Identification of Novel Thiazolo[5,4-b]Pyridine Derivatives as Potent Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
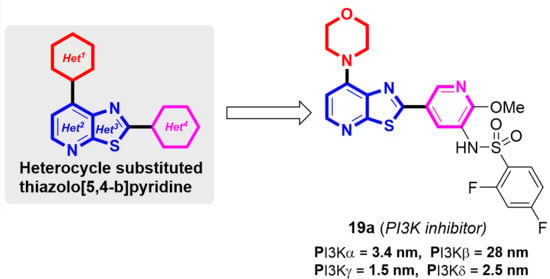
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Enzymatic Assay
2.3. Molecular Docking Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. Synthesis of 4-(2-chloro-3-nitropyridin-4-yl)morpholine (12)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 4-(3-nitro-2-thiocyanatopyridin-4-yl)morpholine (13)
3.2.3. Synthesis of 7-morpholinothiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-amine (14)
3.2.4. Synthesis of 4-(2-bromothiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-7-yl)morpholine (15)
3.2.5. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Aryl Borates 18a–18f
3.2.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Target Compounds 19a–19f
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balaban, A.T. Aromaticity as a Cornerstone of Heterocyclic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2777–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A.D.G. Rings in Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. 2012 FDA Drug Approvals. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Delost, M.D.; Qureshi, M.H.; Smith, D.T.; Njardarson, J.T. A Survey of the Structures of US FDA Approved Combination Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4265–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertl, P.; Jelfs, S.; Mühlbacher, J.; Schuffenhauer, A.; Selzer, P. Quest for the Rings. In Silico Exploration of Ring Universe To Identify Novel Bioactive Heteroaromatic Scaffolds. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4568–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitt, W.R.; Parry, D.M.; Perry, B.G.; Groom, C.R. Heteroaromatic Rings of the Future. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2952–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.; McGuire, R.; Rees, D.C. Principal Components Describing Biological Activities and Molecular Diversity of Heterocyclic Aromatic Ring Fragments. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, P.N.; Karad, S.C.; Raval, D.K. A Review on Diverse Heterocyclic Compounds as the Privileged Scaffolds in Antimalarial Drug Discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 5, 917–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaku, E.; Smith, D.T.; Njardarson, J.T. Analysis of the Structural Diversity, Substitution Patterns, and Frequency of Nitrogen Heterocycles among U.S. FDA Approved Pharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10257–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.P.; Robinson, R.P.; Fobian, Y.M.; Blakemore, D.C.; Jones, L.H.; Fadeyi, O. Modern Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry in Drug Discovery. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6611–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppast, B.; Fahmy, H. Thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidines as a Privileged Scaffold in Drug Discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 113, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cee, V.J.; Frohn, M.; Lanman, B.A.; Golden, J.; Muller, K.; Neira, S.; Pickrell, A.; Arnett, H.; Buys, J.; Gore, A.; et al. Discovery of AMG 369, a Thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridine Agonist of S1P1 and S1P5. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, A.U.; Palani, A.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Aslanian, R.G.; West, R.E., Jr.; Williams, S.M.; Wu, R.; Hwa, J.; Sondey, C.; et al. Synthesis and Structure–activity Relationships of 2-(1,4′-bipiperidin-1′-yl)thiazolopyridine as H3 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6176–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, M.G.; Raichurkar, A.; Hameed, P.S.; Waterson, D.; McKinney, D.; Manjunatha, M.R.; Kranthi, U.; Koushik, K.; Jena, L.K.; Shinde, V.; et al. Thiazolopyridine Ureas as Novel Antitubercular Agents Acting through Inhibition of DNA Gyrase, B. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8834–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Mao, S.; Xin, M.; Lu, S.; Mei, Q.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and Anticancer Effects Evaluation of 1-alkyl-3-(6-(2-methoxy-3-sulfonylaminopyridin-5-yl)benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)urea as Anticancer Agents with Low Toxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6477–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebernitz, G.R.; Beaulieu, V.; Dale, B.A.; Deacon, R.; Duttaroy, A.; Gao, J.; Grondine, M.S.; Gupta, R.C.; Kakmak, M.; Kavana, M.; et al. Investigation of Functionally Liver Selective Glucokinase Activators for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6142–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Pathway in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katso, R.; Okkenhaug, K.; Ahmadi, K.; White, S.; Timms, J.; Waterfield, M.D. Cellular Function of Phosphoinositide 3-kinases: Implications for Development, Homeostasis, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 615–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.W.; Knight, Z.A.; Goldenberg, D.D.; Yu, W.; Mostov, K.E.; Stokoe, D.; Shokat, K.M.; Weiss, W.A. A Dual PI3 Kinase/mTOR Inhibitor Reveals Emergent Efficacy in Glioma. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burger, M.T.; Pecchi, S.; Wagman, A.; Ni, Z.J.; Knapp, M.; Hendrickson, T.; Atallah, G.; Pfister, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bartulis, S.; et al. Identification of NVP-BKM120 as a Potent, Selective, Orally Bioavailable Class I PI3 Kinase Inhibitor for Treating Cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherlin, D.P.; Bao, L.; Berry, M.; Castanedo, G.; Chuckowree, I.; Dotson, J.; Folks, A.; Friedman, L.; Goldsmith, R.; Gunzner, J.; et al. Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available Class I Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Kinase Inhibitor (GDC-0980) for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7579–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.M.; Bagrodia, S.; Bailey, S.; Edwards, M.; Hoffman, J.; Hu, Q.Y.; Kania, R.; Knighton, D.R.; Marx, M.A.; Ninkovic, S.; et al. Discovery of the Highly Potent PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitor PF-04691502 Through Structure Based Drug Design. Med. Chem. Comm. 2010, 1, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, S.D.; Adams, N.D.; Burgess, J.L.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Darcy, M.G.; Donatelli, C.A.; Luengo, J.I.; Newlander, K.A.; Parrish, C.A.; Ridgers, L.H.; et al. Discovery of GSK2126458, a Highly Potent Inhibitor of PI3K and the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wang, C.; Ji, M.; Wu, D.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, Y.; Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of 2-Amino-4-methylquinazoline Derivatives as Highly Potent Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6087–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, S.L.; Hendrick, C.E.; Wang, Q. Copper-Catalyzed Electrophilic Amination of Heteroarenes and Arenes by C−H Zincation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4667–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |




| Compd | X | R1 | R2 | cLogP a | PSA a | PI3Kα (nm) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19a | N | OMe |  | 4.1 | 105.0 | 3.6 |
| 19b | N | OMe |  | 4.4 | 105.0 | 4.6 |
| 19c | N | OMe |  | 4.3 | 105.0 | 8.0 |
| 19d | N | OMe | Me | 2.1 | 105.0 | 53 |
| 19e | CH | OMe |  | 4.4 | 92.6 | 501 |
| 19f | N | H |  | 3.3 | 95.7 | 4.0 |
| Enzymatic Assay | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| PI3Kɑ | 3.6 |
| PI3Kβ | 34 |
| PI3Kγ | 1.6 |
| PI3Kδ | 2.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, K.; Tian, H.; Dong, Y.; Xu, H. Identification of Novel Thiazolo[5,4-b]Pyridine Derivatives as Potent Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204630
Xia L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Lin S, Zhang K, Tian H, Dong Y, Xu H. Identification of Novel Thiazolo[5,4-b]Pyridine Derivatives as Potent Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204630
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Liang, Yan Zhang, Jingbo Zhang, Songwen Lin, Kehui Zhang, Hua Tian, Yi Dong, and Heng Xu. 2020. "Identification of Novel Thiazolo[5,4-b]Pyridine Derivatives as Potent Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204630
APA StyleXia, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Lin, S., Zhang, K., Tian, H., Dong, Y., & Xu, H. (2020). Identification of Novel Thiazolo[5,4-b]Pyridine Derivatives as Potent Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 25(20), 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204630