Template Synthesis of Porous Ceria-Based Catalysts for Environmental Application
Abstract
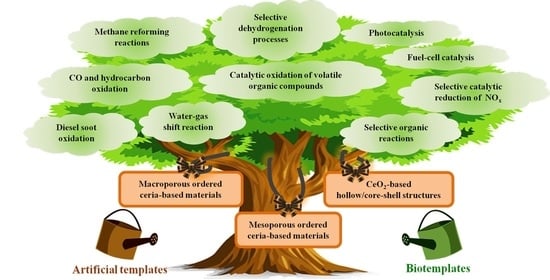
:1. Introduction
2. General Strategies for Template Synthesis of Porous Catalysts Based on CeO2
3. Ceria Preparation Methods Based on Artificial Templates
3.1. Soft Template Methods
3.1.1. Ionic Surfactants as Soft Templates
- Template can significantly improve the textural properties of both unmodified and modified ceria, but the careful choice of dopant is needed, because some modifiers can hinder the pore structure formation in synthesized material. For instance, the one-step CTAB-templated method results in the formation of the Ni/CeO2 and Ni/CeZrOx (Ni/CZ) oxide systems active in CO2 methanation while the similar technique used for modification of CeZrOx with Mn in [31] did not lead to highly effective catalysts for CO oxidation;
- A well-developed porous structure is a beneficial quality for a heterogeneous catalyst, but many other factors may outweigh its influence on catalytic properties. Nickel particle size [33] or the degree of supported nickel reduction [32] were proposed as the key factors, which determine the catalytic action of Ni/CZ in the methanation of carbon oxides, but tuning of reaction conditions and composition of reaction mixture provide the way to achieve the desirable values of these parameters;
- The nature of cation and anion in polar templates can play significant role during ceramic synthesis. Thus, the presence of residual anions in the oxides prepared by CTAB-assisted method can affect the surface morphology and therefore catalytic activity. However, the degree of exposure to such ions is difficult to predict, since the effect depends on their concentration, nature of template, preparation conditions, catalyst composition, and type of catalytic reaction.
3.1.2. Non-Ionic Surfactants and Polymers as Soft Templates
3.2. Hard Template Methods
3.2.1. Carbon-Based Hard Templates
3.2.2. Polymers, SiO2 and Other Hard Templates
3.3. Combined Methods
4. Bio-Templated CeO2-Based Catalysts
4.1. Cellulose and Wood Fiber Templates
4.2. Raw Biotemplates
4.2.1. Plant Biotemplates
4.2.2. Biotemplates of Animal and Microbiological Origins
4.2.3. Biopolymers, Extracts and Amino Acids as Biotemplates
4.2.4. Biotemplates for the Synthesis of Ceria Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Monte, R.; Kašpar, J. Nanostructured CeO2-ZrO2mixed oxides. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A.; De Leitenburg, C.; Boaro, M.; Dolcetti, G. The utilization of ceria in industrial catalysis. Catal. Today 1999, 50, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrute, A.P.; Mondelli, C.; Moser, M.; Novell-Leruth, G.; Lopez, N.; Rosenthal, D.; Farra, R.; Schuster, M.E.; Teschner, D.; Schmidt, T.; et al. Performance, structure, and mechanism of CeO2 in HCl oxidation to Cl2. J. Catal. 2012, 286, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beste, A.; Overbury, S.H. Pathways for Ethanol Dehydrogenation and Dehydration Catalyzed by Ceria (111) and (100) Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-Z.; Lu, Y.; Fan, F.; Yu, S.-H. Selective hydrogenation of nitroaromatics by ceria nanorods. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.M.; Gilbank, A.L.; García, T.; Solsona, B.; Agouram, S.; Torrente-Murciano, L. The prevalence of surface oxygen vacancies over the mobility of bulk oxygen in nanostructured ceria for the total toluene oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, L. Ceria-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laosiripojana, N.; Chadwick, D.; Assabumrungrat, S. Effect of high surface area CeO2 and Ce-ZrO2 supports over Ni catalyst on CH4 reforming with H2O in the presence of O2, H2, and CO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 138, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Rothensteiner, M.; Alxneit, I.; Van Bokhoven, J.A.; Wokaun, A. First demonstration of direct hydrocarbon fuel production from water and carbon dioxide by solar-driven thermochemical cycles using rhodium-ceria. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrente-Murciano, L.; Chapman, R.S.L.; Narvaez-Dinamarca, A.; Mattia, D.; Jones, M.D. Effect of nanostructured ceria as support for the iron catalysed hydrogenation of CO2 into hydrocarbons. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 15496–15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, M.G.; Shin, D.; Han, J.W. Design of Ceria Catalysts for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. ChemCatChem 2019, 12, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaiah, D.; Reddy, L.H.; Park, S.E.; Reddy, B.M. Ceria-zirconia mixed oxides: Synthetic methods and applications. Catal. Rev. 2018, 60, 177–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.A.; Wu, Z.; Dai, S. Shape-Controlled Ceria-based Nanostructures for Catalysis Applications. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deo, S.; Dooley, K.; Janik, M.J.; Rioux, R.M. Influence of metal nuclearity and physicochemical properties of ceria on the oxidation of carbon monoxide. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yeung, K.L.; Bañares, M.A. Ceria and its related materials for VOC catalytic combustion: A review. Catal. Today 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Nanostructured ceria-based catalysts for soot combustion: Investigations on the surface sensitivity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; An, J.; Wang, F. Transformations of Biomass, Its Derivatives, and Downstream Chemicals over Ceria Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8788–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakane, M.; Ueda, W. Ordered Porous Crystalline Transition Metal Oxides. In Porous Materials; Bruce, D.W., O’Hare, D., Walton, R.I., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 147–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, R. Hollow Micro/Nanostructured Ceria-Based Materials: Synthetic Strategies and Versatile Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 31, 1800592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Morphology Genetic Materials Templated from Nature Species. In Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China; Zhang, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfbeisser, A.; Sophiphun, O.; Bernardi, J.; Wittayakun, J.; Föttinger, K.; Rupprechter, G. Methane dry reforming over ceria-zirconia supported Ni catalysts. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Teng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Enhanced catalytic performance of cobalt and iron co-doped ceria catalysts for soot combustion. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 55, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumruangwong, M.; Wongkasemjit, S. Anionic surfactant-aided preparation of high surface area and high thermal stability ceria/zirconia-mixed oxide from cerium and zirconium glycolates via sol-gel process and its reduction property. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 22, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacani, R.; Toscani, L.M.; Martins, T.S.; Fantini, M.C.A.; Lamas, D.; Larrondo, S. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous NiO2/ZrO2-CeO2 catalysts for total methane conversion. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 7851–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, J.; Qiao, N. Catalytic behavior and synergistic effect of nanostructured mesoporous CuO-MnOx-CeO2 catalysts for chlorobenzene destruction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 297, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Lai, S.Y. Comparison of the catalytic benzene oxidation activity of mesoporous ceria prepared via hard-template and soft-template. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 198, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Cho, E.B.; Kim, D. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous silica/ceria-silica composites and their high catalytic performance for solvent-free oxidation of benzyl alcohol at room temperature. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9213–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Long, K.Z.; Wu, F.; Xue, B.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y. Efficient synthesis of dimethyl carbonate via transesterification of ethylene carbonate over a new mesoporous ceria catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 484, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoncheva, T.; Ivanova, R.; Henych, J.; Dimitrov, M.; Kormunda, M.; Kovacheva, D.; Scotti, N.; Santo, V.D.; Štengl, V. Effect of preparation procedure on the formation of nanostructured ceria-zirconia mixed oxide catalysts for ethyl acetate oxidation: Homogeneous precipitation with urea vs template-assisted hydrothermal synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 502, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Golubina, E.V.; Shishova, V.V.; Maslakov, K.I.; Fionov, A.V.; Isaikina, O.Y.; Lunin, V.V. Efficiency of manganese modified CTAB-templated ceria-zirconia catalysts in total CO oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Rombi, E.; Meloni, D.; Sini, M.F.; Monaci, R.; Cutrufello, M.G. CO and CO2 Co-Methanation on Ni/CeO2-ZrO2 Soft-Templated Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzori, L.; Cutrufello, M.G.; Meloni, D.; Cannas, C.; Gazzoli, D.; Monaci, R.; Sini, M.; Rombi, E. Highly active NiO-CeO2 catalysts for synthetic natural gas production by CO2 methanation. Catal. Today 2018, 299, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Aslam, S.; Yan, Z.; Naeem, M.; Ullah, R.; Etim, U. Size regulation and dispersion of ceria using confined spaces for adsorptive desulfurization. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.X.; Sun, L.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; Si, R.; Feng, W.; Zhang, H.P.; Liu, H.C.; Yan, C.H. Shape-Selective Synthesis and Oxygen Storage Behavior of Ceria Nanopolyhedra, Nanorods, and Nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24380–24385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengac, H.; Rao, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Mao, W.; Han, L.; Zhang, P.; Dai, S. Confined Ultrathin Pd-Ce Nanowires with Outstanding Moisture and SO2 Tolerance in Methane Combustion. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9091–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Rosei, F.; Ma, D.; Chen, G. Dual Template Engaged Synthesis of Hollow Ball-in-Tube Asymmetrical Structured Ceria. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1700367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengac, H.; Dong, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Bao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; et al. Active and stable Pt-Ceria nanowires@silica shell catalyst: Design, formation mechanism and total oxidation of CO and toluene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 256, 117807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, A.; Amadori, R.; Lucarelli, C.; Cutrufello, M.G.; Rombi, E.; Cavani, F.; Albonetti, S. Hard-template preparation of Au/CeO2 mesostructured catalysts and their activity for the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 226, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeprasertkul, C.; Longloilert, R.; Chaisuwan, T.; Wongkasemjit, S. Impressive low reduction temperature of synthesized mesoporous ceria via nanocasting. Mater. Lett. 2014, 130, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombi, E.; Cutrufello, M.G.; Atzori, L.; Monaci, R.; Ardu, A.; Gazzoli, D.; Deiana, P.; Ferino, I. CO methanation on Ni-Ce mixed oxides prepared by hard template method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 515, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, W.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Ye, C.; Sun, G. Design of Porous/Hollow Structured Ceria by Partial Thermal Decomposition of Ce-MOF and Selective Etching. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39594–39601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Long, X.; Zhao, H.; Su, L.; Duan, Z.; Xiong, Y. ZIF-8 directed templating synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles and its oxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shen, X.; Ding, W.; Shi, L. Preparation and CO conversion activity of ceria nanotubes by carbon nanotubes templating method. J. Rare Earths 2008, 26, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rood, S.; Ahmet, H.B.; Gomez-Ramon, A.; Torrente-Murciano, L.; Ramírez-Reina, T.; Eslava, S. Enhanced ceria nanoflakes using graphene oxide as a sacrificial template for CO oxidation and dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 242, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, X.; Zeng, R.; Chen, J.; Xiao, W.; Ding, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N. Constructing copper-ceria nanosheets with high concentration of interfacial active sites for enhanced performance in CO oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chan, Y.M.; Bian, Z.; Song, F.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Kawi, S. Enhanced performance and selectivity of CO2 methanation over g-C3N4 assisted synthesis of Ni CeO2 catalyst: Kinetics and DRIFTS studies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15191–15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malonzo, C.D.; De Smith, R.M.; Rudisill, S.G.; Petkovich, N.D.; Davidson, J.H.; Stein, A. Wood-Templated CeO2 as Active Material for Thermochemical CO Production. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 26172–26181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.A.C.; Barreiros, M.A.; Abanades, S.; Caetano, A.P.; Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C. Solar thermochemical CO2 splitting using cork-templated ceria ecoceramics. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 26, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Golubina, E.; Maslakov, K.; Strokova, N.E.; Chernyak, S.; Lunin, V. Sawdust as an effective biotemplate for the synthesis of Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 and CuO-Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 catalysts for total CO oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51359–51372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X. Hydrothermal Biotemplated Synthesis of Biomorphic Porous CeO2 and Their Catalytic Performance. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2012, 23, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, M. Improved visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of CeO2 microspheres obtained by using lotus flower pollen as biotemplate. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Shan, C.; Liu, Q. CeO2/Co3O4 hollow microsphere: Pollen-biotemplated preparation and application in photo-catalytic degradation. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Biotemplated fabrication of hierarchical mesoporous CeO2 derived from diatom and its application for catalytic oxidation of CO. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3260–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekajski, M.; Babić, B.; Bučevac, D.; Pantic, J.; Gulicovski, J.; Miljkovic, M.; Matović, B. Synthesis and characterization of biomorphic CeO2 obtained by using egg shell membrane as template. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2014, 8, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Guo, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhuang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, J.; Li, Q. Bovine serum albumin templated porous CeO2 to support Au catalyst for benzene oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2020, 486, 110849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C.; Gil, L.; Oliveira, F.A.C. Biomimetic cork-based CeO2 ecoceramics for hydrogen generation using concentrated solar energy. Ciênc. Tecnol. Mater. 2016, 28, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, K.; Conklin, D.R.; Mukarakate, C.; Vardon, D.R.; Nimlos, M.R.; Ciesielski, P. Hierarchically Structured CeO2 Catalyst Particles From Nanocellulose/Alginate Templates for Upgrading of Fast Pyrolysis Vapors. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.Q.; Guo, J.B. Mesoporous CeO2 Catalyst Synthesized by Using Cellulose as Template for the Ozonation of Phenol. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 41, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jing, L.; Chen, M.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F.; Oh, W.C. Biotemplate Synthesis of Micron Braid Structure CeO2-TiO2 Composite and Analysis of its Catalytic Behavior for CO Oxidation. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2017, 54, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Liu, C.B.; Chen, Z.G. Biotemplate Synthesis of Porous Ceria Fiber and Study on its Catalytic Performance. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 745, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.L.; Guzman, J. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline and mesostructured CeO2: Influence of the amino acid template. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, W.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, Q. Facile morphology control of 3D porous CeO2 for CO oxidation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21658–21663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Song, G.; Zhao, W.; Gao, D.; Wei, Y.; Li, C. Carbon sphere-assisted solution combustion synthesis of porous/hollow structured CeO2-MnOx catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorolla-Rosario, D.; Davó-Quiñonero, A.; Bailón-García, E.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; Bueno-López, A. Key-lock Ceria Catalysts for the Control of Diesel Engine Soot Particulate Emissions. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; With, P.C.; Srivastava, V.C.; Shukla, K.; Gläser, R.; Mishra, I.M. Dimethyl carbonate synthesis from carbon dioxide using ceria-zirconia catalysts prepared using a templating method: Characterization, parametric optimization and chemical equilibrium modeling. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110235–110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Q. 1D Ceria Nanomaterials: Versatile Synthesis and Bio-application. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Antonietti, M. Metal nanoparticles at mesoporous N-doped carbons and carbon nitrides: Functional Mott-Schottky heterojunctions for catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suib, S.L. A Review of Recent Developments of Mesoporous Materials. Chem. Rec. 2017, 17, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Lü, T.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, H. Molecular Packing Parameter in Bolaamphiphile Solutions: Adjustment of Aggregate Morphology by Modifying the Solution Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Lin, T.; Chen, Y. Toluene oxidation over monolithic MnOx/La-Al2O3 catalyst prepared by a CTAB-assisted impregnation method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 526, 146714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.P.; Troncéa, S.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Granger, P. Unexpected kinetic behavior of structured Pd/CeO2-ZrO2 toward undesired ammonia formation and consumption during nitrites reduction: Role of the reactivity of oxygen from ceria. Catal. Today 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoncheva, T.; Mileva, A.; Issa, G.; Dimitrov, M.; Kovacheva, D.; Henych, J.; Scotti, N.; Kormunda, M.; Atanasova, G.; Štengl, V. Template-assisted hydrothermally obtained titania-ceria composites and their application as catalysts in ethyl acetate oxidation and methanol decomposition with a potential for sustainable environment protection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, H. Half-Encapsulated Au Nanorods@CeO2 Core@Shell Nanostructures for Near-Infrared Plasmon-Enhanced Catalysis. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Hierarchically porous ceria with tunable pore structure from particle-stabilized foams. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4366–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, E.V.; Okhlopkova, L.B.; Sukhova, O.B.; Ismagilov, I.Z.; Kerzhentsev, M.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Effects of preparation mode and doping on the genesis and properties of Ni/Ce1−xMxOy nanocrystallites (M = Gd, La, Mg) for catalytic applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, X. Highly active and coking resistant Ni/CeO2-ZrO2 catalyst for partial oxidation of methane. Fuel 2005, 84, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Niobium oxide confined by ceria nanotubes as a novel SCR catalyst with excellent resistance to potassium, phosphorus, and lead. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Tikhonov, A.V.; Zhilyaev, K.A.; Golubina, E.; Maslakov, K.; Kamaev, A.O.; Isaikina, O.Y. Templated Synthesis of Copper Modified Tin-Doped Ceria for Catalytic CO Oxidation. Top. Catal. 2020, 63, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassimiro, V.; Monteiro, R.; Bacani, R.; Toscani, L.; Lamas, D.; Larrondo, S.; Fantini, M.C.A. Effect of swelling agent in the synthesis of porous nanocrystalline nickel-zirconia-ceria composite. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19617–19626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Pullar, R.C. Comparison of low and high pressure infiltration regimes on the density and highly porous microstructure of ceria ecoceramics made from sustainable cork templates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheeva, N.; I Zaikovskii, V.; Mamontov, G. Synthesis of ceria nanoparticles in pores of SBA-15: Pore size effect and influence of citric acid addition. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Santiago, V.; Davó-Quiñonero, A.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; López, A.B. On the soot combustion mechanism using 3DOM ceria catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 234, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davó-Quiñonero, A.; González-Mira, J.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; López, A.B. Templated Synthesis of Pr-Doped Ceria with Improved Micro and Mesoporosity Porosity, Redox Properties and Catalytic Activity. Catal. Lett. 2017, 148, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davó-Quiñonero, A.; González-Mira, J.; Such-Basañez, I.; Juan-Juan, J.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; López, A.B. Improved CO Oxidation Activity of 3DOM Pr-Doped Ceria Catalysts: Something Other Than an Ordered Macroporous Structure. Catalysts 2017, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Santiago, V.; Bailón-García, E.; Davó-Quiñonero, A.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; López, A.B. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous PrOx: An improved alternative to ceria catalysts for soot combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Shao, Z. Well-crystallized mesoporous samaria-doped ceria from EDTA-citrate complexing process with in situ created NiO as recyclable template. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 491, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, V.; Goodall, R.; Thompson, A.; Ruocco, C.; Renda, S.; Leach, R.; Martino, M. Ceria-coated replicated aluminium sponges as catalysts for the CO-water gas shift process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, B.; Makajić-Nikolić, D.; Labus, N.J.; Ilić, S.; Maksimović, V.; Lukovic, J.; Bučevac, D. Preparation and properties of porous, biomorphic, ceria ceramics for immobilization of Sr isotopes. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9645–9649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ma, S.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Bian, H.; Liang, X.; Jin, W.; Yang, H. Synthesis and gas sensing application of porous CeO2-ZnO hollow fibers using cotton as biotemplates. Mater. Lett. 2016, 165, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegmayer, M.Á.; Milt, V.G.; Miró, E. Biomorphic synthesis of cobalt oxide and ceria microfibers. Their application in diesel soot oxidation. Catal. Commun. 2020, 139, 105984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Z.-G.; Liu, C.B.; Wu, Z.Y.; Lu, Q.Y.; Yu, L. Synthesis of Biomorphic Ceria Templated from Crucian Fish Scales. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 562, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, H.; Ghazavi, H.; Darroudi, M. Size-controlled and bio-directed synthesis of ceria nanopowders and their in vitro cytotoxicity effects. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 4123–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Wei, Q.; Huang, Y. Facile fabrication of CeO2 hollow microspheres with yeast as bio-templates. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Shao, Q.; Hao, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ge, S.; Guo, Z. Yeast-template synthesized Fe-doped cerium oxide hollow microspheres for visible photodegradation of acid orange 7. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigapov, A.; Graham, G.; McCabe, R.W.; Plummer, H. The preparation of high-surface area, thermally-stable, metal-oxide catalysts and supports by a cellulose templating approach. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 210, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, G.; Jen, H.; McCabe, R.; Straccia, A.; Haack, L. Characterization of model automotive exhaust catalysts: Pd on Zr-rich ceria–zirconia supports. Catal. Lett. 2000, 67, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, A.A.; Boitsova, T.B.; Stozharov, V.M.; Isaeva, E.I. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Cerium(IV) Fibrous Nanostructures. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2020, 90, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.; Murugesan, B.; Loganathan, A.; Sivakumar, P. Synthesis of ZnO nanowire and ZnO/CeO2 solid solution nanowire by bio-morphing and its characterization. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 78, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Ng, D.H. Biomass-derived hierarchically porous CoFe-LDH/CeO2hybrid with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric sensing of H2O2 and glucose. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Golubina, E.; Maslakov, K.; Chernyak, S.A.; Lunin, V. Promoting effect of potassium and calcium additives to cerium-zirconium oxide catalysts for the complete oxidation of carbon monoxide. Kinet. Catal. 2017, 58, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, X.; Yang, D.; Yu, G.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, Z. Loofa sponage derived multi-tubular CuO/CeO2-ZrO2 with hierarchical porous structure for effective soot catalytic oxidation. Fuel 2019, 258, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Qian, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F. Novel 3D porous graphene decorated with Co3O4/CeO2 for high performance supercapacitor power cell. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Li, J.; Sun, F.S.; Dickon, H.L.N.; Kwong, F.L. Synthesis of Biomorphic ZrO2-CeO2 Nanostructures by Silkworm Silk Template. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 23, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, N.; Bi, W.; Li, C. Litchi-peel-like hierarchical hollow copper-ceria microspheres: Aerosol-assisted synthesis and high activity and stability for catalytic CO oxidation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 22775–22786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, V.; Asghari, M.; Dashti, A. A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev. 2015, 2, 204–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, L.; Oskuee, R.K.; Sadri, K.; Nourmohammadi, E.; Mohajeri, M.; Mardani, Z.; Hashemzadeh, A.; Darroudi, M. Green synthesis of labeled CeO2 nanoparticles with 99mTc and its biodistribution evaluation in mice. Life Sci. 2018, 212, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Narayan, A.; Bramhecha, I.; Sheikh, J. Development of multifunctional linen fabric using chitosan film as a template for immobilization of in-situ generated CeO2 nanoparticles. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorrami, M.B.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Pasdar, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Riahi-Zanjani, B.; Darroudi, M. Role of Pullulan in preparation of ceria nanoparticles and investigation of their biological activities. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1157, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifontes, A.; González, G.; Ochoa, J.; Tovar, L.; Zoltan, T.; Cañizales, E. Chitosan as template for the synthesis of ceria nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 1794–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifontes, A.B.; Rosales, M.; Méndez, F.J.; Oviedo, O.; Zoltan, T.; Mé Ndez, F.J. Effect of Calcination Temperature on Structural Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Ceria Nanoparticles Synthesized Employing Chitosan as Template. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uppal, S.; Aashima; Kumar, R.; Sareen, S.; Kaur, K.; Mehta, S.K. Biofabrication of cerium oxide nanoparticles using emulsification for an efficient delivery of Benzyl isothiocyanate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; Mandal, B.K.; Reddy, L.V.K.; Sen, D. Biogenic Ceria Nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) for Effective Photocatalytic and Cytotoxic Activity. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elahi, B.; Mirzaee, M.; Darroudi, M.; Sadri, K.; Oskuee, R.K. Bio-based synthesis of Nano-Ceria and evaluation of its bio-distribution and biological properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Catalytic Process | Composition of the Catalyst | Template | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO oxidation | CeZrO2, MnOx-CeZrO2 | CTAB | [31] |
| CeZrO2, CuOx-CeZrO2 | CTAB, pine sawdust | [50] | |
| CeSnO2, CuOx-CeSnO2 | CTAB, Pluronic P123 | [79] | |
| CeO2 | Carbon nanotubes | [44] | |
| CeO2 | Graphene oxide | [45] | |
| Cu-CeO2 nanosheets | Graphene oxide | [46] | |
| CePrO2 | PMMA | [84] | |
| MnOx/CeO2 | Carbon spheres | [64] | |
| Au/HBT-CeO2 | SiO2 spheres + Ce(OH)CO3 nanorods | [37] | |
| CeO2-TiO2 | Filter paper | [60] | |
| CeO2 | Diatom frustule | [54] | |
| CeO2 hollow microspheres | Yeast | [94] | |
| Nanocrystalline CeO2 | Crucian fish scales | [92] | |
| CuO/CeO2 | Dextrin | [105] | |
| CeO2 | Amino acids | [63] | |
| Soot oxidation | Co-Fe/CeO2 | CTAB | [23] |
| Cu/3DOM CeO2 | PMMA | [41] | |
| 3DOM CeO2 | PMMA + Pluronic F127 | [65] | |
| CeO2, Co3O4, Co3O4-CeO2 hollow microfibers | Cotton | [91] | |
| CuO/CeZrOx | Loofa sponge | [102] | |
| Oxidation and destruction of organic compounds and dyes | CeZrOx | CTAB | [22] |
| CuO-MnOx-CeO2 | CTAB | [26] | |
| CeO2-SiO2 | CTAB | [28] | |
| CeO2-TiO2 | CTAB | [73] | |
| CeO2 | Pluronic F127 + SBA-15, SBA-15 | [27] | |
| Au/CeO2 | SBA-15 | [39] | |
| Fibrous CeO2 | Cellulose fibers | [61,98] | |
| CeO2 | Microcrystalline cellulose | [59] | |
| CeO2 powder | Clover stems | [51] | |
| Au/CeO2 | Bovine serum albumin | [56] | |
| M/CeO2, where M = Pd or Pt | NP-5 (polyethylene glycol mono-4-nonylphenyl ether) | [36] | |
| Methane reforming, CO methanation | Ni/CeO2 | CTAB | [22,33] |
| NiO/CeO2-ZrO2 | CTAB | [32] | |
| NiO/CeO2-ZrO2 | Pluronic F123 | [77] | |
| NiO/CeO2 | SBA-15 | [41] | |
| NiO/CeO2 | g-C3N4 | [47] | |
| NiO/CeO2 | Graphene oxide | [45] | |
| Water-gas shift reaction | CeO2 | Al foam, Al sponge | [88] |
| SCR of NOx | NbOx@CeO2 nanotubes | Pluronic F123 | [78] |
| CO2 reduction to CO | CeO2 | Eastern white pine wood | [48] |
| Autothermal ethanol reforming | Ni/Ce(M)O2, where M = La, Mg, Gd | Pluronic F127 | [76] |
| Dimethyl carbonate synthesis | CeO2 | CTAB | [29] |
| CeZrOx | Pluronic F-127 + spherical activated carbon | [66] | |
| Hydrodesulphurization | CeO2/3DOM SiO2 | KIT-6 + Pluronic 123 | [34] |
| Gas sensors | ZnO-CeO2 | Cotton | [90] |
| CoFe-LDH/CeO2 LDH = Layered double hydroxide | Kapok fiber | [100] | |
| Fuel-cell catalysis | CeZrOx, Ni/CeZrOx | Pluronic F123 | [80] |
| NiO/CeSmOx | NiO | [87] | |
| Co3O4-CeO2/graphene | Rape flower stem | [103] | |
| Photocatalysis | Au@CeO2 | CTAB | [74] |
| Fibrous CeO2 | Cellulose fibers | [98] | |
| ZnO/CeO2 nanowires | Cellulosic fibrils (banana pseudo stem) | [99] | |
| 3DOM CeO2 | Cork | [57] | |
| Microspheric N-doped CeO2 | Lotus pollen | [52] | |
| Co3O4/CeO2 | Lotus pollen | [53] | |
| Nanosquared CeO2/RGO (reduced graphene oxide) | Rape flower stem | [61] | |
| CeO2 and Fe-CeO2 hollow microspheres | Yeast | [95] | |
| CeO2 nanoparticles | Chitosan | [110,111] | |
| CeO2 nanoparticles | Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract | [113] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaplin, I.Y.; Lokteva, E.S.; Golubina, E.V.; Lunin, V.V. Template Synthesis of Porous Ceria-Based Catalysts for Environmental Application. Molecules 2020, 25, 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184242
Kaplin IY, Lokteva ES, Golubina EV, Lunin VV. Template Synthesis of Porous Ceria-Based Catalysts for Environmental Application. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184242
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaplin, Igor Yu., Ekaterina S. Lokteva, Elena V. Golubina, and Valery V. Lunin. 2020. "Template Synthesis of Porous Ceria-Based Catalysts for Environmental Application" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184242
APA StyleKaplin, I. Y., Lokteva, E. S., Golubina, E. V., & Lunin, V. V. (2020). Template Synthesis of Porous Ceria-Based Catalysts for Environmental Application. Molecules, 25(18), 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184242