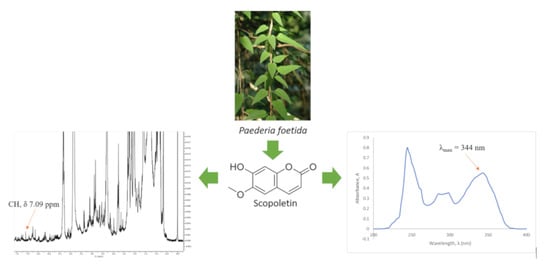
Rapid Quantification and Validation of Biomarker Scopoletin in Paederia foetida by qNMR and UV–Vis for Herbal Preparation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. NMR Analysis
2.1.1. Internal Standard (IS) Selection
2.1.2. Optimization of Solvents
2.1.3. Number of Scans
2.1.4. Pulse Angle and Relaxation Delay
2.1.5. 1H-NMR Spectra of Extracts
2.1.6. Specificity and Selectivity
2.1.7. Linearity
2.1.8. Accuracy
2.1.9. Precision
2.1.10. Limit of Detection and Quantification
2.1.11. Sample Stability
2.1.12. Robustness
2.2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Analysis
2.2.1. Optimization of Solvents
2.2.2. Linearity
2.2.3. Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantification
2.2.4. Accuracy
2.2.5. Precision
2.2.6. Robustness and Ruggedness
2.3. Application to Herbal Medicine Using qNMR and UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Reagents
3.2. Sample Collection and Extraction
3.3. Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
3.3.1. Preparation of Standard and Internal Standard Solutions
3.3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3.3. 1H-NMR Acquisition Parameter
3.3.4. qNMR Analysis
3.3.5. COSY Measurement Parameter
3.3.6. Method Validation
3.4. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer
3.4.1. Preparation of Standard and Internal Standard Solutions
3.4.2. Sample Preparation
3.4.3. Microplate UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Conditions
3.4.4. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tapsell, L.C.; Hemphill, I.; Cobiac, L.; Sullivan, D.R.; Fenech, M.; Patch, C.S.; Roodenrys, S.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M.; Williams, P.G.; et al. Health benefits of herbs and spices: The past, the present, the future. Med. J. Aust. 2006, 185, S1–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamshidi-Kia, F.; Lorigooini, Z.; Amini-Khoei, H. Medicinal plants: Past history and future perspective. J. Herbmed Pharmacol. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Valinger, D.; Benković, M.; Tušek, A.J.; Jurina, T.; Komes, D.; Kljusurić, J.G. Integrated approach for bioactive quality evaluation of medicinal plant extracts using HPLC-DAD, spectrophotometric, near infrared spectroscopy and chemometric techniques. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2463–S2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.C.; Kassim, N.K.; Ismail, I.S.; Hamid, M.; Bustamam, M.S.A. Identification of Antidiabetic Metabolites from Paederia foetida L. Twigs by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Docking Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7603125-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.C.; Idris, K.I.; Kassim, N.K.; Lim, P.C.; Ismail, I.S.; Hamid, M.; Ng, R.C. Comparative study of the antidiabetic potential of Paederia foetida twig extracts and compounds from two different locations in Malaysia. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bansal, G. HPLC-UV/FD Methods for Scopoletin and Asiatic acid: Development, Validation and Application in WHO Recommended Stability Testing of Herbal Drug Products. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 4, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixandre-Tudo, J.L.; Du Toit, W. The Role of UV-Visible Spectroscopy for Phenolic Compounds Quantification in Winemaking. In Frontiers and New Trends in the Science of Fermented Food and Beverages; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-1-78985-496-1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Numata, M.; Mackay, L.; Warren, J.; Jiao, H.; Westwood, S.; Song, D. Advanced approaches and applications of qNMR. Metrologia 2020, 57, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, G.F. qNMR—A versatile concept for the validation of natural product reference compounds. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Roy, R. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 35, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Li, W.; Chai, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y. Determination of scutellarin in breviscapine preparations using quantitative proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.Y.; Welbeck, E.; Wang, R.F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.B.; Chou, G.X.; Bi, K.S.; Hu, F. A Universal Quantitative 1 H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (qNMR) Method for Assessing the Purity of Dammarane-type Ginsenosides. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 26, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, D. Simultaneous Determination of Three Coumarins in Angelica dahurica by 1H-qNMR Method: A Fast and Validated Method for Crude Drug Quality Control. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8987560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kassim, N.K.; Rahmani, M.; Ismail, A.; Sukari, A.; Ee, G.C.L.; Nasir, N.M.; Awang, K. Antioxidant activity-guided separation of coumarins and lignan from Melicope glabra (Rutaceae). Food Chem. 2013, 139, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Liang, X.; Du, L.; Su, F.; Su, W. Quantitative determination and validation of avermectin B1a in commercial products using quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Appendix K: Guidelines for Dietary Supplements and Botanicals. AOAC Off. Methods Anal. 2013, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hlavacek, R.J. Codex alimentarius commission. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 58, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidelines for the Validation of Chemical Methods in Food, Feed, Cosmetics, and Veterinary Products, 3rd ed.; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019; pp. 1–39.
- Zailer, E.; Diehl, B.W.K. Alternative determination of blood alcohol concentration by 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 119, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borman, P.; Elder, D. Q2(R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures. In ICH Quality Guidelines; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 127–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Jin, M.; Zhou, X.; Ni, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. The Application of Quantitative 1H-NMR for the Determination of Orlistat in Tablets. Molecules 2017, 22, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, P.V.; Bhingare, C.L.; Nikam, R.Y.; Pawar, S.A. Development and validation of UV Spectrophotometric method for the estimation of Curcumin in cream formulation. Pharm. Methods 2013, 4, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris-Vicente, J.; Esteve-Romero, J.; Carda-Broch, S. Validation of Analytical Methods Based on Chromatographic Techniques: An Overview. In Analytical Separation Science; Anderson, J.L., Berthod, A., Estévez, V.P., Stalcup, A.M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 1757–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; An, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, K. Quantitative effect of temperature to the absorbance of aqueous glucose in wavelength range from 1200 nm to 1700 nm. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 6887–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rink, A.; Lewis, D.F.; Varma, S.; Vitkin, A.; Jaffray, D.A. Temperature and hydration effects on absorbance spectra and radiation sensitivity of a radiochromic medium. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 4545–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guimarães, D.; Noro, J.; Loureiro, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Quantification of drugs encapsulated in liposomes by 1H NMR. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, G.S.; Bauman, J.N.; Ryder, T.F.; Smith, E.B.; Spracklin, D.K.; Obach, R.S. Biosynthesis of Drug Metabolites and Quantitation Using NMR Spectroscopy for Use in Pharmacologic and Drug Metabolism Studies. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soininen, P. Quantitative 1H NMR Spectroscopy—Chemical and Biological Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland, 10 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinal, N.; Alfajri, R.; Arifin, B. Isolation and Characterization of Scopoletin from The Bark of fagraea ceilanica thumb and Antioxidants Tests. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2015, 5, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the plant extract and compounds are available from the authors. |





| Accuracy Level (%) | Scopoletin in Extract (Ao) | Scopoletin Added (As) | Scopoletin Obtained (Ax) | Recovery (%) | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 0.03130 | 0.02500 | 0.05510 | 95.20 | Mean = 94.08 %RSD = 1.06 |
| 0.03200 | 0.02560 | 0.05600 | 93.75 | ||
| 0.03160 | 0.02530 | 0.05520 | 93.28 | ||
| 100 | 0.02250 | 0.02700 | 0.05170 | 108.15 | Mean = 108.45 %RSD = 0.39 |
| 0.02260 | 0.02350 | 0.04820 | 108.94 | ||
| 0.02240 | 0.02180 | 0.04600 | 108.26 | ||
| 120 | 0.04000 | 0.06000 | 0.10000 | 100 | Mean = 98.93 %RSD = 1.00 |
| 0.04320 | 0.06120 | 0.10320 | 98.04 | ||
| 0.03950 | 0.04800 | 0.08690 | 98.75 |
| No. | Calculated Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.03130 |
| 2 | 0.03140 |
| 3 | 0.03150 |
| 4 | 0.03140 |
| 5 | 0.03150 |
| 6 | 0.03140 |
| Mean | 0.03142 |
| Standard deviation | 0.00007 |
| %RSD | 0.23961 |
| No. | Intraday Calculated Concentration (mg/mL) | Interday Calculated Concentration (mg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.00 a.m. | 11.00 a.m. | 1.00 p.m. | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | |
| 1 | 0.04427 | 0.04425 | 0.04424 | 0.04427 | 0.04424 | 0.04422 |
| 2 | 0.04426 | 0.04425 | 0.04425 | 0.04426 | 0.04425 | 0.04423 |
| 3 | 0.04427 | 0.04426 | 0.04426 | 0.04427 | 0.04425 | 0.04423 |
| 4 | 0.04427 | 0.04427 | 0.04427 | 0.04427 | 0.04426 | 0.04424 |
| 5 | 0.04425 | 0.04424 | 0.04424 | 0.04425 | 0.04425 | 0.04423 |
| 6 | 0.04426 | 0.04425 | 0.04425 | 0.04426 | 0.04425 | 0.04422 |
| Mean | 0.04426 | 0.04425 | ||||
| Standard deviation | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | ||||
| %RSD | 0.02468 | 0.03702 | ||||
| Time (h) | Assay (%) | Differences (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 99.70 | NA |
| 8 | 99.70 | 0.00 |
| 16 | 99.70 | 0.00 |
| 24 | 99.69 | 0.01 |
| 48 | 99.65 | 0.04 |
| Average | 99.69 | |
| %RSD | 0.022 | |
| Parameters (Target Value) | Change | Assay (%) | Differences (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of scans (8) | 4 | 99.65 | 0.43 |
| 12 | 100.02 | 0.06 | |
| Relaxation delay (60 s) | 50 s | 100.05 | 0.03 |
| 70 s | 99.98 | 0.10 | |
| Acquisition time (3.4918 s) | 2.4918 s | 99.96 | 0.12 |
| 4.4918 s | 100.02 | 0.06 | |
| Spectral width (15 ppm) | 10 ppm | 99.88 | 0.20 |
| 20 ppm | 99.96 | 0.12 |
| Recovery Level (%) | Theoretical Amount Concentration 1 (µg/mL) | Amount Added Concentration 1 (µg/mL) | %Recovery | %RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 0.65740 | 0.52590 | 100.25 | 1.22711 |
| 100 | 0.65740 | 0.65740 | 103.40 | 1.06936 |
| 120 | 0.65740 | 0.78890 | 105.37 | 1.41745 |
| Concentration (µg/mL) | Absorbance | Statistical Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.771 | Mean = 0.773 SD = 0.004 %RSD = 0.569 |
| 20 | 0.766 | |
| 20 | 0.773 | |
| 20 | 0.775 | |
| 20 | 0.770 | |
| 20 | 0.778 |
| Concentration Taken (µg/mL) | Absorbance 1 | Mean | SD | %RSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:30 a.m. | 12:30 p.m. | 2:30 p.m. | ||||
| 20 | 0.769 | 0.765 | 0.760 | 0.765 | 0.004 | 0.558 |
| 30 | 1.081 | 1.074 | 1.068 | 1.074 | 0.007 | 0.640 |
| 40 | 1.386 | 1.377 | 1.366 | 1.376 | 0.010 | 0.718 |
| Concentration Taken (µg/mL) | Absorbance 1 | Mean | SD | %RSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | ||||
| 20 | 0.754 | 0.747 | 0.733 | 0.746 | 0.011 | 1.446 |
| 30 | 1.059 | 1.049 | 1.030 | 1.046 | 0.015 | 1.412 |
| 40 | 1.358 | 1.348 | 1.330 | 1.345 | 0.014 | 1.052 |
| Conc. (µg/mL) | 339 nm | 344 nm | 349 nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | Statistical Analysis | Absorbance | Statistical Analysis | Absorbance | Statistical Analysis | |
| 20 | 0.746 | Mean = 0.746 SD = 0.005 %RSD = 0.608 | 0.748 | Mean = 0.748 SD = 0.004 %RSD = 0.554 | 0.724 | Mean = 0.725 SD = 0.004 %RSD = 0.557 |
| 20 | 0.753 | 0.755 | 0.731 | |||
| 20 | 0.741 | 0.744 | 0.721 | |||
| 20 | 0.744 | 0.747 | 0.724 | |||
| 20 | 0.742 | 0.744 | 0.720 | |||
| 20 | 0.749 | 0.750 | 0.727 | |||
| Analyst 1: Dai Chuan Tan | Analyst 2: Alexandra Quek | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (µg/mL) | Absorbance | Statistical Analysis | Concentration (µg/mL) | Absorbance | Statistical Analysis |
| 20 | 0.772 | Mean = 0.780 SD = 0.008 %RSD = 1.038 | 20 | 0.779 | Mean = 0.786 SD = 0.008 %RSD = 1.033 |
| 20 | 0.784 | 20 | 0.771 | ||
| 20 | 0.790 | 20 | 0.775 | ||
| 20 | 0.789 | 20 | 0.781 | ||
| 20 | 0.795 | 20 | 0.794 | ||
| 20 | 0.787 | 20 | 0.779 | ||
| Results | qNMR | UV-vis |
|---|---|---|
| %Label claim | 101.80 | 103.69 |
| %RSD | 1.24 | 0.82 |
| Scopoletin content | ||
| Paederia foetida | ||
| Hexane | ND | 2.10% (20.99 mg/g) |
| Chloroform | 7.34% (73.44 mg/g) | 3.85% (38.54 mg/g) |
| Methanol | ND | 1.20% (11.99 mg/g) |
| Melicope latifolia | ||
| Hexane | 7.31% (73.11 mg/g) | 6.75% (67.46 mg/g) |
| Chloroform | 11.75% (117.49 mg/g) | 10.67% (100.67 mg/g) |
| Methanol | 5.61% (56.07 mg/g) | 4.05% (40.47 mg/g) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, D.C.; Quek, A.; Kassim, N.K.; Ismail, I.S.; Lee, J.J. Rapid Quantification and Validation of Biomarker Scopoletin in Paederia foetida by qNMR and UV–Vis for Herbal Preparation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215162
Tan DC, Quek A, Kassim NK, Ismail IS, Lee JJ. Rapid Quantification and Validation of Biomarker Scopoletin in Paederia foetida by qNMR and UV–Vis for Herbal Preparation. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215162
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Dai Chuan, Alexandra Quek, Nur Kartinee Kassim, Intan Safinar Ismail, and Joanna Jinling Lee. 2020. "Rapid Quantification and Validation of Biomarker Scopoletin in Paederia foetida by qNMR and UV–Vis for Herbal Preparation" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215162
APA StyleTan, D. C., Quek, A., Kassim, N. K., Ismail, I. S., & Lee, J. J. (2020). Rapid Quantification and Validation of Biomarker Scopoletin in Paederia foetida by qNMR and UV–Vis for Herbal Preparation. Molecules, 25(21), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215162