α-Tocomonoenol Is Bioavailable in Mice and May Partly Be Regulated by the Function of the Hepatic α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Animal Performance
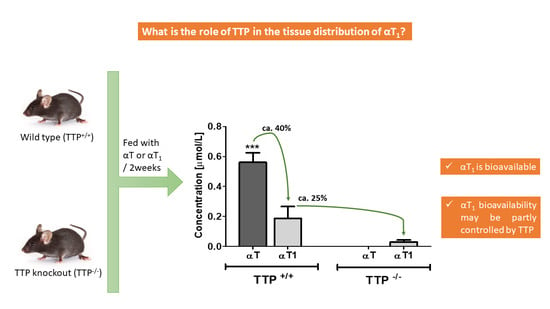
2.2. Bioavailability of αT and αT1 in TTP+/+ and TTP−/− Mice
2.3. αT and αT1 in Experimental Diets
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Test Compounds and Diets
3.2. Animal Experiment
3.3. HPLC Analysis
3.4. GC/MS Analysis
3.5. Western Blot Analysis of TTP Expression
3.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galli, F.; Azzi, A.; Birringer, M.; Cook-Mills, J.M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Frank, J.; Cruciani, G.; Lorkowski, S.; Özer, N.K. Vitamin E: Emerging aspects and new directions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, S.; Nakano, K.; Kijima, S. Identification of New Vitamin E in Plant Oil. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 44, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butinar, B.; Bučar-Miklavčič, M.; Mariani, C.; Raspor, P. New vitamin E isomers (gamma-tocomonoenol and alpha-tocomonoenol) in seeds, roasted seeds and roasted seed oil from the Slovenian pumpkin variety ‘Slovenska golica’. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammann, S.; Englert, M.; Müller, M.; Vetter, W. Accelerated separation of GC-amenable lipid classes in plant oils by countercurrent chromatography in the co-current mode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 9019–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irías-Mata, A.; Stuetz, W.; Sus, N.; Hammann, S.; Gralla, K.; Cordero-Solano, A.; Vetter, W.; Frank, J. Tocopherols, Tocomonoenols, and Tocotrienols in Oils of Costa Rican Palm Fruits: A Comparison between Six Varieties and Chemical versus Mechanical Extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7476–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmölz, L.; Birringer, M.; Lorkowski, S.; Wallert, M. Complexity of vitamin E metabolism. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 14–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebenstein, N.; Schumacher, M.; Graeve, L.; Frank, J. α-Tocopherol transfer protein is not required for the discrimination against γ-tocopherol in vivo but protects it from side-chain degradation in vitro. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for α-tocopherol transfer protein as a determinant of the biological activities of vitamin E analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosomi, A.; Goto, K.; Kondo, H.; Iwatsubo, T.; Yokota, T.; Arita, M.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Localization of a-tocopherol transfer protein in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 256, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaempf-Rotzoll, D.E.; Igarashi, K.; Aoki, J.; Jishage, K.; Suzuki, H.; Tamai, H.; Linderkamp, O.; Arai, H. α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein Is Specifically Localized at the Implantation Site. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, T.; Shiojiri, T.; Gotoda, T.; Arita, M.; Arai, H.; Ohga, T.; Kanda, T.; Suzuki, J.; Imai, T.; Matsumoto, H.; et al. Friedreich-like ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa caused by the His101Gln mutation of the α-Tocopherol transfer protein gene. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 41, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulatowski, L.; Manor, D. Vitamin E Trafficking in Neurologic Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2013, 33, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.W.; Terasawa, Y.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Traber, M.G. Incorporation of deuterated RRR- or all-rac-α-tocopherol in plasma and tissues of α-tocopherol transfer protein–null mice. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Podda, M.; Weber, C.; Traber, M.G.; Packer, L. Simultaneous determination of tissue tocopherols, tocotrienols, ubiquinols, and ubiquinones. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 893–901. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, S.; Patel, V.; Rink, C.; Roy, S.; Sen, C. Delivery of orally supplemented α-tocotrienol to vital organs of rats and tocopherol-transport protein deficient mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchida, T.; Abe, C.; Nomura, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Ikeda, S. Tissue Distribution of α- and γ-Tocotrienol and γ-Tocopherol in Rats and Interference with Their Accumulation by α-Tocopherol. Lipids 2012, 47, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Nomura, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Abe, C.; Ikeda, S. Tissue Distribution of Vitamin E Metabolites in Rats after Oral Administration of Tocopherol or Tocotrienol. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2011, 57, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, S.; Tohyama, T.; Yoshimura, H.; Hamamura, K.; Abe, K.; Yamashita, K. Dietary alpha-tocopherol Decreases alpha-tocotrienol but not gamma-tocotrienol concentration in rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, K.; Siebers, M.; Most, E.; Scheibe, S.; Weissmann, N.; Gessner, D.K. An excess dietary vitamin E concentration does not influence Nrf2 signaling in the liver of rats fed either soybean oil or salmon oil. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.-K.; Chi, E.; Liu, A.; Yang, C.S. Methods for efficient analysis of tocopherols, tocotrienols and their metabolites in animal samples with HPLC-EC. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Lee, M.-J.; Cheung, C.; Ju, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liu, B.; Hu, L.-Q.; Yang, C.S. Analysis of Multiple Metabolites of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols in Mice and Humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4844–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gohil, K.; Oommen, S.; Quach, H.T.; Vasu, V.T.; Aung, H.H.; Schock, B.; Cross, C.E.; Vatassery, G.T. Mice lacking α-tocopherol transfer protein gene have severe α-tocopherol deficiency in multiple regions of the central nervous system. Brain Res. 2008, 1201, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gotoh, N.; Watanabe, H.; Oka, T.; Mashimo, D.; Noguchi, N.; Hata, K.; Wada, S. Dietary Marine-Derived Tocopherol has a Higher Biological Availability in Mice Relative to Alpha-Tocopherol. Lipids 2009, 44, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birringer, M.; Pfluger, P.; Kluth, D.; Landes, N.; Brigelius-Flohé, R. Identities and Differences in the Metabolism of Tocotrienols and Tocopherols in HepG2 Cells. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Nomura, S.; Sakuma, E.; Hanzawa, F.; Ikeda, S. α-Tocopherol does not Accelerate Depletion of γ-Tocopherol and Tocotrienol or Excretion of their Metabolites in Rats. Lipids 2013, 48, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, W.A.; Madère, R. Kinetics of tissue RRR-alpha-tocopherol depletion and repletion. Effect of cold exposure. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1990, 1, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, F.; Kondo, H.; Kasatani, S.; Aoki, Y.; Gotoh, N. Quantitative Analysis of the Accumulation of Marine-derived Tocopherol in the Tissue of Mice Fed with Salmon Roe Oil Using HPLC-fluorescence. J. Oleo Sci. 2018, 67, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.F.; Huang, C.J. Dietary oxidized frying oil enhances tissue alpha-tocopherol depletion and radioisotope tracer excretion in vitamin E-deficient rats. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, M.; Hammann, S.; Vetter, W. Countercurrent chromatographic isolation and purification of 11′-α-tocomonoenol from the vitamin E extract of palm oil. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, J.M.; Smith, G.M.; Mcgrath, M.C.; Speijers, E.J.; Allen, J.G. Plasma and tissue concentrations of α-tocopherol during vitamin E depletion in sheep. Br. J. Nutr. 1993, 69, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, Y.; Itoh, N.; Hayakawa, M.; Habuchi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Cynshi, O.; Jishage, K.; Arai, H.; Niki, E. The role of α-tocopherol in motor hypofunction with aging in α-tocopherol transfer protein knockout mice as assessed by oxidative stress biomarkers. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaedicke, S.; Zhang, X.; Schmelzer, C.; Lou, Y.; Doering, F.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. Vitamin E dependent microRNA regulation in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3542–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grebenstein, N.; Frank, J. Rapid baseline-separation of all eight tocopherols and tocotrienols by reversed-phase liquid-chromatography with a solid-core pentafluorophenyl column and their sensitive quantification in plasma and liver. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1243, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irías-Mata, A.; Sus, N.; Hug, M.-L.; Müller, M.; Vetter, W.; Frank, J. α-Tocomonoenol Is Bioavailable in Mice and May Partly Be Regulated by the Function of the Hepatic α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein. Molecules 2020, 25, 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204803
Irías-Mata A, Sus N, Hug M-L, Müller M, Vetter W, Frank J. α-Tocomonoenol Is Bioavailable in Mice and May Partly Be Regulated by the Function of the Hepatic α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204803
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrías-Mata, Andrea, Nadine Sus, Maria-Lena Hug, Marco Müller, Walter Vetter, and Jan Frank. 2020. "α-Tocomonoenol Is Bioavailable in Mice and May Partly Be Regulated by the Function of the Hepatic α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204803
APA StyleIrías-Mata, A., Sus, N., Hug, M. -L., Müller, M., Vetter, W., & Frank, J. (2020). α-Tocomonoenol Is Bioavailable in Mice and May Partly Be Regulated by the Function of the Hepatic α-Tocopherol Transfer Protein. Molecules, 25(20), 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204803