka, Y.; Nagaoka, T.; Tran, Q.K.; Kadota, S. Triterpene saponins from Vietnamese ginseng (Panax vietnamensis) and their hepatocytoprotective activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 456–461. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. The antistress effect of majonoside-R2, a major saponin component of Vietnamese ginseng: Neuronal mechanisms of action. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 20, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Ichiishi, E.; Murakami, T.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Cancer chemopreventive activity of majonoside-R2 from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis. Cancer Lett. 1999, 147, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Anti-tumor-promoting activity of majonoside-R2 from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv.(I). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Le, T.H.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Increase in Protective Effect of Panax vietnamensis by Heat Processing on Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Cell Toxicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Win, N.N.; Piow, W.C.; Huynh, K.L.V.; Hoang, N.N.; Minh, K.; Hoai, N.T.; Duc, H.V.; Nguyen, M.D.J.C.; et al. Anti-melanogenic activity of ocotillol-type ginsenosides from Panax vietnamesis Ginseng. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax ginseng. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Yan, Y.Z.; Jin, X.-j.; Kim, Y.K.; Uddin, M.R.; Kim, Y.B.; Bae, H.B.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S.W.; Park, S.U. Ginsenoside Content in The Leaves and Roots of Panax ginseng at Different Ages. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 679–683. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, C.; Bai, Y.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; You, J.; Zhang, H. Study on ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax quinquefolius L. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, C.Z.; Wu, J.A.; Osinski, J.; Yuan, C.S. Determination of major ginsenosides in Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng) using high-performance liquid chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 2005, 16, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zou, K.; Cai, S.; Meselhy, M.R.; Komatsu, K. Simultaneous determination of triterpene saponins in ginseng drugs by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.N.; Ha, Y.W.; Shin, H.; Son, S.H.; Wu, S.J.; Kim, Y.S. Simultaneous quantification of 14 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Korean red ginseng) by HPLC-ELSD and its application to quality control. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.-B.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Simultaneous determination of 11 saponins in Panax notoginseng using HPLC-ELSD and pressurized liquid extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fitzloff, J.F. Determination of 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 in North American ginseng using high performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 25, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.V.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Nguyen, N.K.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, M.D. Simultaneous Quantitative Analysis of Major Saponins in Vietnamese Ginseng by HPLC. J. Med. Mater. 2012, 17, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Nguyen, M.C.; Nguyen, M.D. HPLC Quantitative Determination of Majonoside-R2 in Vietnamese Ginseng. J. Med. Mater. 2010, 15, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.W.; In, G.; Han, S.T.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, B.G.; Han, G.H.; Chang, I.M. Simultaneous determination of 30 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng preparations using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, A.J.; Woo, S.O.; Koh, H.L. Analysis of saponins in raw and steamed Panax notoginseng using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1011, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of ginsenosides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 717–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of ginseng and standard compounds of ginsenoside-Rb1, -Rd, -Rg1, -Re, notoginsenoside-R1, majonoside-R1, -R2, vinaginsenoside-R2, -R11, and pseudoginsenoside-RT4 are available from the authors. |






| Saponin | ELSD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | Range (mg/mL) | LOQ (mg/mL) | LOD (mg/mL) | |
| N-R1 | y = 16,095,158 × x1.6081 | 0.9985 | 0.013–1.040 | 0.0220 | 0.0060 |
| M-R1 | y = 18,280,672 × x1.5972 | 0.9804 | 0.013–1.010 | 0.0220 | 0.0060 |
| G-Rg1 | y = 14,505,168 × x1.5687 | 0.9983 | 0.007–0.955 | 0.0220 | 0.0070 |
| G-Re | y = 15,540,853 × x1.6196 | 0.9977 | 0.013–1.075 | 0.0220 | 0.0070 |
| M-R2 | y = 20,958,157 × x1.6685 | 0.9984 | 0.019–0.61 | 0.0190 | 0.0040 |
| P-RT4 | y = 20,123,608 × x1.6351 | 0.9990 | 0.009–0.56 | 0.0160 | 0.0065 |
| V-R11 | y = 4,707,057 × x1.6007 | 0.9994 | 0.055–1.69 | 0.0550 | 0.0260 |
| V-R2 | y = 22,774,081 × x1.6510 | 0.9994 | 0.007–0.56 | 0.0130 | 0.0035 |
| G-Rb1 | y = 30,016,270 × x1.6916 | 0.9991 | 0.007–0.495 | 0.0130 | 0.0038 |
| G-Rd | y = 28,974,603 × x1.7116 | 0.9993 | 0.007–0.495 | 0.0120 | 0.0039 |
| UV | |||||
| N-R1 | y = 8,225,894x − 12,872 | 1 | 0.0004–1.0400 | 0.0020 | 0.0004 |
| M-R1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| G-Rg1 | y = 9,069,242x + 12,434 | 0.9997 | 0.0019–1.9100 | 0.0018 | 0.0004 |
| G-Re | y = 9,069,242x + 12,434 | 0.9997 | 0.0019–1.9100 | 0.0018 | 0.0004 |
| M-R2 | y = 188,174.90x − 166.66 | 1 | 0.009–2.4400 | 0.04 | 0.010 |
| P-RT4 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| V-R11 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| V-R2 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| G-Rb1 | y = 6,675,167x − 221 | 0.9999 | 0.00097–0.9900 | 0.0010 | 0.0002 |
| G-Rd | y = 7,278,735x + 1457 | 1 | 0.00098–1.0000 | 0.0010 | 0.0002 |
| Saponin | ELSD | UV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | Intra-Day Precision | Inter-Day Precision | |||||
| Contents (mg/g) | % R.S.D. | Contents (mg/g) | % R.S.D. | Contents (mg/g) | % R.S.D | Contents (mg/g) | % R.S.D. | |
| N-R1 | ND | NA | ND | NA | 1.5 ± 0.03 | 2.01 | 1.5 ± 0.11 | 2.24 |
| M-R1 | ND | NA | ND | NA | ND | NA | ND | NA |
| G-Rg1 | 35.80 ± 0.2 | 0.75 | 36.6 ± 1.1 | 3.03 | 37.3 ± 0.1 | 0.27 | 37.2 ± 0.14 | 0.378 |
| G-Re | ND | NA | ND | NA | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 1.53 | 0.9 ± 0.05 | 5.91 |
| MR2 | 62.8 ± 0.3 | 0.51 | 64.1 ± 1.5 | 2.43 | 65.1 ± 1.3 | 1.99 | 66.8 ± 1.4 | 2.20 |
| p-RT4 | 16.8 ± 0.2 | 1.4 | 17.6 ± 0.6 | 3.78 | ND | NA | ND | NA |
| VR11 | 6.70 ± 0.2 | 3.03 | 7.70 ± 0.18 | 2.37 | ND | NA | ND | NA |
| VR2 | 1.50 ± 0.05 | 3.77 | 1.70 ± 0.06 | 3.87 | ND | NA | ND | NA |
| G-Rb1 | 10.1 ± 0.00 | 0.09 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 2.96 | 10.1 ± 0.02 | 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.07 | 0.75 |
| G-Rd | 5.60 ± 0.06 | 1.14 | 5.60 ± 0.12 | 2.26 | 5.6 ± 0.01 | 0.27 | 5.6 ± 0.026 | 0.46 |
| Saponin | ELSD | UV | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original (mg) | Spiked (mg) | Observed (mg) | Recovery (%) | R.S.D. (%) | Original (mg) | Spiked (mg) | Observed (mg) | Recovery (%) | R.S.D. (%) | |
| N-R1 | ND | NA | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 98 | 6.9 | |||
| 0.11 | 0.26 | 97.8 | 5.7 | |||||||
| M-R1 | ND | NA | ND | NA | ||||||
| G-Rg1 | 3.66 | 2.4 | 5.95 | 94.8 | 3.27 | 3.72 | 2.4 | 6.11 | 99.5 | 1.66 |
| 3.02 | 6.69 | 100.2 | 1.18 | 3.02 | 6.83 | 100.2 | 1.14 | |||
| G-Re | ND | NA | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 81.6 | 0.3 | |||
| 0.12 | 0.19 | 84.5 | 0.4 | |||||||
| M-R2 | 6.41 | 3.98 | 10.17 | 94.3 | 4.15 | ND | NA | |||
| 4.98 | 11.21 | 96.5 | 0.4 | |||||||
| p-RT4 | 1.71 | 1.02 | 2.72 | 98.5 | 4.49 | ND | NA | |||
| 1.23 | 2.81 | 89.4 | 0.9 | |||||||
| V-R11 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 1.17 | 111.5 | 4.06 | ND | NA | |||
| 0.62 | 1.31 | 102.3 | 0.42 | |||||||
| V-R2 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 103.7 | 5.4 | ND | NA | |||
| 0.1 | 0.28 | 101 | 6.36 | |||||||
| G-Rb1 | 1.01 | 1.0 | 1.98 | 97 | 2.3 | 1.01 | 1.0 | 2.01 | 101 | 1.62 |
| 1.2 | 2.12 | 92 | 7.63 | 1.2 | 2.15 | 96 | 5.75 | |||
| G-Rd | 0.56 | 0.52 | 1.05 | 95 | 0.96 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 1.1 | 106.3 | 2.86 |
| 0.63 | 1.13 | 90 | 3.07 | 0.63 | 1.19 | 98 | 6.45 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Van Le, T.H.; Ma, C.T.; Lee, G.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules 2020, 25, 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133086
Vu-Huynh KL, Nguyen HT, Van Le TH, Ma CT, Lee GJ, Kwon SW, Park JH, Nguyen MD. Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules. 2020; 25(13):3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133086
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu-Huynh, Kim Long, Huy Truong Nguyen, Thi Hong Van Le, Chi Thanh Ma, Gwang Jin Lee, Sung Won Kwon, Jeong Hill Park, and Minh Duc Nguyen. 2020. "Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD" Molecules 25, no. 13: 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133086
APA StyleVu-Huynh, K. L., Nguyen, H. T., Van Le, T. H., Ma, C. T., Lee, G. J., Kwon, S. W., Park, J. H., & Nguyen, M. D. (2020). Accumulation of Saponins in Underground Parts of Panax vietnamensis at Different Ages Analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules, 25(13), 3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25133086